Abstract
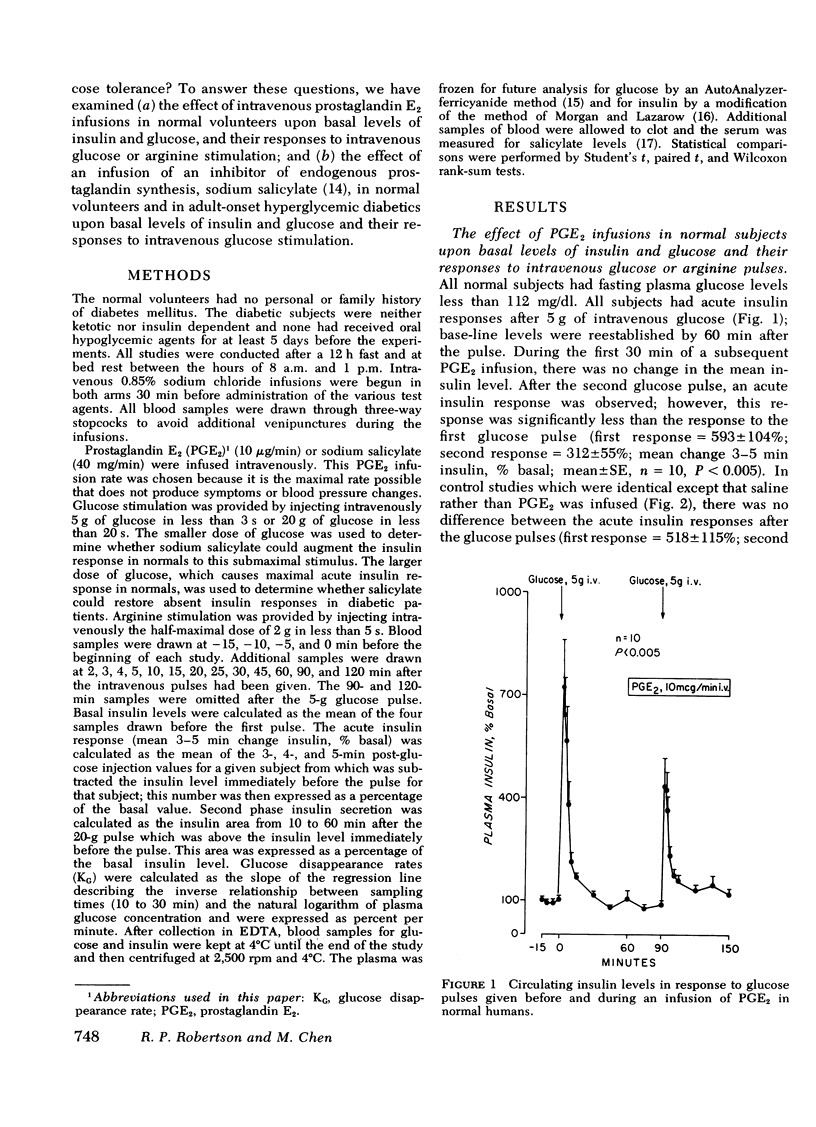
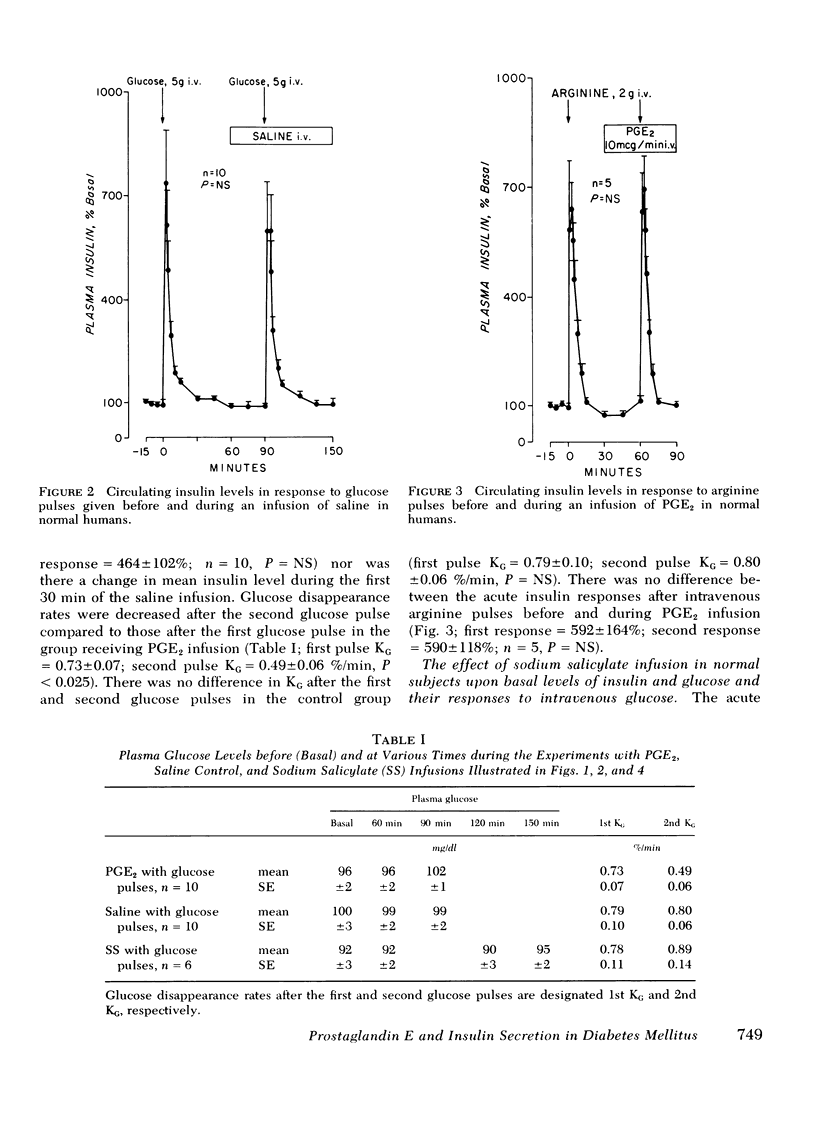
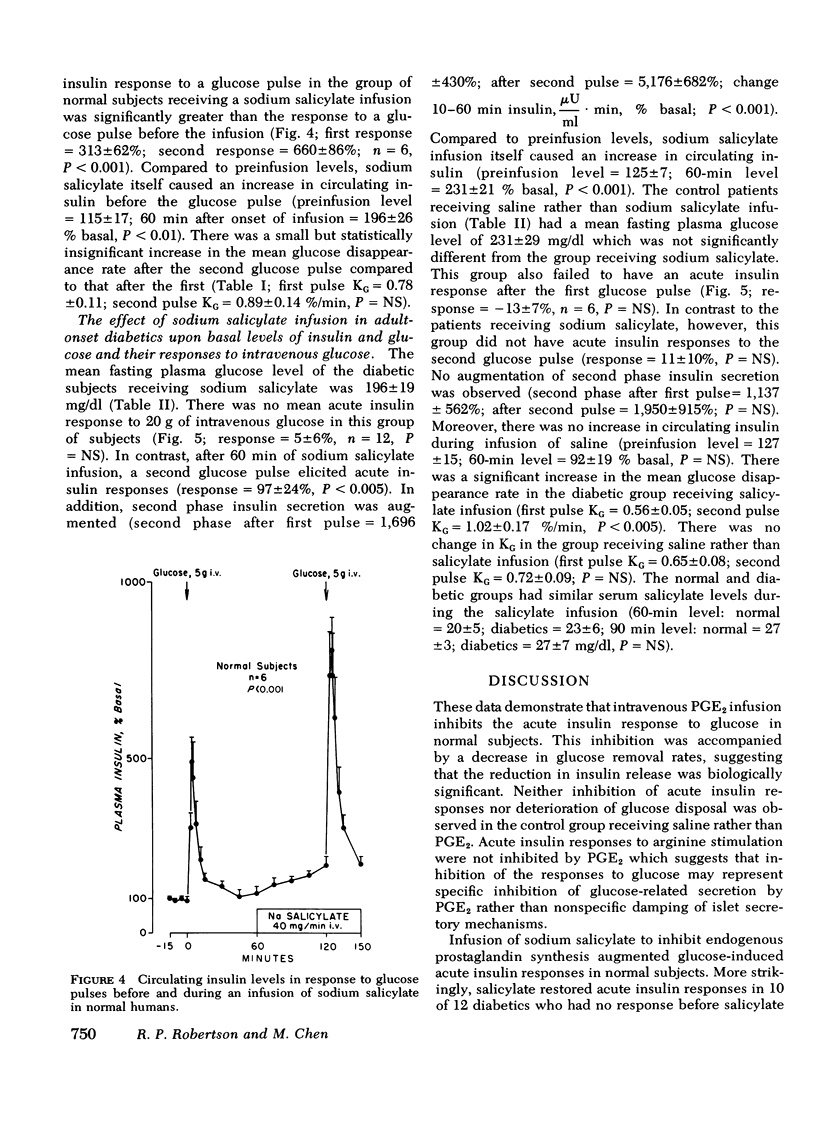
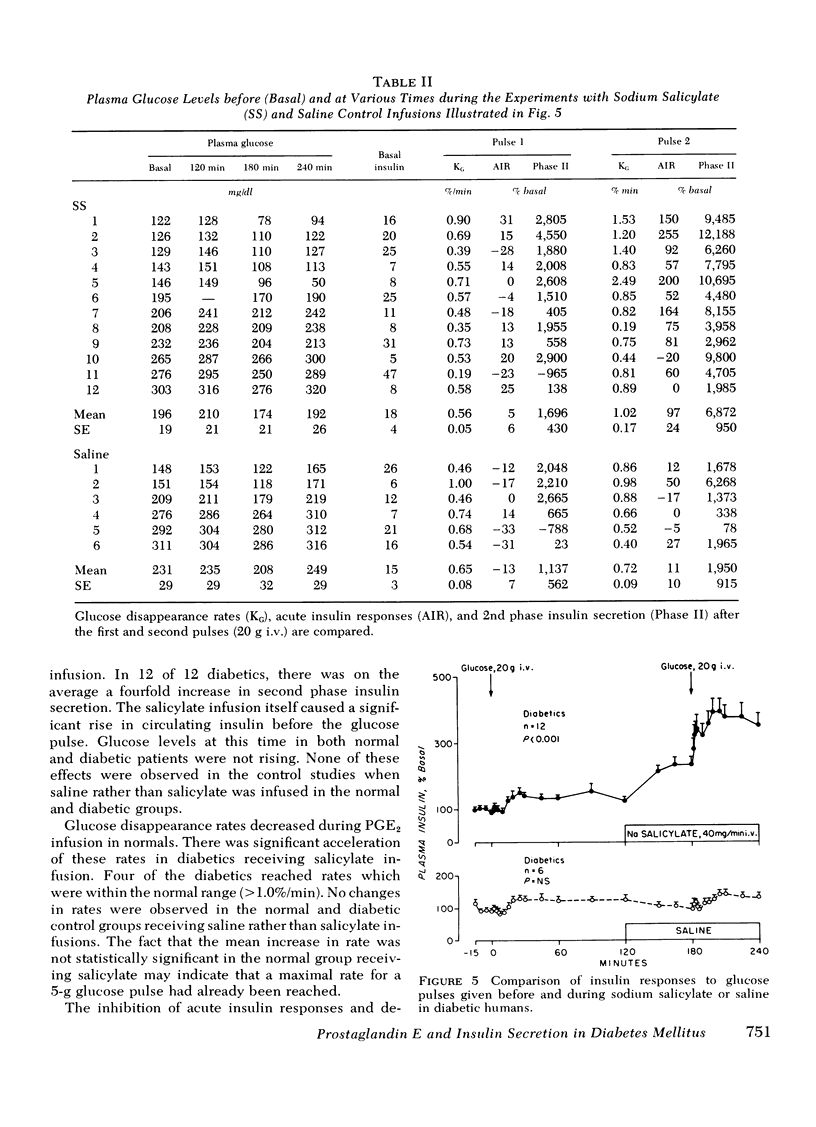
Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) infusion in normal humans inhibited acute insulin responses to a glucose (5 g i.v.) pulse (response before PGE2 = 593 ± 104%; during PGE2 = 312±55%; mean±SE, mean change 3-5 min insulin,% basal, P < 0.005). This effect was associated with a decrease in glucose disappearance rates (KG before PGE2 = 0.73±0.07; during PGE2 = 0.49±0.06%/min, P < 0.025). Acute insulin responses to arginine (2 g i.v.) were not affected by PGE2 (response before PGE2 = 592±164%; during PGE2 = 590±118%; P = NS). Infusion of sodium salicylate (SS), an inhibitor of endogenous prostaglandin synthesis, augmented acute insulin responses to glucose in normals (response before SS = 313±62%; during SS = 660±86%; P < 0.001). In adult-onset diabetes with fasting hyperglycemia, SS restored absent acute insulin responses to glucose (20 g i.v.) pulses (response before SS = 5±6%; during SS = 97±24%; P < 0.005). This was accompanied by a fourfold augmentation in second phase insulin secretion (second phase before SS = 1,696±430%; during SS = 5,176±682%; change 10-60 min insulin, μU/ml·min,% basal, P < 0.001) and by acceleration of glucose disappearance rates (KG before SS = 0.56±0.06; during SS = 1.02±0.17%/min, P < 0.005). These findings uniquely demonstrate that (a) PGE2 inhibits glucose-induced acute insulin responses and decreases glucose disposal in nondiabetic humans and (b) SS restores acute insulin responses, augments second phase insulin secretion, and accelerates glucose disposal in hyperglycemic, adultonset diabetics. It is hypothesized that endogenous PGE synthesis may play a role in defective insulin secretion and glucose intolerance in diabetes mellitus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti K. G., Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Seyer-Hansen K., Orskov H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1299–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Robertson R. P., Lerner R. L., Hazzard W. R., Ensinck J. W., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr Relationships between fasting plasma glucose levels and insulin secretion during intravenous glucose tolerance tests. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Feb;42(2):222–229. doi: 10.1210/jcem-42-2-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockford P. M., Hazzard W. R., Williams R. H. Insulin response to glucagon. The opposing effects of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes. 1969 Apr;18(4):216–224. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.4.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. B., Boyle C., Remer A. Effect of salicylate infusion on plasma-insulin and glucose tolerance in healthy persons and mild diabetics. Lancet. 1967 Jun 3;1(7501):1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92842-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHT A., GOLDNER M. G. Reappraisal of the hypoglycemic action of acetylsalicylate. Metabolism. 1959 Jul 1;8(4 Pt 1):418–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamberg M. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in man. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):720–726. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90470-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams D. E., Howard A. N., Evans I. E., Davison S. H. The effect of 3-methyl salicylic (O-cresotinic) acid on plasma insulin and glucose tolerance in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1971 Apr;7(2):94–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00443888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. L., Porte D., Jr Relationship between intravenous glucose loads, insulin responses and glucose disappearance rate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Sep;33(3):409–417. doi: 10.1210/jcem-33-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer C. H., Tunbridge W. M., Carr D., Yeomans L., Lind T., Coy D. H., Bloom S. R., Kastin A., Mallinson C. N., Besser G. M. Effects of growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone on circulating glucagon, insulin, and growth hormone in normal, diabetic, acromegalic, and hypopituitary patients. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):697–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92903-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Benson J. W., Walter R. M., Ensinck J. W. Arginine-stimulated acute phase of insulin and glucagon secretion in diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):565–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI108502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID J., MACDOUGALL A. I., ANDREWS M. M. Aspirin and diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1957 Nov 9;2(5053):1071–1074. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5053.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Gavareski D. J., Porte D., Jr, Bierman E. L. Inhibition of in vivo insulin secretion by prostaglandin E1. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):310–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI107766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr A role for alpha-adrenergic receptors in abnormal insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):791–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI108338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Porte D., Jr Adrenergic modulation of basal insulin secretion in man. Diabetes. 1973 Jan;22(1):1–8. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Porte D., Jr The glucose receptor. A defective mechanism in diabetes mellitus distinct from the beta adrenergic receptor. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):870–876. doi: 10.1172/JCI107251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. In vivo insulin secretion: prostaglandin and adrenergic interrelationships. Prostaglandins. 1974 Jun 25;6(6):501–508. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80060-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saccà L., Perez G., Rengo F., Pascucci I., Condorelli M. Reduction of circulating insulin levels during the infusion of different prostaglandins in the rat. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1975 Jun;79(2):266–274. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0790266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spellacy W. N., Buhi W. C., Holsinger K. K. The effect of prostaglandin F 2 and E 2 on blood glucose and plasma insulin levels during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1971 Sep 15;111(2):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(71)90896-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


