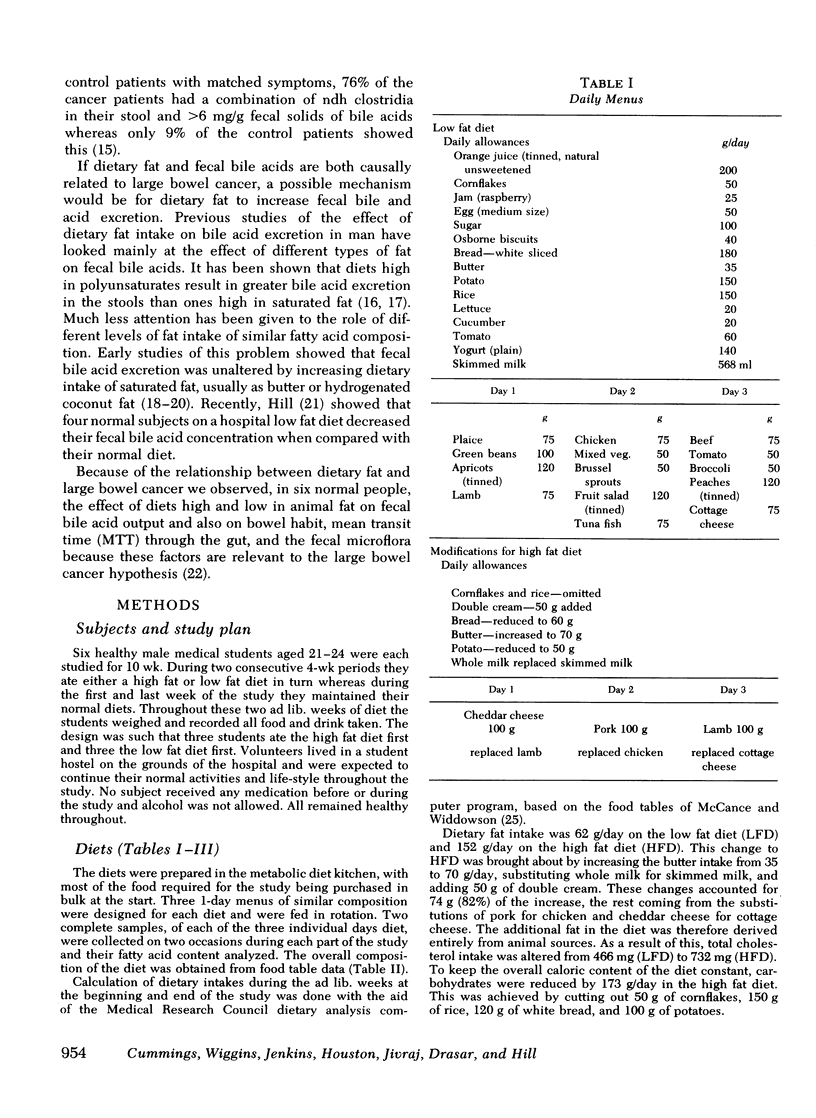
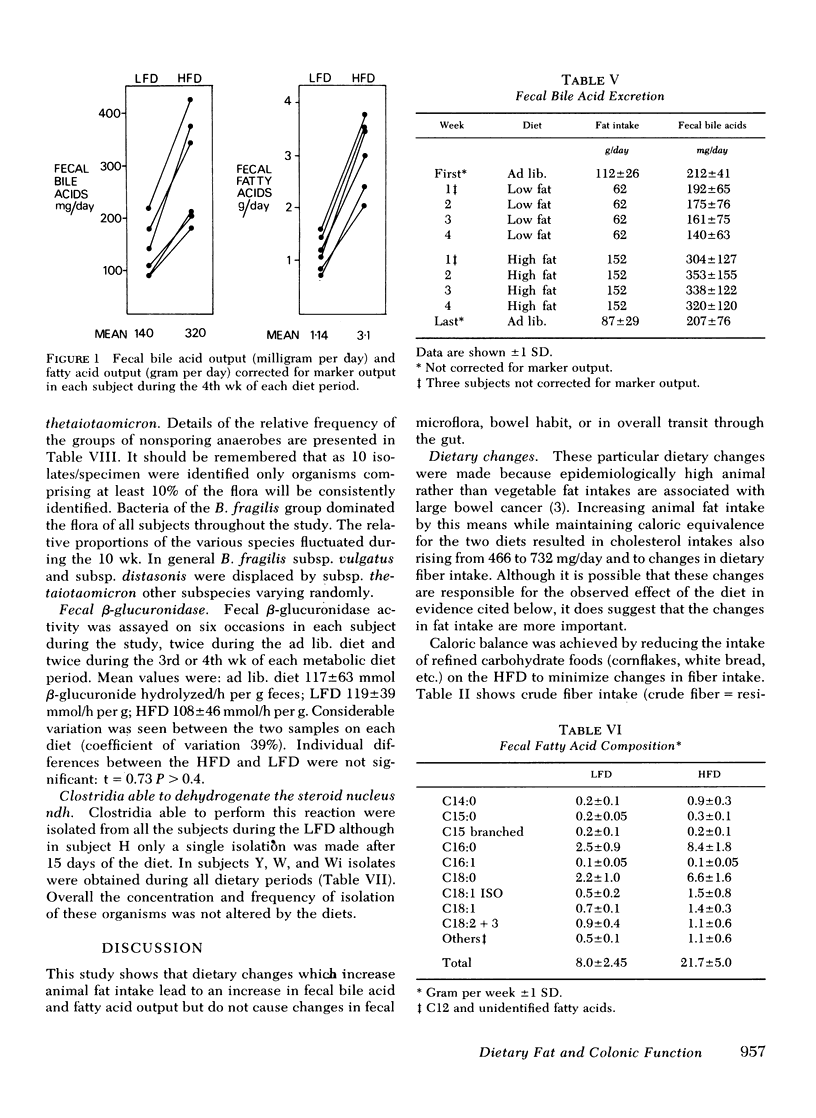
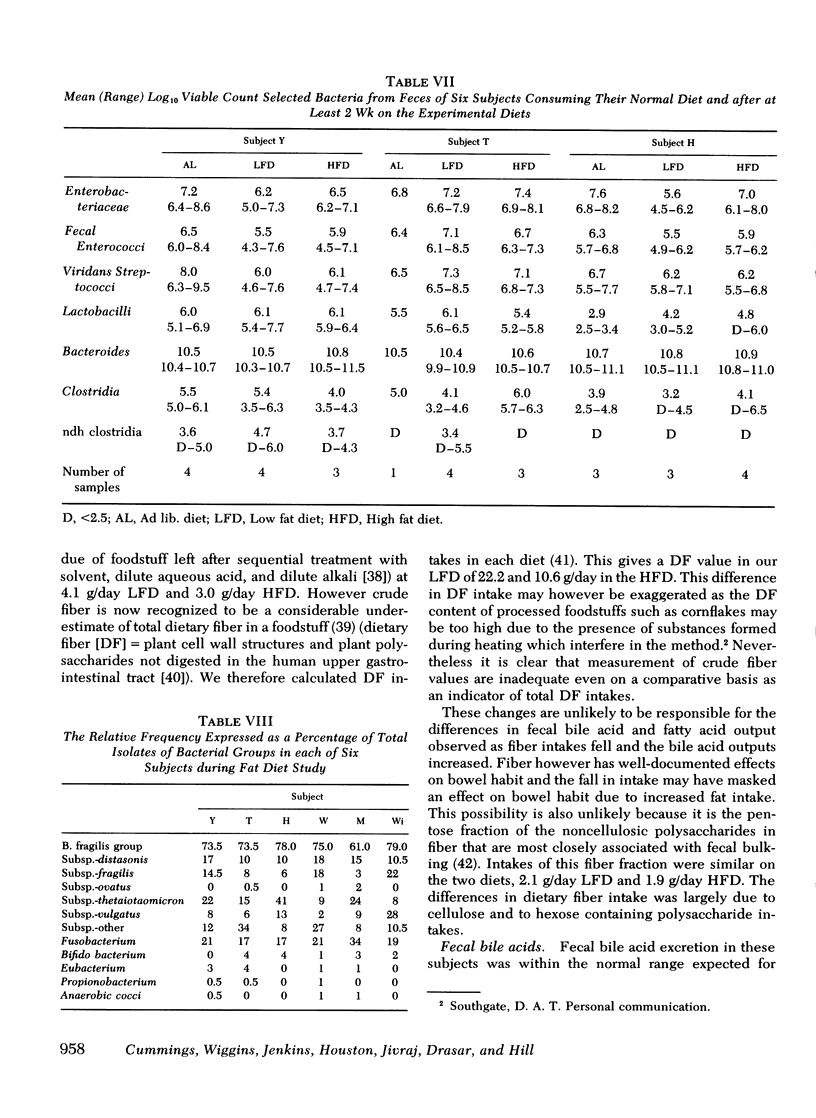
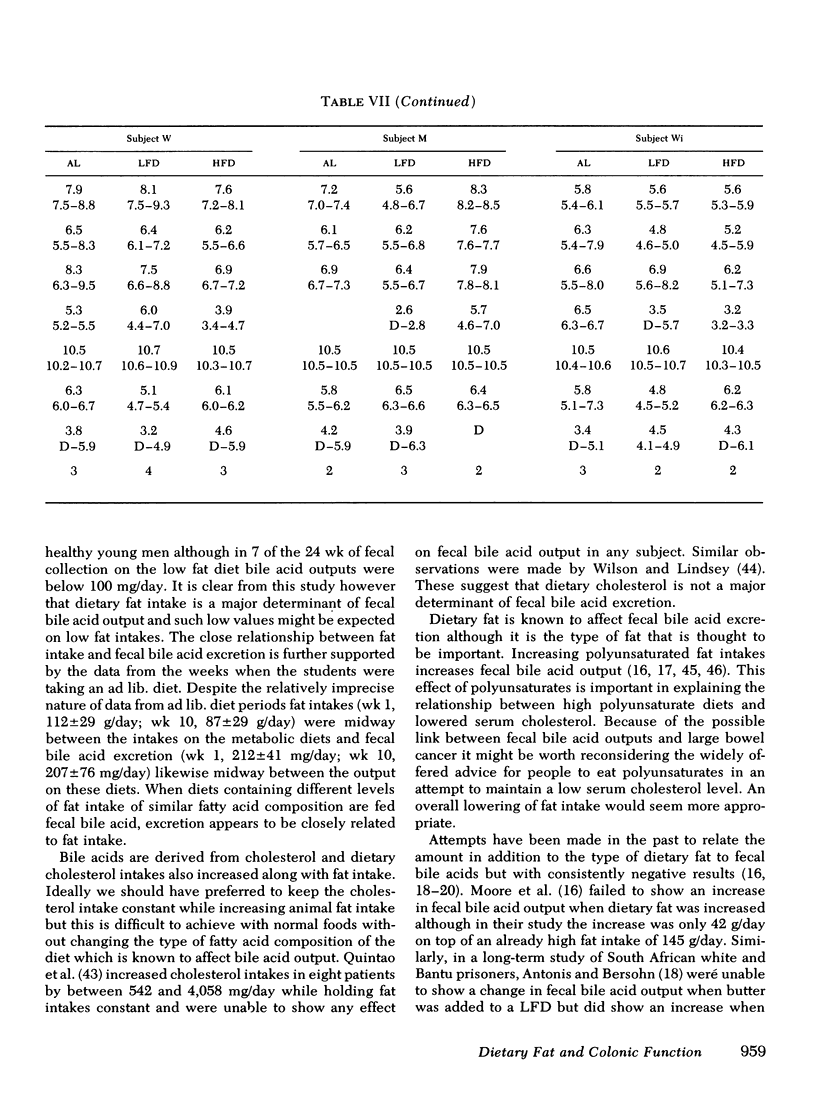
Abstract
Epidemiological observations and animal experiments suggest that large bowel cancer is related to serveral factors. Among them, high dietary intakes of animal fat, the presence in the colon of relatively high levels of bile acids, specific patterns of intestinal microflora, slow transit through the gut, and low stool weights. Under metabolic conditions we have observed the effect on these variables of dietes containing 62 or 152 g/day of fat mainly of animal origin in six healthy young men over 4-wk periods. No change attributable to the diet was observed in the subjects' bowel habit, fecal weight, mean transit time through the gut, or in the excretion of dry matter. Total fecal bile acid excretion was significantly higher on the high fat diet (320 +/- 120 mg/day) than on the low fat diet (139.7) +/- 63 mg/day) t test = 7.78 P less than 0.001 as also was the total fecal fatty acid excretion, 3.1+/-0.71 and 1.14+/-0.35 g/day, respectively t test = 11.4 P less than 0.001). The fecal microflora including the nuclear dehydrogenating clostridia were unaltered by the dietary changes as was fecal beta-glucuronidase activity. Dietary changes which increase animal fat intake clearly influence fecal bile acid excretion in a way that would favor the development of large bowel cancer if current theories prove to be true. Dietary fat however has no effect on overall colonic function so other components of the diet must be responsible for the observed associations of bowel cancer with slow transit and reduced fecal bulk.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANTONIS A., BERSOHN I. The influence of diet on fecal lipids in South African white and Bantu prisoners. Am J Clin Nutr. 1962 Aug;11:142–155. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/11.2.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of colonic water and electrolyte absorption by fatty acids in man. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):744–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammon H. V., Phillips S. F. Inhibition of ileal water absorption by intraluminal fatty acids. Influence of chain length, hydroxylation, and conjugation of fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):205–210. doi: 10.1172/JCI107539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arank A., Syed S. A., Kenney E. B., Freter R. Isolation of anaerobic bacteria from human gingiva and mouse cecum by means of a simplified glove box procedure. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):568–576. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.568-576.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong B., Doll R. Environmental factors and cancer incidence and mortality in different countries, with special reference to dietary practices. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):617–631. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avigan J., Steinberg D. Sterol and bile acid excretion in man and the effects of dietary fat. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1845–1856. doi: 10.1172/JCI105292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P. Epidemiology of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1971 Jul;28(1):3–13. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197107)28:1<3::aid-cncr2820280104>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt D. P., Walker A. R., Painter N. S. Effect of dietary fibre on stools and the transit-times, and its role in the causation of disease. Lancet. 1972 Dec 30;2(7792):1408–1412. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92974-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor W. E., Witiak D. T., Stone D. B., Armstrong M. L. Cholesterol balance and fecal neutral steroid and bile acid excretion in normal men fed dietary fats of different fatty acid composition. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1363–1375. doi: 10.1172/JCI106102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S., Drasar B. S., Hill M. J., Maclennan R., Magnin D., Peach S., Teoh-chan C. H. Faecal steroids and bacteria and large bowel cancer in Hong Kong by socio-economic groups. Br J Cancer. 1976 Aug;34(2):191–198. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther J. S. Transport and storage of faeces for bacteriological examination. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;34(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Hill M. J., Jenkins D. J., Pearson J. R., Wiggins H. S. Changes in fecal composition and colonic function due to cereal fiber. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Dec;29(12):1468–1473. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.12.1468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Jenkins D. J., Wiggins H. S. Measurement of the mean transit time of dietary residue through the human gut. Gut. 1976 Mar;17(3):210–218. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.3.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. H., Wiggins H. S. Transit through the gut measured by analysis of a single stool. Gut. 1976 Mar;17(3):219–223. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S. Cultivation of anaerobic intestinal bacteria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):417–427. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Goddard P., Heaton S., Peach S., West B. Clostridia isolated from faeces. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Feb;9(1):63–71. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Irving D. Environmental factors and cancer of the colon and breast. Br J Cancer. 1973 Feb;27(2):167–172. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1973.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Jenkins D. J. Bacteria, diet, and large bowel cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Dec;29(12):1410–1416. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.12.1410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Jenkins D. J., Cummings J. H. The influence of a diet rich in wheat fibre on the human faecal flora. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Nov;9(4):423–431. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-4-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Renwick A. G., Williams R. T. The role of the gut flora in the metabolism of cyclamate. Biochem J. 1972 Oct;129(4):881–890. doi: 10.1042/bj1290881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard E., Janssen G. Gas-liquid chromatographic determination of human fecal bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1968 Mar;9(2):226–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L. Effect of diet on human fecal flora: comparison of Japanese and American diets. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1456–1469. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Flora D. J., Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L. Fecal bacteriology of colonic polyp patients and control patients. Cancer Res. 1975 Nov;35(11 Pt 2):3407–3417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON H., LEWIS B., EALES L., BROCK J. F. Dietary fat and cholesterol metabolism; faecal elimination of bile acids and other lipids. Lancet. 1957 Dec 28;273(7009):1299–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91636-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard P., Fernandez F., West B., Hill M. J., Barnes P. The nuclear dehydrogenation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Aug;8(3):429–435. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-3-429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor O., Toman R., Prusová F. Gastrointestinal cancer and nutrition. Gut. 1969 Dec;10(12):1031–1034. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.12.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUST H. L., BEVERIDGE J. M. Effect of varying type and quantity of dietary fat on the fecal excretion of bile acids in humans subsisting on formula diets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Dec;78(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90361-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S., Hawksworth G., Aries V., Crowther J. S., Williams R. E. Bacteria and aetiology of cancer of large bowel. Lancet. 1971 Jan 16;1(7690):95–100. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90837-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J., Drasar B. S., Williams R. E., Meade T. W., Cox A. G., Simpson J. E., Morson B. C. Faecal bile-acids and clostridia in patients with cancer of the large bowel. Lancet. 1975 Mar 8;1(7906):535–539. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91556-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J. The effect of some factors on the faecal concentration of acid steroids, neutral steroids and urobilins. J Pathol. 1971 Aug;104(4):239–245. doi: 10.1002/path.1711040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill M. J. The etiology of colon cancer. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1975 Oct;4(1):31–82. doi: 10.1080/10408447509163834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Poley J. R. Role of bile acid malabsorption in pathogenesis of diarrhea and steatorrhea in patients with ileal resection. I. Response to cholestyramine or replacement of dietary long chain triglyceride by medium chain triglyceride. Gastroenterology. 1972 May;62(5):918–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Boulding E. T. Degradation of blood group antigens in human colon ecosystems. I. In vitro production of ABH blood group-degrading enzymes by enteric bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):63–73. doi: 10.1172/JCI108270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVER A., GORDON R. S., Jr Procedure for quantitative analysis of faces with special reference to facal fatty acids. J Lab Clin Med. 1962 May;59:878–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasper H. Faecal fat excretion, diarrhea, and subjective complaints with highly dosed oral fat intake. Digestion. 1970;3(6):321–330. doi: 10.1159/000197052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS B. Effect of certain dietary oils on bile-acid secretion and serum-cholesterol. Lancet. 1958 May 24;1(7030):1090–1092. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)91847-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekjian H. S., Phillips S. F., Hofmann A. F. Colonic secretion of water and electrolytes induced by bile acids: perfusion studies in man. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1569–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI106644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. B., Anderson J. T., Taylor H. L., Keys A., Frantz I. D., Jr Effect of dietary fat on the fecal excretion of cholesterol and its degradation products in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1517–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI105845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach S., Fernandez F., Johnson K., Drasar B. S. The non-sporing anaerobic bacteria in human faeces. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):213–221. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. R., Wiggins H. S., Drasar B. S. Conversion of long-chain unsaturated fatty acids to hydroxy acids by human intestinal bacteria. J Med Microbiol. 1974 May;7(2):265–275. doi: 10.1099/00222615-7-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintão E., Grundy S. M., Ahrens E. H., Jr Effects of dietary cholesterol on the regulation of total body cholesterol in man. J Lipid Res. 1971 Mar;12(2):233–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Narisawa T., Maronpot R., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Animal models for the study of dietary factors and cancer of the large bowel. Cancer Res. 1975 Nov;35(11 Pt 2):3421–3426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Effects of dietary fat level and dimethylhydrazine on fecal acid and neutral sterol excretion and colon carcinogenesis in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):507–511. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Weisburger J. H., Wynder E. L. Fecal bacterial beta-glucuronidase: control by diet. Science. 1974 Feb 1;183(4123):416–417. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4123.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy B. S., Wynder E. L. Large-bowel carcinogenesis: fecal constituents of populations with diverse incidence rates of colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jun;50(6):1437–1442. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.6.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers A. E., Newberne P. M. Dietary effects on chemical carcinogenesis in animal models for colon and liver tumors. Cancer Res. 1975 Nov;35(11 Pt 2):3427–3431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodhi H. S., Wood P. D., Schlierf G., Kinsell L. W. Plasma, bile and fecal sterols in relation to diet. Metabolism. 1967 Apr;16(4):334–344. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate D. A., Bailey B., Collinson E., Walker A. F. A guide to calculating intakes of dietary fibre. J Hum Nutr. 1976 Oct;30(5):303–313. doi: 10.3109/09637487609144013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. J. Identification of some enteric bacteria which convert oleic acid to hydroxystearic acid in vitro. Gastroenterology. 1972 Mar;62(3):430–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest P. J., McQueen R. W. The chemistry and estimation of fibre. Proc Nutr Soc. 1973 Dec;32(3):123–130. doi: 10.1079/pns19730029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. E., Kelleher J., Davies T., Smith C. L., Losowsky M. S. Influence of dietary fat on fecal fat. Gastroenterology. 1973 Feb;64(2):233–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. M., Roy C. C., Chartrand L., Lepage G., Dufour O. L., Morin C. L., Lasalle R. Relationship between bile acid malabsorption and pancreatic insufficiency in cystic fibrosis. Gut. 1976 Apr;17(4):295–299. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A. M., Roy C. C., Morin C. L., Lasalle R. Malabsorption of bile acids in children with cystic fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Nov 8;289(19):1001–1005. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197311082891903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. D., Lindsey C. A., Jr Studies on the influence of dietary cholesterol on cholesterol metabolism in the isotopic steady state in man. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1805–1814. doi: 10.1172/JCI105288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate D. L., Krag E., Mekhjian H. S., Phillips S. F. Relationships between ion and water movement in the human jejunum, ileum and colon during perfusion with bile acids. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1973 Nov;45(5):593–606. doi: 10.1042/cs0450593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollaeger E. E. Role of the ileum in fat absorption. Mayo Clin Proc. 1973 Dec;48(12):836–843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Reddy B. Studies of large-bowel cancer: human leads to experimental application. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 May;50(5):1099–1106. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L., Shigematsu T. Environmental factors of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1967 Sep;20(9):1520–1561. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196709)20:9<1520::aid-cncr2820200920>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynder E. L. The epidemiology of large bowel cancer. Cancer Res. 1975 Nov;35(11 Pt 2):3388–3394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


