Abstract
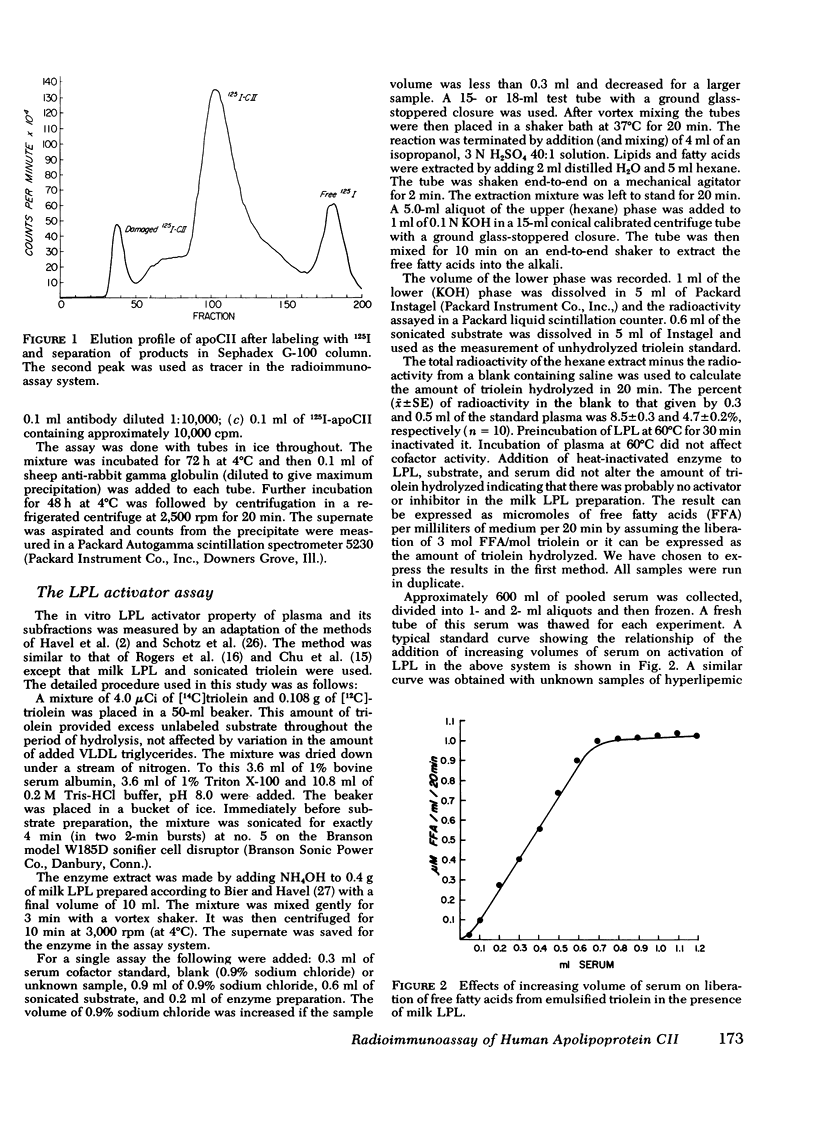
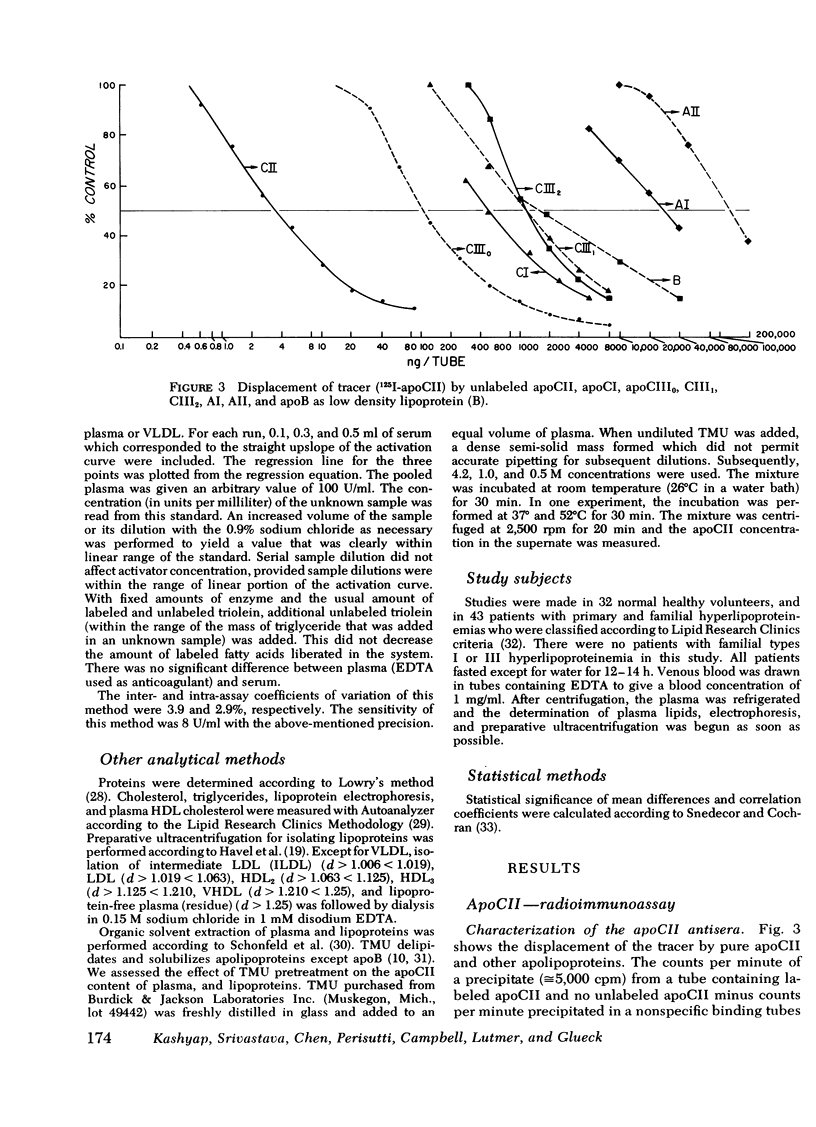
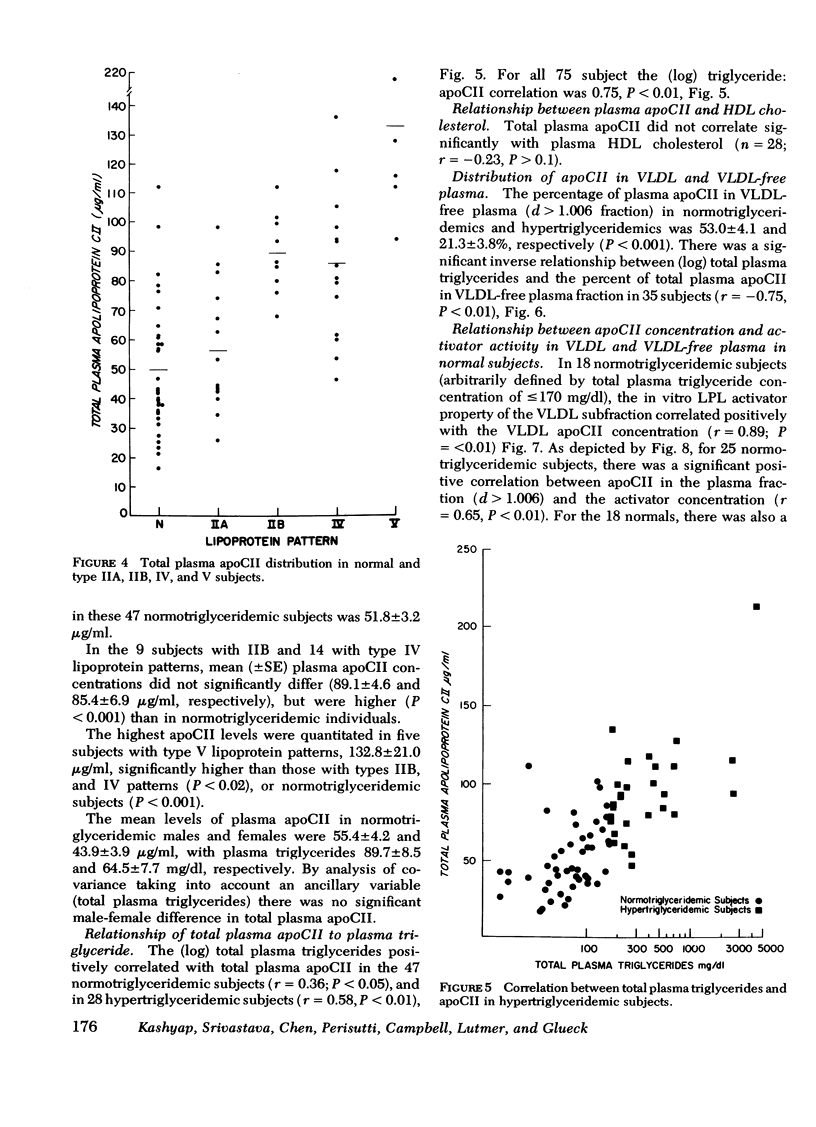
A specific, precise, and sensitive double-antibody radioimmunoassay for the measurement of human apolipoprotein CII (apoCII) was developed. ApoCII was labeled with 125I (chloramine-T) and monospecific antibody was raised in rabbits. No appreciable cross-reactivity with apolipoproteins CI, CIII, AI, AII, low density lipoproteins, and lipoprotein-free plasma was observed. Lipoproteins containing apoCII displaced the standard curve in parallel. ApoCII measurement was not affected by pretreatment of plasma with tetramethylurea, ethanol-diethyl ether, or heating.
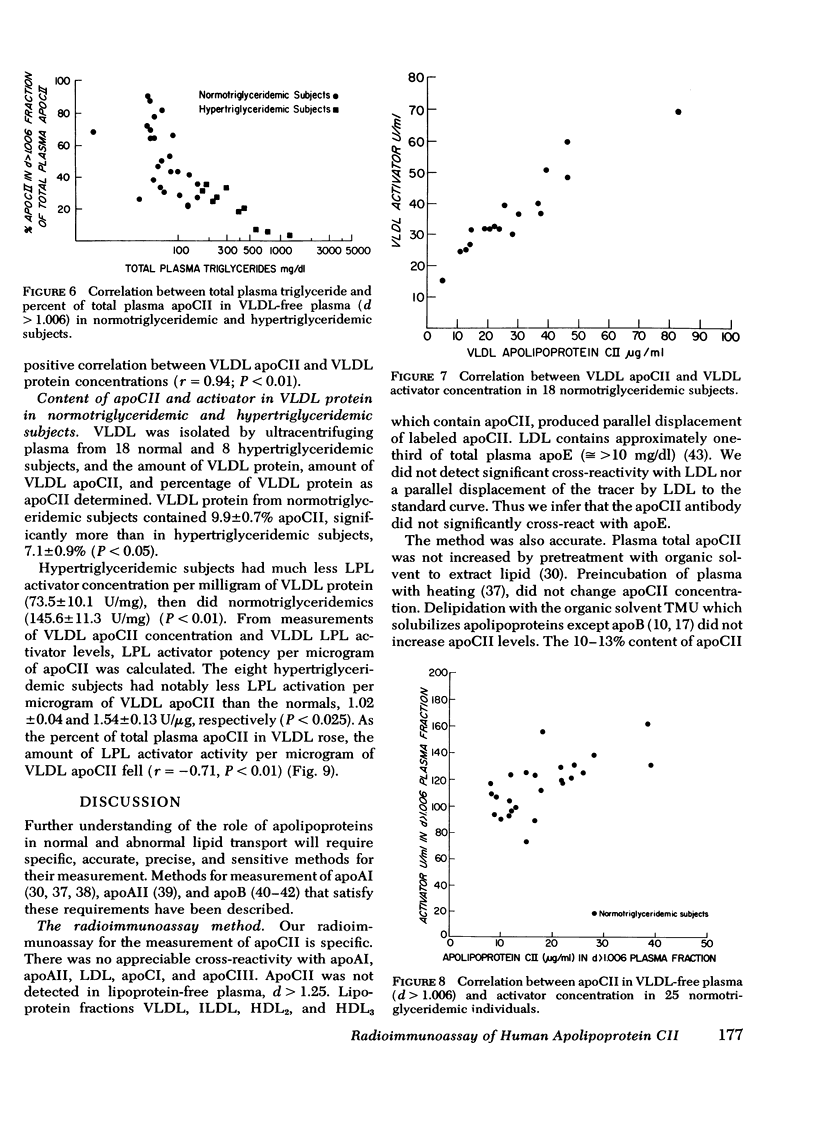
Mean (±SE) plasma-immunoreactive apoCII in 47 normotriglyceridemic subjects was 51.8±3.2 μg/ml, generally comparable with previous estimates of its concentration by other methods. ApoCII levels in 9 subjects with type IIB lipoprotein pattern, 14 with the type IV lipoprotein pattern, and 5 with type V lipoprotein pattern were respectively, 89.9±4.6, 85.4±6.9, 132.8±21.0 μg/ml, all higher than normals (P < 0.001). Plasma apoCII and triglyceride concentrations correlated in normo- and hypertriglyceridemics (r = 0.36 and 0.58, P < 0.05). Plasma triglycerides correlated inversely with the fraction of total apoCII in very low density lipoprotein (VLDL)-free plasma (r = −0.75, P < 0.01). There was no correlation between plasma apoCII and high density lipoprotein cholesterol.
In normotriglyceridemics, VLDL apoCII levels correlated with in vitro lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activator activities (r = 0.89, P < 0.01). In hypertriglyceridemic subjects the mean concentrations of apoCII per milligrams VLDL protein, LPL activator activity per milligrams VLDL protein, and LPL activator activity per micrograms VLDL apoCII were all lower than in normotriglyceridemics, P < 0.05.
As plasma triglycerides and apoCII increase, apoCII is redistributed from high density lipoprotein to VLDL. However, the amount of apoCII per milligram VLDL protein and its LPL activator potency per milligram VLDL protein are reduced. These factors may contribute to impaired VLDL catabolism.
Full text
PDF


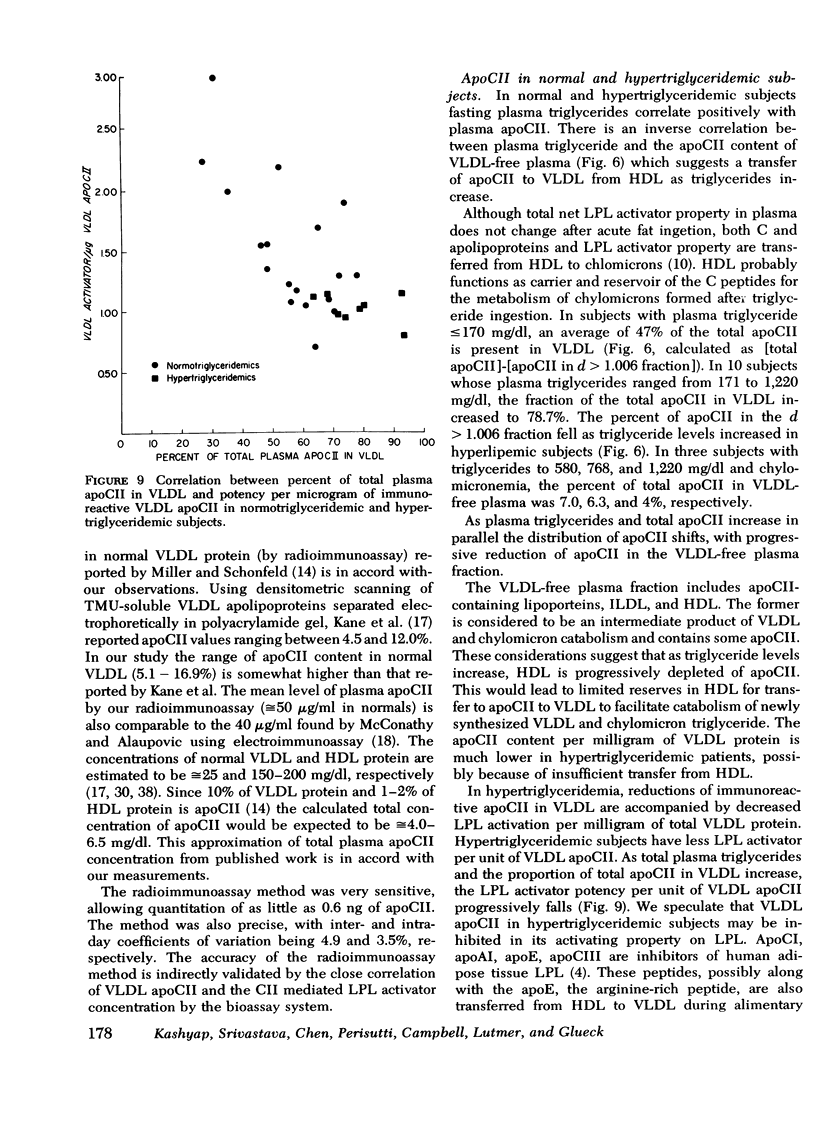


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Cabana V. G., Hazzard W. R. Immunoassay of human plasma apolipoprotein B. Metabolism. 1975 Dec;24(12):1339–1351. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Wahl P. W., Cabana V. G., Hazzard W. R., Hoover J. J. Quantitation of apolipoprotein A-I of human plasma high density lipoprotein. Metabolism. 1976 Jun;25(6):633–644. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautovich G. J., Simons L. A., Williams P. F., Turtle J. R. Radioimmunoassay of human plasma apolipoproteins part 1. assay of apolipoprotein-B. Atherosclerosis. 1975 Mar-Apr;21(2):217–234. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(75)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier D. M., Havel R. J. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by lipoprotein fractions of human serum. J Lipid Res. 1970 Nov;11(6):565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Shulman R., Herbert P., Ronan R., Wehrly K. The complete amino acid sequence of alanine apolipoprotein (apoC-3), and apolipoprotein from human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4975–4984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Baginsky M. L. Inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by an apoprotein of human very low density lipoprotein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):375–382. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further characterization of apolipoproteins from the human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1970 Dec 25;245(24):6588–6594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu P., Miller A. L., Mills G. L. Assay of an activator for lipoprotein lipase. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jan 16;66(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P., Ledford J. H., Popović M. Determination of human apolipoprotein E by electroimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 9;439(2):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1975;13:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekman R., Nilsson-Ehle P. Effects of apolipoproteins on lipoprotein lipase activity of human adipose tissue. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Aug 18;63(1):29–35. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan D., Bradford R. H., Ganesan G., McConathy W. J., Alaupovic P., Bass H. B. Purified postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase in primary hyperlipoproteinemias. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Dec;39(6):1022–1033. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.6.1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Shore V. G., Shore B., Bier D. M. Role of specific glycopeptides of human serum lipoproteins in the activation of lipoprotein lipase. Circ Res. 1970 Oct;27(4):595–600. doi: 10.1161/01.res.27.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J. K., Ehnholm C., Kekki M., Nikkilä E. A. Post-heparin plasma lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in normal subjects and in patients with hypertriglyceridaemia: correlations to sex, age and various parameters of triglyceride metabolism. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Apr;50(4):249–260. doi: 10.1042/cs0500249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M. A study of the cystine-containing apolipoprotein of human plasma high density lipoproteins: characterization of cyanogen bromide and tryptic fragments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):36–47. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. A rapid electrophoretic technique for identification of subunit species of apoproteins in serum lipoproteins. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jun;53(2):350–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Sata T., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Apoprotein composition of very low density lipoproteins of human serum. J Clin Invest. 1975 Dec;56(6):1622–1634. doi: 10.1172/JCI108245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin J. B., Juhn D. J., Starr J. I., Scanu A. M., Rubenstein A. H. Measurement of human high density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-1 in serum by radioimmunoassay. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):30–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krauss R. M., Herbert P. N., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Further observations on the activation and inhibition of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoproteins. Circ Res. 1973 Oct;33(4):403–411. doi: 10.1161/01.res.33.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Herbert P., Lux S. E., Fredrickson D. S. A specific apoprotein activator for lipoprotein lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostlund-Lindqvist A. M., Iverius P. H. Activation of highly purified lipoprotein lipase from bovine milk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 18;65(4):1447–1455. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Frank A., Shames D. M., Berman M., Steinberg D. Very low density lipoprotein triglyceride transport in type IV hyperlipoproteinemia and the effects of carbohydrate-rich diets. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2281–2297. doi: 10.1172/JCI106448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M. P., Barnett D., Robinson D. S. Clearing factor lipase (lipoprotein lipase) activator. A method for the measurement of the net activating ability of human sera. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Sep;24(3):551–564. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Pfleger B. The structure of human high density lipoprotein and the levels of apolipoprotein A-I in plasma as determined by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):236–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI107758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schotz M. C., Garfinkel A. S., Huebotter R. J., Stewart J. E. A rapid assay for lipoprotein lipase. J Lipid Res. 1970 Jan;11(1):68–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twu J. S., Garfinkel A. S., Schotz M. C. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from human heart. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jul-Aug;24(1-2):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J., Robbins J. B., Nieschlag E., Ross G. T. A method for producing specific antisera with small doses of immunogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):988–991. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



