Abstract
Although human antibodies to Factor VIII inactivate its procoagulant activity, they do not form immunoprecipitates when tested with this antigen. To understand this observation, we have examined the interaction of normal human Factor VIII with four high-titer human anti-Factor VIII, two from transfused hemophiliacs and two “spontaneous” antibodies from nonhemophilic individuals. An estimate of the size of complexes formed by these antibodies has been obtained by agarose gel filtration of mixtures of anti-Factor VIII with cryoprecipitate. Complexed anti-Factor VIII was detected by the method of Allain and Frommel: acid dissociation of complexes at pH 3.5.
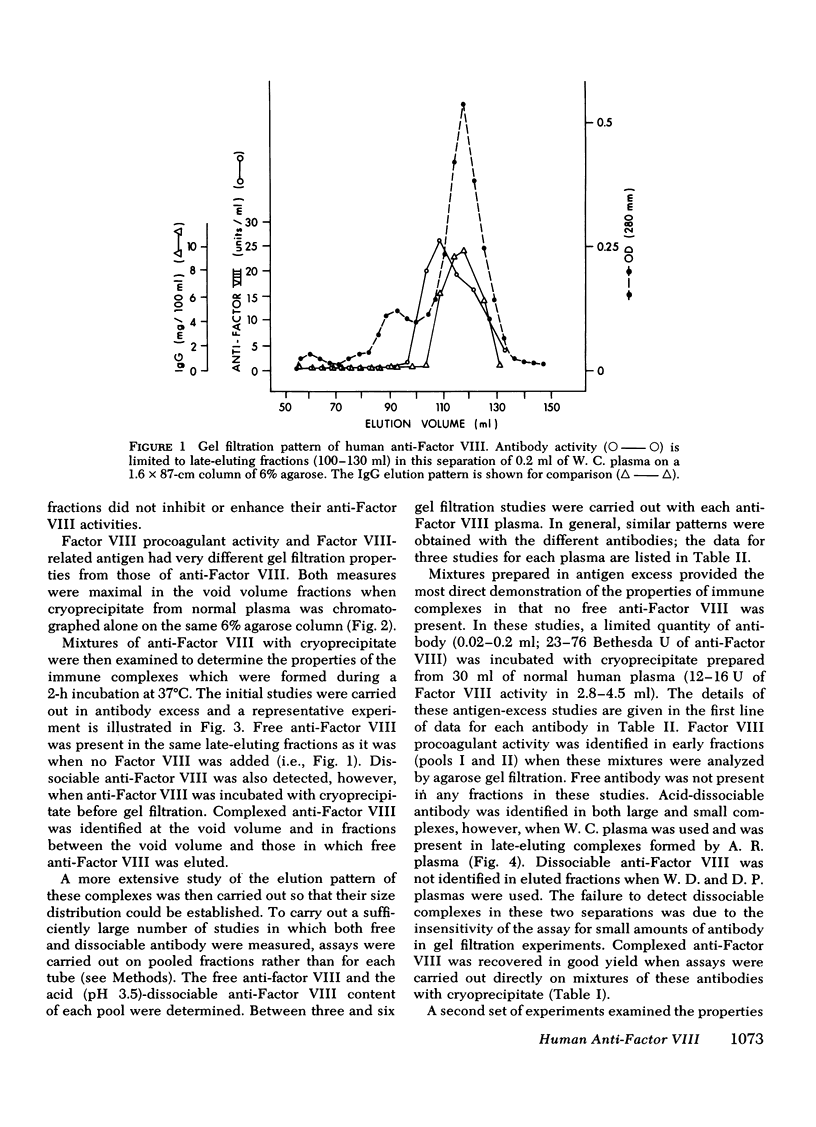
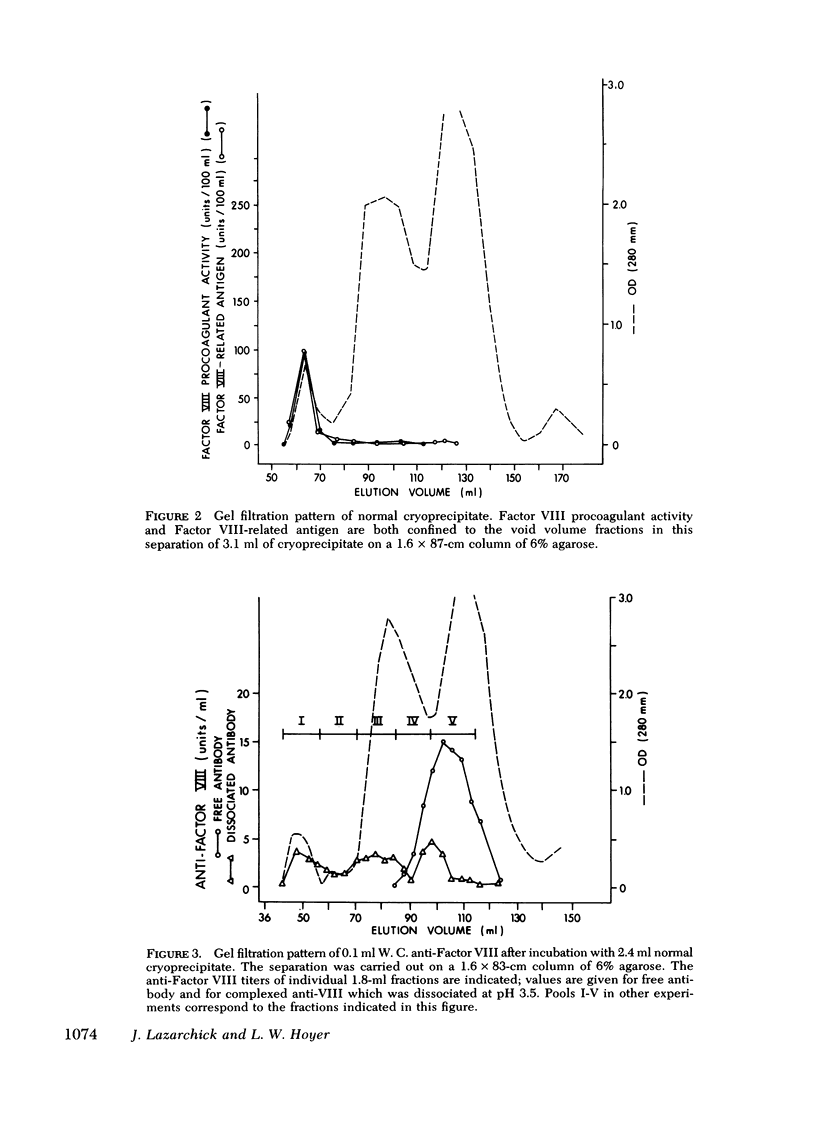
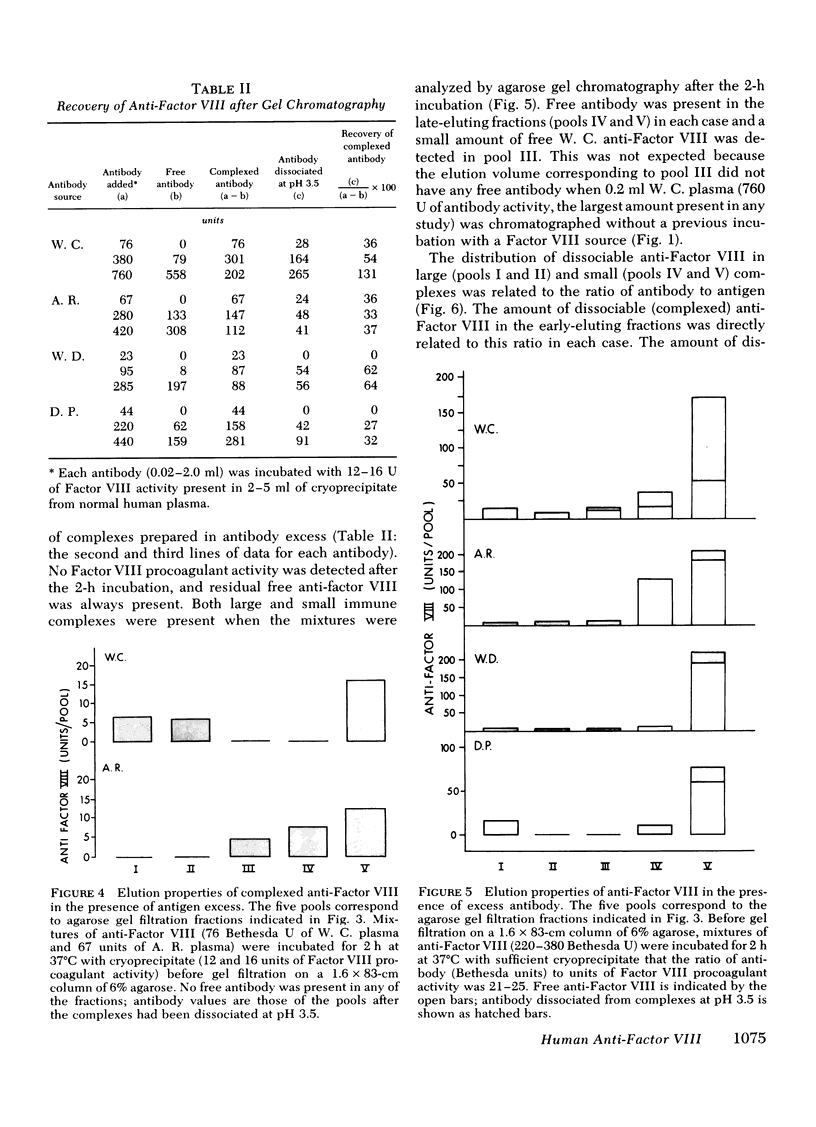
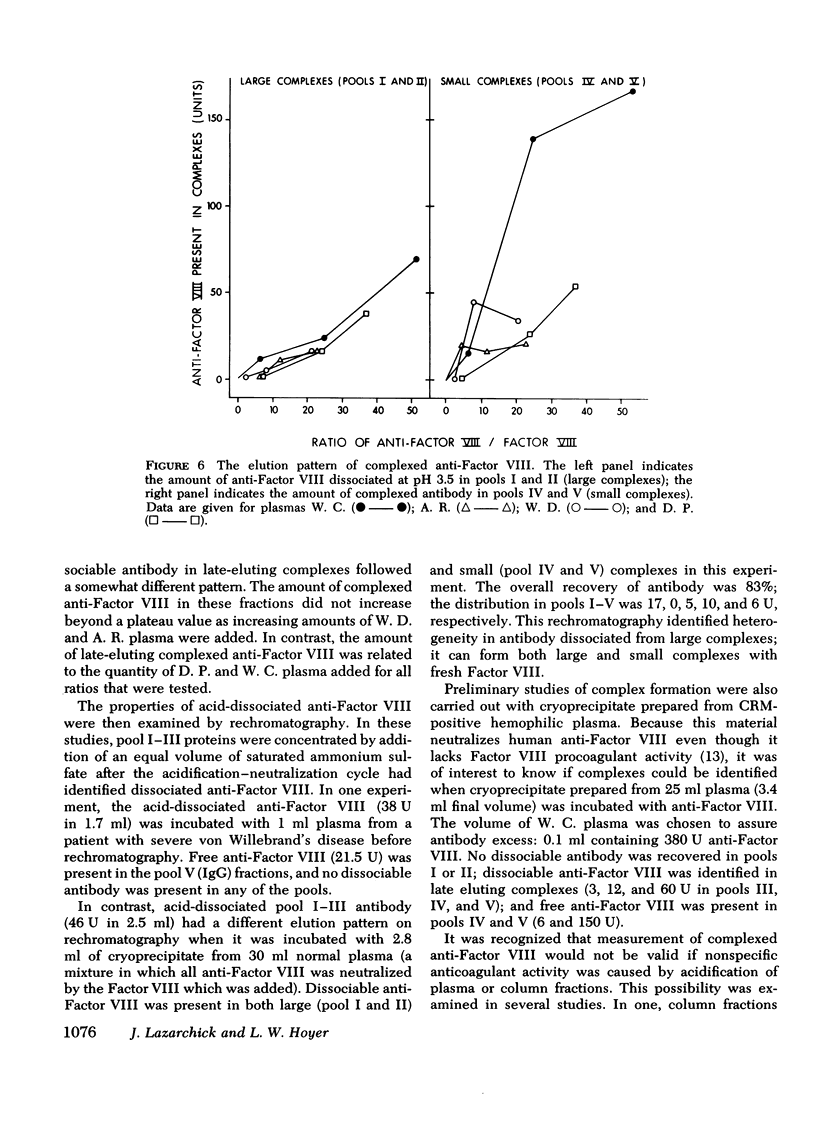
Complexed anti-Factor VIII was detected in column fractions eluting between the void volume and those which correspond to the elution volume of human IgG. In contrast, Factor VIII procoagulant activity was restricted to void volume fractions when separations were carried out in antigen excess, and free anti-Factor VIII was limited to late-eluting fractions when separations were carried out in antibody excess. A small proportion of the complexed anti-Factor VIII was present in void volume fractions; the quantity was directly related to the ratio of antibody to antigen.
Thus, although some complexed anti-Factor VIII is detected in void volume fractions, as would be expected for complexes formed with a very large plasma protein, most immune complexes elute in fractions that indicate interaction with a smaller antigen. These findings suggest that human anti-Factor VIII inactivates procoagulant activity by forming a complex with a small, apparently univalent, component of Factor VIII. This property may prevent immunoprecipitate formation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allain J. P., Frommel D. Antibodies to factor VIII. I. Variations in stability of antigen-antibody complexes in hemophilia A. Blood. 1973 Sep;42(3):437–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRECKENRIDGE R. T., RATNOFF C. D. Studies on the nature of the circulating anticoagulant directed against antihemophilic factor: with notes on an assay for anthemophilic factor. Blood. 1962 Aug;20:137–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. A., Reisner F. F., Hall M., Wagner R. H. Effects of thrombin treatment of preparations of factor VIII and the Ca2+-dissociated small active fragment. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):751–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI108146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein D. I., Rapaport S. I., Chong M. N. Immunologic characterization of 12 factor VIII inhibitors. Blood. 1969 Jul;34(1):85–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougie C., Sargeant R. B., Brown J. E., Baugh R. F. Evidence that factor VIII and the ristocetin aggregating factor (VIIIRist) are separate molecular entities. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Oct;147(1):58–61. doi: 10.3181/00379727-147-38280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., Breckenridge R. T. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII): cross-reacting material in a genetic variant of hemophilia A. Blood. 1968 Dec;32(6):962–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic properties of antihemophilic factor. Prog Hematol. 1973;8:191–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). 3. Comparative binding properties of human and rabbit anti-AHF. Blood. 1972 Apr;39(4):481–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). IV. Radioimmunoassay of AHF antigen. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Dec;80(6):822–833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. J., Morse E. E. Factor V activity in fresh frozen and cryoprecipitate-removed plasma. Vox Sang. 1972 Jan;22(1):39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1972.tb03964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavergne J. M., Meyer D., Reisner H. Characterization of human anti-factor VIII antibodies purified by immune complex formation. Blood. 1976 Dec;48(6):931–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letter: A more uniform measurement of factor VIII inhibitors. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1975 Dec 15;34(3):869–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen W. G., Wagner R. H. Antihemophilic factor: separation of an active fragment following dissociation by salts or detergents. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Jul 31;27(3):502–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon M. C., Ratnoff O. D. Evidence that functional subunits of antihemophilic factor (Factor VIII) are linked by noncovalent bonds. Blood. 1976 Jul;48(1):87–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Activation of low molecular weight fragment of antihaemophilic factor (factor VIII) by thrombin. Nature. 1974 Nov 29;252(5482):404–405. doi: 10.1038/252404a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Immunologic studies of antihemophilic factor (AHF, factor VIII). V. Immunologic properties of AHF subunits produced by salt dissociation. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):737–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Molecular weight of human factor VIII procoagulant activity. Thromb Res. 1975 Dec;7(6):909–916. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rick M. E., Hoyer L. W. Thrombin activation of factor VIII: the effect of inhibitors. Br J Haematol. 1977 Aug;36(4):585–597. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles F. R., Hoyer L. W., Rick M. E., Ahr D. J. The effects of epinephrine infusion in patients with von Willebrand's disease. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1618–1625. doi: 10.1172/JCI108432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robboy S. J., Lewis E. J., Schur P. H., Colman R. W. Circulating anticoagulants to factor VIII. Immunochemical studies and clinical response to factor VIII concentrates. Am J Med. 1970 Dec;49(6):742–752. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(70)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S. Characterization of factor VIII antibodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jan 20;240:350–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb53374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. S. The immunologic character of acquired inhibitors of antihemophilic globulin (factor 8) and the kinetics of their interaction with factor 8. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):147–156. doi: 10.1172/JCI105517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., McKee P. A. Studies on human antihemophilic factor. Evidence for a covalently linked subunit structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):925–937. doi: 10.1172/JCI108369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Hoyer I. W. Von Willebrand factor: dissociation from antihemophilic factor procoagulant activity. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Rogers J., Brand H. Defective ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in von Willebrand's disease and its correction by factor VIII. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2697–2707. doi: 10.1172/JCI107464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Edgington T. S. Factor VIII coagulant activity and factor VIII-like antigen: independent molecular entities. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1015–1020. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. S., Ratnoff O. D., Powell A. E. Immunologic differentiation of classic hemophilia (factor 8 deficiency) and von Willebrand's dissase, with observations on combined deficiencies of antihemophilic factor and proaccelerin (factor V) and on an acquired circulating anticoagulant against antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jan;50(1):244–254. doi: 10.1172/JCI106480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


