Abstract
A marked suppression of the thymusderived (T)-lymphocyte response to concanavalin A has been demonstrated in vitro during renal infection. Suppression of the T-lymphocyte response in vitro was seen as early as 2 h after the induction of renal infection, but maximum suppression was found 24-72 h later. A population of suppressor cells in the splenic lymphocyte population, generated during the host's response to infection, contributed to the depressed lymphocyte response. Removal of suppressor cells restored the mitogenic responsiveness of the remaining splenic lymphocytes. Conversely, in co-culture experiments, a suppressor cell present in the splenic lymphocyte population of pyelonephritic animals was shown to be capable of suppressing the mitogenic responsiveness of normal splenic lymphocytes. Significantly reduced host vs. graft responses by the pyelonephritic animals confirmed, in vivo, the depression of cell-mediated immune mechanisms.
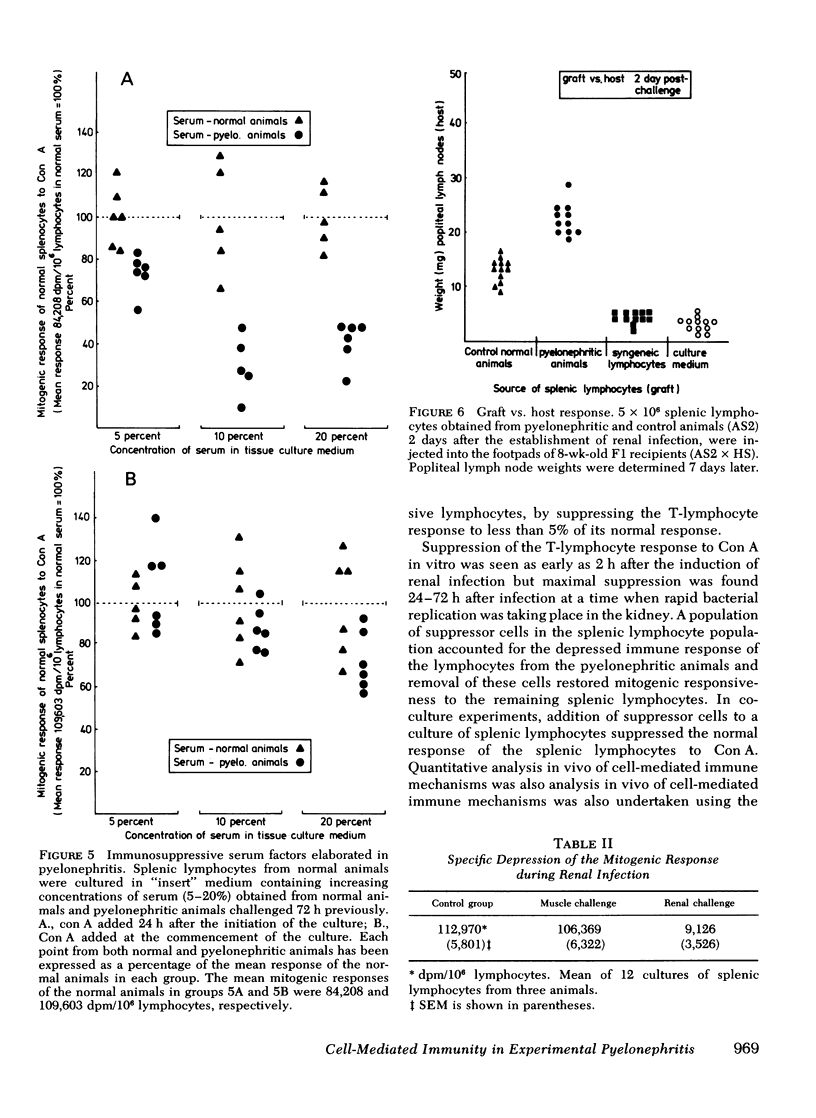
An additional suppressive factor was found in the serum of pyelonephritic animals which depressed in vitro the mitogenic responsiveness of splenic lymphocytes from normal animals. Support for the suppressive role of this serum factor was found when splenic lymphocytes from pyelonephritic animals were tested in vivo in the absence of homolgous serum (graft vs. host). Under these conditions, the lymphocytes showed an enhanced reaction compared with lymphocytes from normal animals. The presence of a suppressor cell population and a serum factor, both capable of depressing cell-mediated mechanisms, may be major factors contributing to the establishment of infection in the kidney.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bash J. A., Singer A. M., Waksman B. H. The suppressive effect of immunization on the proliferative responses of rat T cells in vitro. II. Abrogation of antigen-induced suppression by selective cytotoxic agents. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1350–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bash J. A., Waksman B. H. The suppressive effect of immunization on the proliferative responses of rat T cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):782–787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. G., Brent L., Kilshaw P. J., New R. R., Pinto M. Specific unresponsiveness to skin allografts in mice. IV. Immunological reactivity of mice treated with liver extracts, Bordetella pertussis, and antilymphocyte serum. Transplantation. 1975 Feb;19(2):134–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNEW I., BRAUDE A. I. Depression of phagocytosis by solutes in concentrations found in the kidney and urine. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI104652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch S., Roser B. The effect of antigenic strength and immunisation on the popliteal lymph node allograft response. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Jun;54(3):265–276. doi: 10.1038/icb.1976.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M. G., Hosking C. S. Plasma inhibitors of lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin in children with recurrent infections. Immunology. 1976 Jan;30(1):33–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. Regulation of lymphocyte responses in vitro. V. Suppressor activity of adherent and nonadherent rat lymphoid cells. Cell Immunol. 1973 Oct;9(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90163-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. I. Activity of thymus-dependent adherent cells: changes with age and stress. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):127–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folch H., Waksman B. H. The splenic suppressor cell. II. Suppression of mixed lymphocyte reaction by thymus-dependent adherent cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):140–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Burr W., Simonsen M. A lymph node weight assay for the graft-versus-host activity of rat lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1970 Sep;10(3):258–266. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197009000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jodal U., Ahlstedt S., Carlsson B., Hanson L. A., Lindberg U., Sohl A. Local antibodies in childhood urinary tract infection: a preliminary study. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(4):537–546. doi: 10.1159/000231248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J. D., Smith J. W., Miller T. E., Barnett J. A., Sanford J. P. Local immune response in experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2541–2550. doi: 10.1172/JCI105936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbrook J. Primary immune response in cultures of spleen cells. Lancet. 1967 Dec 16;2(7529):1279–1281. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster R., Levy J. G. Immunosuppression of normal lymphoid cells by serum from mice undergoing chronic graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1400–1403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Burnham S., North J. D. Immunological enhancement in the pathogenesis of pyelonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 May;24(2):336–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., North D. The cellular kinetics of the immune response in pyelonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Dec;78(6):891–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Robinson K. B. Experimental pyelonephritis: a new method for inducing pyelonephritis in the rat. J Infect Dis. 1973 Mar;127(3):307–310. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Scott L., Simpson G., Ormrod D. J. Depression of the T-lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin by renal cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):492–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Simpson G., Ormrod D. J. Quantitation of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes and the lymphocyte response to PHA in experimental pyelonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Sep;21(3):474–484. doi: 10.1002/aic.690210307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. E., Smith J. W., Sanford J. P. Antibody synthesis in kidney, spleen and lymph nodes in acute and healed focal pyelonephritis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1971 Dec;52(6):678–683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T., North D. Studies of the local immune response to pyelonephritis in the rabbit. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):195–201. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw I. A., Bretscher P. A., Parish C. R. Regulation of the immune response. I. Suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by T cells from mice expressing humoral immunity. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Oct;6(10):674–679. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Adkins M. J., McCreary D. Local immune response in experimental pyelonephritis in the rabbit. I. Morphological and functional features of the lymphocytic infiltrate. Immunology. 1975 Dec;29(6):1067–1076. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Hand W. L., Sanford J. P. Local synthesis of secretory IgA in experimental pyelonephritis. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):867–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Kaijser B. The local immune response to Escherichia coli O and K antigen in experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):276–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI108469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Holmgren J., Ahlstedt S., Hanson L. A. Local antibody production in experimental pyelonephritis: amount, avidity, and immunoglobulin class. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):411–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.411-415.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stobo J. D., Paul S., Van Scoy R. E., Hermans P. E. Suppressor thymus-derived lymphocytes in fungal infection. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):319–328. doi: 10.1172/JCI108283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney R. B., Levy J. G. Effects of sera from tumor-bearing mice on mitogen and allogeneic cell stimulation of normal lymphoid cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Mar;54(3):733–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney R. B., Levy J. G. Suppression of mitogen responses by serum from tumour-bearing mice. Eur J Cancer. 1974 Nov;10(11):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(74)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Friedlander A. M., Lyons J. M., Braude A. I. Cellular immunity in pyelonephritis: identification of suppressor cell activity of spleen cells in response to concanavalin A and inhibition of lymphocyte-mediated L cell cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1976 Mar;116(3):778–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


