Abstract
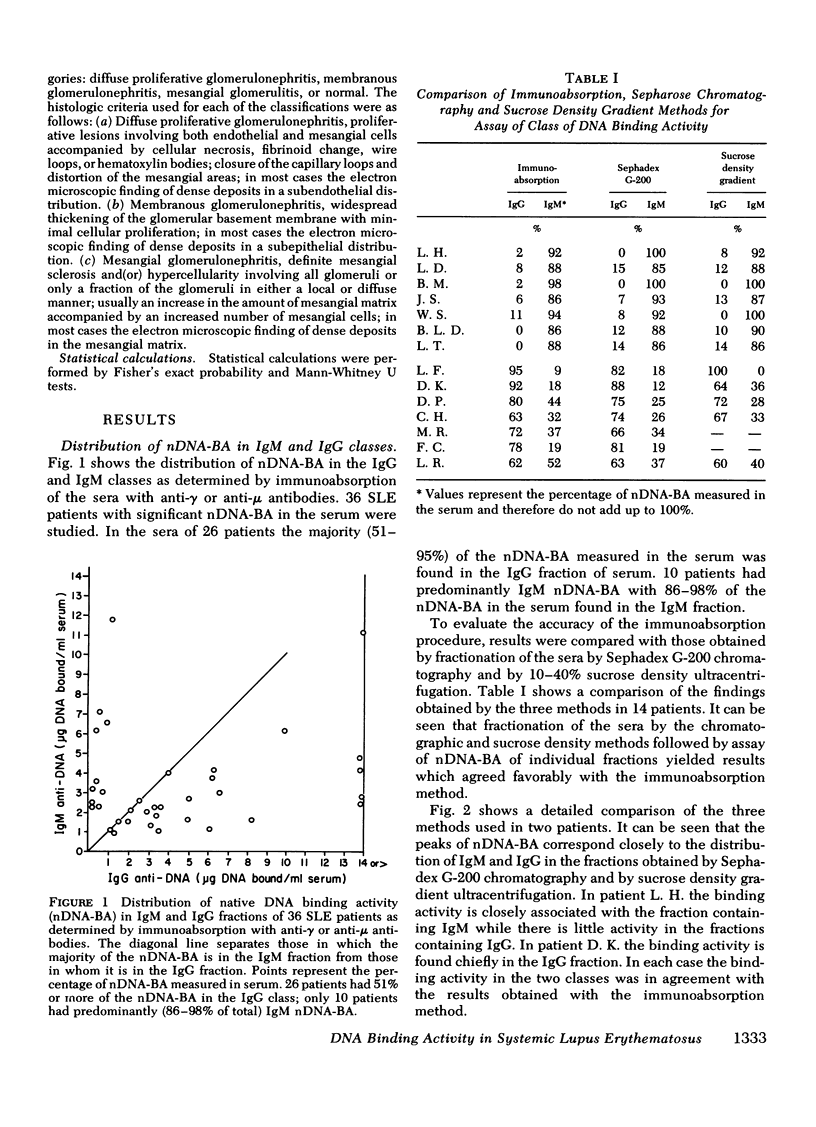
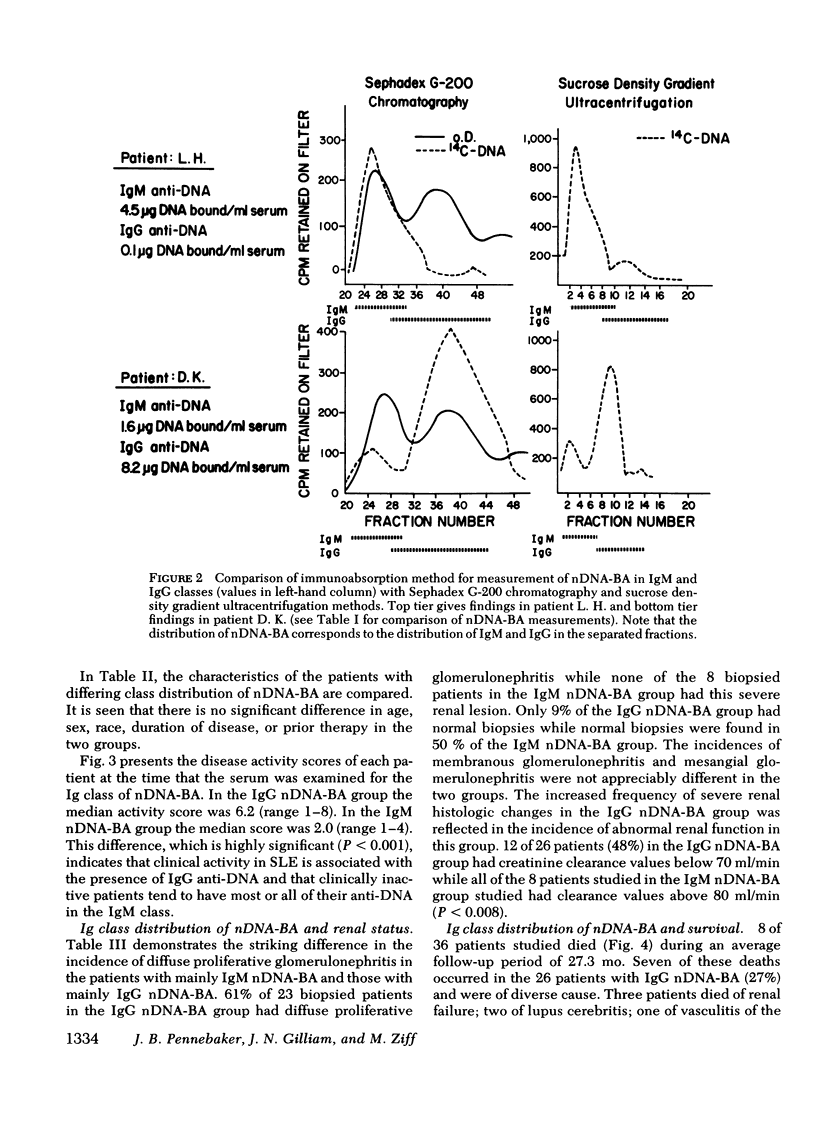
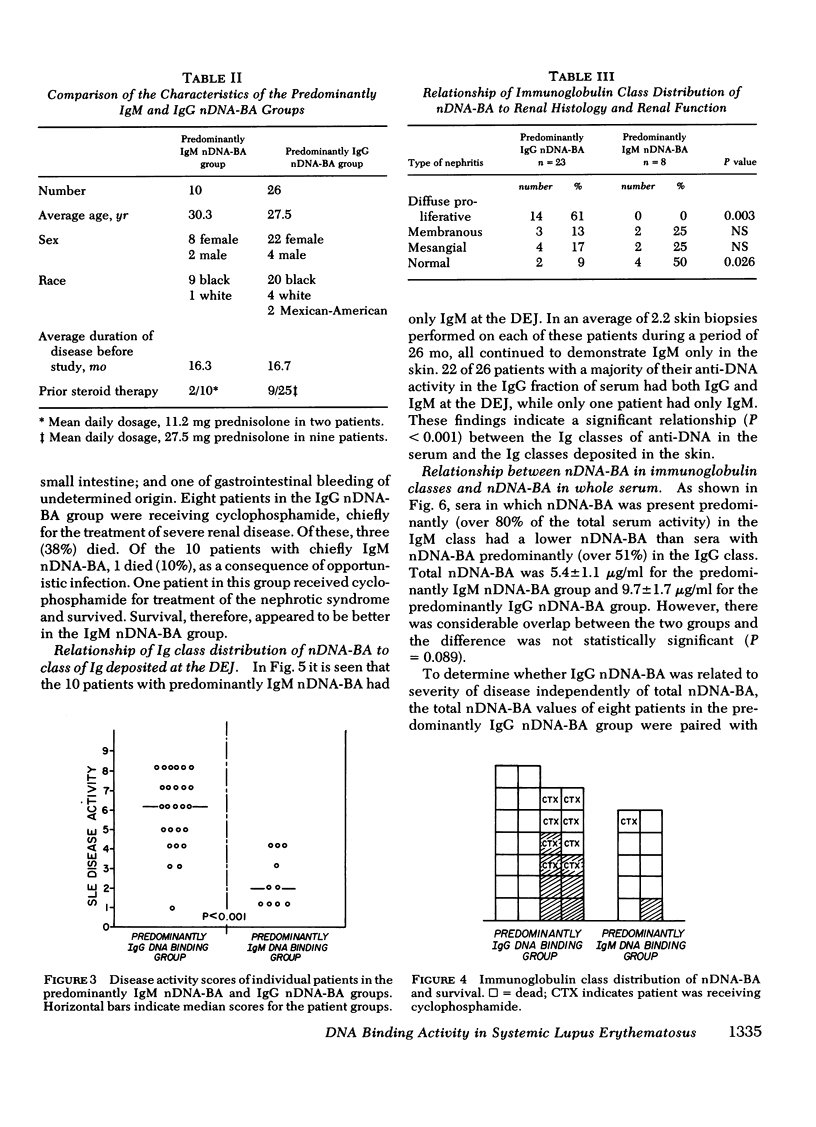
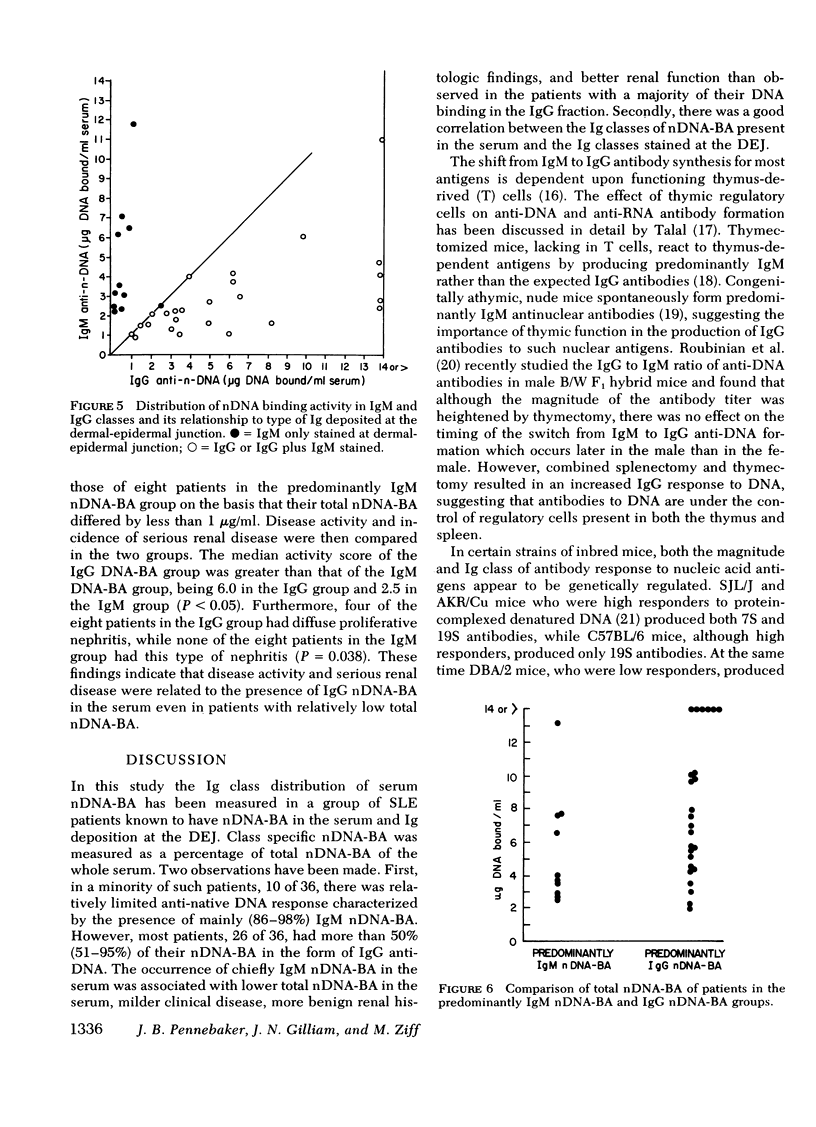
36 systemic lupus erythematosus patients with native DNA binding activity (nDNA-BA) in the serum and subepidermal immunoglobulin deposits were studied to determine the relationship of the immunoglobulin (Ig) class distribution of serum nDNA-BA to the clinical characteristics of their disease and to the Ig class present at the dermal-epidermal junction (DEJ). The patients with predominantly (86-98%) IgM nDNA-BA in the serum had less active disease, mild or no renal involvement, and longer survival than those with predominantly (51-95%) IgG nDNA-BA in the serum. Renal biopsies in eight patients with predominantly IgM nDNA-BA in the serum showed relatively benign histologic changes in the kidney. In contrast, renal tissue from 23 patients with predominantly IgG nDNA-BA showed more severe histologic changes. All patients had multiple skin biopsies. Patients with predominantly IgM nDNA-BA consistently had only IgM at the DEJ. Patients with predominantly IgG nDNA-BA had IgG, usually in association with IgM, at the DEJ. The findings demonstrate that a minority of systemic lupus erythematosus patients may exhibit a limited anti-nDNA response characterized by the presence of chiefly IgM nDNA-BA in the serum and that this is reflected by the presence of mild disease and IgM alone at the DEJ. The development of IgG nDNA-BA is associated with more severe and active disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davie J. M., Paul W. E. Role of T lymphocytes in the humoral immune response. I. Proliferation of B lymphocytes in thymus-deprived mice. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1438–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch C., Barnett E. V. The occurrence and nature of precipitating antibodies in anti-DNA sera. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Apr;2(3):310–321. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommel D., Dupuy J. M., Litman G. W., Good R. A. Use of immunoadsorption techniques in the preparation of chemical agammaglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1292–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs S., Mozes E., Stollar B. D. The nature of murine immune response to nucleic acids. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliam J. N., Cheatum D. E., Hurd E. R., Stastny P., Ziff M. Immunoglobulin in clinically uninvolved skin in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1434–1440. doi: 10.1172/JCI107691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg B., Keiser H. A Millipore filter assay for antibodies to native DNA in sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Mar-Apr;16(2):199–207. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez E. N., Rothfield N. F. Immunoglobulin class and pattern of nuclear fluorescence in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 16;274(24):1333–1338. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606162742401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Edmonds J. P., Holborow E. J. Precipitating antibody to D.N.A. detected by two-stage electroimmunodiffusion. Study in S.L.E. and in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1973 Oct 20;2(7834):883–885. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The regulatory influence of activated T cells on B cell responses to antigen. Adv Immunol. 1972;15:1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60683-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Agnello V., Carr R. I., Kunkel H. G. Anti-DNA antibodies and renal lesions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):933–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monier J. C., Sepetjian M. Spontaneous antinuclear autoimmunisation in Swan and nude mice: comparative study. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1975 Jan;126(1):63–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoian R., Pillarisetty R., Talal N. Immunological regulation of spontaneous antibodies to DNA and RNA. II. Sequential switch from IgM to IgG in NZB/NZW F1 mice. Immunology. 1977 Jan;32(1):75–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picazo J. J., Tan E. M. Specificities of antibodies to native DNA. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1975;11:35–41. doi: 10.3109/03009747509095627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield N. F., Stollar B. D. The relation of immunoglobulin class, pattern of anti-nuclear antibody, and complement-fixing antibodies to DNA in sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1785–1794. doi: 10.1172/JCI105669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schur P. H., Sandson J. Immunologic factors and clinical activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1968 Mar 7;278(10):533–538. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196803072781004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Steward M. W. The immunopathological significance of the heterogeneity of antibody affinity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Aug;9(2):193–199. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N. Disordered immunologic regulation and autoimmunity. Transplant Rev. 1976;31:240–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb01456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Pillarisetty R. J., DeHoratius R. J., Messner R. P. Immunologic regulation of spontaneous antibodies to DNA and RNA I. Significance of IgM and IgG antibodies in SLE patients and asymptomatic relatives. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Sep;25(3):377–382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Pillarisetty R. IgM and IgG antibodies to DNA, RNA, and DNA:RNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 May;4(1):24–31. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo T., Friou G. J. Lupus nephritis: varying complement-fixing properties of immunoglobulin G antibodies to antigens of cell nuclei. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):904–906. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo T., Friou G. J., Spiegelberg H. L. Immunoglobulin G subclass of human antinuclear antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Jan;6(1):145–151. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and further properties of single-strand-specific nuclease from Aspergillus oryzae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):192–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfield J. B., Faiferman I., Koffler D. Avidity of anti-DNA antibodies in serum and IgG glomerular eluates from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Association of high avidity antinative DNA antibody with glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):90–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


