Abstract
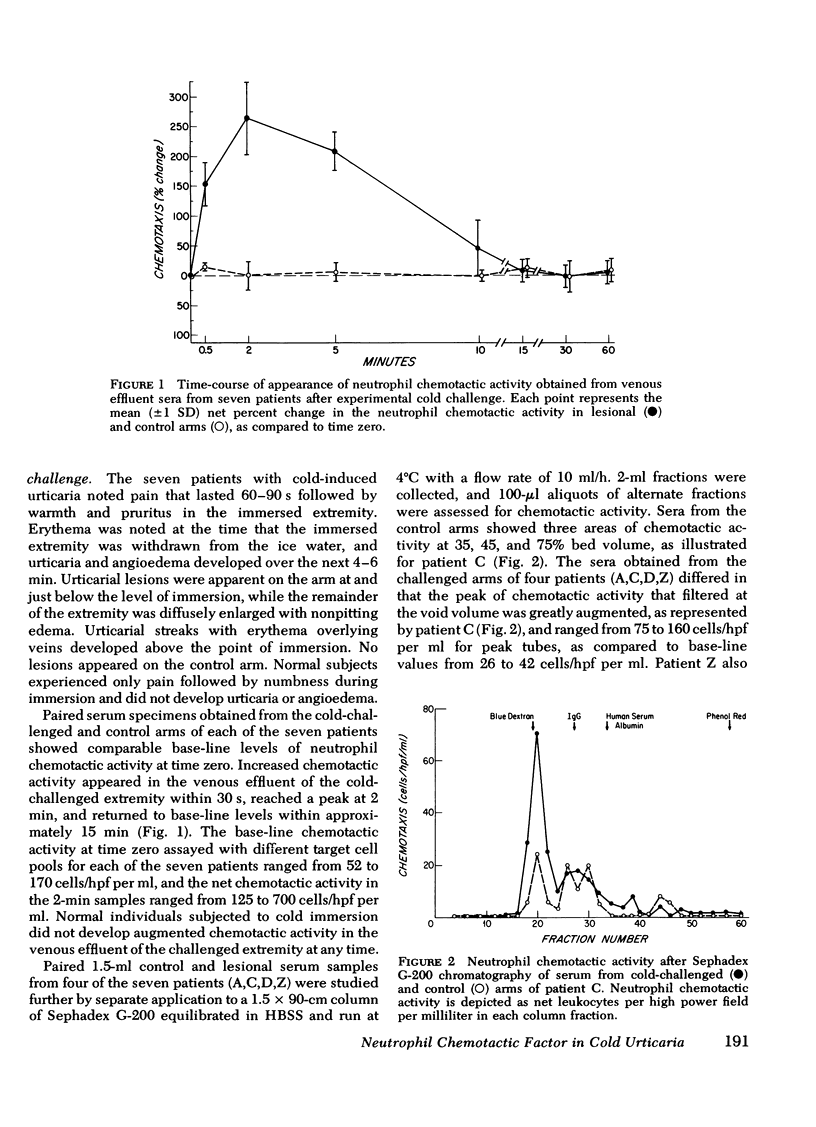
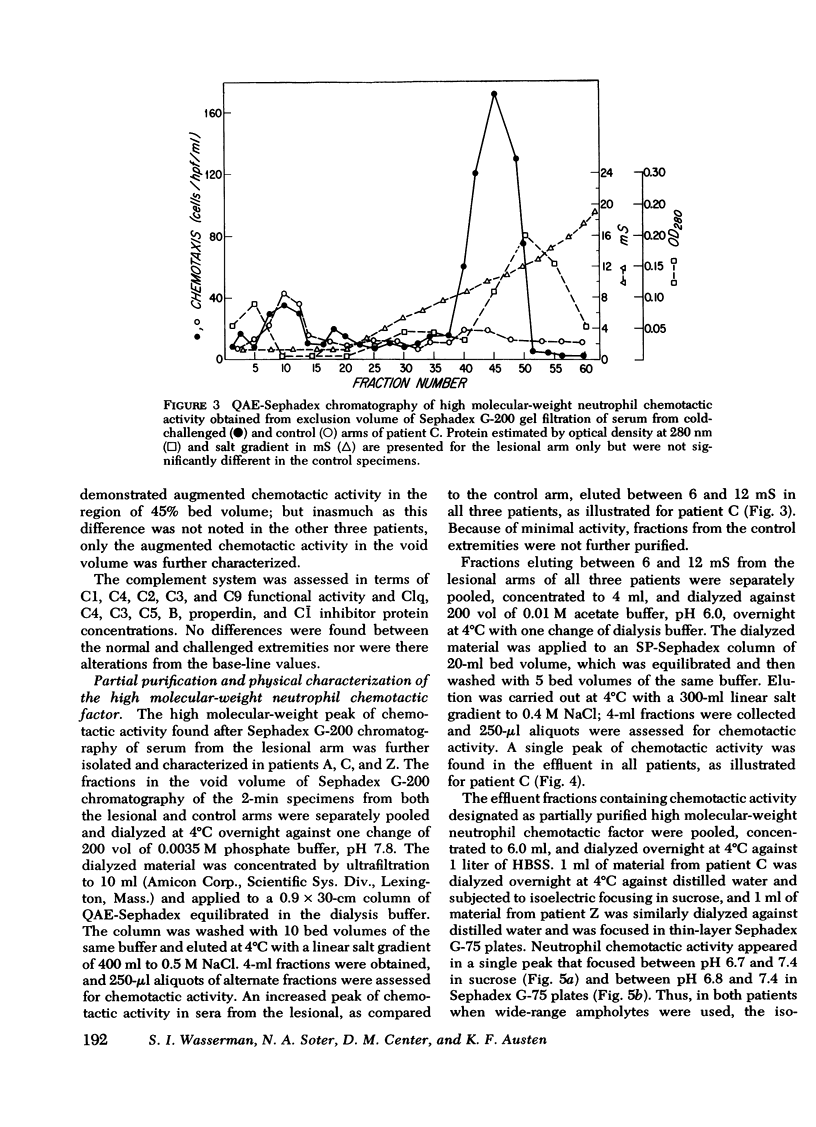
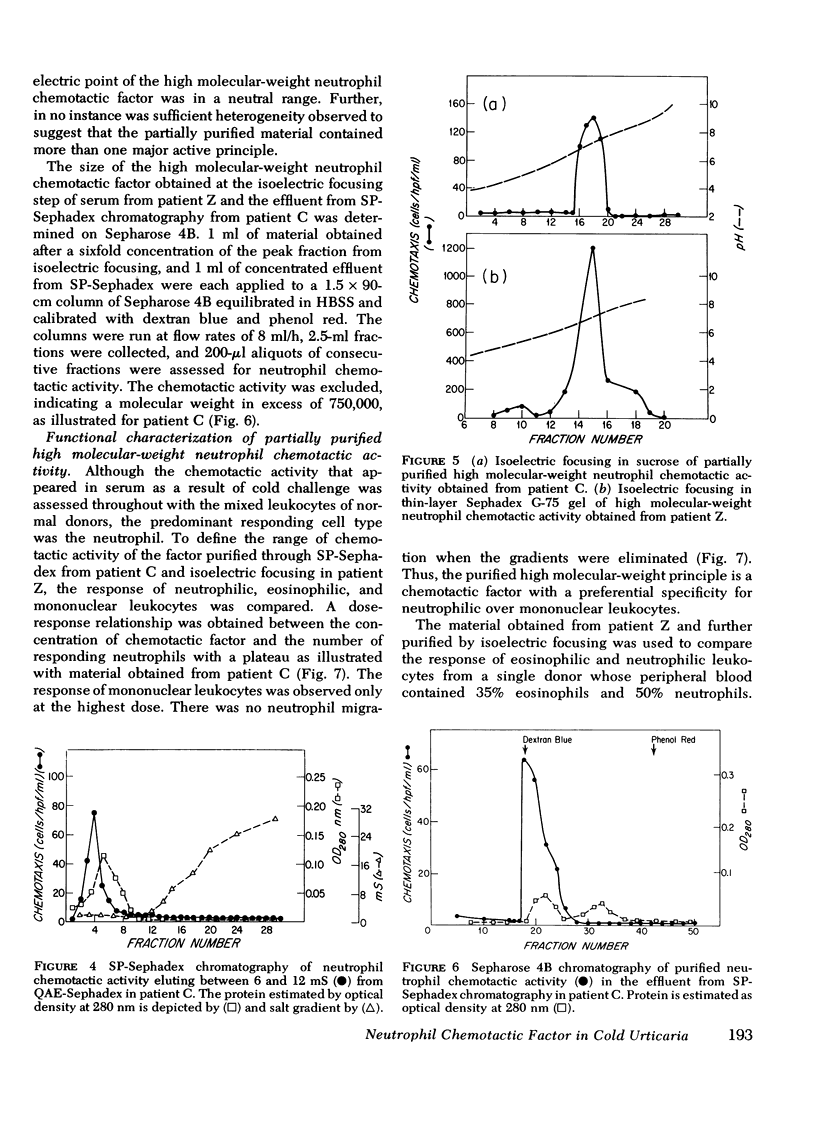
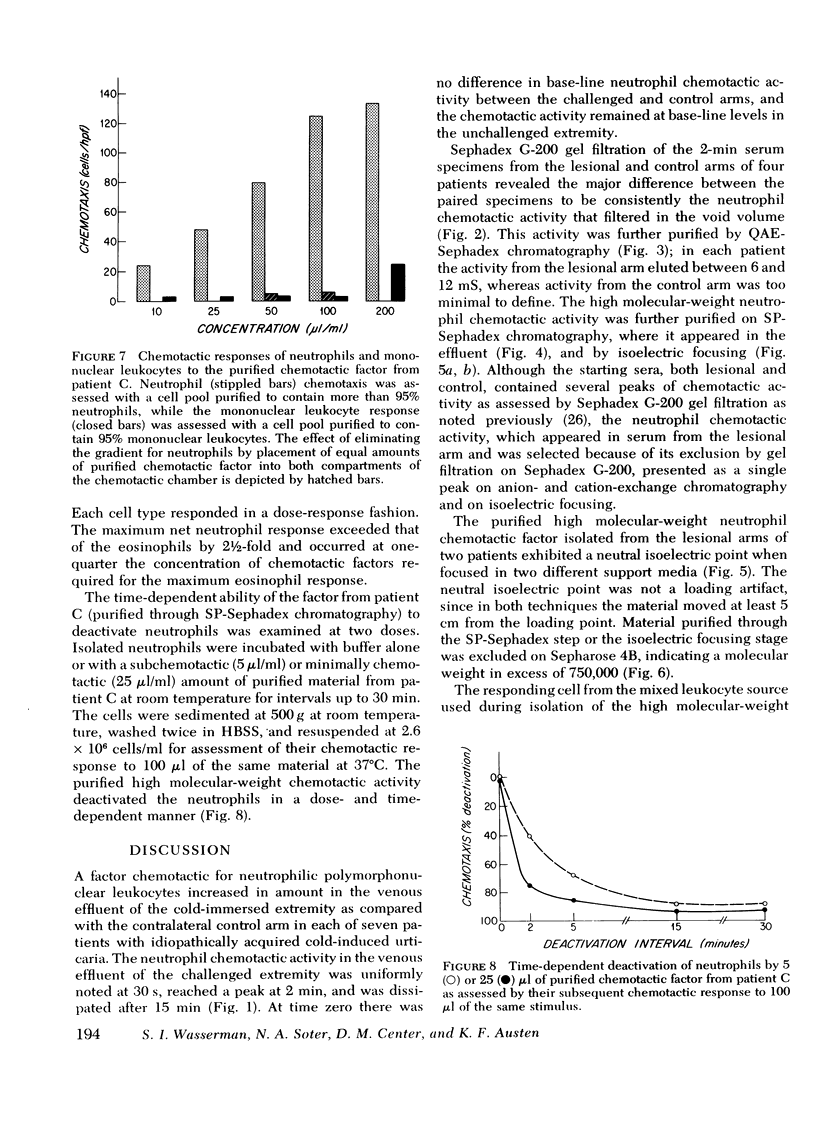
Sera were obtained from the venous effluents of cold-challenged arms of patients with idiopathic cold urticaria without plasma or serum cryoproteins; these sera exhibited increased neutrophil chemotactic activity without alterations of the complement system. A two- to fourfold augmentation of the base-line neutrophil chemotactic activity of serum from the immersed extremity began within 1 min, peaked at 2 min, and returned to base-line levels within 15 min, whereas there was no change in the serum chemotactic activity in the control arm. The augmented chemotactic activity in the serum specimens from the challenged arm of each patient appeared in a high molecular-weight region, as assessed by the difference in activity recovered after Sephadex G-200 gel filtration of the paired lesional and control specimens. Sequential purification of this high molecular-weight activity by anion- and cation-exchange chromatography revealed a single peak of activity at both steps. The partially purified material continued to exhibit a high molecular weight, being excluded on Sepharose 4B, and had a neutral isoelectric point. The partially purified material showed a preferential chemotactic activity for neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes, required a gradient for expression of this function, and exhibited a capacity to deactivate this cell type. This active principle, termed high molecular-weight neutrophil chemotactic factor, exhibited a time-course of release that could be superimposed upon that of histamine and the low molecular-weight eosinophil chemotactic factor and may represent another mast cell-derived mediator.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins P. C., Norman M., Weiner H., Zweiman B. Release of neutrophil chemotactic activity during immediate hypersensitivity reactions in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Apr;86(4):415–418. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-4-415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEALL G. N. Plasma histamine concentrations in allergic diseases. J Allergy. 1963 Jan-Feb;34:8–15. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(63)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORSOS T., RAPP H. J. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF THE FIRST COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT AND ITS ASSAY ON A MOLECULAR BASIS. J Immunol. 1963 Dec;91:851–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of leucocytes from human blood. Further observations. Methylcellulose, dextran, and ficoll as erythrocyteaggregating agents. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:31–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich J., Hargreave F. E., Chalmers R., Shier K. J., Gauldie J., Bienenstock J. Late cutaneous allergic responses in isolated IgE-dependent reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1973 Jul;52(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(73)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The stoichiometric measurement of the serum inhibition of the first component of complement by the inhibition of immune hemolysis. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1154–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. I. Generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1564–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Structural determinants of the eosinophil: chemotactic activity of the acidic tetrapeptides of eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1424–1437. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser D. D., Arbesman C. E., Ito K., Wicher K. Cold urticaria. Immunologic studies. Am J Med. 1970 Jul;49(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H., Merrill J. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Austen K. F. Metabolism of third complement component (C3) in nephritis. Involvement of the classic and alternate (properdin) pathways for complement activation. N Engl J Med. 1972 Oct 26;287(17):835–840. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197210262871701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENT J. F., FIFE E. H., Jr Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Jan;12:103–116. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1963.12.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Gray L., Shaff R. E., Horakova Z., Beaven M. A. In vivo studies of mediator release in cold urticaria and cholinergic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jun;55(6):394–402. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Immunochemical quantitation of the third, fourth and fifth components of human complement: concentrations in the serum of healthy adults. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1211–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. J., Carpenter C. B., Schur P. H. Serum complement component levels in human glomerulonephritis. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Oct;75(4):555–560. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Goetzl E. J., Wasserman S. I., Valone F. H., Rubin R. H., Austen K. F. The release of four mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from human leukemic basophils. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE B. Histamine, hormones, and hypersensitivity. J Allergy. 1954 Mar;25(2):168–189. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(54)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. A stoichiometric assay for the fourth component of complement in whole human serum using EAC'la-gp and functionally pure human second component. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1162–1172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. C3 inactivator of man. I. Hemolytic measurement by the inactivation of cell-bound C3. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):533–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F. The complement system in rheumatoid synovitis. I. An analysis of complement component activities in rheumatoid synovial fluids. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Nov-Dec;13(6):713–723. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Depressed synovial fluid levels of properdin and properdin factor B in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):289–295. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Klemperer M. R., Rosen F. S., Austen K. F., Kumate J. Hereditary deficiency of the second component of complement (C2) in man: correlation of C2 haemolytic activity with immunochemical measurements of C2 protein. Immunology. 1970 Jun;18(6):943–954. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN W. B., SEEBOHM P. M. Passive transfer of cold urticaria. J Allergy. 1950 Sep;21(5):414–424. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(50)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solley G. O., Gleich G. J., Jordon R. E., Schroeter A. L. The late phase of the immediate wheal and flare skin reaction. Its dependence upon IgE antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):408–420. doi: 10.1172/JCI108485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soter N. A., Austen K. F., Gigli I. The complement system in necrotizing angiitis of the skin. Analysis of complement component activities in serum of patients with concomitant collagen-vascular diseases. J Invest Dermatol. 1974 Aug;63(2):219–226. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12679439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soter N. A., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Cold urticaria: release into the circulation of histamine and eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis during cold challenge. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 25;294(13):687–690. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603252941302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. I., Whitmer D., Geotzl E. J., Austen K. F. Chemotactic deactivation of human eosinophils by the eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis (38527). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jan;148(1):301–306. doi: 10.3181/00379727-148-38527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


