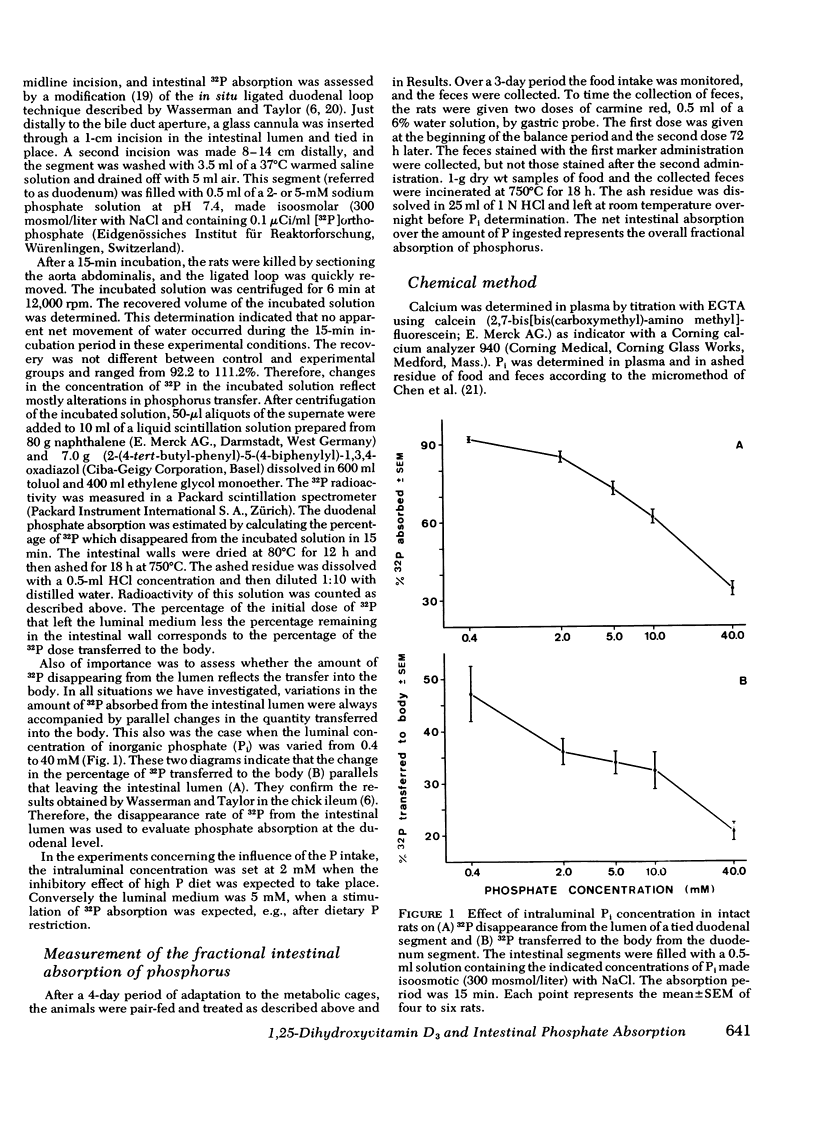
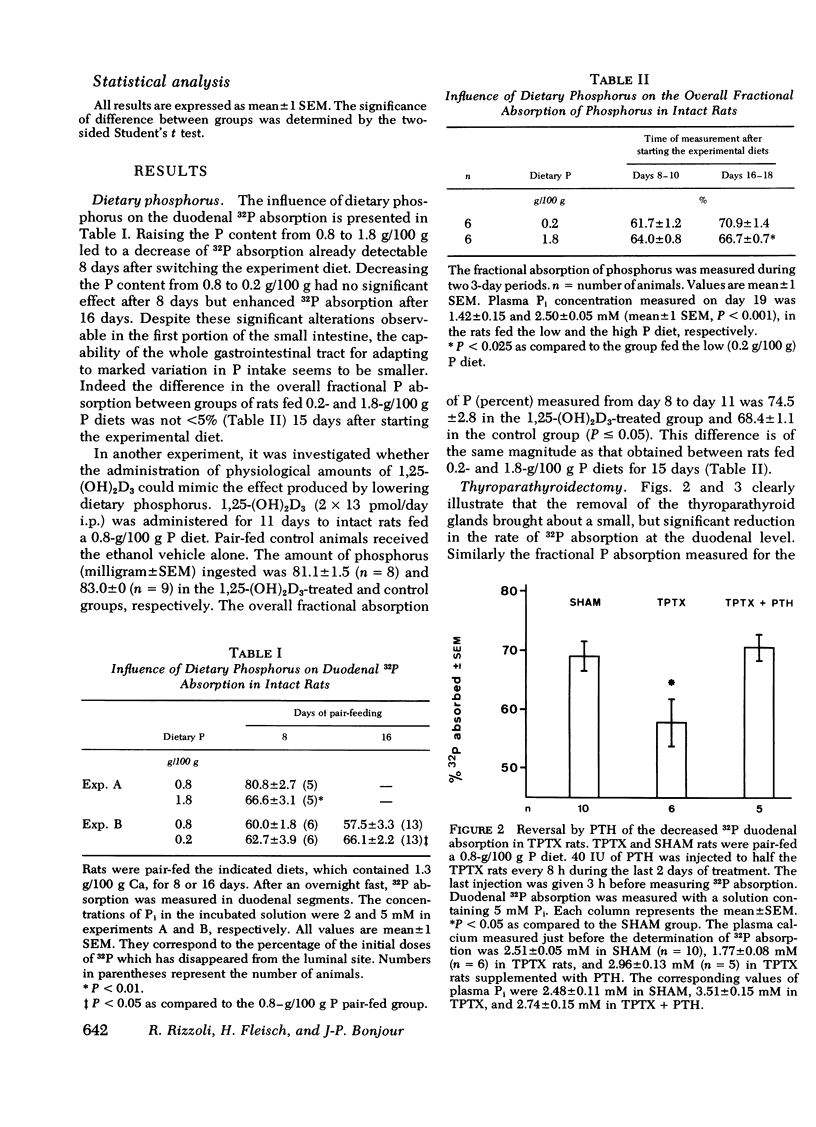
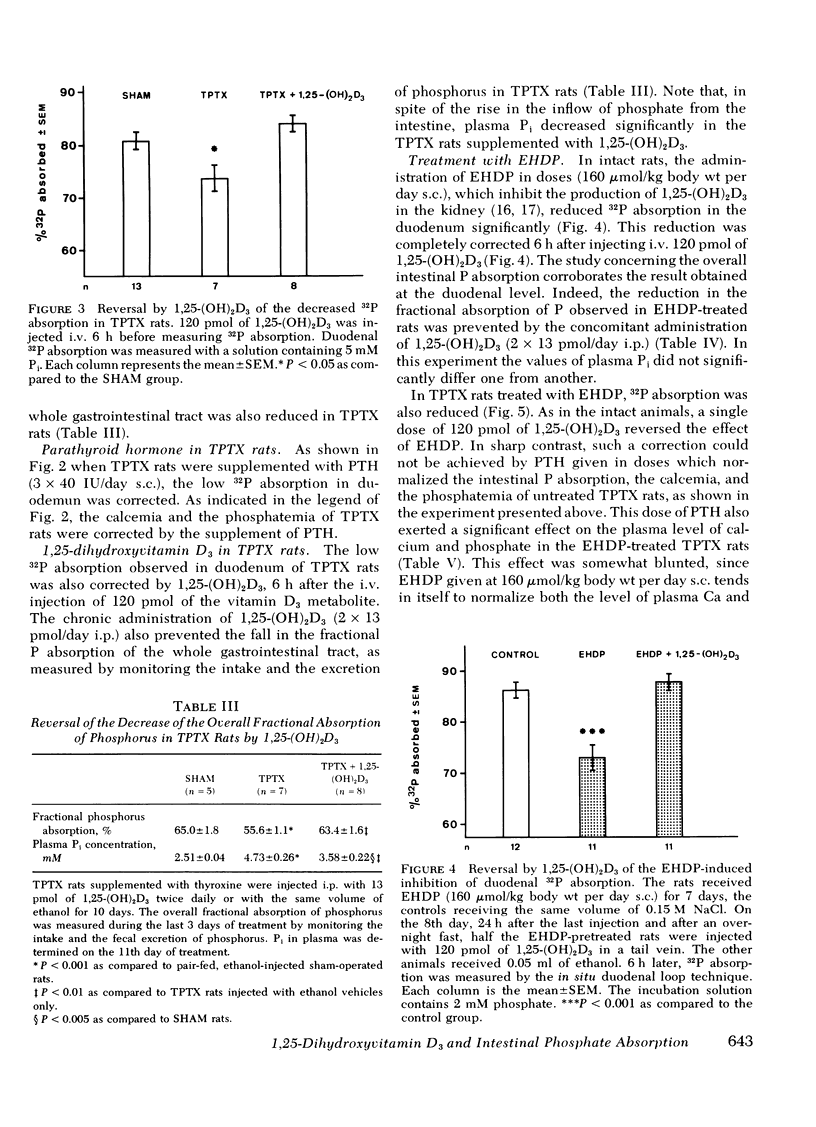
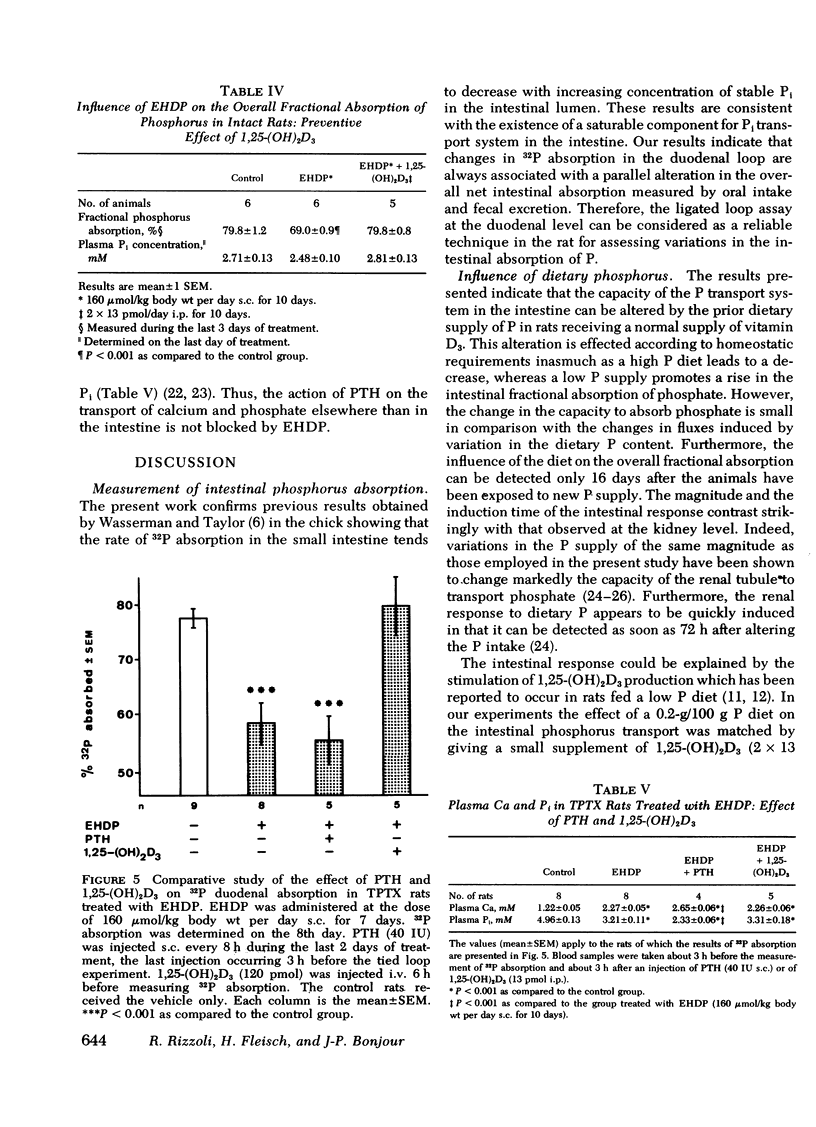
Abstract
In vitamin D-deficient rats, impaired intestinal phosphorus (P) absorption can be corrected by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3[1,25-(OH)2D3]. In the present study, it was investigated whether changes in 1,25-(OH)2D3 production can influence intestinal P transport also in animals with a normal supply of vitamin D. The intestinal P absorption was evaluated in rats using both the in situ duodenal loop technique and the determination of the overall gastrointestinal absorption under three conditions known to influence the production of 1,25-(OH)2D3: (a) variation in dietary P, (b) thyroparathyroidectomy (TPTX) with or without administration of parathyroid hormone (PTH), and (c) treatment with disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate (EHDP). In all circumstances changes in duodenal absorption paralleled the changes in the overall fractional absorption. (a) Lowering dietary P stimulated P absorption. (b) TPTX decreased P absorption. This effect was corrected either by the administration of PTH or by the administration of 1,25-(OH)2D3. (c) EHDP, when given at a dose known to inhibit 1,25-(OH)2D3 formation, decreased the duodenal P absorption in both intact and TPTX animals. This effect was corrected by 1,25-(OH)2D3. In the TPTX-EHDP-treated animals, the administration of PTH did not rectify the low duodenal P absorption. These results support the thesis that, in rats with normal vitamin D supply, variations in the endogenous production of 1,25-(OH)2D3 change the rate of P absorption. However, these changes are in such magnitude that they are of relatively small importance when compared to the effect of variation in the dietary intake of P. These results also strongly suggest that the action of PTH on duodenal P transport is mediated by its effect on 1,25-(OH)2D3 production, inasmuch as the effect of the hormone is abolished after blocking the renal 1-hydroxylation with EHDP.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORLE A. B., KEUTMANN H. T., NEUMAN W. F. Role of parathyroid hormone in phosphate transport across rat duodenum. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:705–709. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter L. A., DeLuca H. F. Stimulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3-1alpha-hydroxylase by phosphate depletion. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3158–3161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., DeLuca H. F., Fleisch H., Trechsel U., Matejowec L. A., Omdahl J. L. Reversal of the EHDP inhibition of calcium absorption by 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. Eur J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;3(1):44–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1973.tb00328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H., Trechsel U. Calcium absorption in diphosphonate-treated rats: effect of parathyroid function, dietary calcium and phosphorus. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(1):125–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSSON A. The effect of vitamin D on the absorption of inorganic phosphate. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954 Aug 20;31(4):301–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caniggia A., Gennari C., Bencini M., Palazzuoli V. Intestinal absorption of radio phosphate in osteomalacia before and after vitamin D treatment. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968;2(3):299–300. doi: 10.1007/BF02279218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. C., Castillo L., Korycka-Dahl M., DeLuca H. F. Role of vitamin D metabolites in phosphate transport of rat intestine. J Nutr. 1974 Aug;104(8):1056–1060. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.8.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I., Rivera-Cordero F. Effect of parathyroid function on absorption and excretion of calcium, magnesium and phosphate by rats. Endocrinology. 1971 Feb;88(2):302–308. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-2-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I., Rivera-Cordero F. Effects of endogenous parathyroid hormone on calcium, magnesium and phosphate metabolism in rats. II. Alterations in dietary phosphate. Endocrinology. 1974 Aug;95(2):360–369. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-2-360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I., Rivera-Cordero F. Effects of endogenous parathyroid hormone on calcium, magnesium and phosphate metabolism in rats. Endocrinology. 1973 Jan;92(1):62–71. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-1-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen M. J., Doherty G. F., Ingbar S. H. The effect of hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis on thyroxine metabolism in the rat. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1028–1033. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. R., Kodicek E. Regulation of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol-1-hydroxylase activity in kidney by parathyroid hormone. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 7;241(110):163–166. doi: 10.1038/newbio241163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M., Holick M. F., Deluca H. F., Boyle I. T. Control of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol metabolism by parathyroid glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1673–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M., Tanaka Y., Holick M. F., Deluca H. F. Response of intestinal calcium transport and bone calcium mobilization to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in thyroparathyroidectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1974 Apr;94(4):1022–1027. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-4-1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E., HARRISON H. C. Intestinal transport of phosphate: action of vitamin D, calcium, and potassium. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1007–1012. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill L. F., Lumb G. A., Mawer E. B., Stanbury S. W. Indirect inhibition of the biosynthesis of 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in rats treated with a diphosphonate. Clin Sci. 1973 Apr;44(4):335–347. doi: 10.1042/cs0440335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. R., Brumbaugh P. F., Hussler M. R., Wergedal J. E., Baylink D. J. Regulation of serum 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 by calcium and phosphate in the rat. Science. 1975 Nov 7;190(4214):578–580. doi: 10.1126/science.1188357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz S., Bar A. Site of vitamin D action in chick intestine. Am J Physiol. 1972 Mar;222(3):761–767. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowarski S., Schachter D. Effects of vitamin D on phosphate transport and incorporation into mucosal constituents of rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz F., Harrison H. C., Harrison H. E. Influence of parathyroid function upon the in vitro transport of calcium and phosphate by the rat intestine. Endocrinology. 1969 Apr;84(4):912–917. doi: 10.1210/endo-84-4-912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribovich M. L., DeLuca H. F. The influence of dietary calcium and phosphorus on intestinal calcium transport in rats given vitamin D metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Oct;170(2):529–535. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. G., Mühlbauer R. C., Bisaz S., Williams D. A., Fleisch H. The influence of pyrophosphate, condensed phosphates, phosphonates and other phosphate compounds on the dissolution of hydroxyapatite in vitro and on bone resorption induced by parathyroid hormone in tissue culture and in thyroparathyroidectomised rats. Calcif Tissue Res. 1970;6(3):183–196. doi: 10.1007/BF02196199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele T. H., DeLuca H. F. Influence of dietary phosphorus on renal phosphate reabsorption in the parathyroidectomized rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):867–874. doi: 10.1172/JCI108363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Deluca H. F. The control of 25-hydroxyvitamin D metabolism by inorganic phosphorus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Feb;154(2):566–574. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Frank H., DeLuca H. F. Intestinal calcium transport: stimulation by low phosphorus diets. Science. 1973 Aug 10;181(4099):564–566. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4099.564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A. N. In vitro phosphate transport in chick ileum: effect of cholecalciferol, calcium, sodium and metabolic inhibitors. J Nutr. 1974 Apr;104(4):489–494. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.4.489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trohler U., Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H. Renal tubular adaptation to dietary phosphorus. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):145–146. doi: 10.1038/261145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tröhler U., Bonjour J. P., Fleisch H. Inorganic phosphate homeostasis. Renal adaptation to the dietary intake in intact and thyroparathyroidectomized rats. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):264–273. doi: 10.1172/JCI108277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WASSERMAN R. H., COMAR C. L. The parathyroids and the intestinal absorption of calcium, strontium and phosphate ions in the rat. Endocrinology. 1961 Dec;69:1074–1079. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-6-1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling M. W., Kimberg D. V. Effects of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and Solanum glaucophyllum on intestinal calcium and phosphate transport and on plasma Ca, Mg and P levels in the rat. Endocrinology. 1975 Dec;97(6):1567–1576. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-6-1567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling M. W., Kimberg D. V., Wasserman R. H., Feinberg R. R. Duodenal active transport of calcium and phosphate in vitamin D-deficient rats: effects of nephrectomy, Cestrum diurnum, and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinology. 1976 May;98(5):1130–1134. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-5-1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Taylor A. N. Intestinal absorption of phosphate in the chick: effect of vitamin D and other parameters. J Nutr. 1973 Apr;103(4):586–599. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


