Abstract
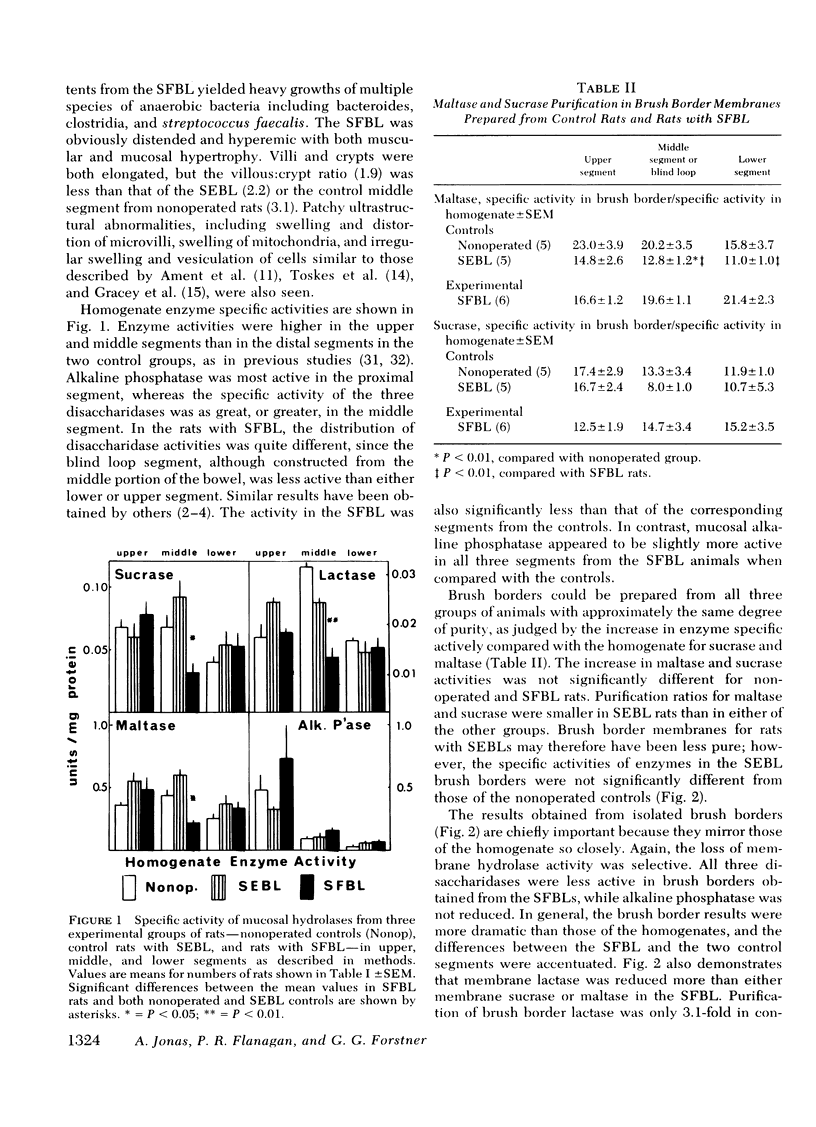
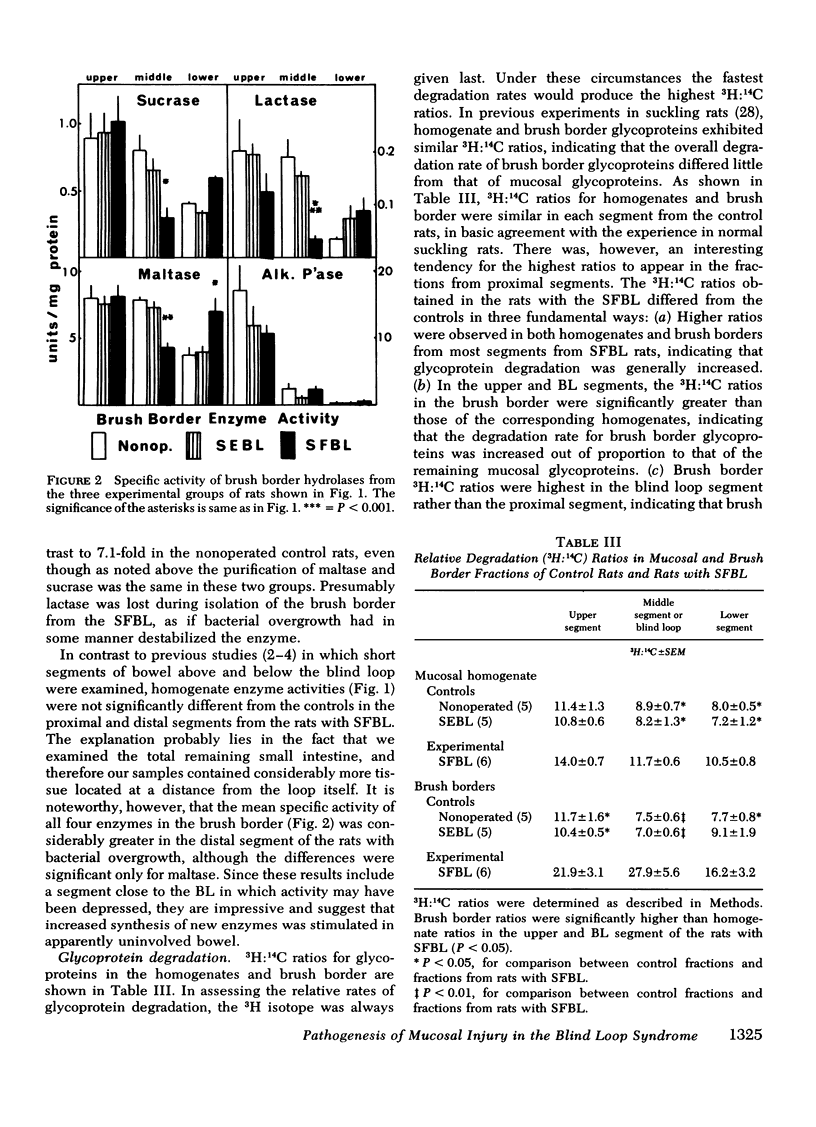
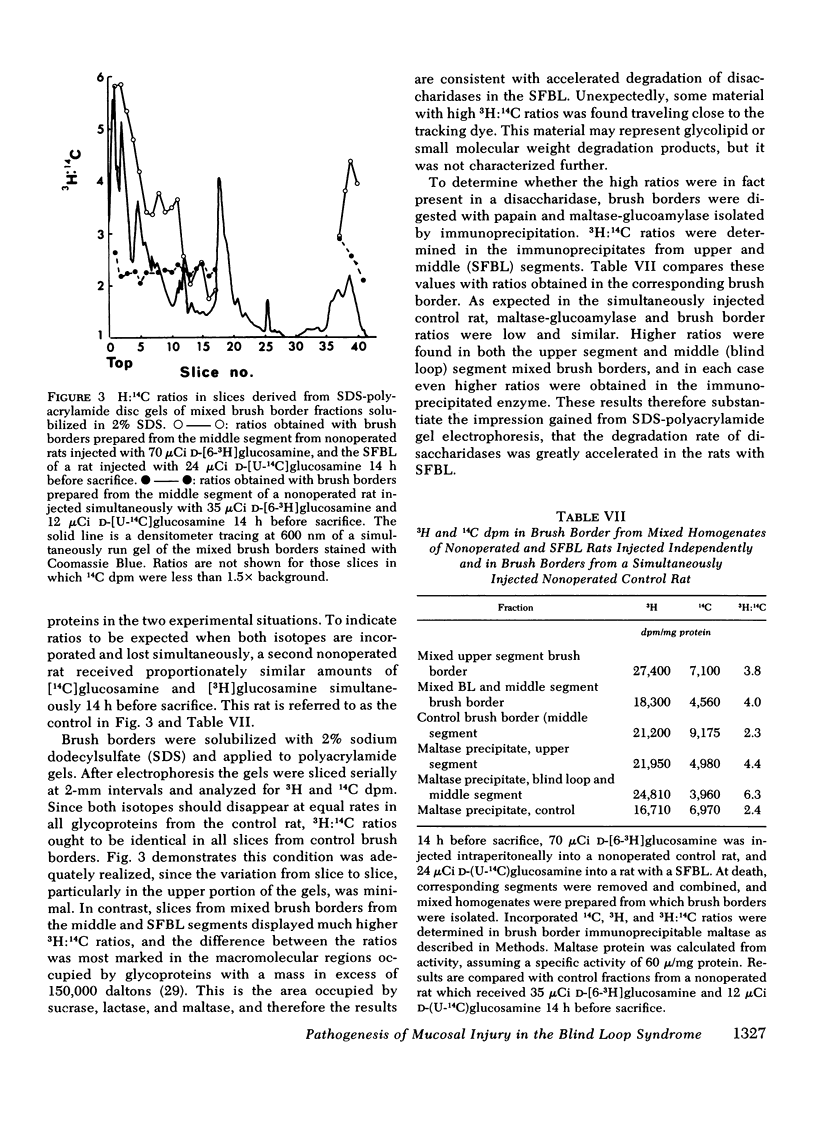
The effect of intestinal bacterial over-growth on brush border hydrolases and brush border glycoproteins was studied in nonoperated control rats, control rats with surgically introduced jejunal self-emptying blind loops, and rats with surgically introduced jejunal self-filling blind loops. Data were analyzed from blind loop segments, segments above and below the blind loops, and three corresponding segments in the nonoperated controls. Rats with self-filling blind loops had significantly greater fat excretion than controls and exhibited significantly lower conjugated:free bile salt ratios in all three segments. Maltase, sucrase, and lactase activities were significantly reduced in homogenates and isolated brush borders from the self-filling blind loop, but alkaline phosphatase was not affected. The relative degradation rate of homogenate and brush border glycoproteins was assessed by a double-isotope technique involving the injection of d-[6-3H]glucosamine 3 h and d-[U-14C]glucosamine 19 h before sacrifice, and recorded as a 3H:14C ratio. The relative degradation rate in both homogenate and brush border fractions was significantly greater in most segments from rats with self-filling blind loops. In the upper and blind loop segments from rats with self-filling blind loops, the 3H:14C ratios were higher in the brush border membrane than in the corresponding homogenates, indicating that the increased rates of degradation primarily involve membrane glycoproteins. Incorporation of d-[6-3H]glucosamine by brush border glycoproteins was not reduced in rats with self-filling blind loops, suggesting that glycoprotein synthesis was not affected. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of brush border glycoproteins from the contaminated segments indicated that the large molecular weight glycoproteins, which include many of the surface hydrolases, were degraded most rapidly. Brush border maltase, isolated by immunoprecipitation, had 3H:14C ratios characteristic of the most rapidly degraded glycoproteins. The results indicate that bacteria enhance the destruction of intestinal surface glycoproteins including disaccharidases. Since alkaline phosphatase, a glycoprotein, is not affected, the destruction is selective and presumably involves only the most exposed membrane components.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS G. D., BAUER H., SPRINZ H. Influence of the normal flora on mucosal morphology and cellular renewal in the ileum. A comparison of germ-free and conventional mice. Lab Invest. 1963 Mar;12:355–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers D. H., Tedesco F. J. The possible role of pancreatic proteases in the turnover of intestinal brush border proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):28–40. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90338-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ament M. E., Shimoda S. S., Saunders D. R., Rubin C. E. Pathogenesis of steatorrhea in three cases of small intestinal stasis syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1972 Nov;63(5):728–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch R., Menge H., Lorenz-Meyer H., Riecken E. O. Morphologische und biochemische Veränderungen der Dünndarmschlemhaut beim Blindsack-Syndrom. Verh Dtsch Ges Inn Med. 1973;79:853–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers R. E., Clamp J. R. An assessment of methanolysis and other factors used in the analysis of carbohydrate-containing materials. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1042/bj1251009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coello-Ramirez P., Lifshitz F. Enteric microflora and carbohydrate intolerance in infants with diarrhea. Pediatrics. 1972 Feb;49(2):233–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr Role of enteric microorganisms in malabsorption. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1426–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Shiner M. The deconjugation of bile salts by human intestinal bacteria. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1237–1238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90242-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichholz A. Studies on the organization of the brush border in intestinal epithelial cells. V. Subfractionation of enzymatic activities of the microvillus membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. (1-14C)glucosamine incorporation by subcellular fractions of small intestinal mucosa. Identification by precursor labeling of three functionally distinct glycoprotein classes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3584–3592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. Incorporation of [1-14C]glucosamine by rat intestinal microvillus membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 11;150(4):736–738. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G. Release of intestinal surface-membrane glycoproteins associated with enzyme activity by brief digestion with papain. Biochem J. 1971 Mar;121(5):781–789. doi: 10.1042/bj1210781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G. G., Sabesin S. M., Isselbacher K. J. Rat intestinal microvillus membranes. Purification and biochemical characterization. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(2):381–390. doi: 10.1042/bj1060381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forstner G., Galand G. The influence of hydrocortisone on the synthesis and turnover of microvillous membrane glycoproteins in suckling rat intestine. Can J Biochem. 1976 Mar;54(3):224–232. doi: 10.1139/o76-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galand G., Forstner G. G. Isolation of microvillus plasma membranes from suckling-rat intestine. The influence of premature induction of digestive enzymes by injection of cortisol acetate. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;144(2):293–302. doi: 10.1042/bj1440293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A., Rout W. R., Toskes P. P. Jejunal brush border injury and impaired sugar and amino acid uptake in the blind loop syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):965–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Oshin A., Barker J., Glasgow E. F. Bacteria, bile salts, and intestinal monosaccharide malabsorption. Gut. 1971 Sep;12(9):683–692. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.9.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Houghton M., Thomas J. Deoxycholate depresses small-intestinal enzyme activity. Gut. 1975 Jan;16(1):53–56. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Papadimitriou J., Bower G. Ultrastructural changes in the small intestines of rats with self-filling blind loops. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):646–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Thomas J., Houghton M. Effect of stasis on intestinal enzyme activities. Aust N Z J Med. 1975 Apr;5(2):141–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1975.tb03643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M., Walter W. M., Jr, Colver E. H. Persistent deficiency of intestinal lactase in apparently cured tropical sprue. Gastroenterology. 1968 Apr;54(4):552–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kottke B. A., Wollenweber J., Owen C. A., Jr Quantitative thin-layer chromatography of free and conjugated cholic acid in human bile and duodenal contents. J Chromatogr. 1966 Mar;21(3):439–447. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström C., Dahlqvist A., Josefsson L. Quantitative determination of enzymes in different parts of the villi and crypts of rat small intestine. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase, disaccharidases and dipepeptidases. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Dec;15(12):713–721. doi: 10.1177/15.12.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinsloo J. G., Wittmann W., Pretorius P. J., Kruger H., Fellingham S. A. Effect of different sugars on diarrhoea of acute kwashiorkor. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Oct;44(237):593–599. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.237.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosper J., Murray R. L., Kern F., Jr Protein starvation and the small intestine. II. Disaccharidase activities. Gastroenterology. 1968 Aug;55(2):223–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Wostmann B. S. Intestinal disaccharidase activities in the growing germfree and conventional rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Mar;113(3):609–616. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaram G. S., Singh H., Sodhi H. S. Thin-layer chromatographic separation of chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Oct;34(3):425–429. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S. The pathophysiological role of small intestinal bacterial flora. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1970;6:139–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toskes P. P., Giannella R. A., Jervis H. R., Rout W. R., Takeuchi A. Small intestinal mucosal injury in the experimental blind loop syndrome. Light- and electron-microscopic and histochemical studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 May;68(5 Pt 1):1193–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. D., Zschiesche O. M., Anderson J., Walker A. Intestinal disaccharidase activity in celiac sprue (gluten-sensitive enteropathy). Arch Intern Med. 1969 Jan;123(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


