Abstract
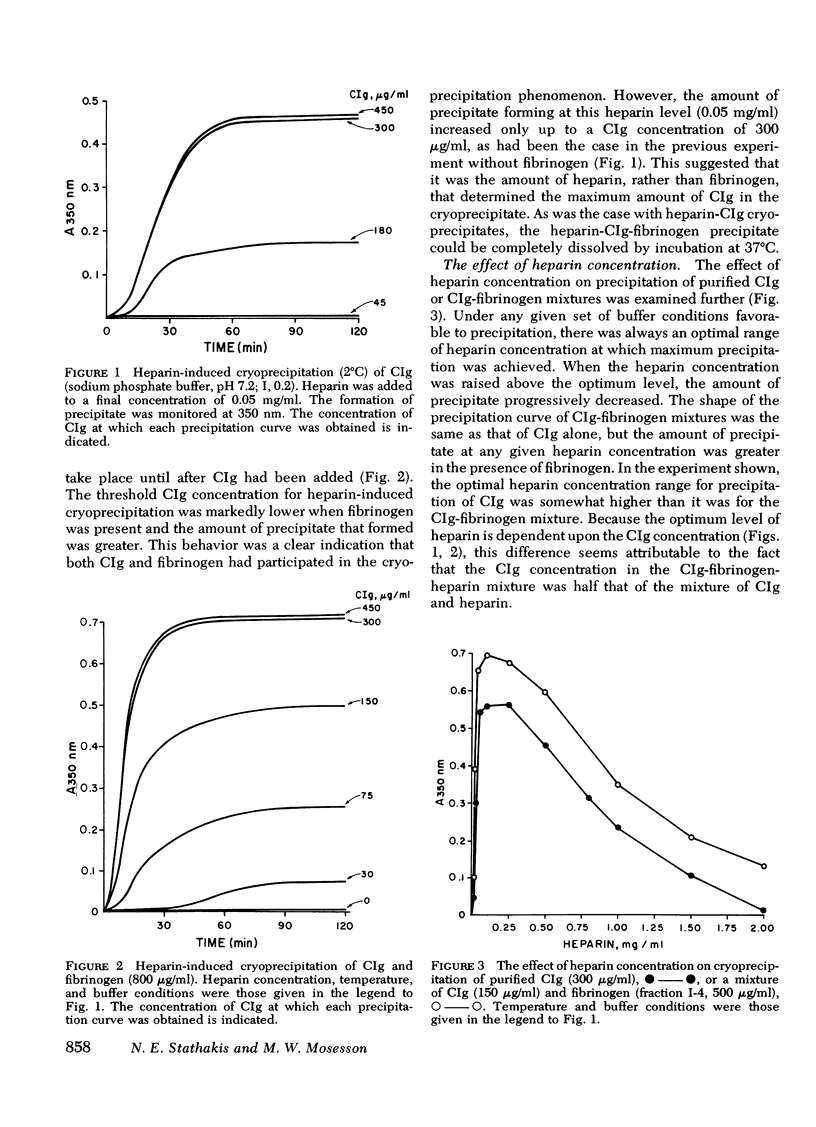
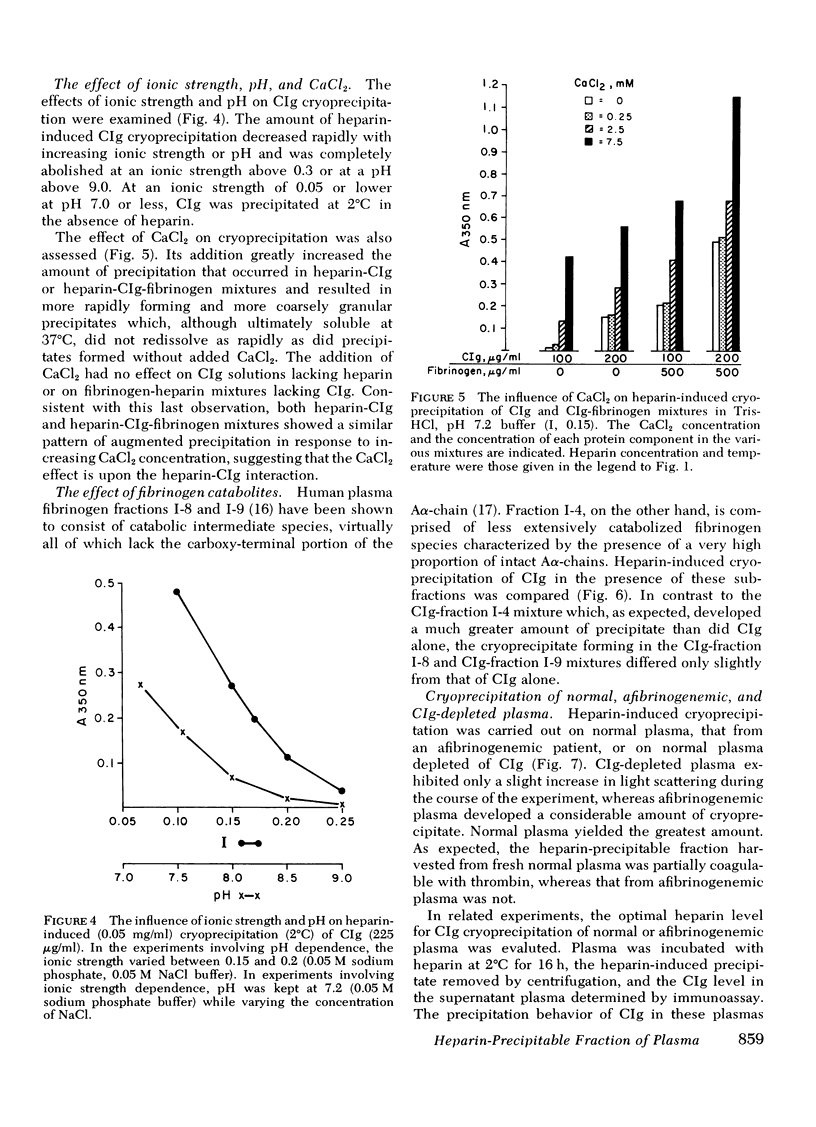
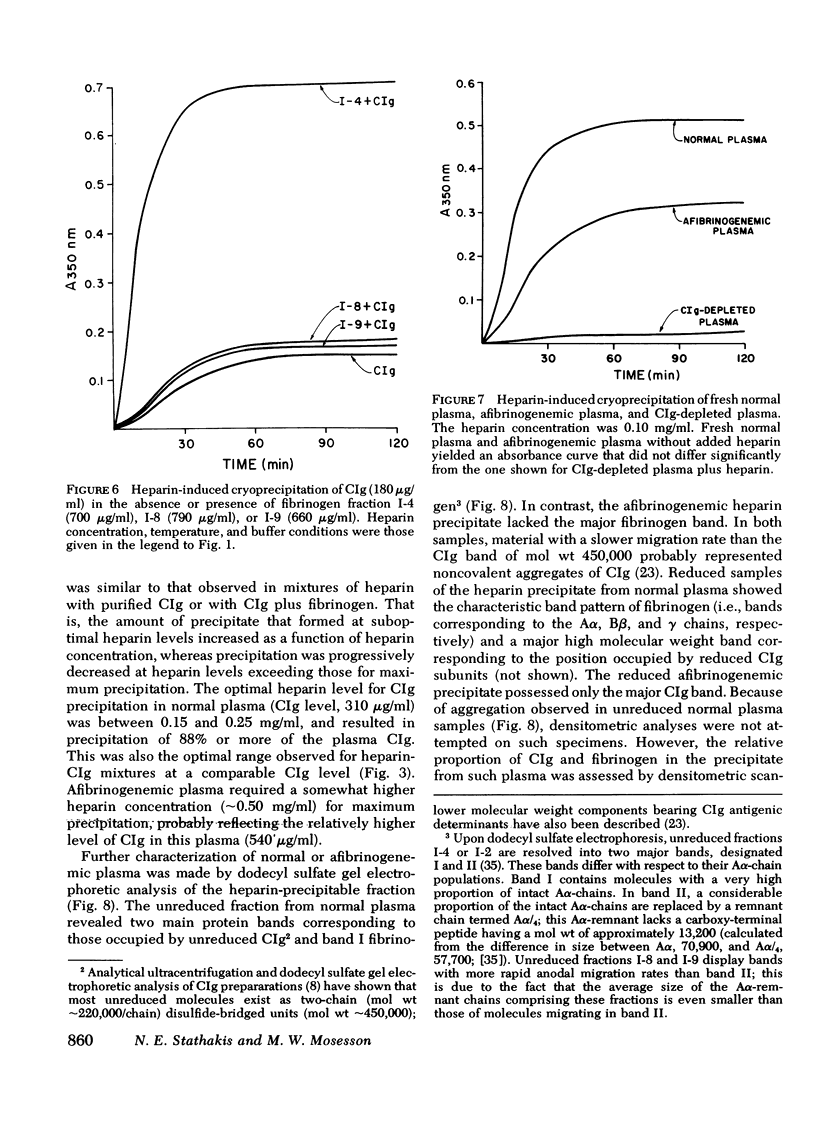
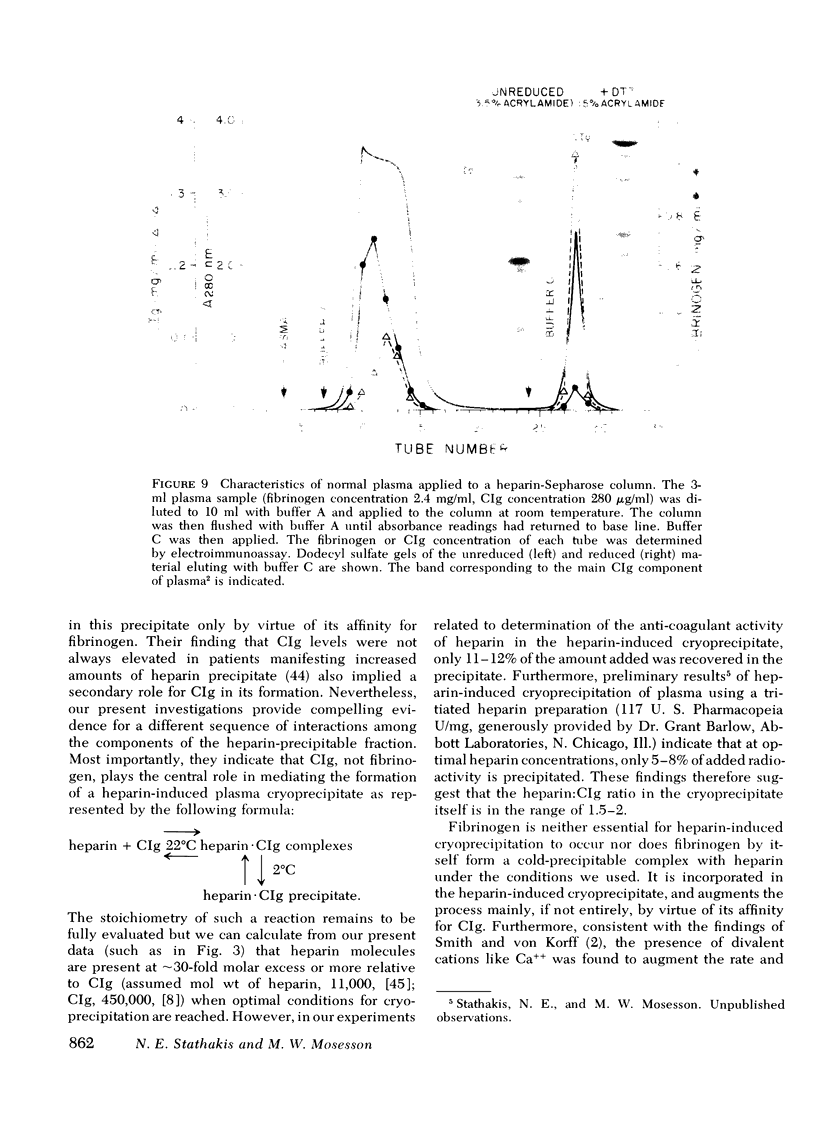
Fibrinogen and the cold-insoluble globulin of plasma (CIg) are the main protein components of the heparin-precipitable fraction of normal plasma. The interactions among these proteins and heparin were examined. Heparin formed a cold-precipitable complex with purified CIg or with mixtures of CIg and fibrinogen but not with purified fibrinogen alone. Cryoprecipitation was augmented by addition of Ca++ or by selection of optimal heparin levels; it was reduced or even abolished by raising the ionic strength or pH or both, or by raising the heparin concentration above that for maximum precipitation of CIg. Fibrinogen reduced the threshold for heparin-induced CIg cryoprecipitation and, by coprecipitating with heparin and CIg, increased the amount of precipitate that formed. In contrast to the heparin-precipitable fraction of normal plasma which contained both fibrinogen and CIg, that from a patient with congenital afibrinogenemia contained CIg but lacked fibrinogen. Normal plasma depleted of CIg by immunoabsorption failed to form a heparin-induced cryoprecipitate. Thus, CIg is essential for heparin-induced cryoprecipitation to occur. Fibrinogen, as assessed by chromatographic experiments with heparin-Sepharose columns, had a considerably lower binding affinity for heparin than did CIg, suggesting that it participates in precipitate formation mainly, if not entirely, by virtue of its affinity for CIg. The region of the fibrinogen molecule accounting for its precipitation with CIg appears to be localized in the carboxy-terminal segment of the Aα-chain; fibrinogen subfractions lacking this region failed to augment cryoprecipitation of heparin-CIg mixtures and, even though such species were present in normal plasma, they failed to coprecipitate in the heparin-induced complex.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abildgaard U. Inhibition of the thrombin-fibrinogen reaction by heparin in the absence of cofactor. Scand J Haematol. 1968;5(6):432–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1968.tb00864.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson L. O., Barrowcliffe T. W., Holmer E., Johnson E. A., Sims G. E. Anticoagulant properties of heparin fractionated by affinity chromatography on matrix-bound antithrombin iii and by gel filtration. Thromb Res. 1976 Dec;9(6):575–583. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Morfin R. Action de l'héparine et de la protamine sur la mobilité électrophorétique des lipoprotéines sériques. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol. 1969 May-Jun;9(3):365–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R. Lipoprotein-polyanion-metal interactions. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11(0):67–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. B., Amrani D. L., Mosesson M. W. Heterogeneity of the cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma (CIg), a circulating cell surface protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 23;493(2):310–322. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. B., Mosesson M. W. An improved method for purification of the cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma (CLg). Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):144–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Wagner R. H., Mosesson M. W. The cold-insoluble globulin of plasma and its relationship to factor VIII. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Aug;84(2):258–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich J., Stivala S. S. Chemistry and pharmacology of heparin. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Apr;62(4):517–544. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlayson J. S., Mosesson M. W., Bronzert T. J., Pisano J. J. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. II. Cross-linking capacity of high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5220–5222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher A. P., Alkjaersig N., O'Brien J., Tulevski V. G. Blood hypercoagulability and thrombosis. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1970;83:159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk J. E., Finlayson J. S. The epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine crosslink and the catalytic role of transglutaminases. Adv Protein Chem. 1977;31:1–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrand O., Solum N. L. Studies on cold insoluble globulin in dermatological patients. I. Immunochemical quantitation in citrated plasma from patients with increased amounts of heparin precipitable fraction (HPF). Thromb Res. 1976 Nov;9(5):447–455. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrand O., Solum N. O. Heparin precipitable fraction (HPF) from dermatological patients. II. Studies on the non-clottable proteins. Identification of cold insoluble globulin as the main non-clottable component. Thromb Res. 1976 May;8(5):659–672. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrand O., Solum N. O., Kierulf P. Heparin precipitable fraction (HPF) from dermatoligical patients. I. Characterization of the thrombin-clottable protein. Thromb Res. 1976 Jan;8(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODAL H. C. Binding of heparin to fibrin(ogen). Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1961;13:550–552. doi: 10.3109/00365516109137324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GODAL H. C. Precipitation of human fibrinogen with heparin. Scalpel (Brux) 1960;12:56–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry P. W., Alexander B. Specific coagulation factor adsorption to insoluble heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):500–509. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90868-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal H. C., Abildgaard U. Gelation of soluble fibrin in plasma by ethanol. Scand J Haematol. 1966;3(5):342–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1966.tb02378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godal H. C. Heparin assay methods for control of in vivo heparin effects. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Feb 28;33(1):77–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINRICH R. A., VONDER HEIDE E. C., CLIMIE A. R. Cryofibrinogen: formation and inhibition in heparinized plasma. Am J Physiol. 1963 Mar;204:419–422. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.3.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilborn J. C., Anastassiadis P. A. Estimation of the molecular weights of acidic mucopolysaccharides by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):88–92. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90465-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hök M., Björk I., Hopwood J., Lindahl U. Anticoagulant activity of heparin: separation of high-activity and low-activity heparin species by affinity chromatography on immobilized antithrombin. FEBS Lett. 1976 Jul 1;66(1):90–93. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAQUES L. B., MONKHOUSE F. C., STEWART M. A method for the determination of heparin in blood. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENT T. C. Studies on fractionated heparin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Feb;92:224–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam L. H., Silbert J. E., Rosenberg R. D. The separation of active and inactive forms of heparin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):570–577. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent T. C. Interaction between proteins and glycosaminoglycans. Fed Proc. 1977 Jan;36(1):24–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Feinman R. D. The role of heparin in the thrombin-antithrombin III reaction. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jul;175(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E. H., Orton C., Feinman R. D. The interaction of thrombin and heparin. Proflavine dye binding studies. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):5012–5017. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinska I., Lipinski B., Gurewich V. Fibrinogen heterogeneity in human plasma. Electrophoretic demonstration and characterization of two major fibrinogen components. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):509–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSESSON M. W., FINLAYSON J. S. SUBFRACTIONS OF HUMAN FIBRINOGEN; PREPARATION AND ANALYSIS. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Oct;62:663–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machovich R., Blaskó G., Pálos L. A. Action of heparin on thrombin-antithrombin reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak E. Binding of heparin in vitro and in vivo to plasma proteins. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Sep;84(3):344–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda M., Saida T., Hasegawa R. Cryofibrinogen in the plasma of patients with skin ulcerative lesions on the legs: a complex of fibrinogen and cold insoluble globulin. Thromb Res. 1976 Dec;9(6):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(76)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDuffie N. M., Dietrich C. P., Nader H. B. Electrofocusing of heparin: fractionation of heparin into 21 components distinguishable from other acidic mucopolysaccharides. Biopolymers. 1975 Jul;14(7):1473–1486. doi: 10.1002/bip.1975.360140713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. Amino acid analysis: aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent for the ninhydrin reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6281–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Alkjaersig N., Sweet B., Sherry S. Human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Comparative biophysical, biochemical, and biological studies with fibrinogen of lower solubility. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):3279–3287. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Chen A. B., Huseby R. M. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma: studies of its essential structural features. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 29;386(2):509–524. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Colman R. W., Sherry S. Chronic intravascular coagulation syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1968 Apr 11;278(15):815–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196804112781503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S. Letter: The fibrinogenolytic pathway of fibrinogen catabolism: a rebuttal. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):895–900. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Finlayson J. S., Umfleet R. A., Galanakis D. Human fibrinogen heterogeneities. I. Structural and related studies of plasma fibrinogens which are high solubility catabolic intermediates. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5210–5219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Galanakis D. K., Finlayson J. S. Comparison of human plasma fibrinogen subfractions and early plasmic fibrinogen derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4656–4664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Sherry S. The preparation and properties of human fibrinogen of relatively high solubility. Biochemistry. 1966 Sep;5(9):2829–2835. doi: 10.1021/bi00873a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Action of fibrin-stabilizing factor on cold-insoluble globulin and alpha2-macroglobulin in clotting plasma. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1639–1645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Cross-linking of cold-insoluble globulin by fibrin-stabilizing factor. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6614–6621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossel H. L., Yudelman I., Canfield R. E., Butler V. P., Jr, Spanondis K., Wilner G. D., Qureshi G. D. Measurement of fibrinopeptide A in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jul;54(1):43–53. doi: 10.1172/JCI107749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Porter M. C., Shanberge J. N. Interaction of heparin with the plasma proteins in relation to its antithrombin activity. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1854–1863. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. D., Damus P. S. The purification and mechanism of action of human antithrombin-heparin cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6490–6505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Vaheri A. Interaction of soluble fibroblast surface antigen with fribrinogen and fibrin. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):497–501. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T. A heparin-precipitable fraction of human plasma. II. Occurrence and significance of the fraction in normal individuals and in various disease states. J Clin Invest. 1957 Apr;36(4):605–616. doi: 10.1172/JCI103460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T., VON KORFF R. W. A heparin-precipitable fraction of human plasma. I. Isolation and characterization of the fraction. J Clin Invest. 1957 Apr;36(4):596–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI103459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., SMITH R. T., VON KORFF R. Cold-precipitation by heparin of a protein in rabbit and human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Aug-Sep;86(4):813–818. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton P. L., Ricketts C. R., Bangham D. R. Heterogeneity of heparin. Br J Haematol. 1966 May;12(3):310–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]