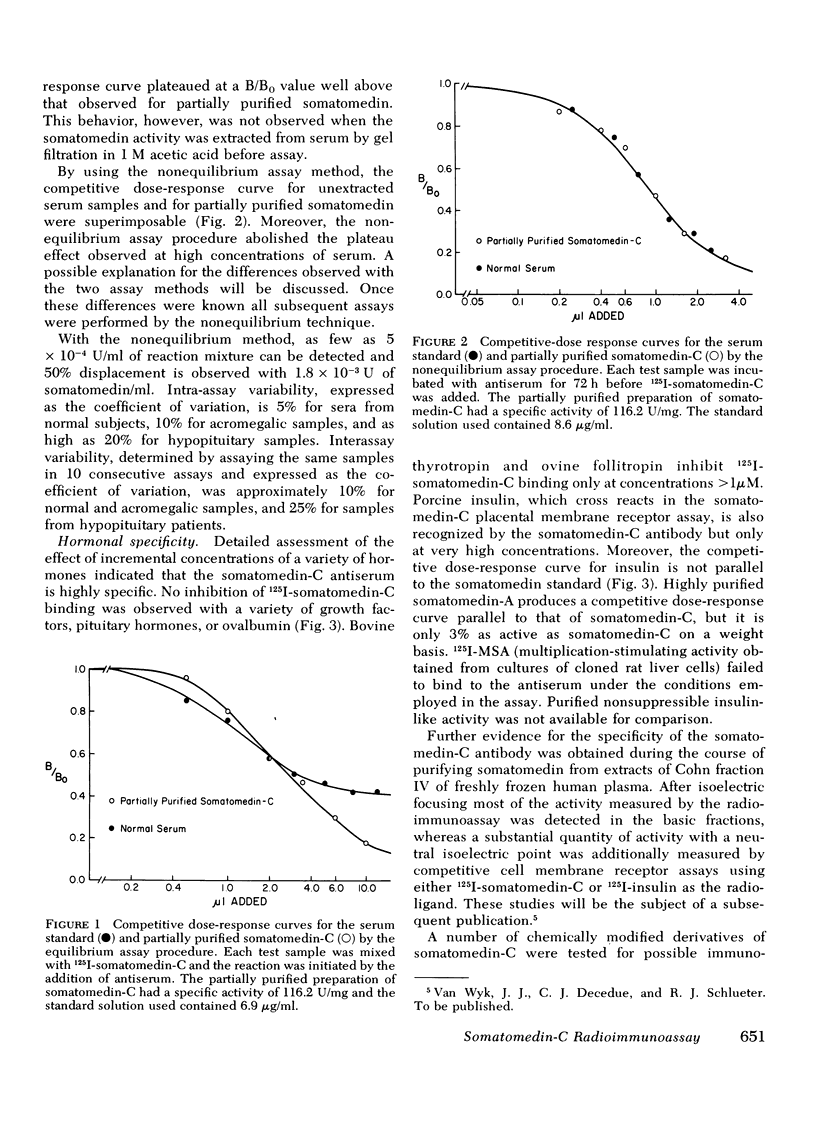
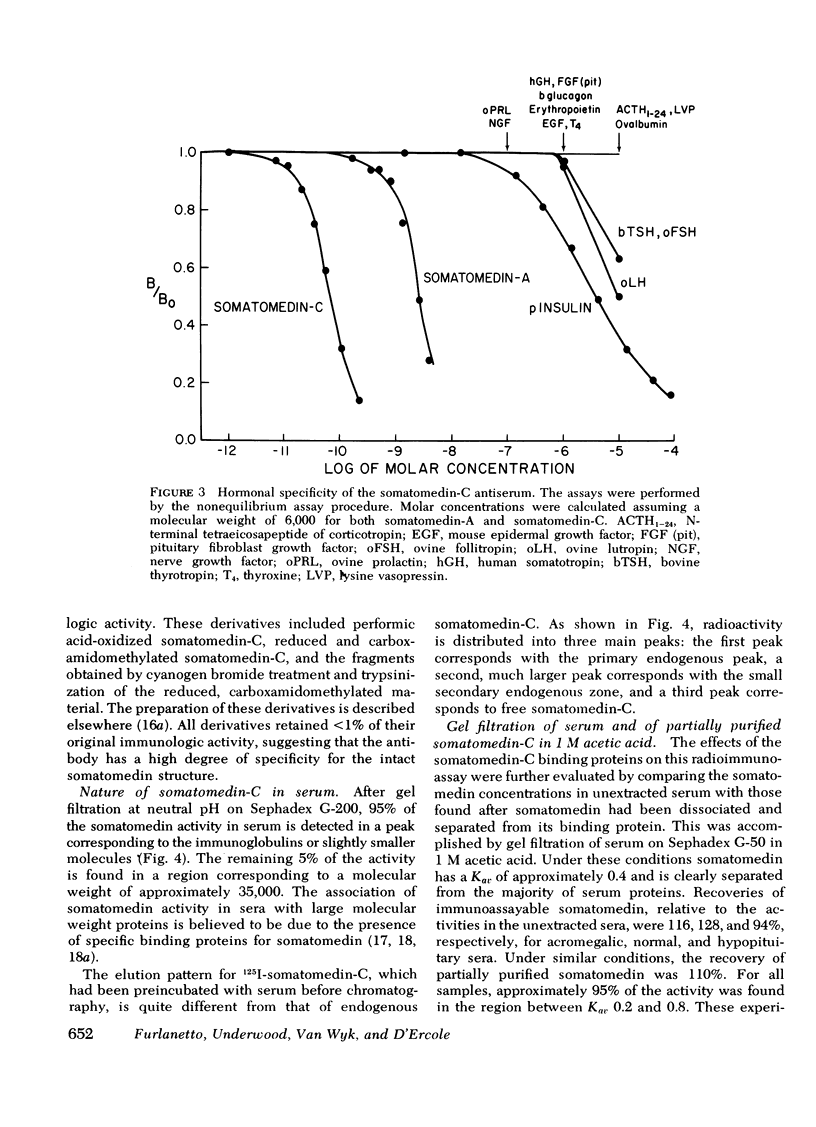
Abstract
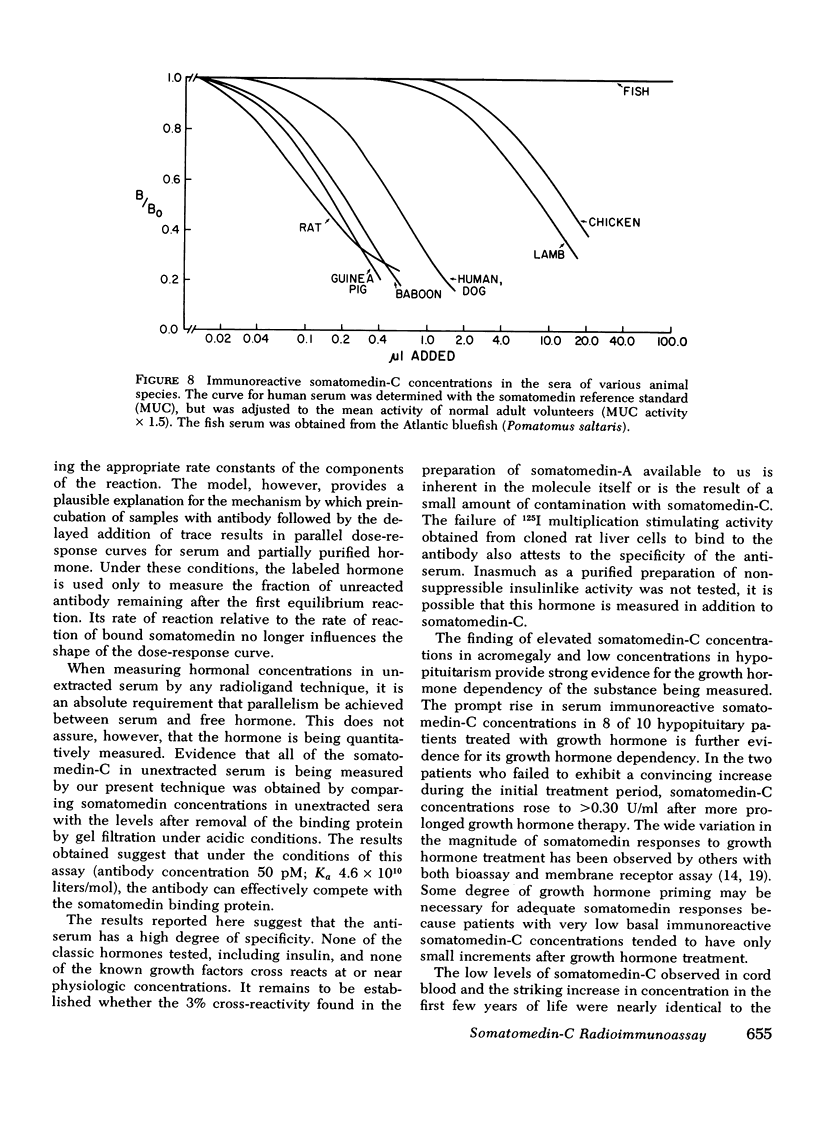
The development of a radioimmunoassay for somatomedin-C has for the first time made it possible to discriminate between serum concentrations of a single peptide or closely related group of peptides and the net somatomedin activity measured by less specific bioassay and radioreceptor techniques. Antibodies to human somatomedin-C were raised in rabbits using a somatomedin-C ovalbumin complex as the antigen. A variety of peptide hormones at concentrations up to 1 μM are not recognized by the antibody. Insulin at concentrations >0.1 μM cross reacts in a non-parallel fashion; purified somatomedin-A is only 3% as active as somatomedin-C; and radiolabeled cloned rat liver multiplication stimulating activity does not bind to the antibody. Immunoreactive somatomedin-C can also be quantitated in the sera of a variety of subhuman species.
Unusual assay kinetics, which are manifest when reactants are incubated under classic “equilibrium” assay conditions, appear to result from the failure of 125I-somatomedin-C to readily equilibrate with the somatomedin-C serum binding protein complex. It is, therefore, necessary to use nonequilibrium assay conditions to quantitate somatomedin-C in serum.
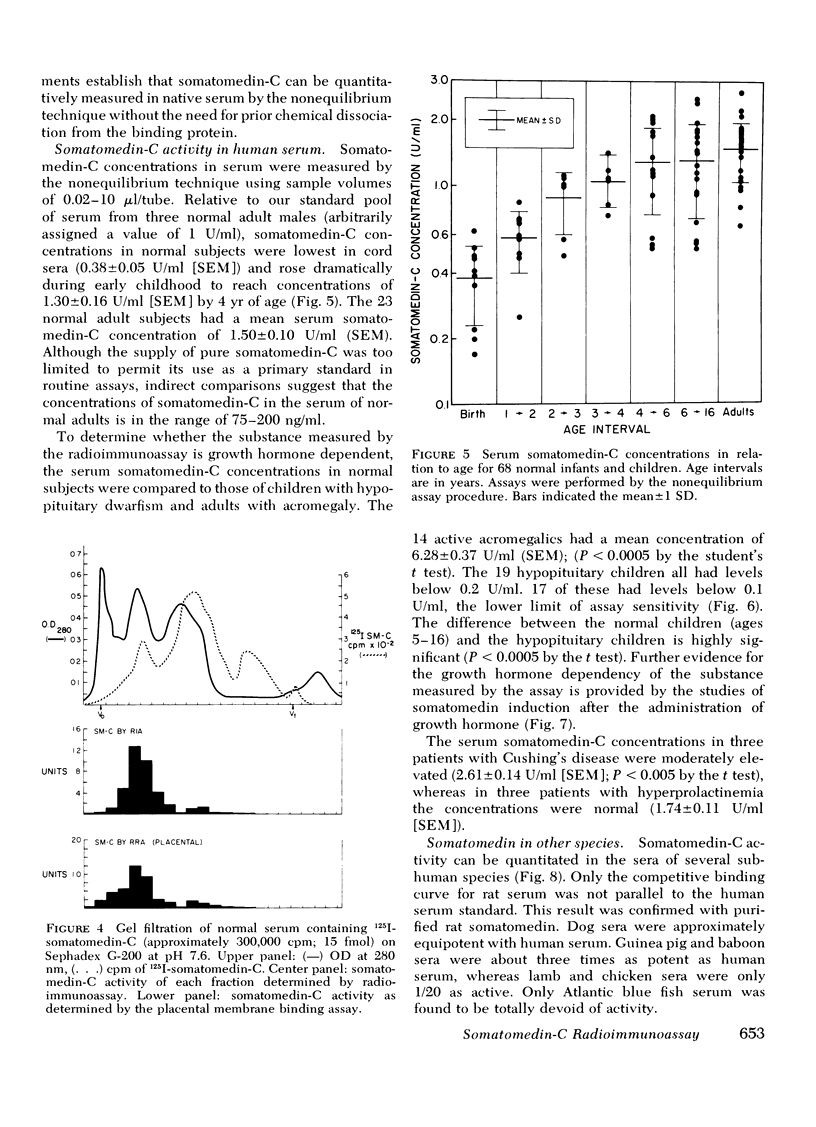
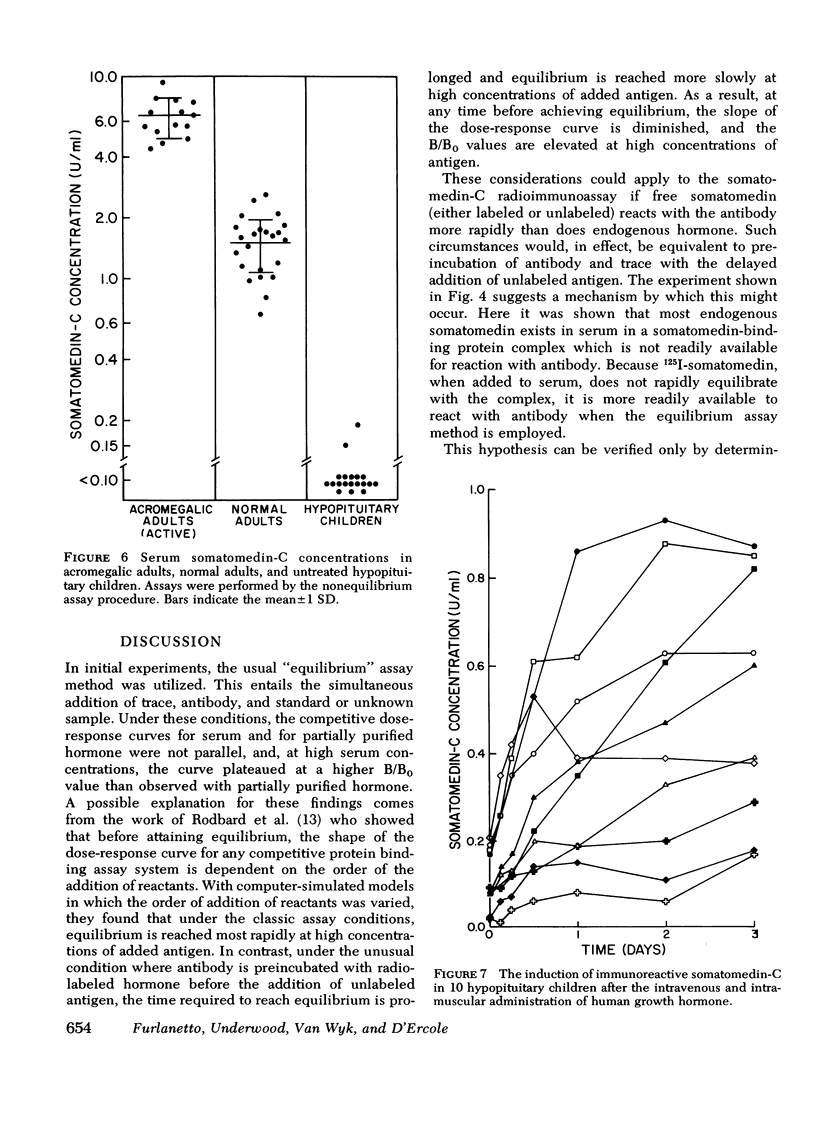
With this assay it is possible to detect somatomedin-C in normal subjects using as little as 0.25 μl of unextracted serum. Serum somatomedin-C concentrations in normal subjects were lowest in cord blood and rose rapidly during the first 4 yr of life to near adult levels. In 23 normal adult volunteers, the mean serum somatomedin-C concentration was 1.50±0.10 U/ml (SEM) when compared to a pooled adult serum standard. 19 children with hypopituitary dwarfism had concentrations below 0.20 U/ml. 17 of these were below 0.1 U/ml, the lower limit of sensitivity of the assay. The mean concentration in 14 adults with active acromegaly was 6.28±0.37 U/ml (SEM), five times greater than the normal volunteers. Significant increases in serum somatomedin-C concentrations were observed in 8 of 10 hypopituitary children within 72 h after the parenteral administration of human growth hormone. Three patients with Cushing's disease had elevated serum somatomedin-C concentrations (2.61±0.14 U/ml [SEM]). Three patients with hyperprolactinemia had normal concentrations (1.74±0.11 U/ml [SEM]).
The important new discovery brought to light by quantitation of immunoassayable somatomedin in patient sera is that all previously used assays detect, in addition to somatomedin-C, serum substances that are not under as stringent growth hormone control.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Ercole A. J., Morris M. A., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J., Feldman J. M. Treatment of Cushing disease in Childhood with cyproheptadine. J Pediatr. 1977 May;90(5):834–835. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Serum somatomedin-C in hypopituitarism and in other disorders of growth. J Pediatr. 1977 Mar;90(3):375–381. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUGHADAY W. H., MARIZ I. K. Conversion of proline U-C14 to labeled hydroxyproline by rat cartilage in vitro: effects of hypophysectomy, growth hormone, and cortisol. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:741–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Hall K., Raben M. S., Salmon W. D., Jr, van den Brande J. L., van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin: proposed designation for sulphation factor. Nature. 1972 Jan 14;235(5333):107–107. doi: 10.1038/235107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Reeder C. Synchronous activation of DNA synthesis in hypophysectomized rat cartilage by growth hormone. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):357–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H. Somatomedin levels in human beings. Adv Metab Disord. 1975;8:159–170. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027308-9.50017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elders M. J., Wingfield B. S., McNatt M. L., Clarke J. S., Hughes E. R. Glucocorticoid therapy in children. Effect on somatomedin secretion. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Dec;129(12):1393–1396. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120490011005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., BUERGI H., RAMSEIER E. B., BALLY P., LABHART A. ANTIBODY-SUPPRESSIBLE AND NONSUPPRESSIBLE INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND THEIR PHYSIOLOGIC SIGNIFICANCE. AN INSULIN ASSAY WITH ADIPOSE TISSUE OF INCREASED PRECISION AND SPECIFICITY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1816–1834. doi: 10.1172/JCI104866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Reichlin M., Sokal J. E. Immunologic and biologic properties of antibodies to a glucagon-serum albumin polymer. Endocrinology. 1970 Nov;87(5):1055–1061. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-5-1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Takano K., Fryklund L. Radioreceptor assay for somatomedin A. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Nov;39(5):973–976. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-5-973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K., Takano K., Fryklund L., Sievertsson H. The measurement of somatomedin A by radioreceptor assay. Adv Metab Disord. 1975;8:61–71. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027308-9.50010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. N., Underwood L. E., Voina S. J., Foushee D. B., Van Wyk J. J. Characterization of the insulin and somatomedin-C receptors in human placental cell membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Aug;39(2):283–292. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-2-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megyesi K., Kahn C. R., Roth J., Froesch E. R., Humbel R. E., Zapf J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin and non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-s): evidence for separate plasma membrane receptor sites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):307–315. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80391-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nessley S. P., Cohen K. L., Rechler M. M. Specific binding of a somatomedin-like polypeptide in rat serum depends on growth hormone. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):137–140. doi: 10.1038/263137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. S., Herington A. C., Daughaday W. H. Steroid hormone effects on sonatomedin. I. Somatomedin action in vitro. Endocrinology. 1975 Oct;97(4):780–786. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-4-780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson R. W., Jr, Temin H. M. The partial purification from calf serum of a fraction with multiplication-stimulating activity for chicken fibroblasts in cell culture and with non-suppressible insulin-like activity. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Jun;79(3):319–330. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040790302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Ruder H. J., Vaitukaitis J., Jacobs H. S. Mathematical analysis of kinetics of radioligand assays: improved sensitivity obtained by delayed addition of labeled ligand. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Aug;33(2):343–355. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-2-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALMON W. D., Jr, DAUGHADAY W. H. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Jun;49(6):825–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlumpf U., Heimann R., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity and sulphaton activity in serum extracts of normal subjects, acromegalics and pituitary dwarfs. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Jan;81(1):28–42. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0810028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano K., Hall K., Ritzén M., Iselius L., Sievertsson H. Somatomedin A in human serum, determined by radioreceptor assay. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Jul;82(3):449–459. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0820449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J., Robbins J. B., Nieschlag E., Ross G. T. A method for producing specific antisera with small doses of immunogen. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Dec;33(6):988–991. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-6-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wyk J. J., Underwood L. E., Baseman J. B., Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Marshall R. N. Explorations of the insulinlike and growth-promoting properties of somatomedin by membrane receptor assays. Adv Metab Disord. 1975;8:127–150. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027308-9.50015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



