Abstract
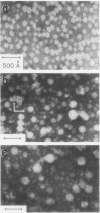
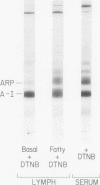
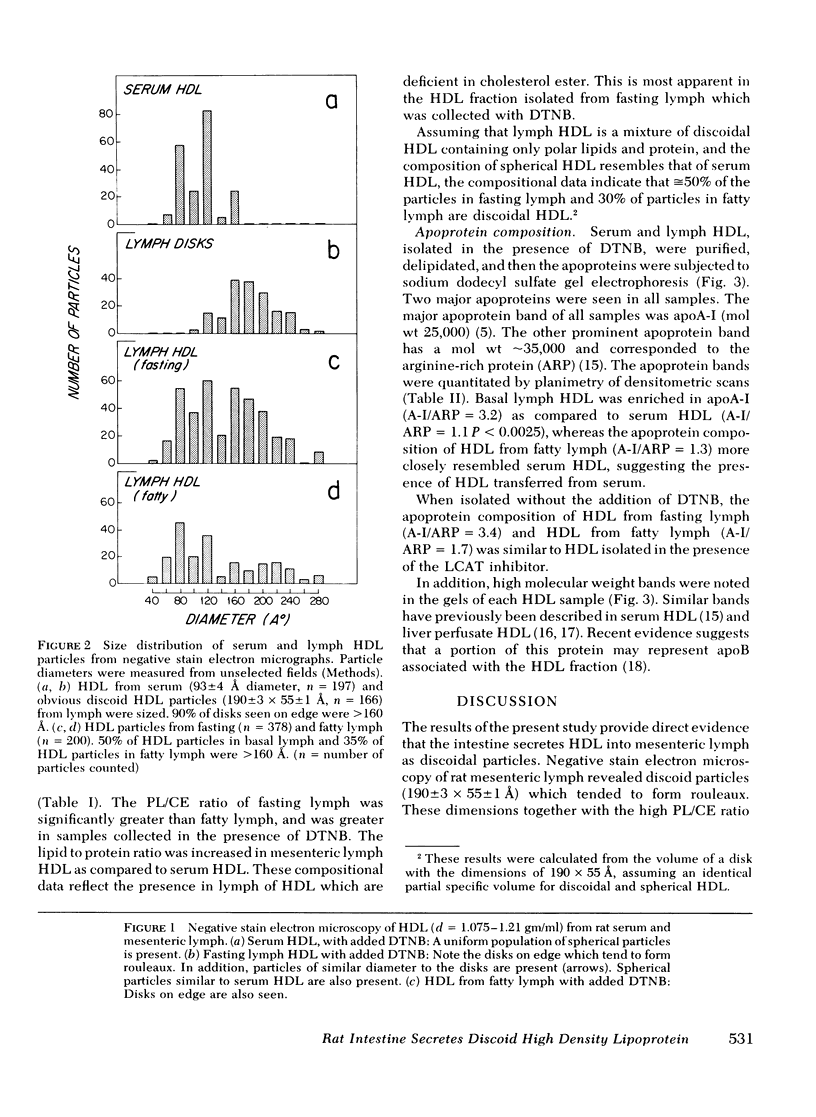
High density lipoprotein was isolated from pooled rat serum and mesenteric lymph of lymph fistula rats. In most experiments, 5,5′-dithionitrobenzoic acid, an inhibitor of the enzyme lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase, was added during the collection of lymph to prevent modification of the lipid composition of newly secreted lipoproteins. Negative staining electron microscopy of lymph high density lipoprotein revealed discoidal particles (190±3 × 55±1 Å) which tended to form rouleaux, smaller spherical particles were also present. Serum high density lipoprotein contained only spherical particles (diameter 93±4 Å). Lipid analysis showed that lymph high density lipoprotein was enriched in phospholipid and deficient in cholesterol esters when compared to serum high density lipoprotein. The phospholipid to cholesterol esters ratio was greatest in basal lymph high density lipoprotein when compared to fatty lymph and serum high density lipoprotein. From analysis of the lipid compositional data and direct particle measurement by electron microscopy, it could be determined that ≅50% of basal lymph high density lipoprotein and 30% of fatty lymph high density lipoprotein was discoid. Basal lymph high density lipoprotein was enriched in apoA-I and deficient in the arginine-rich peptide, and the apoprotein composition of fatty lymph high density lipoprotein more closely resembled serum. These observations demonstrate that intestinal lymph contains two types of high density lipoprotein particles, a discoid nascent particle deficient in cholesterol ester and rich in apoA-I, and spherical high density lipoprotein derived from plasma. A significant amount of lymph high density lipoprotein appears to be secreted by the intestine.
Full text
PDF

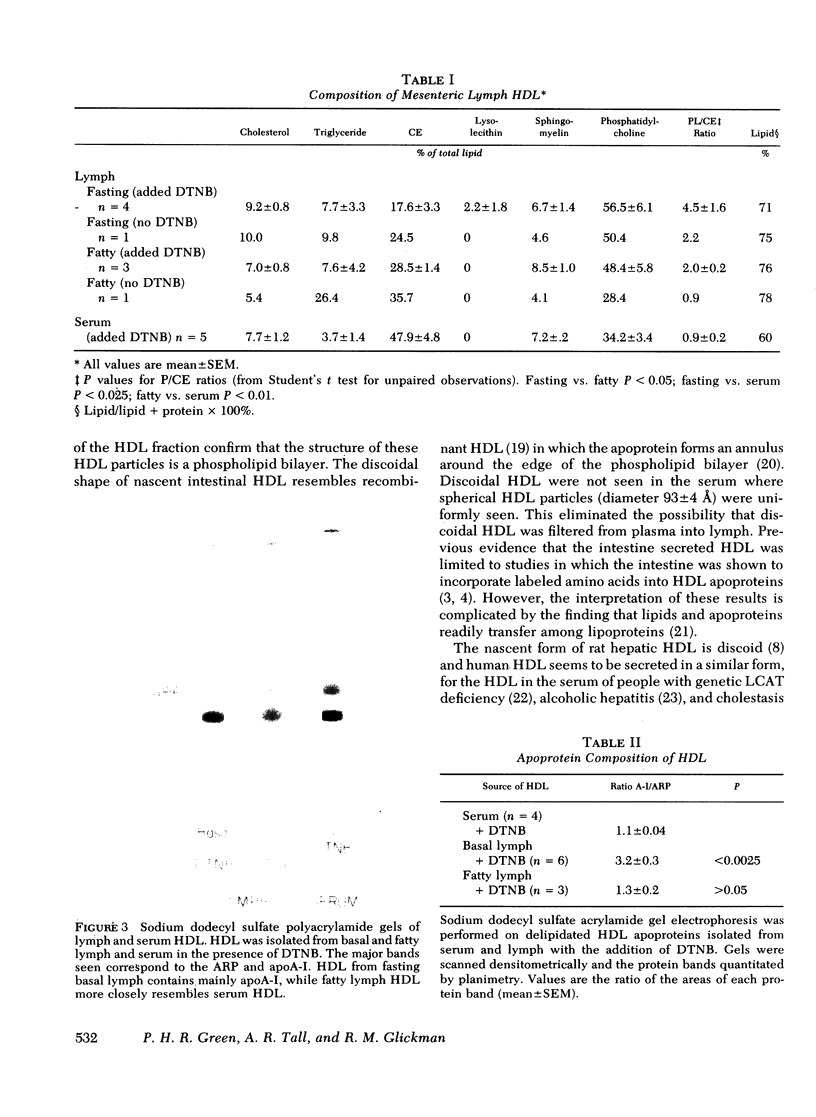


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. V., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Studies of the proteins in human plasma very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5687–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURTICE G. C., MORRIS B. The exchange of lipids between plasma and lymph of animals. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1955 Apr;40(2):138–148. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1955.sp001105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. B., Norum K. R. The lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase activity of rat intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing D. T. Photodensitometry in the thin-layer chromatographic analysis of neutral lipids. J Chromatogr. 1968 Nov 5;38(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(68)85011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Felker T. E., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Evidence that a separate particle containing B-apoprotein is present in high-density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. Metabolism. 1977 Sep;26(9):999–1004. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Felker T. E. Radioimmunoassay of apolipoprotein A-I of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 28;446(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Nichols A. V., Gong E. L., Levy R. I., Lux S. Electron microscopic study on reassembly of plasma high density apoprotein with various lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 5;248(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90026-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H. The intestine as a source of apolipoprotein A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Kirsch K. Lymph chylomicron formation during the inhibition of protein synthesis. Studies of chylomicron apoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2910–2920. doi: 10.1172/JCI107487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A. The plasma lecithins:cholesterol acyltransferase reaction. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):155–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L. Synthesis and secretion of plasma lipoproteins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1972;26(0):7–24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7547-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Williams M. C., Fielding C. J., Havel R. J. Discoidal bilayer structure of nascent high density lipoproteins from perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Sep;58(3):667–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI108513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. Physical chemistry of the lipids of human atherosclerotic lesions. Demonstration of a lesion intermediate between fatty streaks and advanced plaques. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):200–211. doi: 10.1172/JCI108450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Holcombe K. S. Alterations of the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following cholesterol feeding in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Apoproteins of the lipoproteins in a nonrecirculating perfusate of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel S. P., Rubinstein D. Secretion of apolipoproteins in very low density and high density lipoproteins by perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1974 Jul;15(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: origin, composition, and role in lipid transport in the fasting state. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2079–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI106174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roheim P. S., Gidez L. I., Eder H. A. Extrahepatic synthesis of lipoproteins of plasma and chyle: role of the intestine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):297–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI105343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabesin S. M., Hawkins H. L., Kuiken L., Ragland J. B. Abnormal plasma lipoproteins and lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 Mar;72(3):510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Reese H., Eder H. A. Polypeptide composition of rat high density lipoprotein: characterization by SDS-gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R., Small D. M., Deckelbaum R. J., Shipley G. G. Structure and thermodynamic properties of high density lipoprotein recombinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4701–4711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollin A., Jaques L. B. Plasma protein escape from the intestinal circulation to the lymphatics during fat absorption. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Apr;142(4):1114–1117. doi: 10.3181/00379727-142-37188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]