Abstract
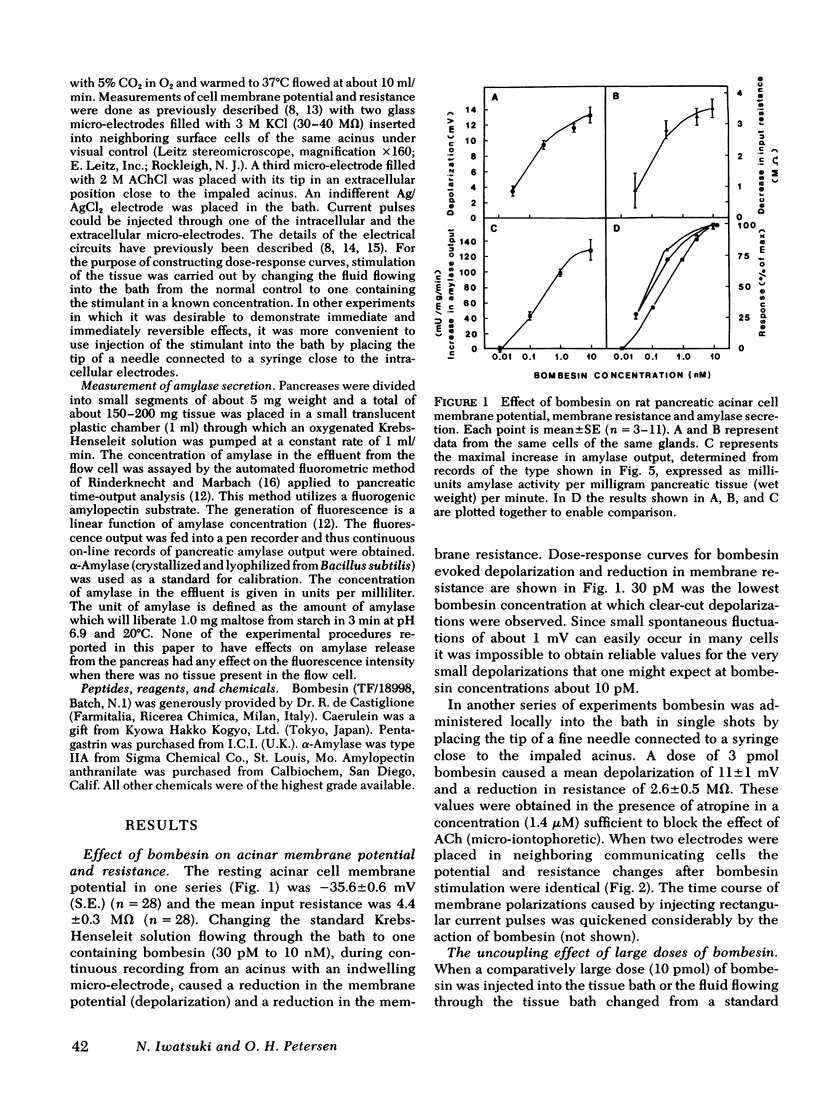
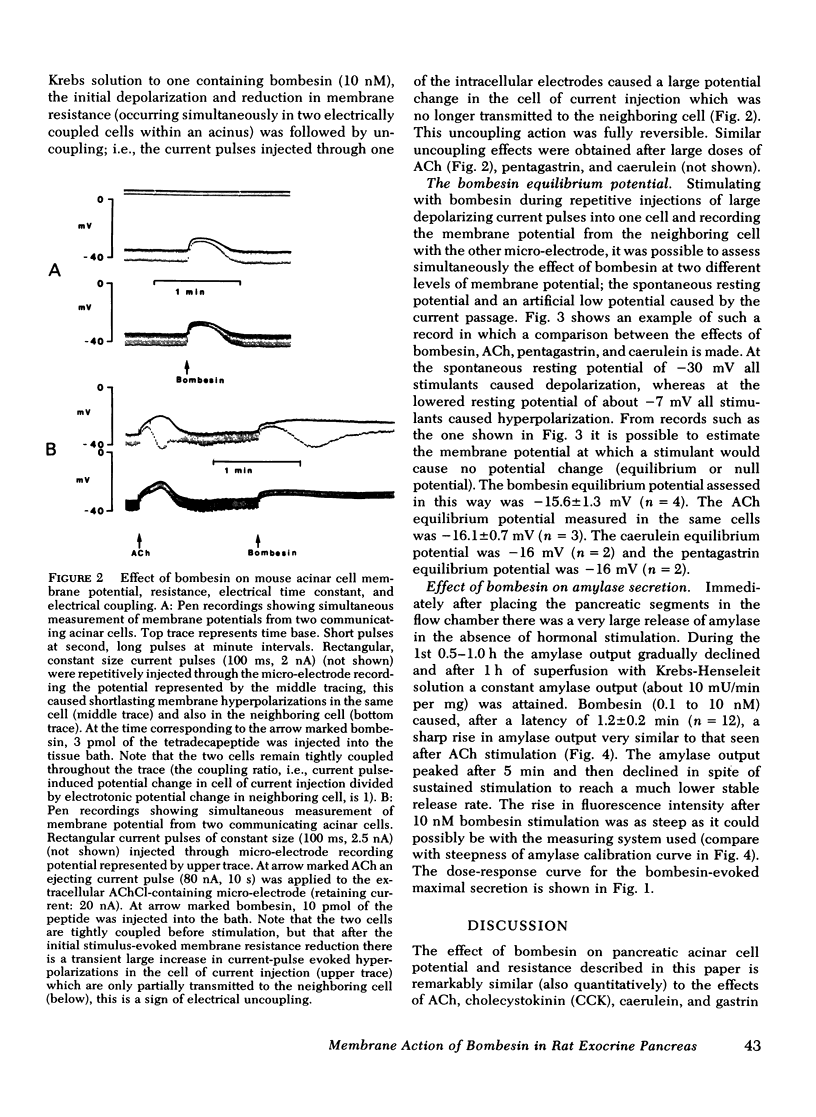
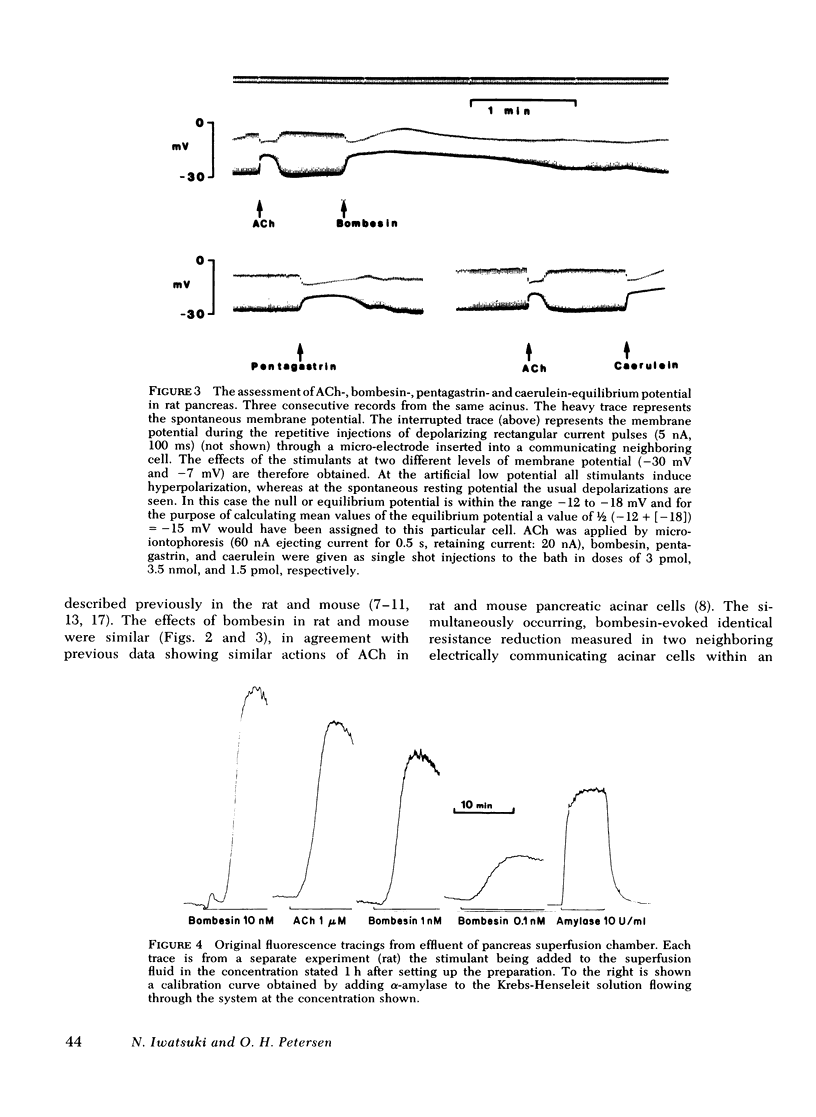
Bombesin caused depolarization of rat or mouse pancreatic acinar cell membrane, reduction of membrane resistance, and a steep rise in amylase output from superfused pancreatic fragments. These effects were similar to those previously described for acetylcholine, cholecystokinin, and gastrin. The dose-response curves for these three effects of bombesin were very similar, with effects being detectable at concentrations of about 30 pM and maximal effects at about 10 nM. The equilibrium potential for the membrane action of bombesin, i.e., the membrane potential at which bombesin did not cause any change in membrane potential, was -16 mV. Similar values for equilibrium potential were obtained with acetylcholine, caerulein and pentagastrin. Bombesin in the higher dose range (10 nM) caused electrical uncoupling of acinar cells within an acinus, i.e., a marked increase in junctional membrane resistance. Similar uncoupling effects were observed after acetylcholine, caerulein, and pentagastrin stimulation. In conclusion, bombesin acts on the pancreatic acinar plasma membrane in exactly the same way as acetylcholine and cholecystokinin-pancreozymin. The electrical uncoupling caused by stimulation is evidence for an increase in cytosol free calcium ion concentration.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argent B. E., Case R. M., Scratcherd T. Stimulation of amylase secretion from the perfused cat pancreas by potassium and other alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):611–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Clausen T. The relationship between calcium exchange and enzyme secretion in the isolated rat pancreas. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):75–102. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler D. E., Williams J. A. Pancreatic acinar cells: effects of lanthanum ions on amylase release and calcium ion fluxes. J Physiol. 1974 Dec;243(3):831–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschodt-Lanckman M., Robberecht P., De Neef P., Lammens M., Christophe J. In vitro action of bombesin and bombesin-like peptides on amylase secretion, calcium efflux, and adenylate cyclase activity in the rat pancreas: a comparison with other secretagogues. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):891–898. doi: 10.1172/JCI108542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erspamer V., Improta G., Melchiorri P., Sopranzi N. Evidence of cholecystokinin release by bombesin in the dog. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;52(2):227–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb09704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W. Generation of end-plate potentials. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jan;56(1):177–247. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner J. D., Conlon T. P., Kleveman H. L., Adams T. D., Ondetti M. A. Action of cholecystokinin and cholinergic agents on calcium transport in isolated pancreatic acinar cells. J Clin Invest. 1975 Aug;56(2):366–375. doi: 10.1172/JCI108101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Kato K., Nishiyama A. The effects of gastrin and gastrin analogues on pancreatic acinar cell membrane potential and resistance. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 May;60(1):147–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1977.tb16759.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Acetylcholine-like effects of intracellular calcium application in pancreatic acinar cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):147–149. doi: 10.1038/268147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Determination of acetylcholine null potential in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):784–786. doi: 10.1038/263784a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: localization of acetylcholine receptors and the importance of chloride and calcium for acetylcholine-evoked depolarization. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;269(3):723–733. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: the acetylcholine equilibrium potential and its ionic dependency. J Physiol. 1977 Aug;269(3):735–751. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Schulz I. Ca++ fluxes in isolated cells of rat pancreas. effect of secretagogues and different Ca++ concentrations. J Membr Biol. 1976 Oct 20;29(1-2):185–203. doi: 10.1007/BF01868959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H., Williams J. A. Analysis of tissue amylase output by an automated method. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):155–160. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90452-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H., Williams J. A. Pancreatic acinar cells: acetylcholine-induced membrane depolarization, calcium efflux and amylase release. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):689–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: ionic dependence of acetylcholine-induced membrane potential and resistance change. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):431–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: membrane potential and resistance change evoked by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):145–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. Electrophysiology of mammalian gland cells. Physiol Rev. 1976 Jul;56(3):535–577. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.3.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Matthews E. K. The effect of pancreozymin and acetylcholine on the membrane potential of the pancreatic acinar cells. Experientia. 1972 Sep 15;28(9):1037–1038. doi: 10.1007/BF01918657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Ueda N. Pancreatic acinar cells: effect of acetylcholine, pancreozymin, gastrin and secretin on membrane potential and resistance in vivo and in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):461–471. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak J. M., Bloom S. R., Hobbs S., Solcia E., Pearse A. G. Distribution of a bombesin-like peptide in human gastrointestinal tract. Lancet. 1976 May 22;1(7969):1109–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulsen J. H., Williams J. A. Effects of the calcium ionophore A23187 on pancreatic acinar cell membrane potentials and amylase release. J Physiol. 1977 Jan;264(2):323–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht H., Marbach E. P. A new automated method for the determination of serum alpha-amylase. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Jul;29(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of a cell junction and the local cytoplasmic free ionized calcium concentration: a study with aequorin. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):87–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01869692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose B., Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of cell junction depends on local cytoplasmic calcium activity. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):250–252. doi: 10.1038/254250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs V. V., Swarts H. G., De Pont J. J., Bonting S. L. Role of calcium in exocrine pancreatic secretion. I. Calcium movements in the rabbit pancreas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 9;404(2):257–267. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90332-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. A., Chandler D. Ca++ and pancreatic amylase release. Am J Physiol. 1975 Jun;228(6):1729–1732. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.6.1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


