Abstract
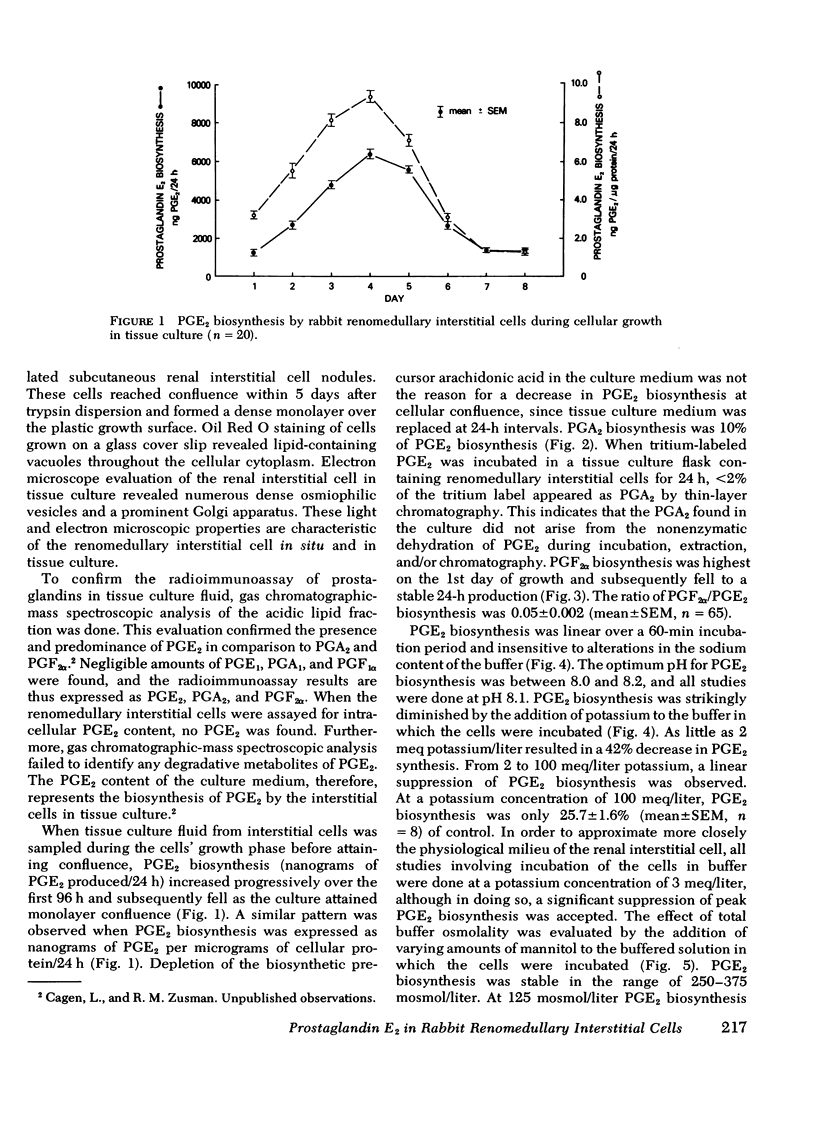
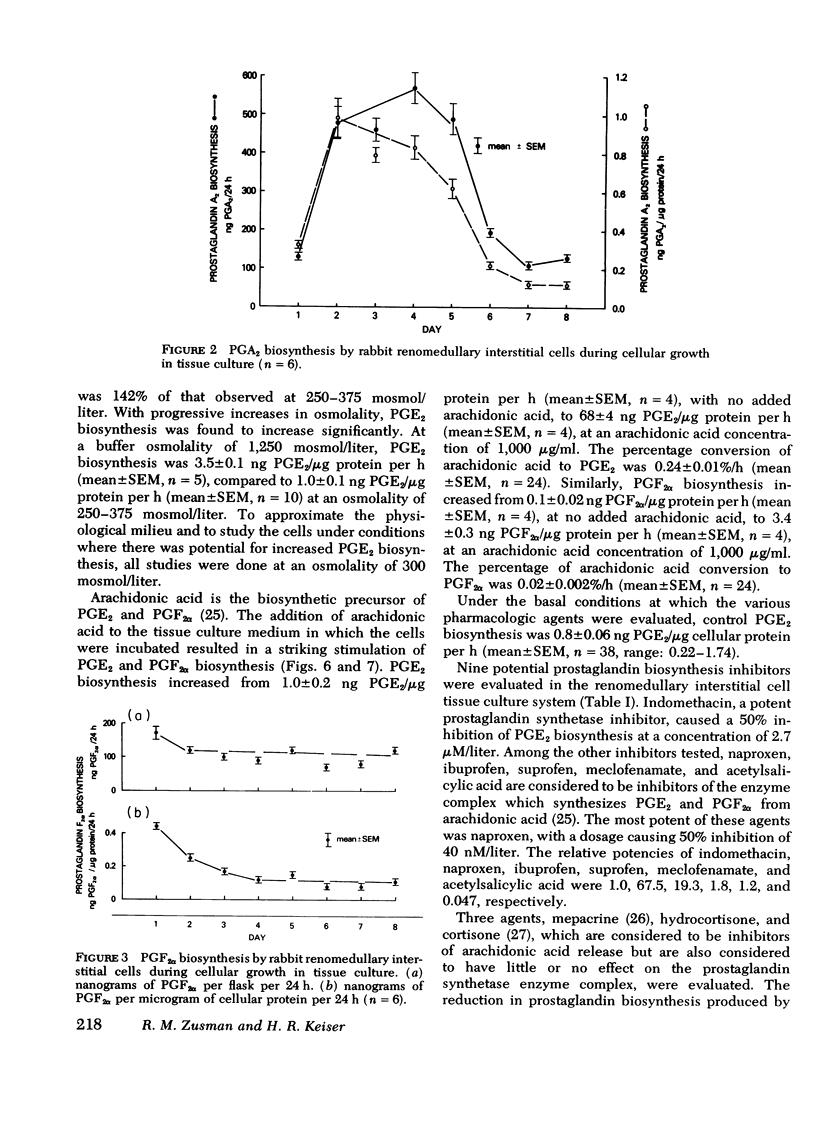
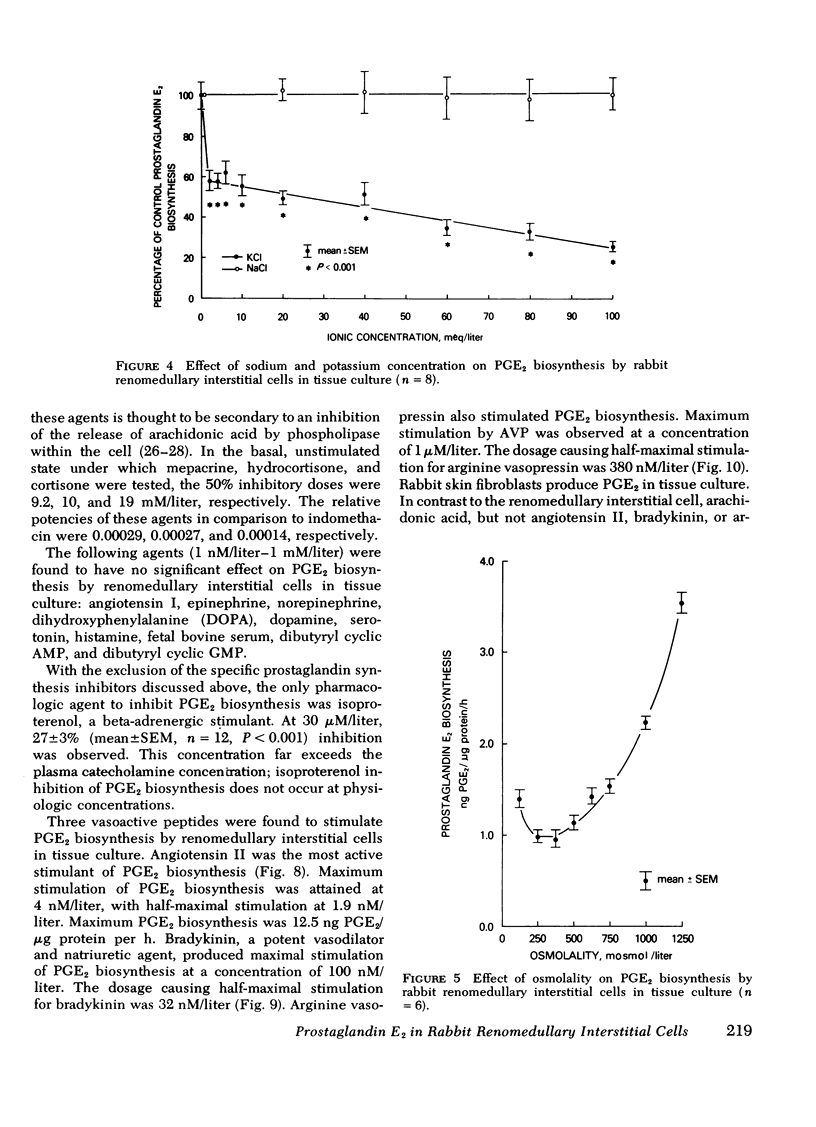
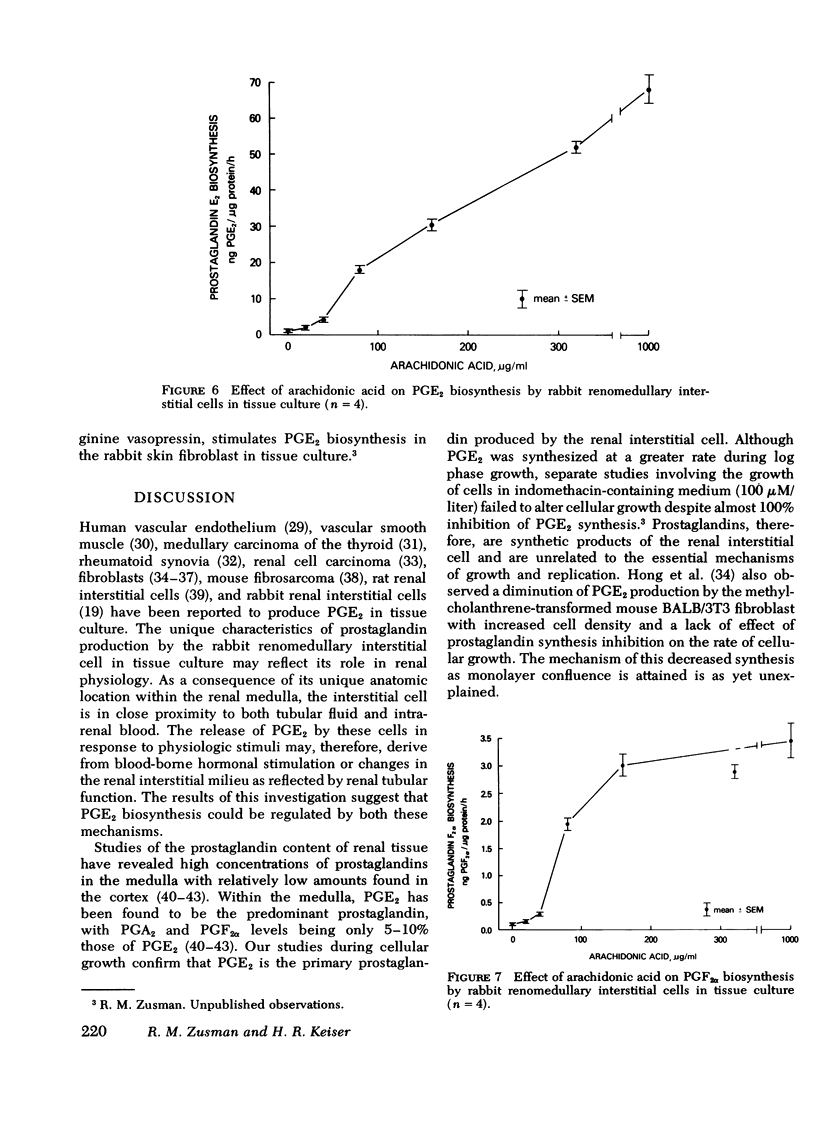
Rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells were isolated and grown in tissue culture. These cells synthesize 0.8 ng of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) per microgram cellular protein per hour in monolayer tissue culture; prostaglandins A2 and F2alpha (PGA2 and PGF2alpha) biosynthesis was 10 and 5% of PGE2 biosynthesis, respectively. Arachidonic acid markedly stimulated the production of PGE2 and PGF2alpha, with conversion rates of 0.24 and 0.02%/h, respectively. Angiotensin II, hyperosmolality, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin each stimulated PGE2 biosynthesis; maximum stimulation was 20, 3.7, 3.6, and 3.2 times basal production, respectively. PGE2 biosynthesis by the renomedullary interstitial cells was inhibited by isoproterenol, potassium, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (indomethacin, naproxen, ibuprofen, suprofen, meclofenamate, and acetylsalicylic acid), mepacrine (a phospholipase inhibitor), hydrocortisone, and cortisone. The rabbit renomedullary interstitial cell in tissue culture is a model system for the study of hormonal regulation of PGE2 biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. W., Vane J. R. Intrarenal prostaglandin release attenuates the renal vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Mar;184(3):678–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert W. C., Handler J. S. Effect of PGE1, indomethacin, and polyphloretin phosphate on toad bladder response to ADH. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1382–1386. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander R. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Stimulation of prostaglandin E synthesis in cultured human umbilical vein smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1617–1620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander R. W., Kent K. M., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R., Cooper T. Regulation of postocclusive hyperemia by endogenously synthesized prostaglandins in the dog heart. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1174–1181. doi: 10.1172/JCI108034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. J., Berl T., McDonald K. D., Schrier R. W. Evidence for an in vivo antagonism between vasopressin and prostaglandin in the mammalian kidney. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):420–426. doi: 10.1172/JCI108108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auletta F. J., Ausman R. M., Caldwell B. V. Development and standardization of radioimmunoassays for prostaglandins E, F, and A. Clin Chem. 1974 Dec;20(12):1580–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai K., Farber S. J., Paulsrud J. R. Analyses of renal medullary lipid droplets from normal, hydronephrotic, and indomethacin treated rabbits. Lipids. 1975 Sep;10(9):555–561. doi: 10.1007/BF02532360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowshaw K., McGiff J. C., Strand J. C., Lonigro A. J., Terrangno N. A. Prostaglandins in dog renal medulla. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;22(4):302–304. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1970.tb08523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowshaw K., Szlyk J. Z. Distribution of prostaglandins in rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):421–424. doi: 10.1042/bj1160421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings K. B., Wheelis R. F., Robertson R. P. Prostaglandin: increased production by renal cell carcinoma. Surg Forum. 1975;26:572–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damas J., Bourdon V. Libération d'acide arachidonique par la bradykinine. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1974;168(10-11-12):1445–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Chang L. C., Sweetman B. J., Nies A. S., Oates J. A. Synthesis of prostaglandins by the rat renal papilla in vitro. Mechanism of stimulation by angiotensin II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 18;388(1):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. J., Staley R. S., Harrison M. Characterization of prostaglandin production in tissue culture of rat renal medullary cells. Prostaglandins. 1976 Jul;12(1):37–49. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(76)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores A. G., Sharp G. W. Endogenous prostaglandins and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1392–1397. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frölich J. C., Wilson T. W., Sweetman B. J., Smigel M., Nies A. S., Carr K., Watson J. T., Oates J. A. Urinary prostaglandins. Identification and origin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):763–770. doi: 10.1172/JCI107987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Alexander R. W. Angiotensin II stimulation of prostaglandin production in cultured human vascular endothelium. Science. 1975 Jul 18;189(4198):219–220. doi: 10.1126/science.1138377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimley P. M., Deftos L. J., Weeks J. R., Rabson A. S. Growth in vitro and ultrastructure of cells from a medullary carcinoma of the human thyroid gland: transformation by simian virus 40 and evidenc of thyrocalcitonin and prostaglandins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Apr;42(4):663–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Samuelsson B., Bjursell G. Prostaglandin levels in normal and transformed baby-hamster-kidney fibroblasts. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 9;243(123):50–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B., Jaffee B. M., Philpott G. W. Prostaglandin production by neuroblastoma, glioma and fibroblast cell lines; stimulation by N6,02'-dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. FEBS Lett. 1973 Oct 15;36(2):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Polsky-Cynkin R., Levine L. Stimulation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by vasoactive substances in methylcholanthrene-transformed mouse BALB/3T3. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):776–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalisker A., Dyer D. C. In vitro release of prostaglandins from the renal medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;19(3):305–309. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson C., Weber P., Anggård E. Arachidonic acid increases and indomethacin decreases plasma renin activity in the rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;28(2):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. B., Crowshaw K., Takman B. H., Attrep K. A. The identification of prostaglandins E(2), F(2alpha) and A(2) from rabbit kidney medulla. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1251–1260. doi: 10.1042/bj1051251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson L. C., Sharp G. W. Effect of prostaglandin E1 on sodium transport and osmotic water flow in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1046–1052. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum G. M., Aisenbrey G. A., Dunn M. J., Berl T., Schrier R. W., McDonald K. M. In vivo effect of indomethacin to potentiate the renal medullary cyclic AMP response to vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):8–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI108624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin-like substance into renal venous blood in response to angiotensin II. Circ Res. 1970 Jul;27(1 Suppl 1):121–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Itskovitz H. D., Terragno A., Wong P. Y. Modulation and mediation of the action of the renal kallikrein-kinin system by prostaglandins. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin E-like substance from canine kidney by bradykinin. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):36–43. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muirhead E. E., Germain G., Leach B. E., Pitcock J. A., Stephenson P., Brooks B., Brosius W. L., Daniels E. G., Hinman J. W. Production of renomedullary prostaglandins by renomedullary interstitial cells grown in tissue culture. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(9 Suppl):161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Colina-Chourio J. Interaction of mineralocorticoids, renal prostaglandins and the renal kallikrein-kinin system. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):189–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen H. M., Bojesen I. On lipid droplets in renal interstitial cells. IV. Isolation and identification. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969 May 23;97(2):274–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00344762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOFF J., HANDLER J. S., BERGSTROM S. EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN (PGE-1) ON THE PERMEABILITY RESPONSE OF TOAD BLADDER TO VASOPRESSIN, THEOPHYLLINE AND ADENOSINE 3',5'-MONOPHOSPHATE. Nature. 1965 Jan 23;205:397–398. doi: 10.1038/205397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi E. M., Stylos W. A. Prostaglandin production in cultures of BALB/3T3 and SV3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):529–533. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr, Levine L. Prostaglandin-stimulated bone resorption by rheumatoid synovia. A possible mechanism for bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1172/JCI108195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Dunlap C. L., Strong C. G. The effect of indomethacin and other anti-inflammatory drugs on the renin-angiotensin system. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):282–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI108470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumpf K. W., Frenzel S., Lowitz H. D., Scheler F. Die Wirkung von Indomethacin auf die basale und stimulierte Plasmareninaktivität beim Menschen. Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Mar 15;54(6):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01468920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D., Zusman R. M., Caldwell B. V., Speroff L. The distribution of prostaglandins A, E, and F in the human kidney. Prostaglandins. 1974 May 10;6(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Voelkel E. F., Goldhaber P., Levine L. Prostaglandins, calcium metabolism and cancer. Fed Proc. 1974 Jan;33(1):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno N. A., Lonigro A. J., Malik K. U., McGiff J. C. The relationship of the renal vasodilator action of bradykinin to the release of a prostaglandin E-like substance. Experientia. 1972 Apr 15;28(4):437–439. doi: 10.1007/BF02008327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Direct effects of prostaglandin on renal function and renin release in anesthetized dog. Am J Physiol. 1968 Feb;214(2):218–221. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vargaftig B. B., Hai N. D. Selective inhibition by mepacrine of the release of "rabbit aorta contracting substance" evoked by the administration of bradykinin. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;24(2):159–161. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zins G. R. Renal prostaglandins. Am J Med. 1975 Jan;58(1):14–24. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Keiser H. R. Prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells in tissue culture. Mechanism of stimulation by angiotensin II, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2069–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M. Quantitative conversion of PGA or PGE to PGB. Prostaglandins. 1972 Feb;1(2):167–168. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(72)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


