Abstract
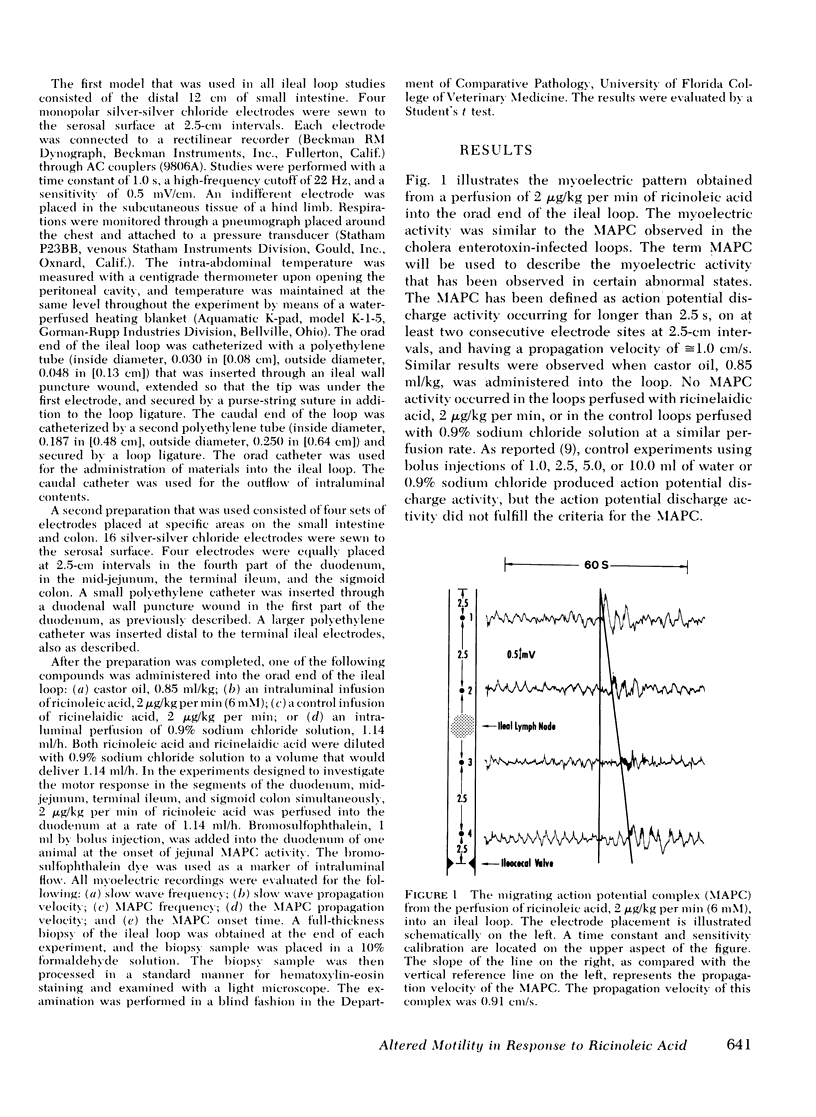
Using myoelectric recording techniques, we examined the myoelectric effects of castor oil; ricinoleic acid (cis isomer), the active ingredient of castor oil; and ricinelaidic acid (trans isomer) in the small intestine of New Zealand white rabbits. Ricinoleic acid, 2 microgram/kg per min (6mM), was perfused into a distal 12-cm ileal loop. An abnormal myoelectric pattern developed that was similar to the alteration in the electrical activity that has previously been reported for cholera enterotoxin. Castor oil, 0.85 ml/kg, had a similar effect. Ricinelaidic acid, 2 microgram/kg per min, induced no activity. A second preparation consisted of an intraluminal perfusion of ricinoleic acid, 2 microgram/kg per min, into the first section of the duodenum. The abnormal myoelectric pattern was observed in the jejunum and the ileum but not the duodenum. The mean onset time for the development of this altered myoelectric state for all experiments was 3.5 h. These studies suggest that an active motility component in addition to the secretory state exists throughout the small intestine that is exposed to castor oil or ricinoleic acid.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of colonic water and electrolyte absorption by fatty acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):744–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of ileal water absorption by intraluminal fatty acids. Influence of chain length, hydroxylation, and conjugation of fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):205–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Thomas P. J., Phillips S. F. Effects of oleic and ricinoleic acids on net jejunal water and electrolyte movement. Perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):374–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI107569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder H. J., Donowitz M. A new look at laxative action. Gastroenterology. 1975 Oct;69(4):1001–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright-Asare P., Binder H. J. Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology. 1973 Jan;64(1):81–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chignell C. F. The effect of phenolphthalein and other purgative drugs on rat intestinal (Na+ + K+) adenosine triphosphatase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Jul;17(7):1207–1212. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Freeman B. W. Circular muscle electromyogram in the cat colon: local effect of sodium ricinoleate. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):1011–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline W. S., Lorenzsonn V., Benz L., Bass P., Olsen W. A. The effects of sodium ricinoleate on small intestinal function and structure. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):380–390. doi: 10.1172/JCI108482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewe K., Hölker B. Einfluss eines diphenolischen Laxans (Bisacodyl) auf den Wasser- und Elektrolyttransport im menschlichen Colon. Klin Wochenschr. 1974 Sep 1;52(17):827–833. doi: 10.1007/BF01468863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., al-Awqati Q., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effect of cholera enterotoxin on ion transport across isolated ileal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):796–804. doi: 10.1172/JCI106874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Lewis J. C., Phillips S. F. Ricinoleic acid effects on rabbit intestine: an ultrastructural study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Sep;51(9):569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaginella T. S., Phillips S. F. Ricinoleic acid (castor oil) alters intestinal surface structure. A scanning electronmiscroscopic study. Mayo Clin Proc. 1976 Jan;51(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart S. L., McColl I. The effect of purgative drugs on the intestinal absorption of glucose. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1967 Jan;19(1):70–71. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1967.tb08004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias J. R., Carlson G. M., DiMarino A. J., Bertiger G., Morton H. E., Cohen S. Intestinal myoelectric activity in response to live Vibrio cholerae and cholera enterotoxin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):91–96. doi: 10.1172/JCI108464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F. Perfusion of the canine colon with unconjugated bile acids. Effect on water and electrolyte transport, morphology, and bile acid absorption. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jul;59(1):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nell G., Overhoff H., Forth W., Kulenkampff H., Specht W., Rummel W. Influx and efflux of sodium in jejunal and colonic segments of rats under the influence of oxyphenisatin. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1973;277(1):53–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00498784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Love A. H., Mitchell T. G., Neptune E. M., Jr Cathartics and the sodium pump. Nature. 1965 Jun 26;206(991):1367–1368. doi: 10.1038/2061367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J., Bass P. Effects of ricinoleic and oleic acids on the digestive contractile activity of the canine small and large bowel. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):371–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. J., Gaginella T. S., Olsen W. A., Bass P. Inhibitory actions of laxatives on motility and water and electrolyte transport in the gastrointestinal tract. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Feb;192(2):458–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



