Abstract
Gonoccocal pili facilitate attachment of virulent Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human cells. To characterize this attachment function, purified gonococcal pili isolated from four strains possessing antigenically distinct pili were radiolabeled with 125I and used to measure the attachment of pili to various human cells in vitro. Human buccal and cervical-vaginal mucosal epithealial cells, fallopian tube mucosa, and sperm bound pili in greater numbers per micrometer2 of surface area (1--10) than fetal tonsil fibroblasts, HeLa M cells, erythrocytes, or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. This cell specificity of attachment suggests a greater density of membrane pili binding sites on cells similar or identical to cells from natural sites of infection. The pili binding sites were quantitated as 1 X 10(4) per cervical-vaginal squamous cell. Pili of all antigenic types attached equally to a given cell type, implying that the attachment moiety of each pilus was similar. Attachement of gonoccocal pili to human cells occurred quickly with saturation of presumed receptor sites within 20--60 min. Attachment was temperature dependent (37 degrees greater than 20 degrees greater than 4 degrees C), and pH dependent (3.5 less than 4.5 less than 5.5 less than 7.5). Attachment was inhibited by antibody to pili (homologous pili Ab greater than heterologous Ab). The extent of possible protection against gonococcal infection due to inhibition of pili-mediated attachment might prove limited as a result of the considerable antigenic heterogeneity among pili and the observation that blockage of pili attachment is maximal only with antibody to pili of the infecting strain.
Full text
PDF


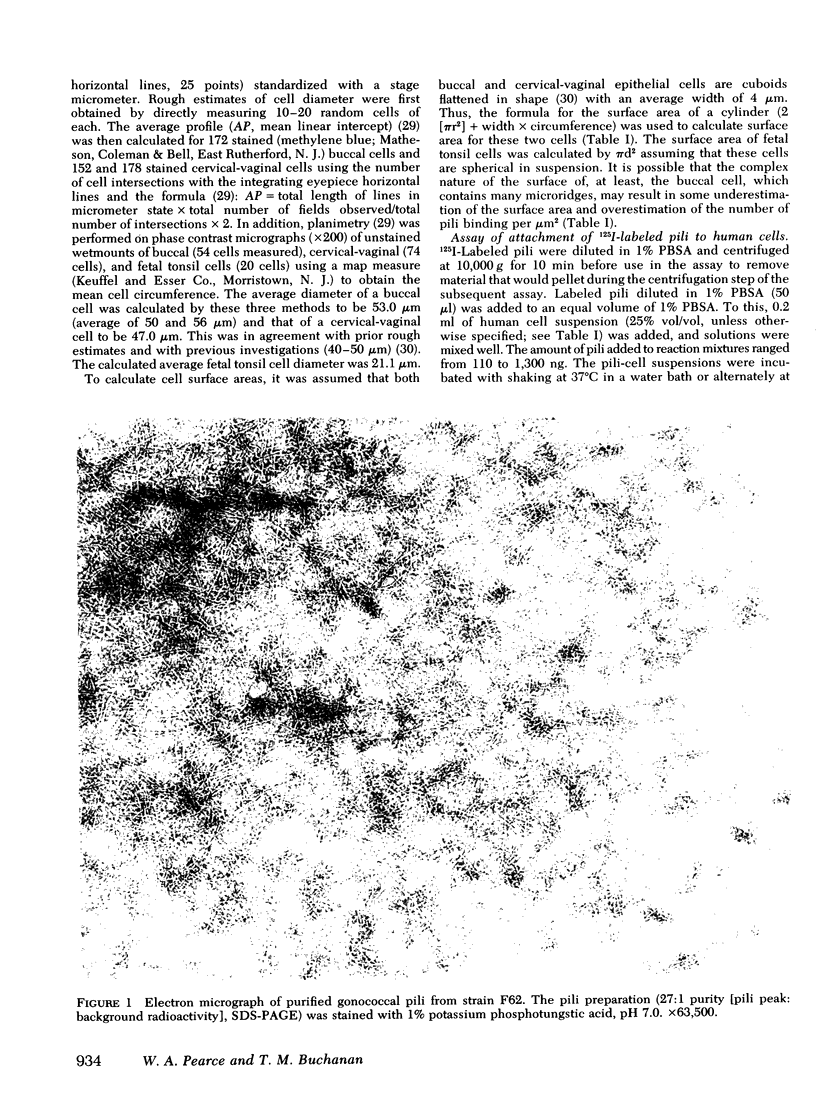

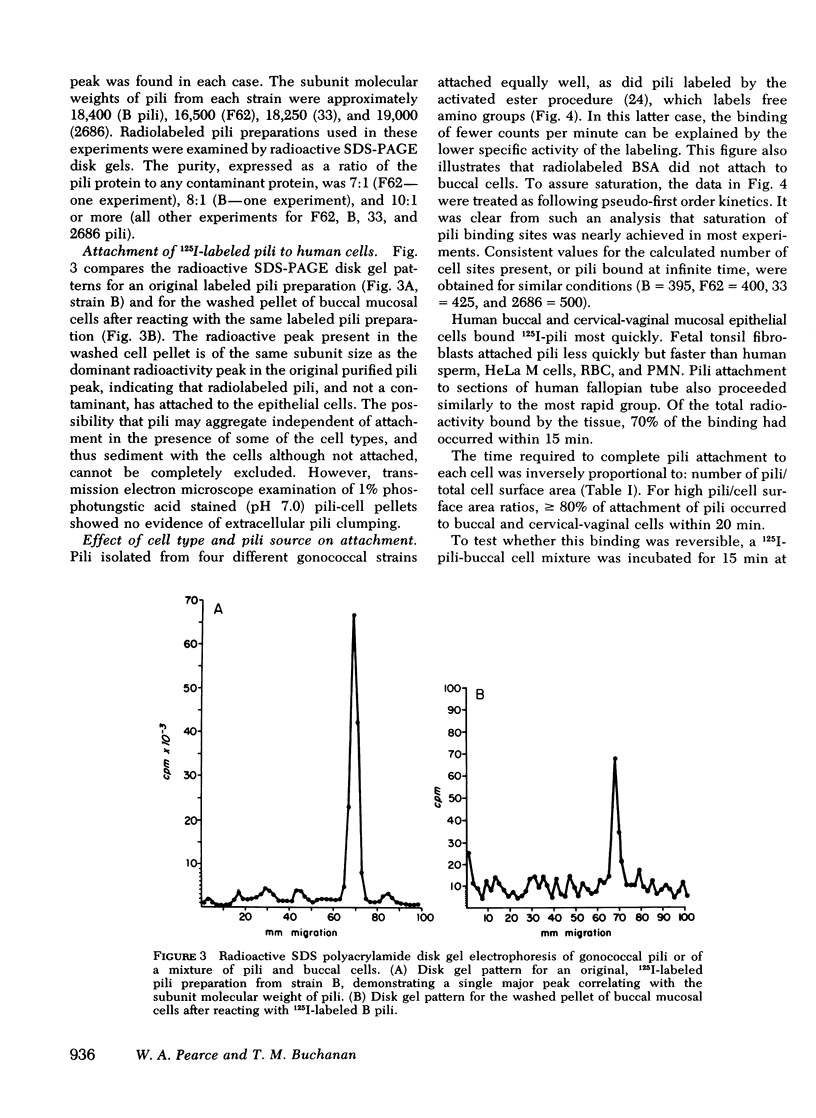



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boatman E., Cartwright F., Kenny G. Morphology, morphometry and electron microscopy of HeLa cells infected with bovine Mycoplasma. Cell Tissue Res. 1976 Jul 20;170(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00220107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M. Antigenic heterogeneity of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Pearce W. A. Pili as a mediator of the attachment of gonococci to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1483–1489. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1483-1489.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan T. M., Swanson J., Holmes K. K., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Quantitative determination of antibody to gonococcal pili. Changes in antibody levels with gonococcal infection. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2896–2909. doi: 10.1172/JCI107486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canham P. B., Burton A. C. Distribution of size and shape in populations of normal human red cells. Circ Res. 1968 Mar;22(3):405–422. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K., Wiseman G. M. A new colonial type of N. gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1975 Aug;51(4):251–256. doi: 10.1136/sti.51.4.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor of liver and fat cell membranes. Fed Proc. 1973 Aug;32(8):1838–1846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor isolated from liver and fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):1980–1991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Kretser D. M., Catt K. J., Paulsen C. A. Studies on the in vitro testicular binding of iodinated luteinizing hormone in rats. Endocrinology. 1971 Feb;88(2):332–337. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufau M. L., Charreau E. H., Catt K. J. Characteristics of a soluble gonadotropin receptor from the rat testis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):6973–6982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Cooney M. K., Hall C. E. The Seattle virus watch. V. Epidemiologic observations of rhinovirus infections, 1965-1969, in families with young children. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Feb;101(2):122–143. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frye L. D., Edidin M. The rapid intermixing of cell surface antigens after formation of mouse-human heterokaryons. J Cell Sci. 1970 Sep;7(2):319–335. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Properties of the luteinizing hormone receptor of isolated bovine corpus luteum plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5042–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Miller R. G. Volume analysis of human peripheral blood leukocytes. Ser Haematol. 1972;5(2):142–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James-Holmquest A. N., Swanson J., Buchanan T. M., Wende R. D., Williams R. P. Differential attachment by piliated and nonpiliated Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human sperm. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):897–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.897-902.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James A. N., Knox J. M., Williams R. P. Attachment of gonococci to sperm. Influence of physical and chemical factors. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Apr;52(2):128–135. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Smith R. M. Ultrastructural localization of insulin receptors on adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones G. W., Rutter J. M. Role of the K88 antigen in the pathogenesis of neonatal diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli in piglets. Infect Immun. 1972 Dec;6(6):918–927. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.6.918-927.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koransky J. R., Scales R. W., Kraus S. J. Bacterial hemagglutination by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):495–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.495-498.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesniak M. A., Gorden P., Roth J., Gavin J. R., 3rd Binding of 125I-human growth hormone to specific receptors in human cultured lymphocytes. Characterization of the interaction and a sensitive radioreceptor assay. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1661–1667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Korant B. D. Early interaction of rhinoviruses with host cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.29-40.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley A. R., Jr Autoradiographic analysis of gonadotropin binding to rat ovarian tissue sections. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1973;36(0):365–378. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3237-4_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moghissi K. S., Syner F. N., Evans T. N. A composite picture of the menstrual cycle. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1972 Oct 1;114(3):405–418. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(72)90617-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh P. A., Westtöm L. Adherence of bacterial to vaginal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):661–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.661-666.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Short J. A., Hughes M., Miler J. J., Syrett C., Turner W. H., Harris J. R., MacLennan I. P. Studies on the mechanism of pathogenicity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Med Microbiol. 1977 Aug;10(3):347–365. doi: 10.1099/00222615-10-3-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Turner W. H. Immunological heterogeneity of pili of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patten S. F., Jr Diagnostic cytology of the uterine cervix. Monogr Clin Cytol. 1969;3:1–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipson L., Lonberg-Holm K., Pettersson U. Virus-receptor interaction in an adenovirus system. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1064–1075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1064-1075.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punsalang A. P., Jr, Sawyer W. D. Role of pili in the virulence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1973 Aug;8(2):255–263. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.2.255-263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Kraus S. J., Gotschlich E. C. Studies on gonococcus infection. I. Pili and zones of adhesion: their relation to gonococcal growth patterns. J Exp Med. 1971 Oct 1;134(4):886–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.4.886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. IV. Pili: their role in attachment of gonococci to tissue culture cells. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):571–589. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebbutt G. M., Veale D. R., Hutchison J. G., Smith H. The adherence of pilate and non-pilate strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to human and guinea-pig epithelial tissues. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Aug;9(3):263–273. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-3-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Inhibition of adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human genital secretions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Specificity of inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):593–595. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.593-595.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE L. A., KELLOGG D. S., Jr NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE IDENTIFICATION IN DIRECT SMEARS BY A FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY-COUNTERSTAIN METHOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:171–174. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.171-174.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitkins S. A. Fimbrial haemagglutination by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Aug;50(4):272–278. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.4.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Watt P. J., Robertson J. N. The human fallopian tube: a laboratory model for gonococcal infection. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jun;129(6):650–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.6.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]