Abstract
Background
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is a common treatment for metabolic acidemia, however little definitive information exists regarding its treatment efficacy and cerebral hemodynamic effects. This pilot observational study quantifies relative changes in cerebral blood flow (rCBF) and oxy and deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations (ΔHbO2 and ΔHb) due to bolus administration of NaHCO3 in patients with mild base deficits.
Methods
Infants and children with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) were recruited prior to cardiac surgery. NaHCO3 was given as needed for treatment of base deficit. Diffuse optical spectroscopies were employed for 15 minutes post-injection to non-invasively monitor ΔHb, ΔHbO2 and rCBF relative to baseline prior to NaHCO3 administration.
Results
Twenty-two anesthetized and mechanically ventilated HLHS patients (1 day to 4 years old) received a median (interquartile range) dose of 1.1 (0.8, 1.8) mEq/kg NaHCO3 administered intravenously over 10–20 seconds to treat a base deficit of −4 (−6, −3) mEq/l. NaHCO3 caused significant dose-dependent increases in rCBF, however population averaged ΔHb or Δ4HbO2 compared to controls were not significant.
Conclusions
Dose-dependent increases in cerebral blood flow (CBF) caused by bolus NaHCO3 are an important consideration in vulnerable populations wherein risk of rapid CBF fluctuations does not outweigh the benefit of treating a base deficit.
INTRODUCTION
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) is a commonly used medication to treat metabolic acidemia from a variety of causes. Intravenous NaHCO3 acts by neutralizing excess acid in the blood to yield carbonic acid which then dissociates into carbon dioxide and water, restoring physiologic pH. The efficacy of NaHCO3 treatment for mild to moderate acidemia, however, is widely debated and controversy exists over whether any true benefit results from the therapy (1–4). In fact, some data suggests that NaHCO3 may be harmful in certain populations. In preterm infants, for example, the use of NaHCO3 has been linked to intraventricular hemorrhage, hypernatremia, and death (2, 5, 6). Nevertheless, treatment of metabolic acidemia with NaHCO3 remains a common practice in many pediatric intensive care units and operating rooms.
Further understanding of the cerebral hemodynamic effects of rapid administration of NaHCO3 may illuminate the link between NaHCO3 and brain injury. It is known that administration of NaHCO3 causes an immediate and transient increase in the production of non-metabolic CO2 (7–10), as well as a slight increase in plasma pH (7, 11), and serum osmolality (12, 13). This increase in serum osmolality leads to a flow of intracellular water into the extracellular space to restore osmotic equilibrium and to an increase in arterial hemoglobin concentration and a decrease in hematocrit (9, 10, 12, 13). However, little definitive and quantitative information exists regarding the effects of NaHCO3 on cerebral hemodynamics.
Several publications studying the effects of NaHCO3 on cerebral blood flow (CBF) report conflicting observations (7, 11, 14–19). Lou et al (17) observed substantial decreases in CBF measured by the Xenon-133 clearance technique five minutes after NaHCO3 administration in 7 newborn infants with respiratory distress. By contrast, Nakashima et al (9) reported significant increases in CBF in 5 healthy adult volunteers following to NaHCO3 administration. Finally, in a study of 6 neonatal dogs, Young et al (19) observed no change in CBF (measured with radioactive tracers) 30 minutes after NaHCO3 injection. These conflicting results may reflect the wide variety of experimental subjects studied (both humans and animals), the severity and cause of the acidemia, the dosage and rapidity of injection of NaHCO3, the use of mechanical ventilation, the anesthetic state, the method of CBF measurement, and the time frame for assessing the cerebral hemodynamic effects following drug administration.
The present observational pilot investigation aimed to quantify the immediate cerebral hemodynamic effects of a rapid (10–20 seconds) bolus of NaHCO3. Pilot data was taken 1 to 15 minutes after bolus injection and was obtained from a subset of pre-operative patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) who were treated for mild acidemia during part of a larger pre-surgical brain imaging study. Noninvasive diffuse optical spectroscopies, namely diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) and diffuse correlation spectroscopy (DCS), were employed for 15 minutes post-injection to monitor regional changes in cerebral oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations (ΔHbO2 and ΔHb, respectively), changes in total hemoglobin concentration (ΔTHC), and changes in CBF (ΔrCBF) relative to baseline prior to rapid NaHCO3 administration.
RESULTS
As seen in Table 1,305 patients were approached for this investigation, parental consent was obtained in 133, and 91 were studied with DOS/DCS. Of the 91 HLHS patients monitored with DOS/DCS, 22 received NaHCO3 treatment for a mild or moderate base deficit: N = 8 pre-Norwood, N = 8 pre-Glenn, and N = 6 pre-Fontan. Furthermore, we selected 22 age and gender matched control patients from the remaining 69 patients. These patients received no interventions but were monitored with DOS/DCS as part of the pre-surgical brain magnetic resonance imaging study. Patient characteristics for the treated and control groups are summarized in Table 2. NaHCO3 treated patients were mostly male (64 %) and ranged in age from 1 day to 4 years old.
Table 1.
Summary of patient recruitment.
| Pre-Norwood | Pre-Glenn | Pre-Fontan | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Approached | 41 | 264 | 305 | |
| Consented | 27 | 35 | 71 | 133 |
| Studied with DOS/DCS | 25 | 24 | 42 | 91 |
| Given NaHCO3 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 22 |
Of the 91 patients monitored with DOS/DCS, 22 received an intravenous bolus of NaHCO3.
Table 2.
Patient Characteristics.
| Variable | Level | NaHCO3
Treated |
Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (N (% of total)) | Male | 14 (64 %) | 12 (55 %) |
| Female | 8 (36 %) | 10 (45 %) | |
| Age (years) | -- | 0.5 (0, 1.8) | 0.4 (0, 1.7) |
| Weight (kg) | -- | 6.2 (3.4, 11.0) | 5.6 (3.3, 8.9) |
| Cardiac Physiology (N (% of total)) |
Pre-Stage I | 8 (36.4 %) | 8 (36.4 %) |
| Pre-Stage II | 8 (36.4 %) | 8 (36.4 %) | |
| Pre-Stage III | 6 (27.3 %) | 6 (27.3 %) |
Median (interquartile range (IQR)) patient characteristics for both NaHCO3 treated and age matched control patients. Patients were monitored on the day of staged cardiac surgical reconstruction, prior to surgery.
Arterial blood gas data obtained prior to administration of NaHCO3 are summarized in Table 3 for patients in the treated and control groups. Patients received a median (interquartile range) dose of 1.1 (0.9, 1.8) mEq/kg NaHCO3 to treat a median (interquartile range) base deficit of −4 (−6, −3) mEq/l. Of note, the majority of patients were normocapnic but mildly hypoxemic with arterial oxygen tensions of 6.3 (8.0, 6.7) kPa. The below normal partial pressures of oxygen were expected due to the presence of intracardiac shunting, a consequence of single ventricle physiology. Furthermore, arterial blood samples were not drawn after NaHCO3 administration, thus changes in the parameters listed in Table 3 due to NaHCO3 are not reported. Baseline heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and transcutaneous oxygen saturation (SpO2) are also reported in Table 3 for both treated and control groups. No differences in these baseline parameters between treated and age-matched controls were observed.
Table 3.
Baseline Systemic Hemodynamics.
| Variable | NaHCO3 Treated | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vital Signs | Heart Rate (bpm) | 138 (120, 147) | 121 (108, 135) |
| MAP (mmHg) | 64 (61, 68) | 63 (56, 71) | |
| SpO2 (%) | 83 (77, 92) | 78 (75, 89) | |
| Arterial Blood Gas |
pH | 7.35 (7.32, 7.38)* | 7.39 (7.37, 7.41) |
| Arterial CO2 tension (kPa) | 5.2 (4.7, 5.7) | 5.3 (5.1, 5.7) | |
| Arterial O2 tension (kPa) | 6.7 (6.3, 7.9) | 6.5 (5.7, 7.6) | |
| Bicarbonate (mmol/L) | 21 (20, 22)* | 24 (22, 26) | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.3 (12.6, 15.6) | 14.3 (12.6, 15.3) | |
| Base Deficit (mEq/L) | −4 (−6, −3)** | −1 (−3, +1) | |
| Dosage NaHCO3 (mEq/kg) | 0.8 (0.6, 0.9) | 0 |
Median (interquartile range) baseline vital signs and measures from arterial blood gas samples taken before administration of sodium bicarbonate in the treated group as well as age matched controls (N = 22). A Wilcoxon signed rank test was carried out to test for differences in each group compared to controls:
p < 0.05,
p < 0.001.
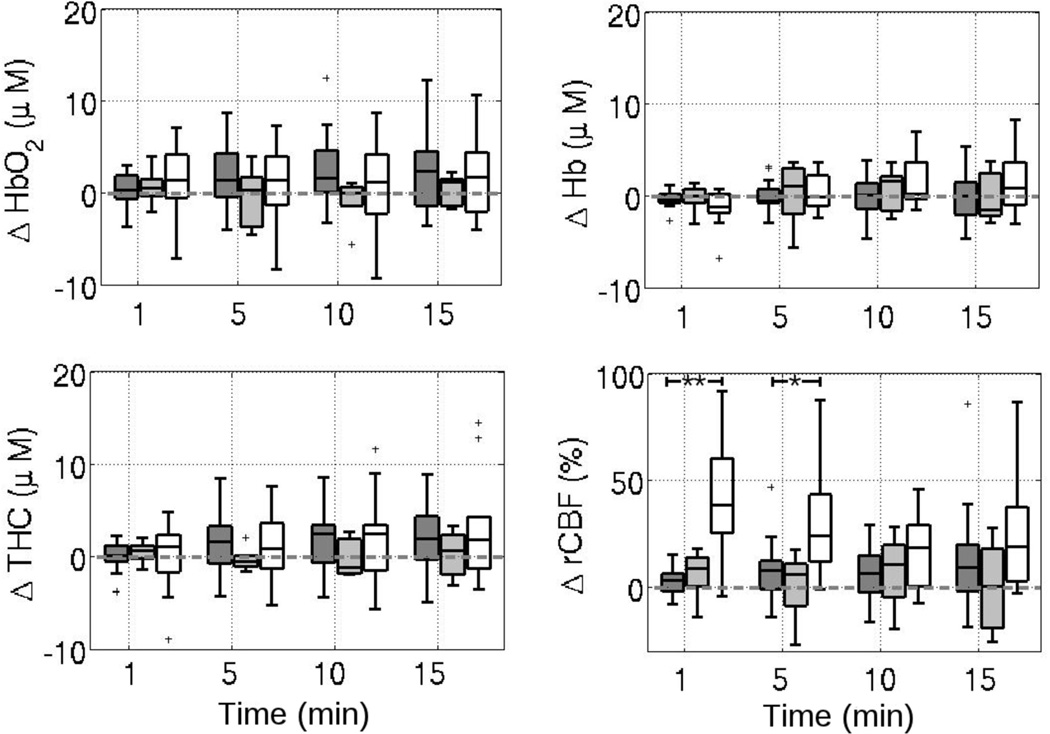
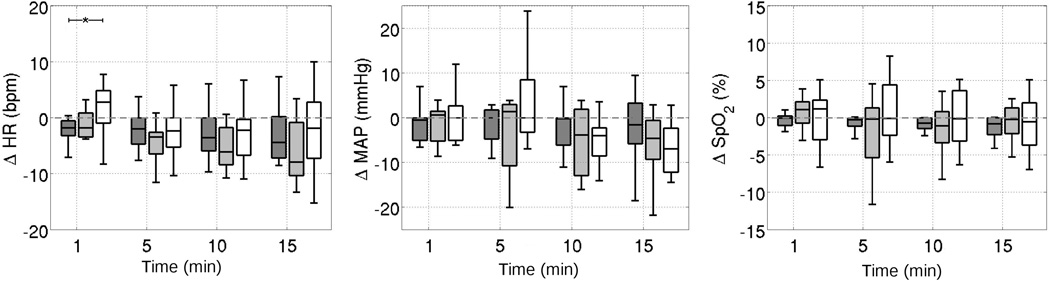
Figure 1 provides boxplots of ΔHb, ΔHbO2, ΔTHC and ΔrCBF over time for the control and treated group following injection of intravenous NaHCO3. Compared to age matched controls, patients showed significant increases in ΔrCBF at 1 minute after NaHCO3 injection (p = 0.0084). No significant changes in DOS measures of ΔHb, ΔHbO2, or ΔTHC were observed, nor were any significant differences in these parameters between the treatment group and the control group observed at any time following injection. Additionally, MAP, HR, and SpO2 did not change following NaHCO3 in the treated patients as compared to controls (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
Boxplots of changes from baseline in (A) deoxy-, (B) oxy-, and (C) total-hemoglobin concentrations (ΔHb, ΔHbO2, and ΔTHC, respectively) as well as (D) cerebral blood flow (ΔrCBF) at times 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes following NaHCO3 administration (grey). The control group who received no intervention is shown in white. The dotted grey lines indicate no change from baseline levels. *p< 0.05.
Figure 2.
Boxplots of changes from baseline in (A) heart rate, (B) mean arterial pressure, and (C) transcutaneous oxygen saturation at times 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes following NaHCO3 administration (grey). The control group who received no intervention is shown in white. The dotted grey lines indicate no change from baseline levels.
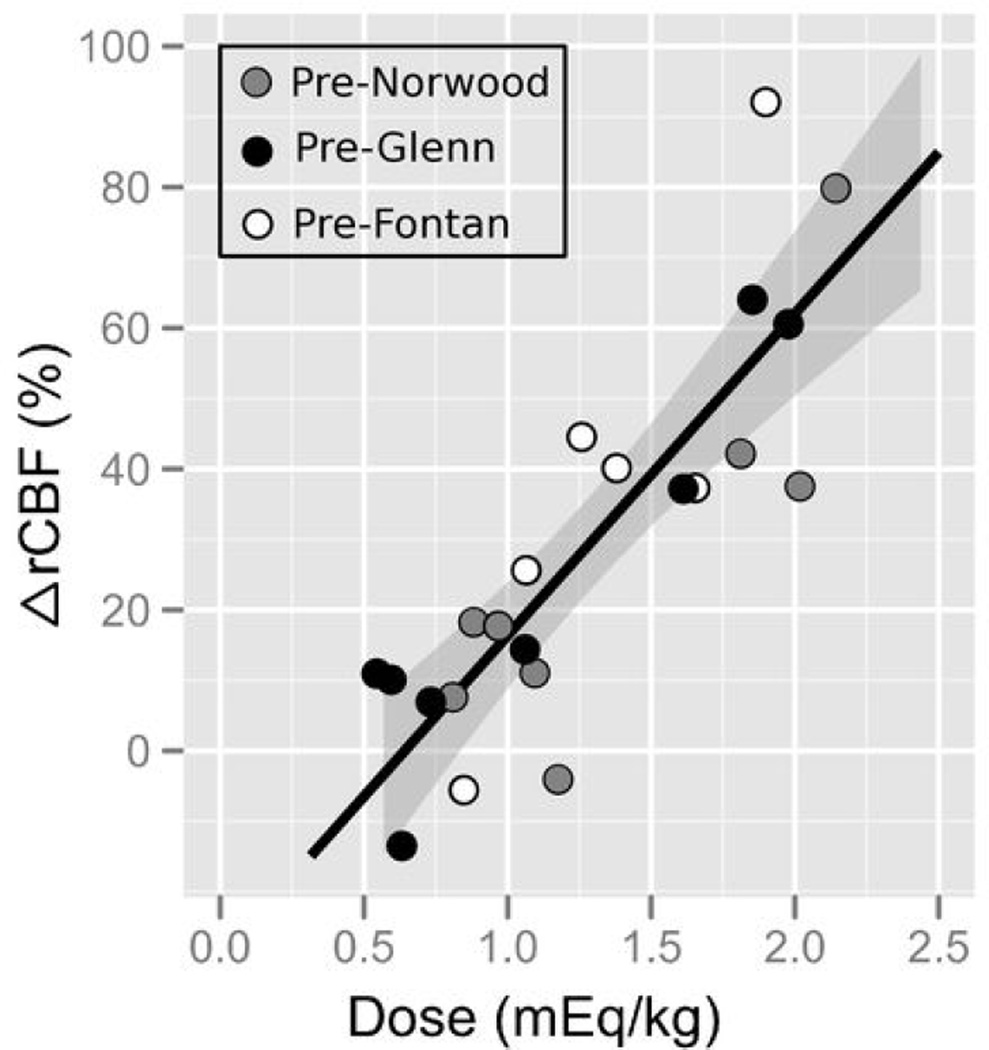
In the NaHCO3 treated group, at 1 minute post-injection the increase in ΔrCBF was highly correlated with NaHCO3 dosage (R2 = 0.71, p = 2.1e-6, slope (95% confidence interval) = 45.7 (32.5, 58.9) %/mEq/kg), see Figure 3. No relationship between change in ΔrCBF at 1 minute post-injection and baseline pH, pCO2, or pO2 was observed (all p > 0.1). The relationship between ΔrCBF and NaHCO3 dosage weakened slightly by 5 minutes post-injection (R2 = 0.51, p = 6.0e-4), and was no longer highly significant by 10 minutes after NaHCO3 administration (at 10 min R2 = 0.12, p = 0.085 and at 15 min, R2 = 0.23, p = 0.042). Furthermore, no relationship was observed between cardiac physiology, age, weight, or arterial hemoglobin concentration and the change in ΔHb, ΔHbO2, ΔTHC or ΔrCBF at any time point.
Figure 3.
Relationship between the dose of sodium bicarbonate administered (in mEq/kg) and the associated change in cerebral blood flow (%) 1 minute after injection. The black line indicates the best linear fit to the data, and the 95% confidence interval to the fit is shown in the grey shaded region. Open circles denote pre-Fontan patients, black circles denote pre-Glenn, and grey circles denote pre-Norwood.
DISCUSSION
In this pilot observational study, we quantify the cerebral hemodynamic effects of NaHCO3 administered rapidly to treat metabolic acidemia in paralyzed, mechanically ventilated children with single ventricle physiology. Diffuse correlation spectroscopy demonstrated significant increases in CBF immediately (within 2 minutes) following bolus administration of NaHCO3. These increases in CBF were strongly associated with dosage of the NaHCO3, increasing in a linear fashion. This relationship between CBF and NaHCO3 dose was observed within all stages of HLHS cardiac physiology studied herein. The present investigation is the first to describe a dose-dependent response of CBF to NaHCO3. Population averaged changes in oxy- or deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations were not significantly different between the control and treated groups. Quantification of the changes in cerebral hemodynamics that occur as a consequence of bolus injection of NaHCO3 may have a significant and beneficial impact on the treatment of metabolic acidemia in patients with congenital heart disease, especially in patients with bidirectional Glenns where pulmonary blood flow is dependent on CBF.
Although this data was obtained on mechanically ventilated patients with single ventricle physiology, these results may be generalized to a larger pediatric population. Understanding the cerebral hemodynamic effects NaHCO3 administration may be especially important in vulnerable populations such as premature infants, patients with impaired autoregulation from hypoxic ischemic injury, or patients with focal or global cerebral edema where the risk of rapid fluctuations in CBF does not outweigh the benefit of treating a metabolic acidemia.
The mechanisms that govern the cerebral hemodynamic responses to a rapid NaHCO3 infusion are complex and not fully understood. Potentially, the observed increase in CBF was caused by an increase in the concentration of CO2, produced as a byproduct of the reaction of NaHCO3 with acid, leading to an intracellular acidosis (8, 9). Although we did not obtain a post-NaHCO3 administration arterial blood gas, previous work suggests that NaHCO3 causes significant increases in the partial pressure of arterial CO2 in mechanically ventilated patients (20). CO2 is a potent vasodilator that induces increases in CBF through local effects on cerebral vasculature. Because our population was paralyzed under general anesthesia, the normal mechanism of responding to elevated arterial CO2 tension by increasing minute ventilation was eliminated. Therefore, it is possible that a more potent effect from NaHCO3 may have been observed in our population compared to patients who are awake and spontaneously breathing.
Relatedly, the increase in CBF may reflect the increase in plasma osmolality following infusion. Siegel et al demonstrated an increase in osmolality as well as a decrease in hematocrit in critically-ill neonates following treatment of metabolic acidemia with NaHCO3 (13). Both increased osmolality and decreased hematocrit have been linked to an increase in CBF via vasodilation and decreased viscosity, respectively (21). Thus, in addition to the vasodilatory effects of CO2, hyperosmolality and/or a drop in hematocrit could be responsible for our observed increase in CBF.
Interestingly, we did not observe significant population averaged changes in oxy-, deoxy-, or total-hemoglobin concentration. Vasodilation caused by CO2 and/or hyperosmolality following NaHCO3 might be expected to lead to increases in oxy- and total-hemoglobin concentrations, as well as a slight decrease in deoxyhemoglobin concentration. However, a decrease in hematocrit after NaHCO3 (as shown in (13)) would likely be accompanied by a drop in oxy- and total hemoglobin concentrations, as well as an increase in deoxy-hemoglobin concentration (22). Possibly, these two phenomena (i.e., vasodilation and a concomitatant drop in hematocrit) have opposite effects on tissue hemoglobin concentrations, leading to a population-averaged effect of no net change (i.e. within the error bars of our measured concentration changes).
Little work has been published on the cerebral effects of NaHCO3 to treat metabolic acidemia in human pediatric populations, and to our knowledge, only one publication has investigated the effects in patients with single ventricle physiology (14). On the whole, our results are consistent with several reports of the cerebral hemodynamic effects of NaHCO3 used to correct metabolic acidemia, although we did observe some disparities with other reports. Van Alfen et al (11) employed continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy and transcranial Doppler ultrasound to study 15 preterm infants with metabolic acidosis treated with bolus administration of NaHCO3. Their cohort presented with more severe acidemia than our cohort, i.e. a base deficit < −6 mmol/l and pH < 7.3, and their cohort also received half the dose (mEq/kg) of our population. As with our results, Van Alfen et al did not observe substantial changes in total hemoglobin concentration at 5 and 15 minutes post-NaHCO3 (they report changes in cerebral blood volume). In contrast to our findings, however, they also did not observe a significant change in CBF as measured by blood flow velocity in the internal carotid artery. This discrepancy may be due to the fact that Doppler ultrasound measures macrovascular changes in arterial flow velocity, while DCS measures microvascular flow directly in cortical tissue, and these two quantities may be disparate. Alternatively, the discrepancy may arise from the differences in age and physiology between the populations, or from the fact that 9 out of 15 patients in their study (11) were spontaneously ventilating, thus permitting the patient to increase their minute ventilation to exhale the extra CO2 produced by NaHCO3.
Lou et al (17) used the 133Xe clearance technique to measure CBF changes five minutes after NaHCO3 injection in seven asphyxiated neonates with respiratory distress and acidosis (base deficit < −8 mEq/l). Interestingly, they found profound decreases in global CBF in these infants, contrary to our findings, despite the fact that they administered the same base deficit dependent dose per kilogram of NaHCO3. It is not clear why these results are contradictory; however, a possible explanation could be the difference in patient population. Unlike our otherwise healthy population with palliated congenital heart disease, their cohort was younger, i.e., preterm neonates, and their cohort had suffered asphyxia and potential damage to the blood brain barrier. Thus, bicarbonate ions, which are normally non-permeable ions, may have been able to penetrate from the plasma to the extracellular fluid, leading to cerebrovasoconstriction and hence decreased CBF.
Bradley et al (14) monitored fourteen patients following bidrectional superior cavopulmonary connections with transcranial Doppler ultrasound of the middle or anterior cerebral artery. Unlike our study, these patients were not acidemic at baseline, i.e. population averaged baseline pH = 7.39. However, the authors also observed a significant increase in cerebral blood flow velocity for up to 15 minutes after a 4 mEq/kg NaHCO3 bolus, similar to the findings observed in our patients. In addition, they observed an increase in systemic arterial saturations following bicarbonate admministration, contrary to the findings in our bidirectional Glenn population.
In summary, a handful of publications that investigate the cerebral effects of NaHCO3 report findings consistent with the ones presented herein. The discrepancies that do arise may reflect the severity and cause of the acidemia, the dosage and injection rate of NaHCO3, the use of mechanical ventilation, the differences in patient population, the anesthetic state, the method of CBF measurement, and the time frame for assessing the cerebral hemodynamic effects following drug administration.
Study Limitations
The results presented herein have several limitations. First, we did not draw a post-NaHCO3 arterial blood gas, as this was merely an observational pilot study. The current clinical practice at CHOP following NaHCO3 is to not draw another arterial blood sample to confirm increases in pH, CO2 tension, and bicarbonate ion concentration. Thus, although we suggest that arterial CO2 levels increased following NaHCO3 due to the abundance of literature suggesting this effect (9, 10, 15, 20) and due to the observed dose-dependent increases in CBF, we cannot definitively confirm that CO2 increased in our cohort. Furthermore, we did not measure baseline albumin concentration, an important non-bicarbonate buffer that may also influence CO2 release following NaHCO3 injection and thus may effect subsequent cerebral hemodynamic changes (20, 23).
Second, we only tracked changes in cerebral and systemic hemodynamics for fifteen minutes following NaHCO3 administration. Despite this limited monitoring time period, by 15 minutes post-injection, CBF was no longer significantly elevated. Thus, we believe a 15 minute window was sufficient to capture the rapid and transient effects of NaHCO3. Additionally, we were limited to studying the effects of rapid infusion of NaHCO3. Future work will investigate variation of the infusion time in order to compare the potential beneficial effects of rapid versus slow infusions.
Third, diffuse optical spectroscopies probe tissues located at shallow depths in the frontal cortex in the region under the optical probe. Although we presume that our frontal cortex measurements are indicative of whole brain response to NaHCO3, absolute quantification of cerebral hemodynamics in other regions of the brain is beyond the scope of this work.
Conclusions
NaHCO3 is a commonly used medication administered for rapid correction of metabolic acidemia in adult, pediatric, and neonatal intensive care units. In pediatric patients with HLHS, we observed substantial increases in CBF following bolus intravenous NaHCO3 administration. These changes in CBF were linearly related to the dose of NaHCO3. On average, cerebral oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations did not change with NaHCO3 administration. Future work will benefit from the investigation the effects of infusion rate on the CBF response to NaHCO3.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Protocol
Infants and children with HLHS at various stages of palliation were recruited and and parental consent was obtained for a pre-surgical brain magnetic resonance imaging and hypercapnia study (described in (24, 25)) approved by the Institutional Review Board at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. After induction of general anesthesia with paralysis in the operating room, patients were tracheally intubated. The anesthetic consisted of sevoflurane in room air for patients over 3 month of age and fentanyl (5 ug/kg) for neonates. Supplemental oxygen was not utilized. Patients were mechanically ventilated using a tidal volume to achieve an arterial CO2 of 4.93 – 5.60 kPa. An arterial catheter was placed in the umbical artery in pre-Norwood patients and in an ulnar or radial artery of pre-Glenn and pre-Fontan patients. Patients were then transferred to the magnetic resonance imaging table, and a non-invasive optical probe (see description below) was placed on the forehead for continuous (0.2 Hz) optical monitoring of cerebral hemodynamics. Heart rate (HR) via electrocardiogram and peripheral hemoglobin-oxygen saturation (SpO2) via pulse-oximetry were monitored and continuously recorded at a rate of 0.5 Hz throughout the duration of the study. Non-invasive (cuff) mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) was measured every 3 minutes.
After the patient was stabilized, an arterial blood gas was drawn. Blood gas analysis was performed using an i-STAT handheld blood analyzer (Abbott Laboratories, Princeton, NJ) to derive blood pH, partial pressure of carbon dioxide and oxygen, base excess or base deficit, bicarbonate ion concentration, hemoglobin concentraction (Hgb), and hematocrit (Hct). As part of routine clinical care during the study, any calculated base deficit less than −2 mEq/l was treated at the attending anesthesiologist’s discretion (not protocolized) with bolus intravenous administration of 8.4% NaHCO3 over a 10 to 30 second period. All patients in this study were hemodynamically stable, including those patients with a base deficit between −2 and −3, where the decision to treat was solely based on practitioner preference. The acuity of patient’s illness did not play a role in the decision to treat. The following formula was used to calculate NaHCO3 dosage: Patient weight (kg) × 1/3 (l/kg) × base deficit (mEq/l). If NaHCO3 was given, a second blood gas was not obtained following NaHCO3 administration.
Cerebral Monitoring
A hybrid diffuse optical instrument combining diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) and diffuse correlation spectroscopy (DCS) was employed to non-invasively monitor cerebral hemodynamics. This instrument has been described previously (24), and the techniques and theoretical analysis have been described at length (26). Briefly, DOS employs 3 near-infrared wavelengths, 688, 787, and 826 nm, and uses a modified Beer-Lambert law (22) to quantify changes in tissue oxy-and deoxy-hemoglobin concentration (ΔHbO2 and ΔHb, respectively) in the region of brain approximately 1–1.5 cm under the optical probe, i.e. in the cortex surface region. The sum of these changes gives variation of total hemoglobin concentration (ΔTHC = ΔHb + ΔHbO2), a quantity which is generally assumed to be proportional to the change in cerebral blood volume. DCS monitors temporal fluctuations of the reflected light intensity; specifically, the temporal intensity autocorrelation function of detected NIR light is computed using a semi-infinite homogeneous approximation in order to derive a blood flow index (BFI) (26). Previous studies have shown that changes of BFI in various model systems agree with changes in cerebral blood flow relative to baseline (ΔrCBF) measured by other techniques (24–28). The sources and detectors for both DOS and DCS were separated by 2.5 cm and held in place by a black rubber probe.
Data Analysis
To quantify the effects of NaHCO3 on hemodynamics, a 1-minute mean of each of the following parameters was obtained immediately prior to, and at 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes after injection of NaHCO3: ΔHbO2, ΔHb, ΔTHC, ΔrCBF, ΔHR, ΔMAP, and ΔSpO2. These time intervals were chosen because the effects of NaHCO3 were expected to be clearly evident due to the rapid onset and transient action of NaHCO3. Changes in each DOS parameter, i.e. Hb, HbO2, and THC, and vital sign parameter, i.e. HR, MAP, and SpO2, were quantified as the difference between a 1-minute average taken 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes after NaHCO3 injection and a 1-minute average immediately prior to injection. Relative changes in DCS-measured CBF were quantified using the following formula:
ΔrCBF = ((〈BFI〉Post/〈BFI〉Pre) − 1) × 100%.
Here brackets 〈 〉 indicate the mean taken over a 1-minute time period, and the subscripts Pre and Post denote means taken before and after NaHCO3 injection, respectively. Note, the four Post averages were quantified at the time points specified above.
A subset of patients who did not receive sodium bicarbonate treatment were used as controls for the NaHCO3 treated group. These control patients were individually matched with each NaHCO3 treated patient for both age (within 4 months) and cardiac physiology. Vital sign and DOS/DCS monitoring were acquired continuously for these patients although they received no intervention. These control patients were intended to elucidate the normal physiologic variations that occur during the monitoring period. The baseline period for these patients was the first minute of DOS/DCS data acquisition, and changes in DOS, DCS, and vital sign parameters were computed in the same fashion as described above at 1, 5, 10, and 15 minutes after the baseline.
Statistical Analysis
A Wilcoxon signed rank test was carried out to test whether the NaHCO3 treated group showed significantly different changes in vital signs and cerebral hemodynamics compared to age- and physiology-matched controls. Furthermore, to quantify the relationship between the dosage of NaHCO3 and the subsequent change in CBF measured with DCS, we fit a simple linear regression model; using this model we estimated Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Pearson’s correlation coefficient, R, varies from 0 to 1.0 and measures the extent to which a linear model explains variability in the data. Analyses were performed using R 2.11 statistical software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Hypotheses tests and associated p-values (p) were two-sided. A Hochberg correction was used to adjust p-values for multiple comparisons. Statistical significance was declared for p-values < 0.05.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Dr. David Busch, Justine Wilson, Dr. Heather Chandler, the Cardiac Anesthesia staff, the Respiratory Therapists, and most importantly, the patients and their families for their participation.
STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL SUPPORT: This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health at the University of Pennsylvania (NS-060653, PI: A.G. Yodh) and at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (grant HL090615, PI: M.A. Fogel; grant NS072338, PI: D.J. Licht; grant NS-052380, PI: D.J. Licht); by the National Center for Research Resources and the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering of the National Institutes of Health through grant P41-EB015893; by the Dana Foundation; and by the Steve and Judy Wolfson Family Trust.
Footnotes
Disclosure: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Aschner JL, Poland RL. Sodium bicarbonate: Basically useless therapy. Pediatrics. 2008;122:831–835. doi: 10.1542/peds.2007-2400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berg CS, Barnette AR, Myers BJ, Shimony MK, Barton AW, Inder TE. Sodium bicarbonate administration and outcome in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 2010;157:684–687. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Corbet AJ, Adams JM, Kenny JD, Kennedy J, Rudolph AJ. Controlled trial of bicarbonate therapy in high-risk premature newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1977;91:771–776. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sabatini S, Kurtzman NA. Bicarbonate therapy in severe metabolic acidosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:692–695. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2007121329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Papile L, Burstein J, Burstein R. Relationship of intravenous sodium bicarbonate infusions and cerebral intraventricular hemorrhage. J Pediatr. 1978;93:834–836. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Simmons MA, Adcock EW, Bard H, Battaglia FC. Hypernatremia and intracranial hemorrhage in neonates. N Engl J Med. 1974;291:6–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197407042910102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Laptook AR. The effects of sodium bicarbonate on brain blood flow and O2 delivery during hypoxemia and acidemia in the piglet. Pediatr Res. 1985;19:815–819. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198508000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ostrea EM, Odell GB. The influence of bicarbonate administration on blood pH in a "closed system": Clinical implications. J Pediatr. 1972;80:671–680. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakashima K, Yamashita T, Kashiwagi S, Nakayama N, Kitahara T, Ito H. The effect of sodium bicarbonate on CBF and intracellular pH in man: Stable Xe-CT and 31P-MRS. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1996;93:96–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1996.tb00561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Singer RB, Deering RC, Clark JK. The acute effects in man of a rapid intravenous infusion of hypertonic sodium bicarbonate solution II Changes in respiration and output of carbon dioxide. J Clin Invest. 1956;35:245–253. doi: 10.1172/JCI103269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Alfen vander Velden A, Hopman JCW, Klaessen J, Feuth T, Sengers RCA, Liem KD. Effects of rapid versus slow infusion of sodium bicarbonate on cerebral hemodynamics and oxygenation in preterm infants. Biol Neonate. 2006;90:122–127. doi: 10.1159/000092411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kravath RE, Aharon AS, Abal G, Finberg L. Clinically significant physiologic changes from rapidly administered hypertonic solutions: acute osmol poisoning. Pediatrics. 1970;46:267–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Siegel SR, Phelps DL, Leake RD, Oh W. The effects of rapid infusion of hypertonic sodium bicarbonate in infants with respiratory distress. Pediatrics. 1973;51:651–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bradley SM, Simsic JM, Mulvihill DM. Hypoventilation improves oxygenation after bidirectional superior cavopulmonary connection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003;126:1033–1039. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5223(03)00203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fanconi S, Burger R, Ghelfi D, Uehlinger J, Arbenz U. Hemodynamic effects of sodium bicarbonate in critically ill neonates. Intensive Care Med. 1993;19:65–69. doi: 10.1007/BF01708362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huseby JS, Gumprecht DG. Hemodynamic effects of rapid bolus hypertonic sodium bicarbonate. Chest. 1981;79:552–554. doi: 10.1378/chest.79.5.552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lou HC, Lassen NA, Friishansen B. Decreased cerebral blood flow after administration of sodium bicarbonate in distressed newborn infants. Acta Neurol Scand. 1978;57:239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1978.tb05871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tibballs J. Bicarbonate and hemodynamics in neonates. Intensive Care Med. 1993;19:63–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01708361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Young RSK, Yagel SK, Woods CL. The effects of sodium bicarbonate on brain blood flow, brain water content, and blood-brain barrier in the neonatal dog. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;65:124–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00690465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Levraut J, Garcia P, Giunti C, et al. The increase in CO2 production induced by NaHCO3 depends on blood albumin and hemoglobin concentrations. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26:558–564. doi: 10.1007/s001340051204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Younkin DP, Reivich M, Jaggi JL, Obrist WD, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M. The effect of hematocrit and systolic pressure on cerebral blood flow in newborn infants. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987;7:295–299. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lee J, Cerussi AE, Saltzman D, Waddington T, Tromberg BJ, Brenner M. Hemoglobin measurement patterns during noninvasive diffuse optical spectroscopy monitoring of hypovolemic shock and fluid replacement. J Biomed Opt. 2007;12 doi: 10.1117/1.2715189. 024001-1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Okamoto H, Hoka S, Kawasaki T, Okuyama T, Takahashi S. Changes in end-tidal carbon dioxide tension following sodium bicarbonate administration: Correlation with cardiac output and haemoglobin concentration. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1995;39:79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.1995.tb05596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Buckley EM, Hance D, Pawlowski T, et al. Validation of diffuse correlation spectroscopic measurements of cerebral blood flow using phase-encoded velocity mapping MRI. J Biomed Opt. 2012;17 doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.17.3.037007. 037007-1-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Durduran T, Zhou CA, Buckley EM, et al. Optical measurement of cerebral hemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in neonates with congenital heart defects. J Biomed Opt. 2010;15 doi: 10.1117/1.3425884. 037004-1-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Durduran T, Choe R, Baker WB, Yodh AG. Diffuse optics for tissue monitoring and tomography. Reports on Progress in Physics. 2010;73:1–43. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/73/7/076701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kim MN, Durduran T, Frangos S, et al. Noninvasive measurement of cerebral blood blow and blood oxygenation using near-infrared and diffuse correlation spectroscopies in critically brain-injured adults. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12:173–180. doi: 10.1007/s12028-009-9305-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zhou C, Eucker SA, Durduran T, et al. Diffuse optical monitoring of hemodynamics in piglet brain with head trauma injury. J Biomed Opt. 2009;14 doi: 10.1117/1.3146814. 034015-1-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]