Abstract
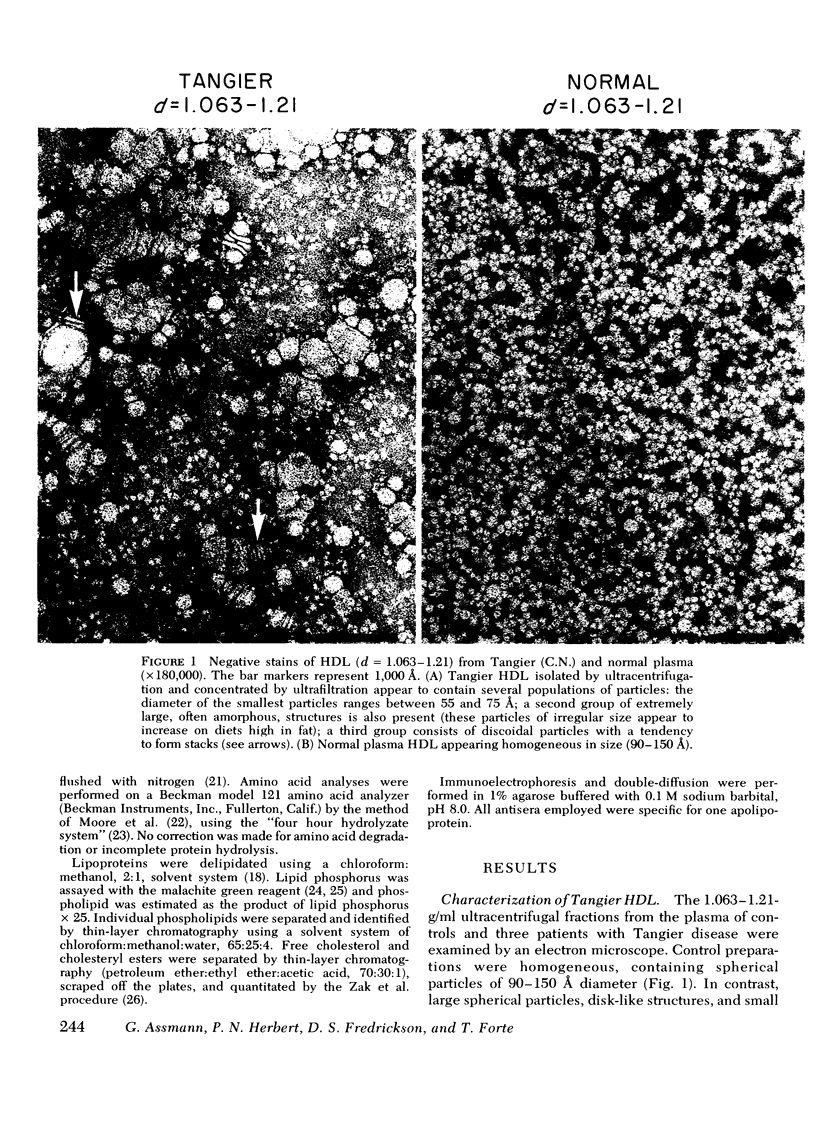
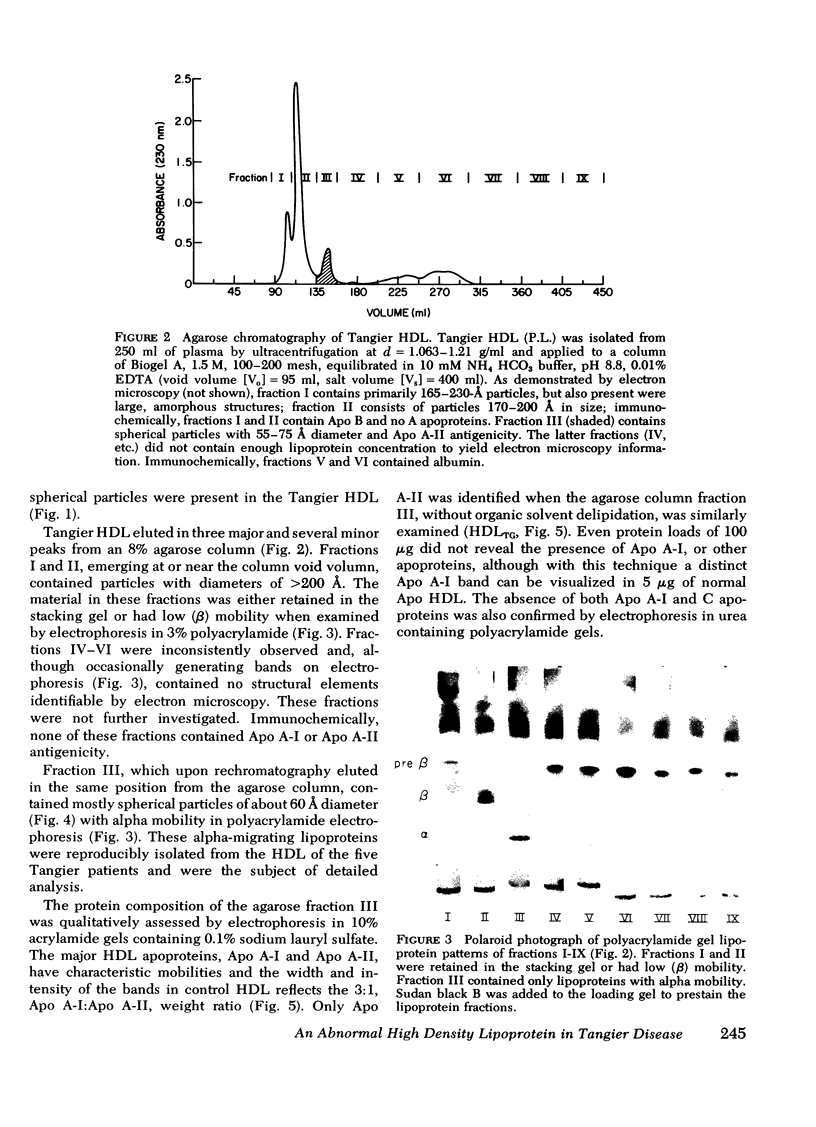
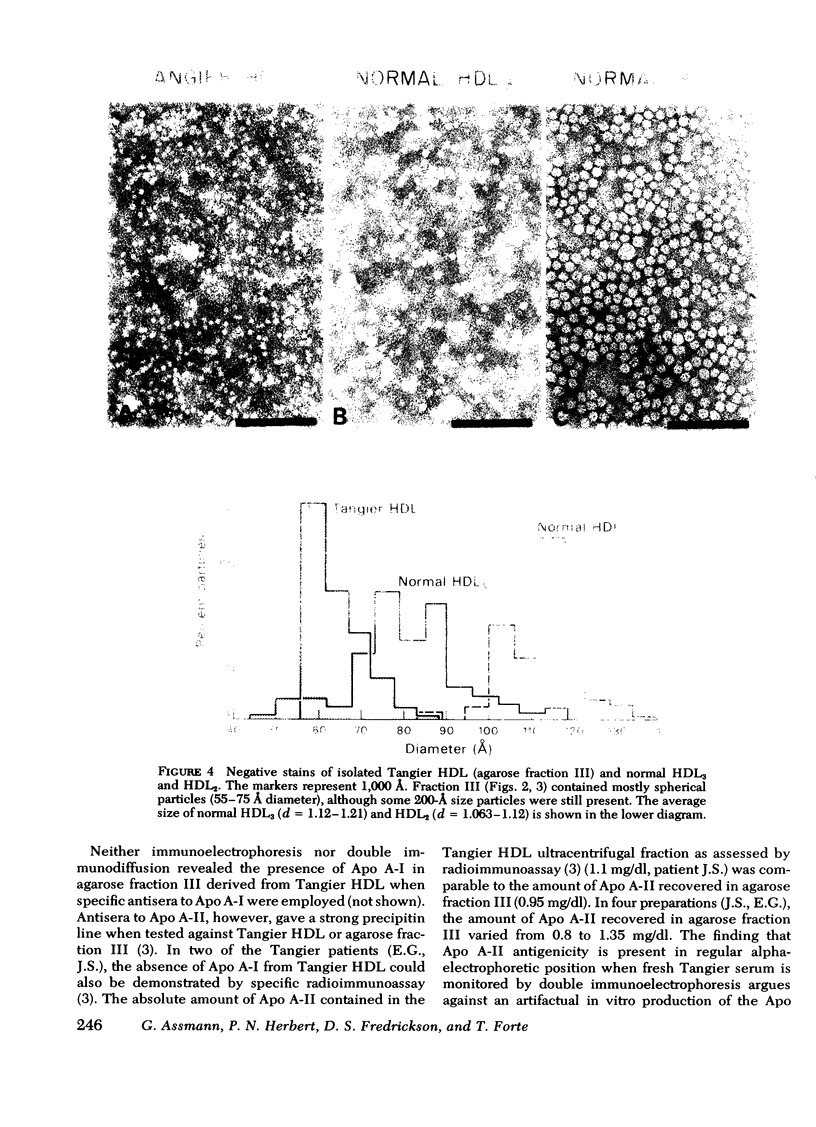
The nature of the high density lipoproteins has been investigated in five patients homozygous for Tangier disease (familial high density lipoprotein deficiency). It has been established that Tangier high density lipoproteins, as isolated by ultracentrifugation, are morphologically heterogenous and contain several proteins (Apo B, albumin, and Apo A-II). An abnormal lipoprotein has been isolated from the d = 1.063-1.21 g/ml ultracentrifugal fraction by agarose-column chromatography which contains apoprotein A-II as the sole protein constituent. In negative-stain electron microscopy, these lipoproteins appeared as spherical particles 55-75 Å in diameter. By a variety of criteria (immunochemical, polyacrylamide electrophoresis, amino acid composition, and fluorescence measurements), apoprotein A-I the major apoprotein of normal high density lipoproteins and the C apoproteins were absent from this lipoprotein. As demonstrated by 125I very low density lipoprotein incubation experiments with Tangier plasma, C apoproteins did not associate with lipoproteins of d = 1.063-1.21 g/ml. Tangier apoprotein A-II, isolated to homogeneity by delipidation of the apoprotein A-II-containing lipoprotein or Sephadex G-200 guanidine-HCl chromatography of the d = 1.063-1.21 g/ml fraction, was indistinguishable from control apoprotein A-II with respect to amino acid composition and migration of tryptic peptides in urea-polyacrylamide electrophoresis. The ability of Tangier apoprotein A-II to bind phospholipid was demonstrated by in vitro reconstitution experiments and morphological and chemical analysis of lipid-protein complexes.
It is concluded that normal high density lipoproteins, as defined by polypeptide composition and morphological appearance, are absent from Tangier plasma and that as a consequence, the impairment of C apoprotein metabolism contributes to the hypertriglyceridemia and fasting chylomicronemia observed in these patients.
Full text
PDF

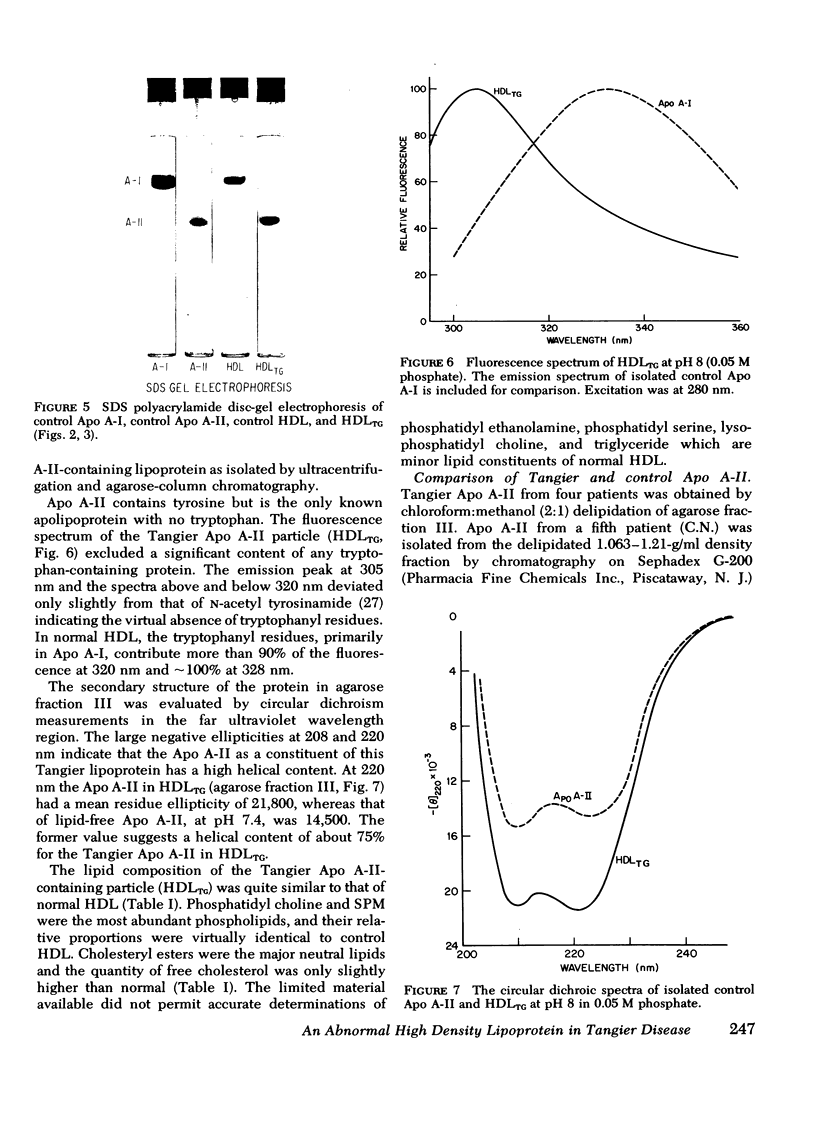
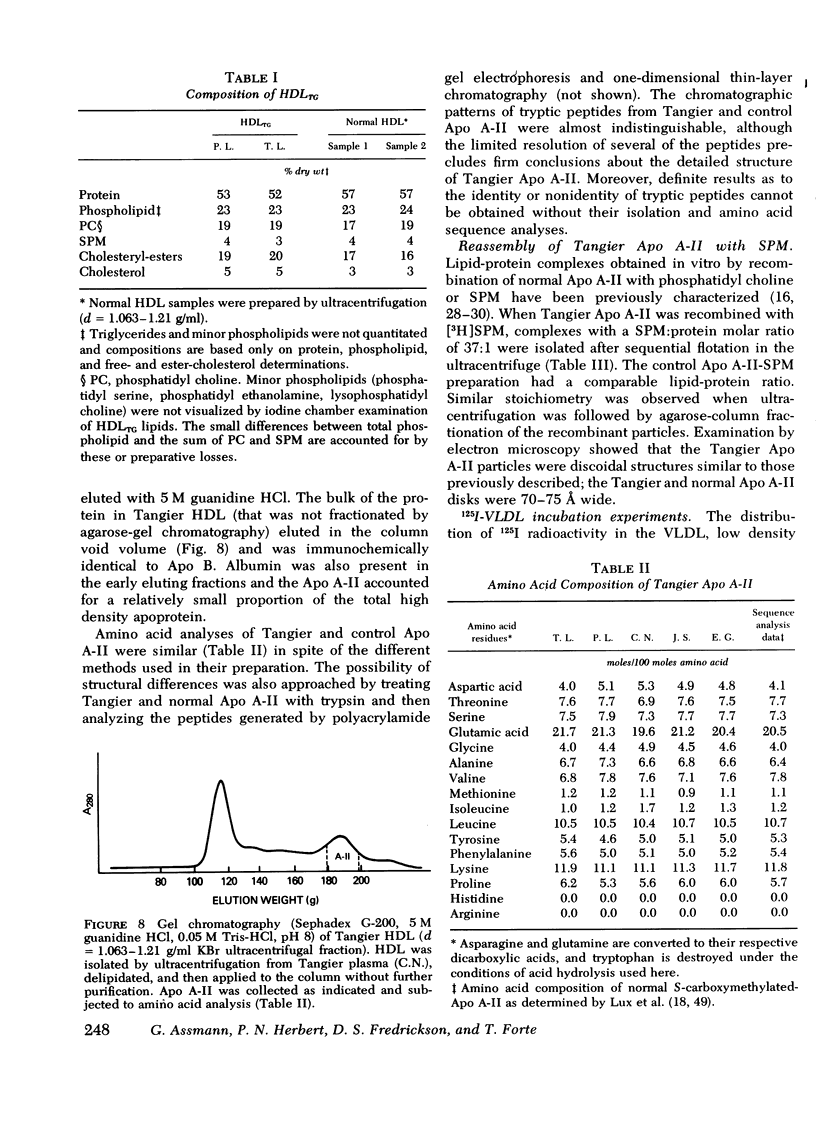
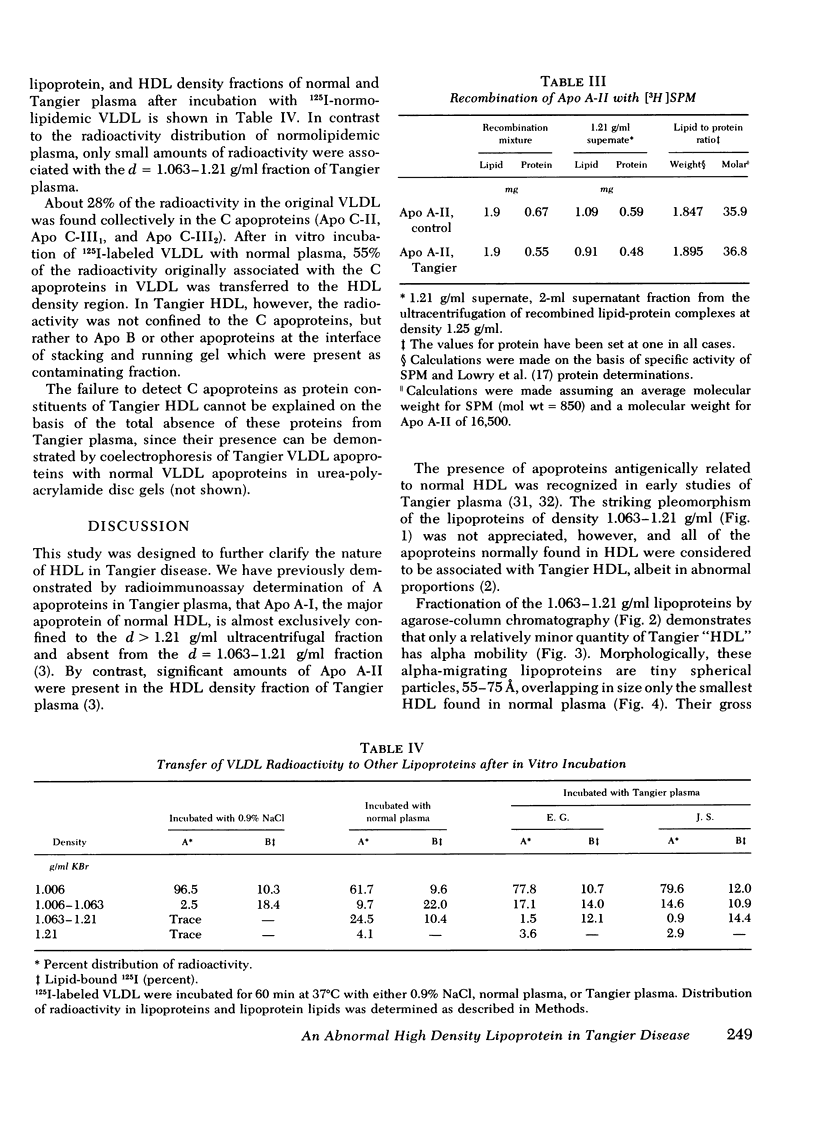



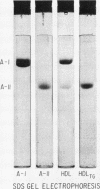
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assmann G., Brewer H. B., Jr Lipid-protein interactions in high density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Smootz E., Adler K., Capurso A., Oette K. The lipoprotein abnormality in Tangier disease: quantitation of A apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):565–575. doi: 10.1172/JCI108672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. S., Wilchek M., Edelhoch H. Structural studies on polypeptide hormones. II. Polarization of fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4398–4405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomhoff J. P. High density lipoproteins in cholestasis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1974;9(6):591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalvardjian A., Rudnicki E. Determination of lipid phosphorus in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson B., Ekman R., Petersson B. G. An abnormal high density lipoprotein in cholestatic plasma isolated by zonal ultracentrifugation. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S. THE INHERITANCE OF HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEIN DEFICIENCY (TANGIER DISEASE). J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:228–236. doi: 10.1172/JCI104907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Fredrickson D. S. The pathology of Tangier disease. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):101–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R. The metabolic role of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase: perspectives form pathology. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11:1–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotto A. M., Shore B. Conformation of human serum high density lipoprotein and its peptide components. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):69–70. doi: 10.1038/224069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield N., Fasman G. D. Computed circular dichroism spectra for the evaluation of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4108–4116. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J., Brewer B., Jr, Edelhoch H. The molecular properties of ApoA-I from human high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2411–2416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman H. N., Fredrickson D. S. Tangier disease (familial high density lipoprotein deficiency). Clinical and genetic features in two adults. Am J Med. 1965 Oct;39(4):582–593. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard R. W. Studies in accelerated amino acid analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jun 9;19(6):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya K., Ui M. A new micromethod for the colorimetric determination of inorganic phosphate. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Sep;14(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. L., Morrisett J. D., Pownall H. J., Gotto A. M., Jr Human high density lipoprotein, apolipoprotein glutamine II. The immunochemical and lipid-binding properties of apolipoprotein glutamine II derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5218–5224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Potts J. T., Jr Improved recovery of methionine after acid hydrolysis using mercaptoethanol. Anal Biochem. 1969 May;29(2):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer K. H., Utermann G., Menzel H. J. On the polypeptide composition of an abnormal high density lipoprotein (LP-E) occurring in LCAT-deficient plasma. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 1;45(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80803-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Isolation and characterization of apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), a plasma high density apolipoprotein containing two identical polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7510–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Fleischer S., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Identification of the lipid-binding cyanogen bromide fragment from the cystine-containing high density apolipoprotein, APOLP-GLN-II. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., John K. M., Ronan R., Brewer H. B., Jr Isolation and characterization of the tryptic and cyanogen bromide peptides of apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), plasma high density apolipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7519–7527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., Levy R. I., Gotto A. M., Fredrickson D. S. Studies on the protein defect in Tangier disease. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2505–2519. doi: 10.1172/JCI107066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masket B. H., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. The use of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in differentiating type 3 hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 May;81(5):794–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V., Forte T., Albers J. J., King W. C., Mitchell C. D., Applegate K. R., Gong E. L., Cabana V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: effects of incubation with lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1975;142:31–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld R. A., Small P. A., Jr Electrophoretic heterogeneity of polypeptide chains of specific antibodies. Science. 1966 May 27;152(3726):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3726.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Hansma H., Ostwald R. Characterization of guinea pig plasma lipoproteins: the appearance of new lipoproteins in response to dietary cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1972 Sep;13(5):624–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. M. The effect of reduction and carboxymethylation on the circular dichroic spectra of two polypeptide classes of serum high density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 31;200(3):570–572. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90114-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Hirz R. On the structure of human serum high-density lipoprotein: studies by the technique of circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Mar;59(3):890–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.3.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A. Studies on the conformation of human serum high-density lipoproteins HDL2 and HDL3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1699–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Toth J., Edelstein C., Koga S., Stiller E. Fractionation of human serum high density lipoprotein in urea solutions. Evidence for polypeptide heterogeneity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3309–3316. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., LeKim D., Tschung T. S. A simple chemical method for labelling phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelin in the choline moiety. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Aug;352(8):1058–1064. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1971.352.2.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoffel W., Zierenberg O., Tunggal B., Schreiber E. 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic evidence for hydrophobic lipid-protein interactions in human high density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3696–3700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Menzel H. J., Langer K. H., Dieker P. Lipoproteins in lecithin-cholesterol-acyltransferase(LCAT)-deficiency. II. Further studies on the abnormal high-density-lipoproteins. Humangenetik. 1975;27(3):185–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00278345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf D. S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Cutaneous cholesterol ester deposition in Tangier disease. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Feb;95(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZAK B., DICKENMAN R. C., WHITE E. G., BURNETT H., CHERNEY P. J. Rapid estimation of free and total cholesterol. Am J Clin Pathol. 1954 Nov;24(11):1307–1315. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/24.11_ts.1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]