Abstract
Human plasma alpha2-plasmin inhibitor in fibrinolytic states was studied using immunochemical methods and radioiodinated plasminogen. The concentration and activity of plasma alpha2-plasmin inhibitor decreased when urokinase was added to plasma in vitro or infused intravenously in man. The decrease was associated with the appearance of plasmin-alpha2-plasmin inhibitor complex which subsequently disappeared from the circulation in a short time. A decrease of other major inhibitors, such as alpha2-macroglobulin and alpha1-antitrypsin, was not observed when the amount of urokinase added or infused was relatively small, and conversion of plasminogen to plasmin was not extensive. The formation of plasmin-alpha2-macroglobulin complex was observed only when plasma plasminogen was activated with a larger amount of urokinase, and after most of the alpha2-plasmin inhibitor was consumed by forming complexes with plasmin. The formation of plasmin-alpha1-antitrypsin complex was not observed even in the highly activated plasma unless exogenous plasmin was added to the plasma. alpha2-Plasmin inhibitor was the only inhibitor of which the concentration in plasma was significantly decreased in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis among the major plasmin inhibitors in plasma. The most reactive inhibitor for regulating plasma fibrinolysis very likely is alpha2-plasmin inhibitor.
Full text
PDF
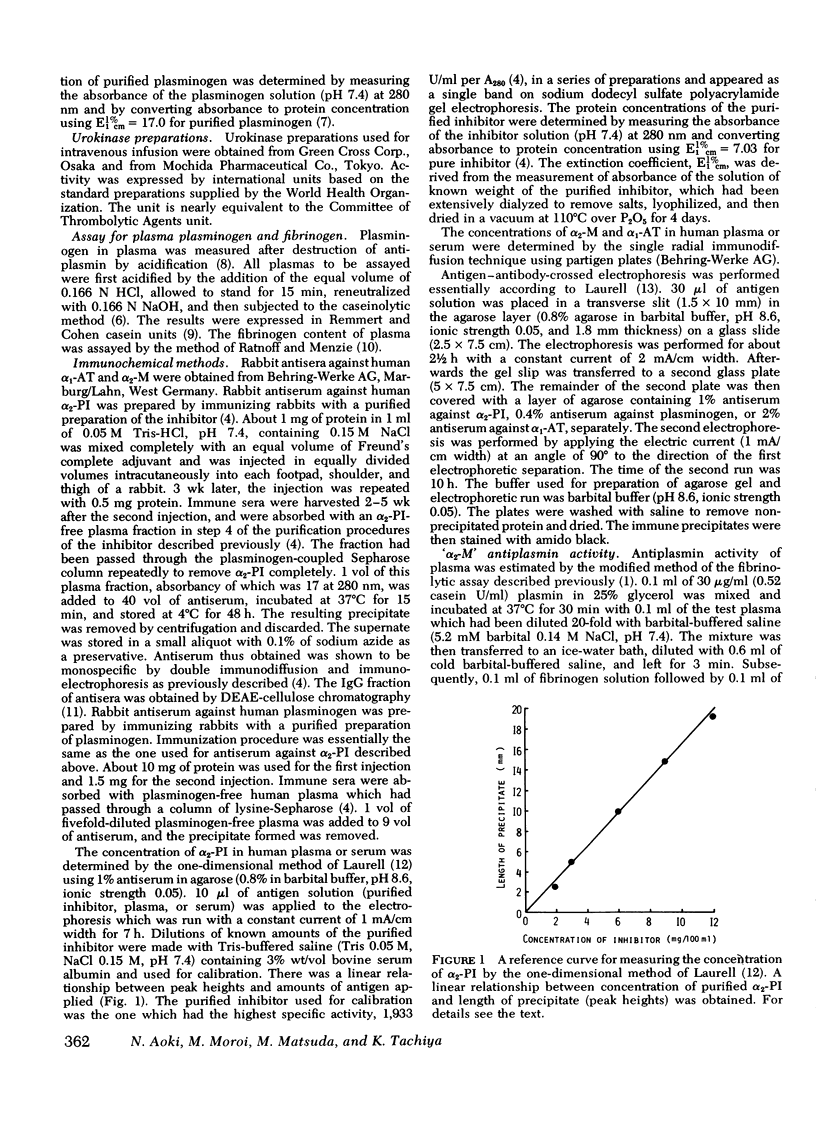


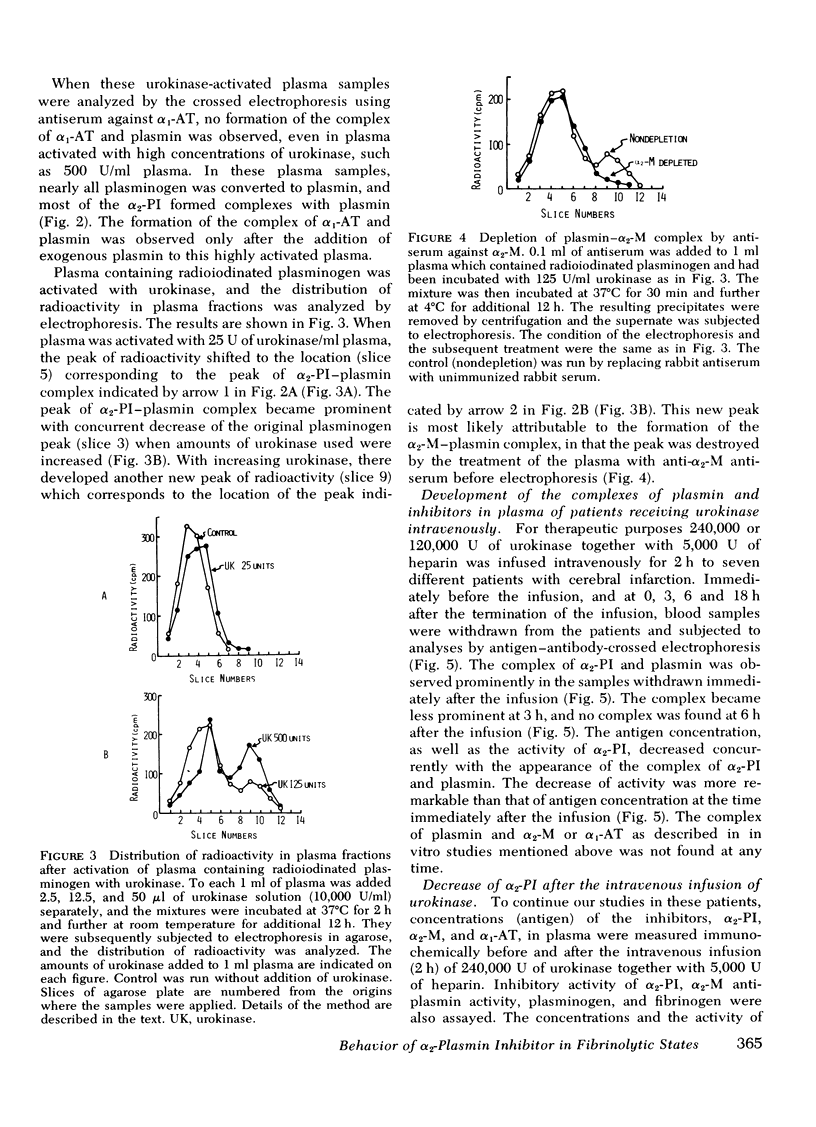
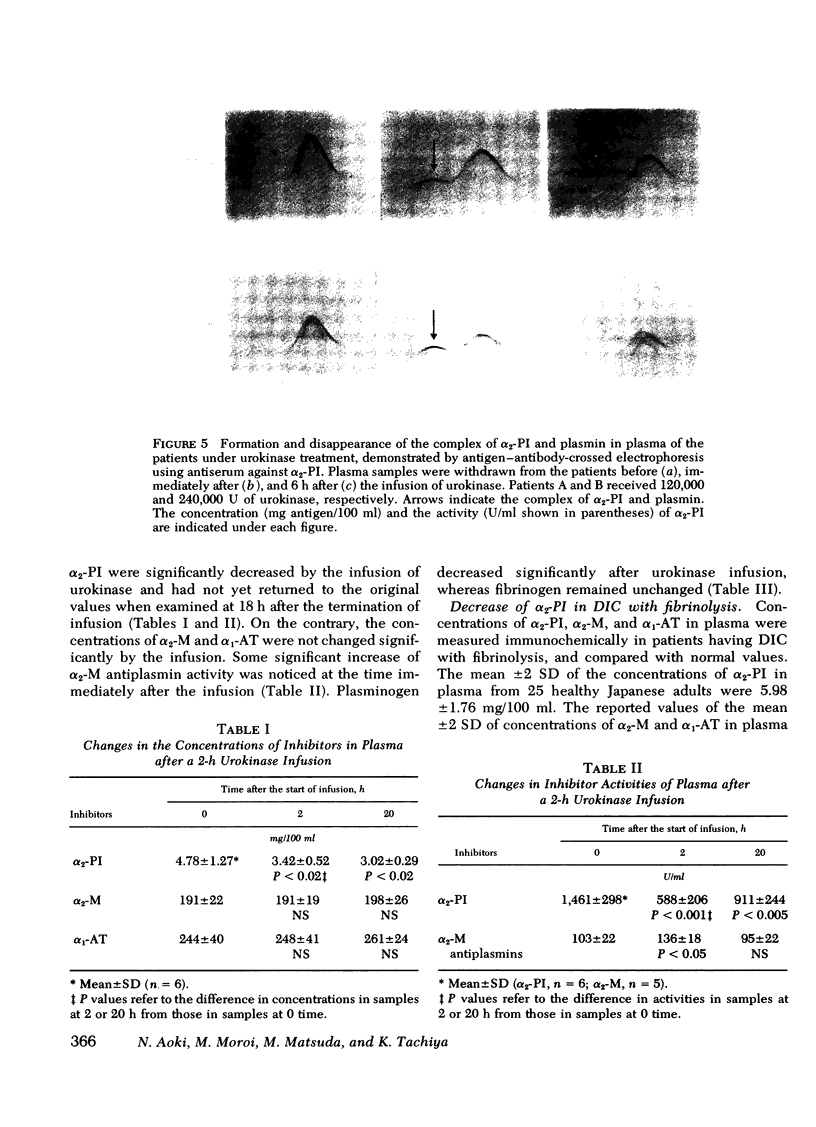



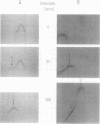
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Kawano T. Inhibition of plasminogen activators by naturally occurring inhibitors in man. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1334–1337. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Moroi M. Distinction of serum inhibitor of activator-induced clot lysis from alpha1-antitrypsin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Jun;146(2):567–570. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki N., Von Kaulla K. N. Human serum plasminogen antiactivator: its distinction from antiplasmin. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1137–1145. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnesen H., Fagerhol M. K. 2 -Macroglobulin, 1 -antitrypsin, and antithrombin III in plasma and serum during fibrinolytic therapy with urokinase. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 May;29(3):259–263. doi: 10.3109/00365517209080240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow G. H., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Molecular weight studies on human plasminogen and plasmin at the microgram level. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1138–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockway W. J., Castellino F. J. Measurement of the binding of antifibrinolytic amino acids to various plasminogens. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jul;151(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90488-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen D., De Cock, Verstraete M. Immunochemical distinction between antiplasmin and alpha-antitrypsin. Thromb Res. 1975 Jul;7(1):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90142-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edy J., De Cock F., Collen D. Inhibition of plasmin by normal and antiplasmin-depleted human plasma. Thromb Res. 1976 Apr;8(4):513–518. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore M. J. Serum inhibitors in fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 1975 Oct;31(2):217–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:39–47. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U. Studies on an inhibitor of plasminogen activation in human serum. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1973 Nov;30(2):414–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hender U., Collen D. Immunochemical distinction between the inhibitors of plasminogen activation and antiplasmin in human plasma. Thromb Res. 1976 Jun;8(6):875–879. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highsmith R. F., Rosenberg R. D. The inhibition of human plasmin by human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4335–4338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto M., Abiko Y. Plasminogen-plasmin system. VI. Preparation of alpha 2-macroglobulin antiplasmin from human plasma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):402–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebreton de Vonne T., Mouray H., Berthillier G., Got R. Influence du vieillissement des a 2 -macroglobulines de lapin sur la formation du complexe a 2 -macroglobuline-enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 29;257(2):365–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L. A rapid method for the purification of bovine thrombin and the inhibition of the purified enzyme wtih phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2501–2506. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONKHOUSE F. C. THE INFLUENCE OF INORGANIC SALTS ON PLASMA ANTITHROMBIN ACTIVITY. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Jul 15;143:387–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T. [Blood coagulation and apoplexy]. Nihon Rinsho. 1976 Jan 10;34(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merskey C., Kleiner G. J., Johnson A. J. Quantitative estimation of split products of fibrinogen in human serum, relation to diagnosis and treatment. Blood. 1966 Jul;28(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi M., Aoki N. Isolation and characterization of alpha2-plasmin inhibitor from human plasma. A novel proteinase inhibitor which inhibits activator-induced clot lysis. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):5956–5965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mui P. T., James H. L., Ganguly P. Isolation and properties of a low molecular weight antiplasmin of human blood platelets and serum. Br J Haematol. 1975 Apr;29(4):627–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb02749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllertz S. Different molecular forms of plasminogen and plasmin produced by urokinase in human plasma and their relation to protease inhibitors and lysis of fibrinogen and fibrin. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):273–283. doi: 10.1042/bj1430273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MENZIE C. A new method for the determination of fibrinogen in small samples of plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Feb;37(2):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REMMERT L. F., COHEN P. P. Partial purification and properties of a proteolytic enzyme of human serum. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):431–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE D. S., FAHEY J. L. A NEW CLASS OF HUMAN IMMUNOGLOBULINS. II. NORMAL SERUM IGD. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:185–199. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spöttl F., Holzknecht F. The influence of inhibitors of plasmin and plasminogen activation on the streptokinase-induced fibrinolytic state. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Oct 31;24(1):101–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]