Abstract
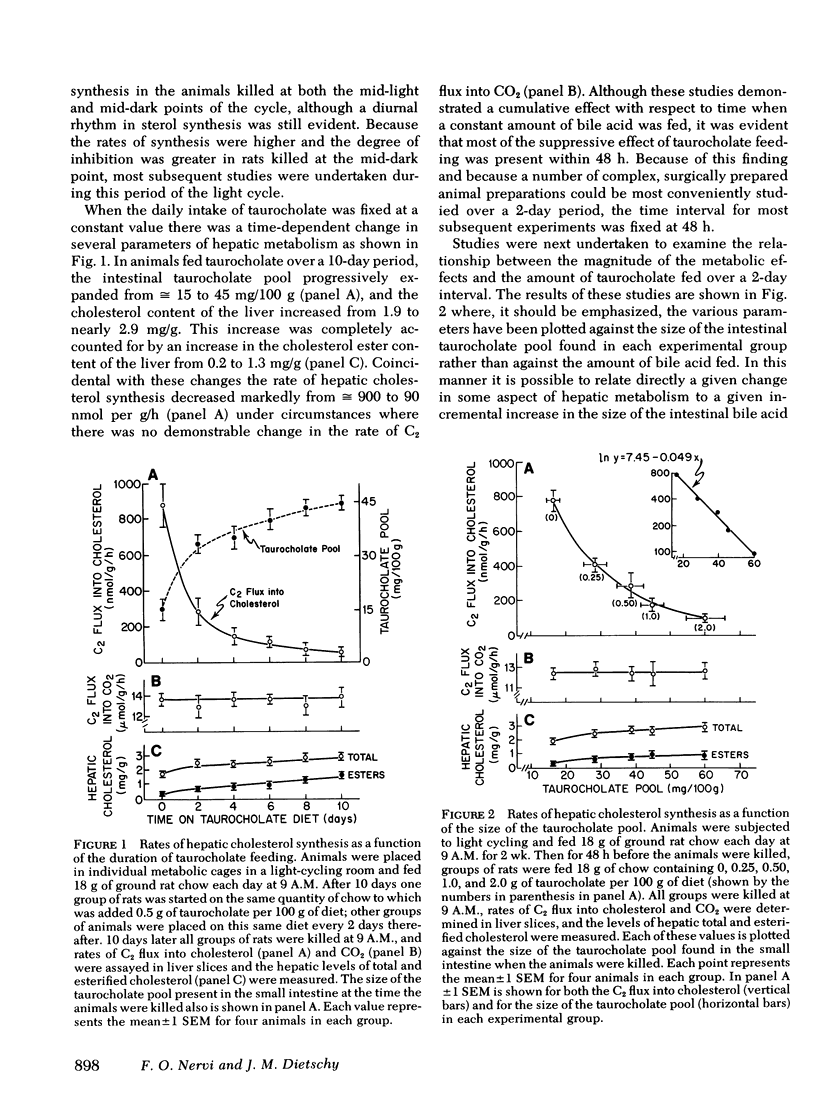
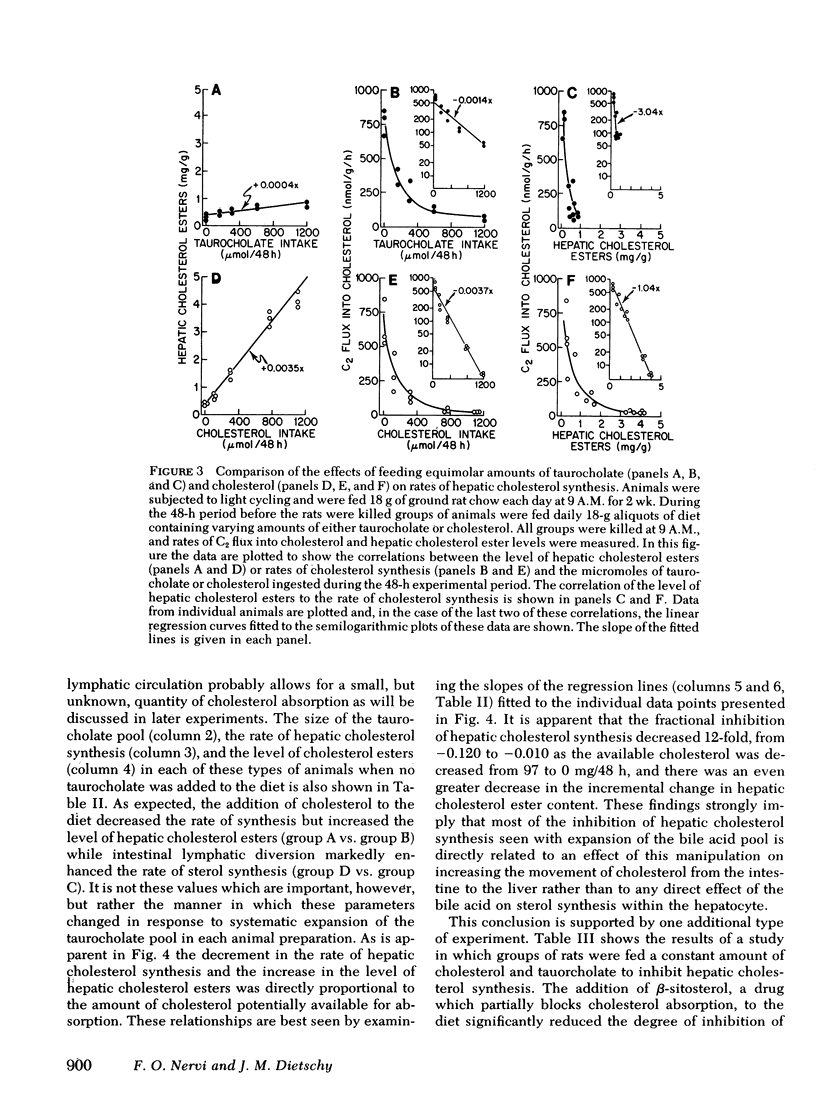
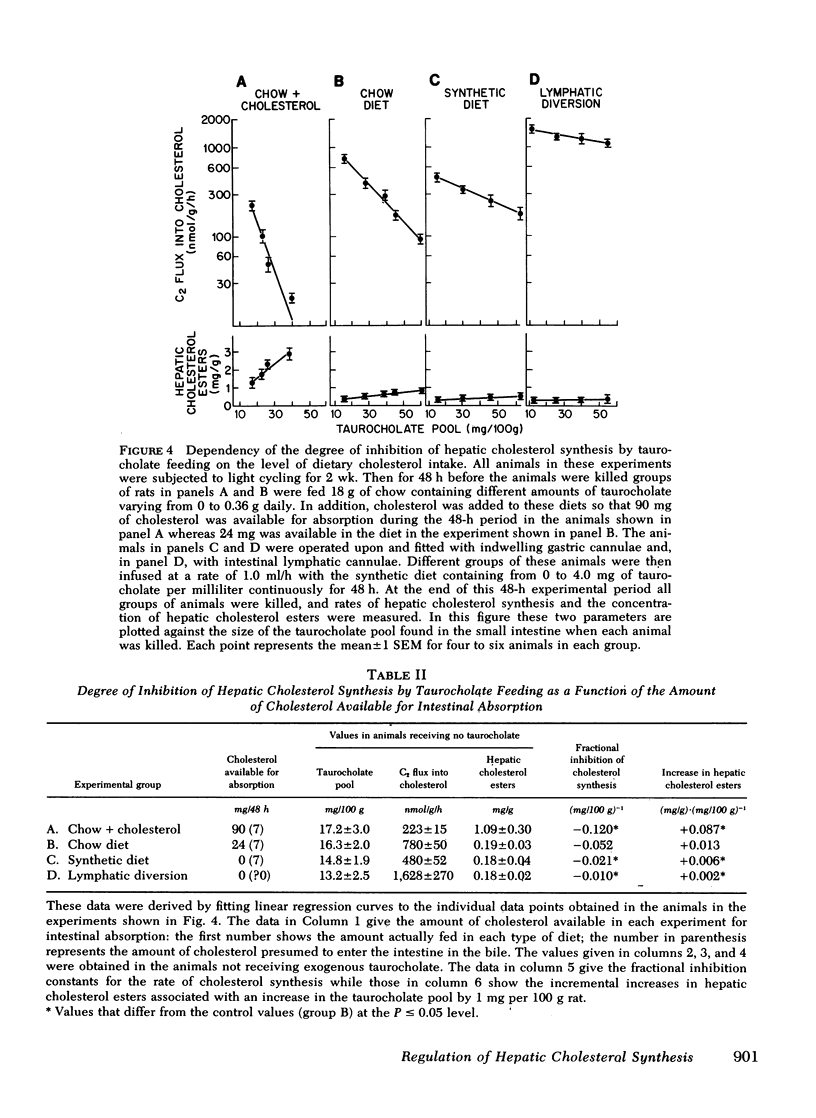
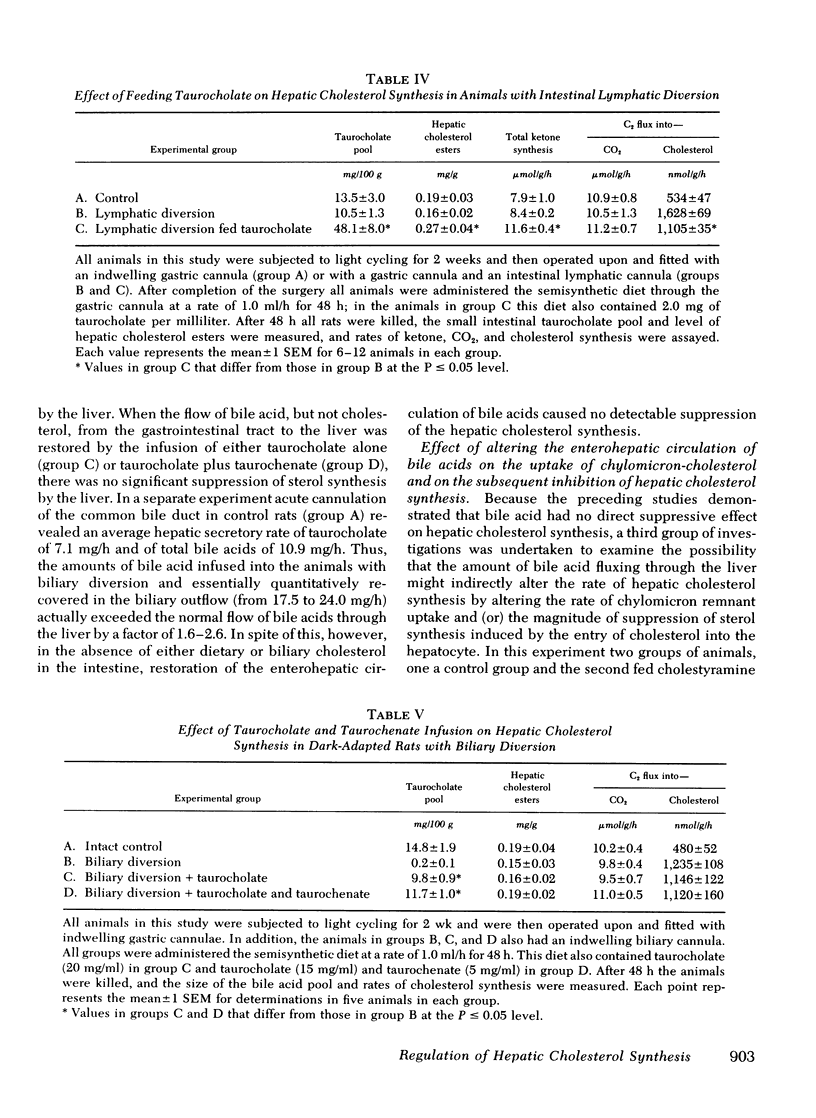
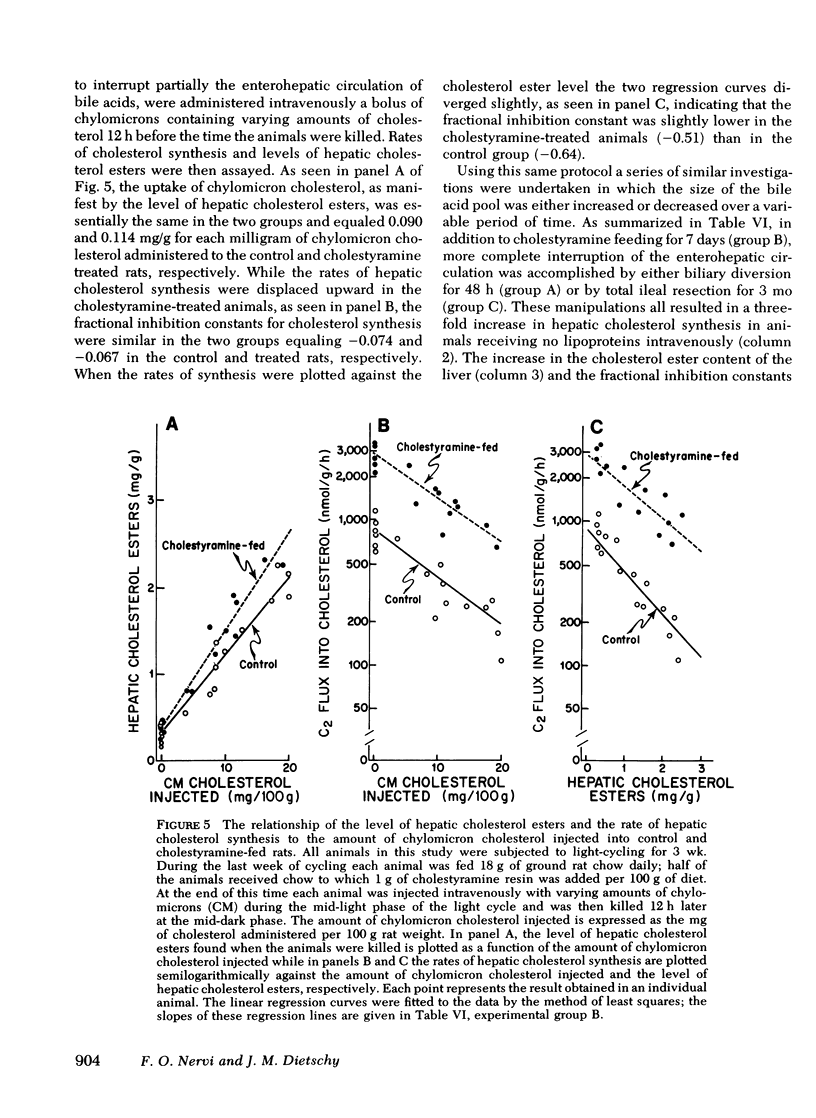
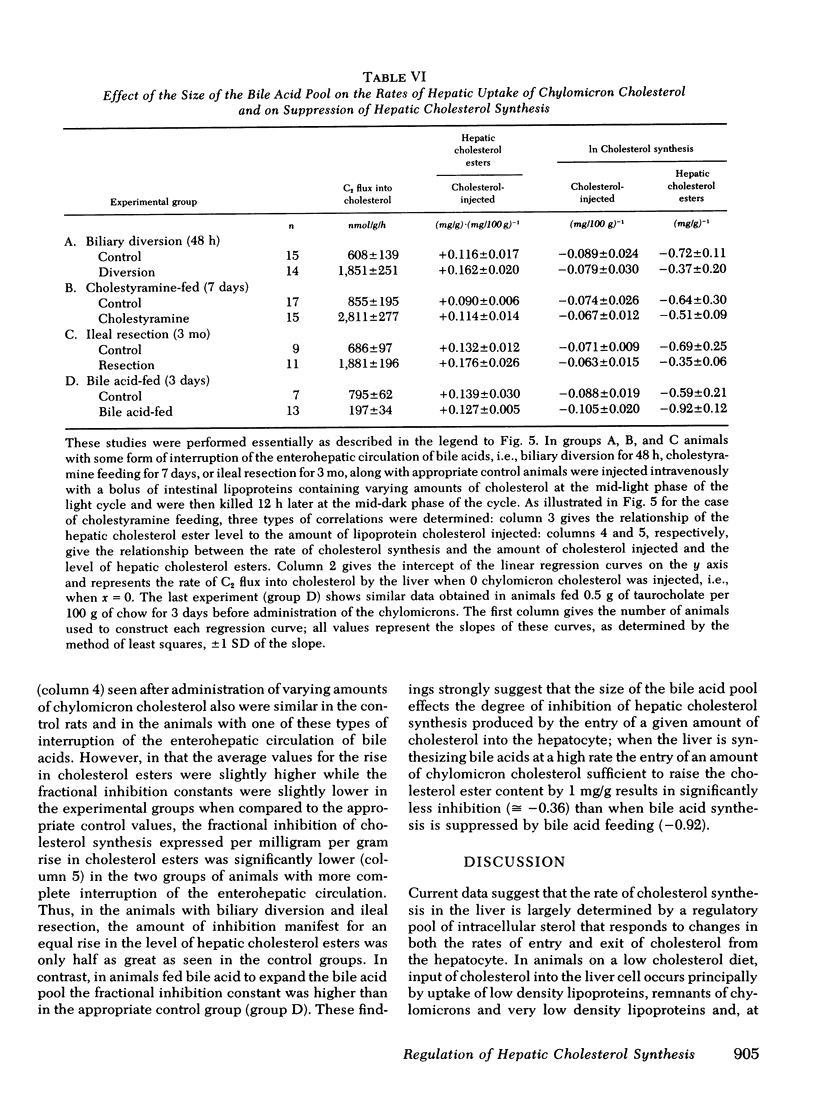
Hepatic cholesterol synthesis is controlled by both the size of the bile acid pool in the enterohepatic circulation and by the amount of cholesterol reaching the liver carried in chylomicron remnants. These studies were undertaken to examine how these two control mechanisms are interrelated. When the size of the pool was systematically varied, the logarithm of the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis varied in an inverse linear fashion with the size of the taurocholate pool between the limits of 0 and 60 mg of bile acid per 100 g of body weight. The slope of this relationship gave the fractional inhibition of cholesterol synthesis associated with expansion of the taurocholate pool and was critically dependent upon the amount of cholesterol available for absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Furthermore, the degree of inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in the liver seen with taurocholate feeding was reduced by partially blocking cholesterol absorption with beta-sitosterol even though the bile acid pool was still markedly expanded. In rats with diversion of the intestinal lymph from the blood, a five-fold expansion of the taurocholate pool resulted in only slight suppression of the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, and even this inhibition was shown to be attributable to small amounts of cholesterol absorbed through collateral lymphatic vessels and (or) to a fasting effect. Similarly, the infusion of either taurocholate or a combination of taurocholate and taurochenate into rats with no biliary or dietary cholesterol available for absorption caused no suppression of hepatic cholesterol synthesis. Finally, the effect of changes in the rate of bile acid snythesis on hepatic cholesterol synthesis was examined. The fractional inhibition of cholesterol synthesis found after administration of an amount of cholesterol sufficient to raise the hepatic cholesterol ester content by 1 mg/g equalled only --0.36 when bile acid snythesis was increased by biliary diversion but was --0.92 when bile acid synthesis was suppressed by bile acid feeding. It is concluded that (a) bile acids are not direct effectors of the rate of hepatic cholesterol synthesis, (b) most of the inhibitory activity seen with bile acid feeding is mediated through increased cholesterol absorption, and (c) bile acids do have an intrahepatic effect in that they regulate hepatic cholesterol synthesis indirectly by altering the flow of cellular cholesterol to bile acids.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of sterol synthesis in 15 tissues of rat. II. Role of rat and human high and low density plasma lipoproteins and of rat chylomicron remnants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3652–3659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of sterol synthesis in adrenal gland of the rat by both high and low density human plasma lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Oct 4;72(3):880–885. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen J. M., Nervi F. O., Dietschy J. M. Rate constants for the uptake of cholesterol from various intestinal and serum lipoprotein fractions by the liver of the rat in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 23;486(2):298–307. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):789–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity in human fibroblasts by lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2162–2166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Familial hypercholesterolemia: defective binding of lipoproteins to cultured fibroblasts associated with impaired regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):788–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrella M., Dietschy J. M. Comparison of the effects of cholic acid and chenic acid feeding on rates of cholesterol synthesis in the liver of the rat. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):318–326. doi: 10.1007/BF01072189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. I., Raicht R. F., Mosbach E. H. Sterol metabolism studies in the rat. Effects of primary bile acids (sodium taurochenodeoxycholate and sodium taurocholate) on sterol metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1977 Mar;18(2):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D. The regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1461–1470. doi: 10.1172/JCI108416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deckelbaum R. J., Lees R. S., Small D. M., Hedberg S. E., Grundy S. M. Failure of complete bile diversion and oral bile acid therapy in the treatment of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1977 Mar 3;296(9):465–470. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197703032960901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Gamel W. G. Cholesterol synthesis in the intestine of man: regional differences and control mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):872–880. doi: 10.1172/JCI106559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., McGarry J. D. Limitations of acetate as a substrate for measuring cholesterol synthesis in liver. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):52–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. Cholesterol synthesis by the gastrointestinal tract: localization and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44(8):1311–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI105237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. Effect of cholesterol feeding and fasting on sterol synthesis in seventeen tissues of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1967 Mar;8(2):97–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. The role of bile salts in controlling the rate of intestinal cholesterogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1968 Feb;47(2):286–300. doi: 10.1172/JCI105725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Wilson J. D. Cholesterol synthesis in the squirrel monkey: relative rates of synthesis in various tissues and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):166–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI105706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Wilson J. D. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism. I. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1128–1138. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECKLES N. E., TAYLOR C. B., CAMPBELL D. J., GOULD R. G. The origin of plasma cholesterol and the rates of equilibration of liver, plasma, and erythrocyte cholesterol. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Sep;46(3):359–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECONOMOU S. G., TEWS B. J., TAYLOR C. B., COX G. E. Studies on lipid metabolism in dogs with altered biliary physiology. Surg Forum. 1957;8:218–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN M., BYERS S. O., MICHAELIS F. Production and excretion of cholesterol in mammals. Iv. Role of liver in restoration of plasma cholesterol after experimentally induced hypocholesteremia. Am J Physiol. 1951 Mar;164(3):789–791. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.3.789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faergeman O., Havel R. J. Metabolism of cholesteryl esters of rat very low density lipoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1210–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI108039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Chylomicron protein content and the rate of lipoprotein lipase activity. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jul;17(4):419–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G. Lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Am J Med. 1951 Aug;11(2):209–227. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G., TAYLOR C. B., HAGERMAN J. S., WARNER I., CAMPBELL D. J. Cholesterol metabolism. I. Effect of dietary cholesterol on the synthesis of cholesterol in dog tissue in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1953 Apr;201(2):519–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh E. H., Heimberg M. Effects of free fatty acids on activity of hepatic microsomal 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase and on secretion of triglyceride and cholesterol by liver. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2822–2826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh E. H., Heimberg M. Stimulation of hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis by oleic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 16;55(2):382–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. G., Swyryd E. A. Sites of control of hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis. J Lipid Res. 1966 Sep;7(5):698–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr, Salen G. Interruption of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in man: comparative effects of cholestyramine and ileal exclusion on cholesterol metabolism. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Jul;78(1):94–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwynne J. T., Mahaffee D., Brewer H. B., Jr, Ney R. L. Adrenal cholesterol uptake from plasma lipoproteins: regulation by corticotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4329–4333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamprecht B., Roscher R., Waltinger G., Nüssler C. Influence of bile acids on the activity of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. 2. Effect of cholic acid in lymph fistula rats. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan 1;18(1):15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Apter J. T. Micellar theory of biliary cholesterol excretion. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):61–67. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. M., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of formation of triglyceride-rich remnant particles from very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2288–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Faust J. R., Bilheimer D. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of cholesterol synthesis by low density lipoprotein in isolated human lymphocytes. Comparison of cells from normal subjects and patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and abetalipoproteinemia. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1531–1549. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F., Thistle J. L. Effect of bile acid feeding on cholesterol metabolism in gallstone patients. Mayo Clin Proc. 1974 Apr;49(4):236–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDSEY C. A., Jr, WILSON J. D. EVIDENCE FOR A CONTRIBUTION BY THE INTESTINAL WALL TO THE SERUM CHOLESTEROL OF THE RAT. J Lipid Res. 1965 Apr;6:173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Hofmann A. F., Northfield T. C., Thistle J. L. Effect of primary bile acid ingestion on bile acid metabolism and biliary lipid secretion in gallstone patients. Gastroenterology. 1975 Dec;69(6):1301–1314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liersch M. E., Barth C. A., Hackenschmidt H. J., Ullmann H. L., Decker K. F. Influence of bile salts on cholesterol synthesis in the isolated perfused rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jan 15;32(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutafis C. D., Myant N. B., Tabaqchali S. The metabolism of cholesterol after resection or by-pass of the lower small intestine. Clin Sci. 1968 Dec;35(3):537–545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervi F. O., Dietschy J. M. Ability of six different lipoprotein fractions to regulate the rate of hepatic cholesterogenesis in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8704–8711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nervi F. O., Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. The kinetic characteristics of inhibition of hepatic cholesterogenesis by lipoproteins of intestinal origin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4145–4151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIPERSTEIN M. D., CHAIKOFF I. L., REINHARDT W. O. C14-Cholesterol. V. Obligatory function of bile in intestinal absorption of cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):111–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Hauser S., Lapar V., Mosbach E. H. Regulatory effects of sterols and bile acids on hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase and cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1973 Sep;14(5):573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shefer S., Salen G., Fedorowski T., Dyrszka H., Mosbach E. H. Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis by chenodeoxycholic acid in the rhesus monkey. J Steroid Biochem. 1975 Nov-Dec;6(11-12):1563–1564. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(75)90215-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thistle J. L., Hofmann A. F. Efficacy and specificity of chenodeoxycholic acid therapy for dissolving gallstones. N Engl J Med. 1973 Sep 27;289(13):655–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197309272891303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. H., Lancaster M. C., Hofmann A. F., Wease D. F., Baggenstoss A. H. Influence of primary bile acid feeding on cholesterol metabolism and hepatic function in the rhesus monkey. Mayo Clin Proc. 1975 Mar;50(3):134–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. Adaptive responses in hepatic and intestinal cholesterogenesis following ileal resection in the rat. Eur J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;4(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1974.tb00369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. Failure of bile acids to control hepatic cholesterogenesis: evidence for endogenous cholesterol feedback. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2398–2408. doi: 10.1172/JCI106206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis H. J., Dietschy J. M. The interaction of various control mechanisms in determining the rate of hepatic cholesterogenesis in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 25;398(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard H., Dietschy J. M. The mechanism whereby bile acid micelles increase the rate of fatty acid and cholesterol uptake into the intestinal mucosal cell. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):97–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI108465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., King K. K. Biliary excretion of lecithin and cholesterol in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1337–1350. doi: 10.1172/JCI106930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. Biosynthetic origin of serum cholesterol in the squirrel monkey: evidence for a contribution by the intestinal wall. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):175–187. doi: 10.1172/JCI105707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Lindsey C. A., Dietschy J. M. Influence of dietary cholesterol on cholesterol metabolism. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Nov 21;149(2):808–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb53837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Reinke R. T. Transfer of locally synthesized cholesterol from intestinal wall to intestinal lymph. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):85–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. The quantification of cholesterol excretion and degradation in the isotopic steady state in the rat: the influence of dietary cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D. The relation between cholesterol absorption and cholesterol synthesis in the baboon. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1450–1458. doi: 10.1172/JCI106941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



