Abstract
The role of gonococcal antigens in serum bactericidal activity was determined for an isolate of Neisseria gonorrhoeae from a patient with disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI). Gonococcal outer membranes were purified by differential ultracentrifugation of sheared organisms treated with EDTA. The membranes were solubilized in an endotoxin-disaggregating buffer, and the proteins were separated from the endotoxin by molecular sieve chromatography. Chemical characterization of the endotoxin from the DGI strain revealed the presence of heptose (7.8% of carbohydrate composition) and 2-keto-3-deoxyoctonate (6.1%, wt/wt) in concentrations similar to rough endotoxins of gram-negative enteric bacteria. Dermal Schwartzman reactions were positive for this endotoxin (4 μg) and the corresponding outer membrane (139 μg), but negative for the protein fraction (>500 μg). The patient's whole serum or the IgG fraction, each with complement, reduced the number of the infecting organisms by greater than 1 log10 in a bactericidal assay. Outer membrane and its protein and endotoxin fractions (0.8-500 μg) from the DGI strain were separately preincubated with the patient's convalescent serum and specific inhibition of bactericidal activity occurred with the endotoxin fraction (25 μg) and the outer membrane (100 μg); the protein (500 μg) exhibited no inhibition. Similar results were obtained by inhibiting the bactericidal activity of rabbit antiserum, prepared by intravenous inoculation of an isolate from a patient with pelvic inflammatory disease, with antigen purified from that strain. That this was specific immune inhibition and not anticomplementary activity was shown by the failure of these antigens to inhibit other complement-dependent bactericidal systems.
Full text
PDF



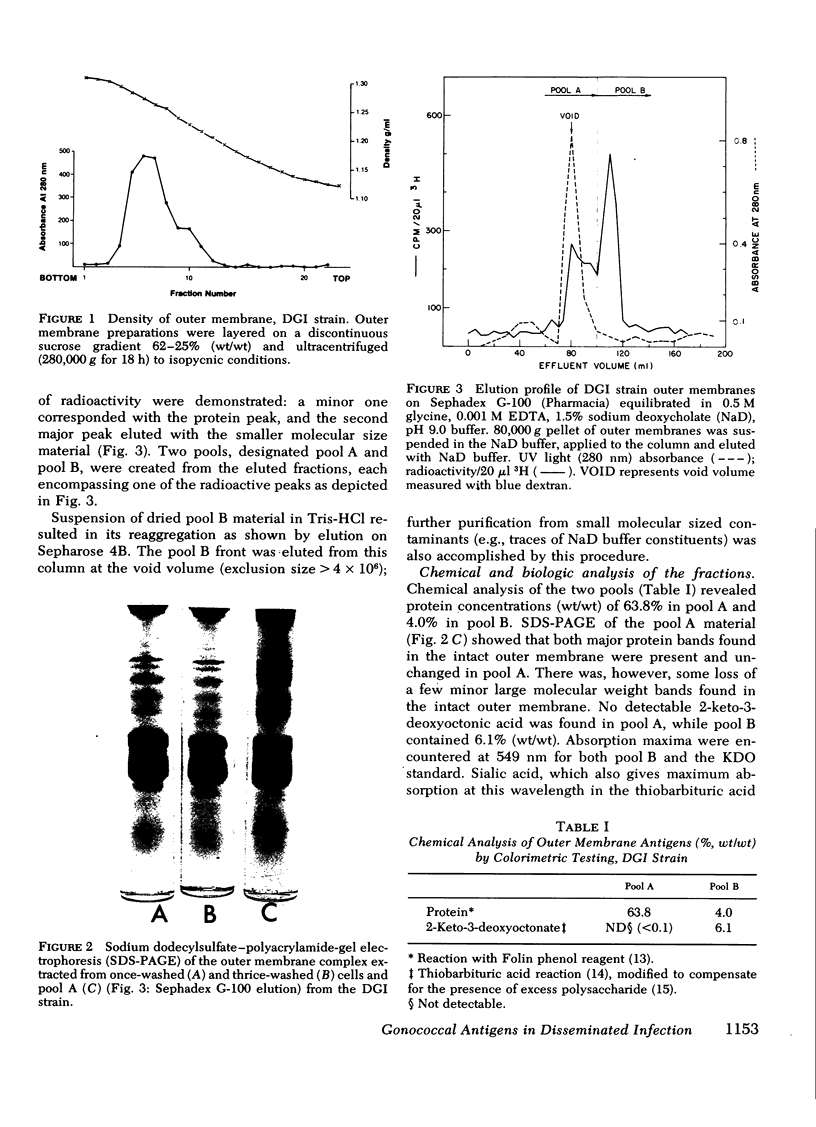
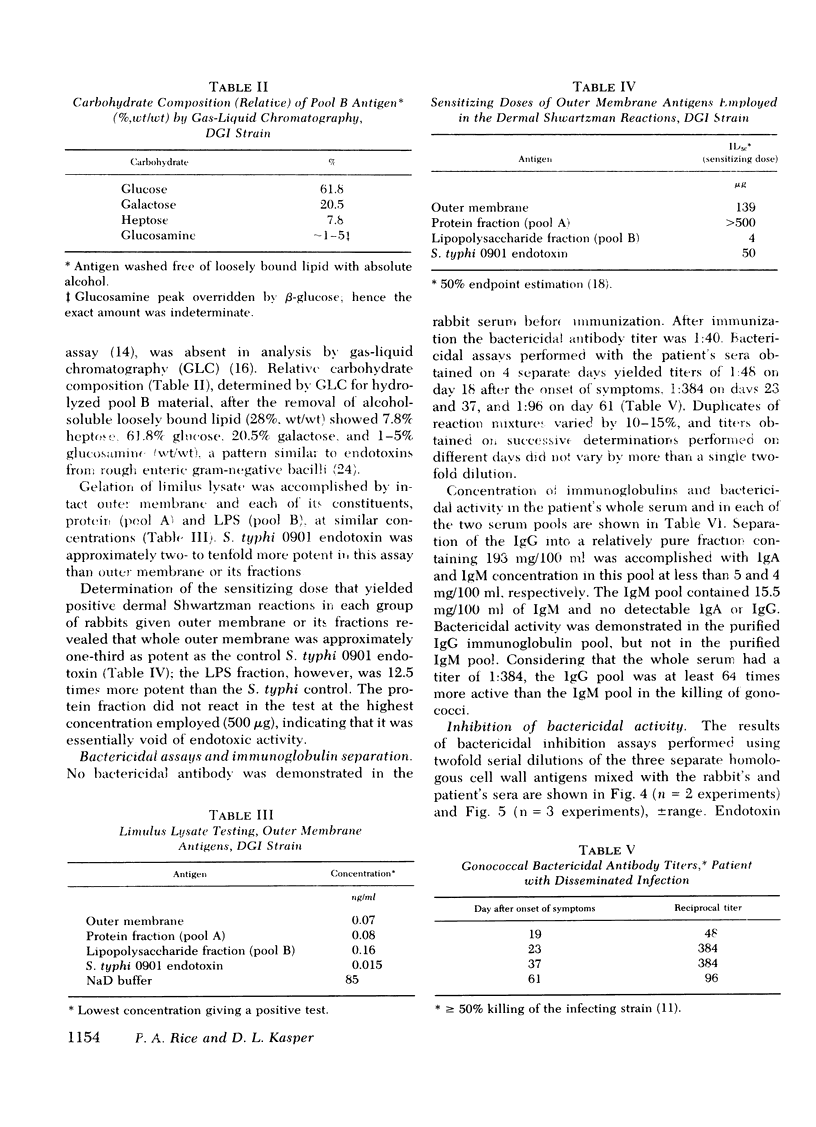
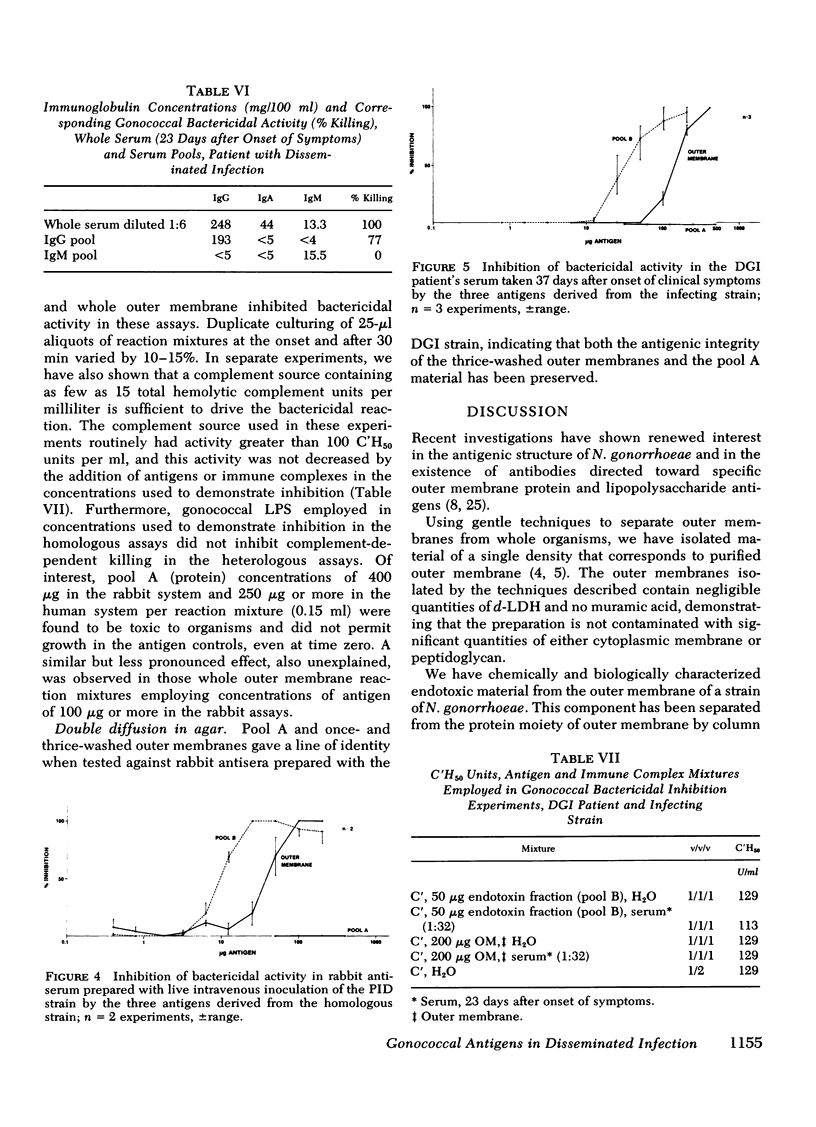



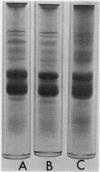
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Allen J. C. Isolation and characterization of the antigen of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):315–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.315-321.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A. Serogrouping of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: identification of four immunologically distinct acidic polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1976 Oct;134(4):377–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Davis C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the "native" type III polysaccharide of group B Streptococcus. J Exp Med. 1976 Feb 1;143(2):258–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore R. S., Kasper D. L., Baker C. J., Goroff D. K. Antigenic specificity of opsonophagocytic antibodies in rabbit anti-sera to group B streptococci. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):673–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks G. F., Israel K. S., Petersen B. H. Bactericidal and opsonic activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae in sera from patients with disseminated gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1976 Nov;134(5):450–462. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.5.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgin-Wolff A., Hernandez R., Just M. Separation of rubella IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies by gel filtration on agarose. Lancet. 1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1278–1280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90600-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn A. A., Ward M. E. Nature and Heterogeneity of the Antigens of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Involved in the Serum Bactericidal Reaction. Infect Immun. 1970 Aug;2(2):162–168. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.2.162-168.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOOK W. A., MUSCHEL L. H. ANTICOMPLEMENTARY EFFECTS AND COMPLEMENT ACTIVITY OF HUMAN SERA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:292–297. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Gotschlich E. C. Isolation and characterization of the outer membrane of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.250-257.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Rice P. A., McCormick W. M. Bactericidal antibody in genital infection due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):243–251. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper D. L., Seiler M. W. Immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex of Bacteroides fragilis subspecies fragilis. J Infect Dis. 1975 Oct;132(4):440–450. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.4.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp J. S., Holmes K. K. Disseminated gonococcal infections caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae with unique nutritional requirements. J Infect Dis. 1975 Aug;132(2):204–208. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J., Poore T. E., Zauber N. P., Oser R. S. Detection of endotoxin in the blood of patients with sepsis due to gran-negative bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1970 Dec 10;283(24):1313–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197012102832404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A. Antigenic properties of various preparations of Neisseria gonorrhoeae endotoxin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(3):413–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb04610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A., Kristoffersen T., Hofstad T. Immunochemical investigations on neisseria gonorrhoeae endotoxin. 2. Serological multispecificity and other properties of phenol-water preparations. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):233–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeland J. A., Kristoffersen T. Immunochemical investigations on Neisseria gonorrhoeae endotoxin. 1. Characterization of phenol-water extracted endotoxin and comparison with aqueous ether preparations. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. A., Levine S., Braude A. I. Influence of colony type on susceptibility of gonococci to killing by human serum. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1652–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medearis D. N., Jr, Camitta B. M., Heath E. C. Cell wall composition and virulence in Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):399–414. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello J. A., Lerner S. A., Bohnhoff M. Characteristics of atypical Neisseria gonorrhoeae from disseminated and localized infections. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1510–1516. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1510-1516.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen B. H., Graham J. A., Brooks G. F. Human deficiency of the eighth component of complement. The requirement of C8 for serum Neisseria gonorrhoeae bactericidal activity. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):283–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI108279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS P. W., UCHIDA T. Determinants of specificity in Salmonella: changes in antigenic structure mediated by bacteriophage. Fed Proc. 1962 Jul-Aug;21:702–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Antibacterial action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1973 Jul;128(Suppl):170–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley D. Sensitivity of rough gram-negative bacteria to the bactericidal action of serum. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1647–1650. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1647-1650.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Buchanan T. M., Holmes K. K. Gonococci causing disseminated gonococcal infection are resistant to the bactericidal action of normal human sera. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1163–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI108569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spink W. W., Keefer C. S. STUDIES OF GONOCOCCAL INFECTION. II. THE BACTERIOLYTIC POWER OF THE WHOLE DEFIBRINATED BLOOD OF PATIENTS WITH GONOCOCCAL ARTHRITIS. J Clin Invest. 1937 Mar;16(2):177–183. doi: 10.1172/JCI100845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumacher R. J., Kovnat M. J., McCabe W. R. Limitations of the usefulness of the Limulus assay for endotoxin. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jun 14;288(24):1261–1264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197306142882402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Artenstein M. S. Cross-reactivity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis and the nature of antigens involved in the bactericidal reaction. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):240–247. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Wilson C. Variability of the lytic susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sera. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1843–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf-Watz H., Elmros T., Normark S., Bloom G. D. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: outer membrane and peptidoglycan composition of penicillin-sensitive and-resistant strains. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1332-1341.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]