Abstract
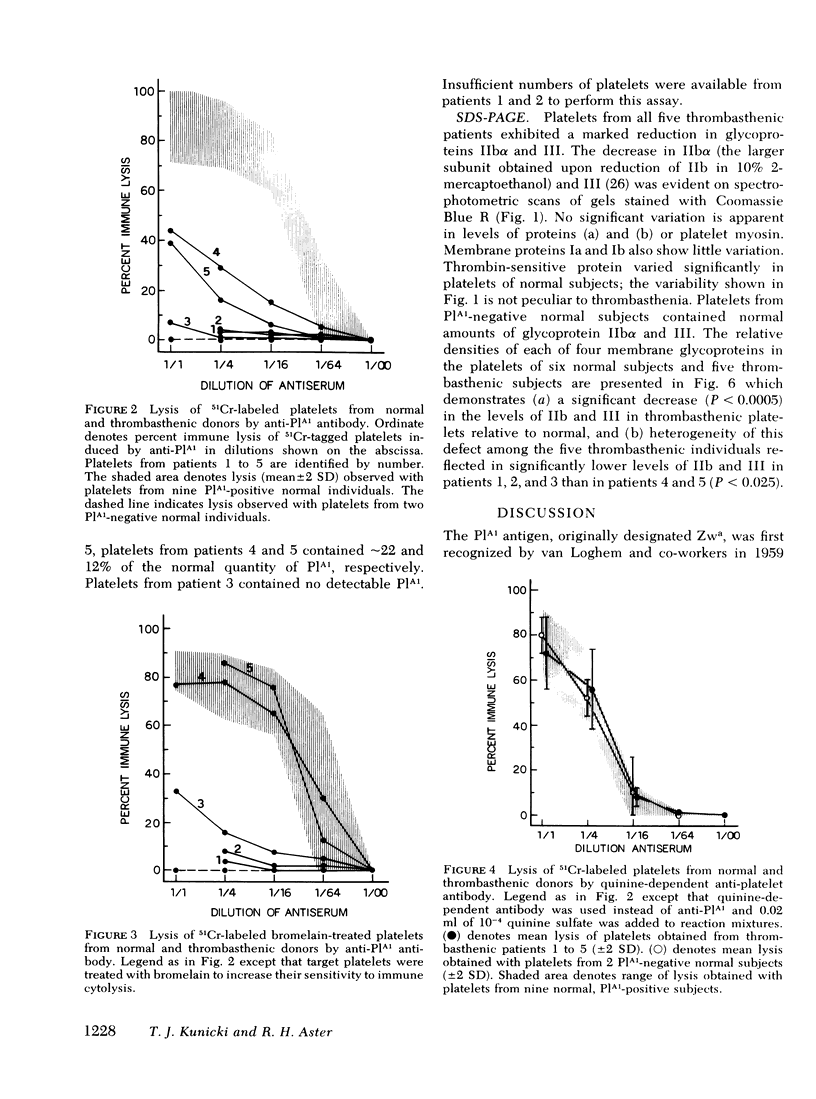
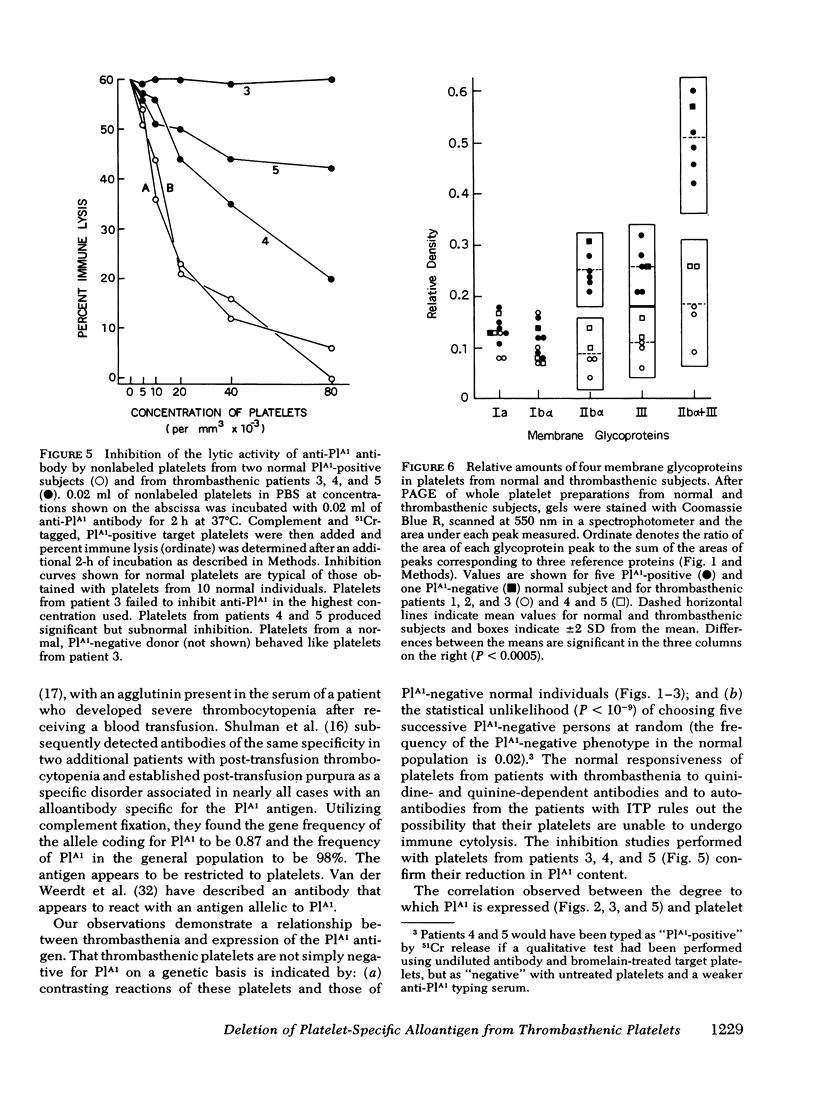
Expression of a Platelet-specific alloantigen (PlA1) was studied in five unrelated patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia using immunologic techniques based on release of 51Cr from tagged platelets by PlA1-specific antibody. Less than 1% of the normal quantity of PlA1 could be detected on platelets of patients 1, 2, and 3; platelets from patients 4 and 5 contained 22 and 12% of normal levels, respectively. After treatment with bromelain, platelets from patients 4 and 5, but not those from patients 1, 2, and 3, released 51Cr as well as normal PlA1-positive platelets when exposed to anti-PlA1. Platelets from each of the five patients reacted normally with drug-dependent antibodies and with autoantibodies specific for platelets.
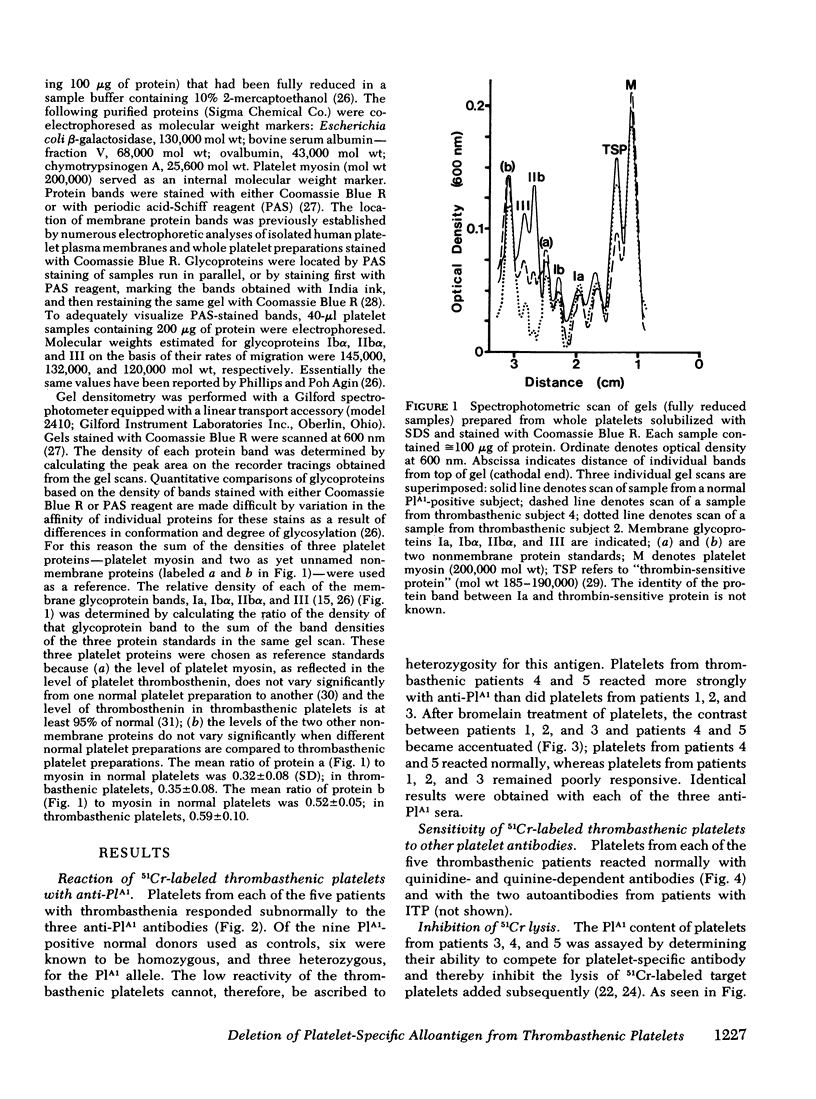
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of thrombasthenic platelets showed marked deficiencies of glycoproteins IIbα and III (P < 0.0005), confirming recent reports of others. Deficiency of the two proteins as determined by gel scanning was more pronounced in patients 1, 2, and 3 than in patients 4 and 5. Normal levels of glycoproteins IIbα and III were found in platelets from normal subjects negative for PlA1.
These observations are consistent with the possibility that the PlA1 antigen is located on one or both of the glycoproteins lacking in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia, although other explanations are possible. They further suggest that patients with thrombasthenia may be heterogeneous in respect to the degree to which these glycoproteins are deleted. The PlA1 antigen can be measured with considerable precision and may provide a marker useful for the diagnosis and study of Glanzmann's disease.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstee D. J., Barker D. M., Judson P. A., Tanner M. J. Inherited sialoglycoprotein deficiencies in human erythrocytes of type En[a-]. Br J Haematol. 1977 Feb;35(2):309–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb00587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aster R. H., Miskovich B. H., Rodey G. E. Histocompatibility antigens of human plasma. Localization to the HLD-3 lipoprotein fraction. Transplantation. 1973 Sep;16(3):205–210. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197309000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. Isolation and properties of a thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2723–2731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F. M., Zschocke D., Hoveke T. P., Rafelson M. E., Jr Microquantitation of thrombosthenin in human platelets by single radial immunodiffusion. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Feb;79(2):344–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booyse F., Kisieleski D., Seeler R., Rafelson M., Jr Possible thrombosthenin defect in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Blood. 1972 Mar;39(3):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaldi P. A., Caen J. Platelet fibrinogen. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Sep;18(5):579–585. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.5.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimo P. L., Pisciotta A. V., Desai R. G., Pino J. L., Aster R. H. Detection of drug-dependent antibodies by the 51Cr platelet lysis test: documentation of immune thrombocytopenia induced by diphenylhydantoin, diazepam, and sulfisoxazole. Am J Hematol. 1977;2(1):65–72. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830020109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I., Glaser T., Seligsohn U. Effects of ADP and ATP on bovine fibrinogen- and ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1975 Nov;31(3):343–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1975.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degos L., Dautigny A., Brouet J. C., Colombani M., Ardaillou N., Caen J. P., Colombani J. A molecular defect in thrombasthenic platelets. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul;56(1):236–240. doi: 10.1172/JCI108074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN L. L., BOWIE E. J., THOMPSON J. H., Jr, OWEN C. A., Jr, BROWN A. L. FAMILIAL GLANZMANN'S THROMBASTHENIA. Mayo Clin Proc. 1964 Dec;39:908–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firkin B. G., Howard M. A., Farmer S. J. Observations on the ultrastructure of platelets in Glanzmann's disease. Br J Haematol. 1974 Jul;27(3):527–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D., Rossi E. C. Disorders of platelet function. Med Clin North Am. 1972 Jan;56(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32421-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M. A., Firkin B. G. Ristocetin--a new tool in the investigation of platelet aggregation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Oct 31;26(2):362–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issitt P. D., Pavone B. G., Goldfinger D., Zwicker H. An En(a-) red cell sample that types as Wr(a-b-). Transfusion. 1975 Jul-Aug;15(4):353–355. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1975.15476034557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpatkin S., Weiss H. J. Deficiency of glutathione peroxidase associated with high levels of reduced glutathione in glanzmann's thrombasthenia. N Engl J Med. 1972 Nov 23;287(21):1062–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197211232872103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebert M., Aster R. H. Expression of HLA-B12 on platelets, on lymphocytes and in serum: a quantitative study. Tissue Antigens. 1977 Apr;9(4):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1977.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh W. L. The Kell blood group, Kx antigen, and chronic granulomatous disease. Mayo Clin Proc. 1977 Mar;52(3):150–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser K., Lechner K., Vinazzer H. A hitherto not described enzyme defect in thrombasthenia: glutathionreductase deficiency. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Mar 31;19(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Marcus A. J. Immunological studies of proteins associated with the subcellular fractions of thrombasthenic and afibrinogenaemic platelets. Br J Haematol. 1968 Aug;15(2):181–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01528.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L. Thrombasthenia: immunologic evidence of a platelet protein abnormality. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Mar;67(3):411–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Br J Haematol. 1974 Oct;28(2):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurden A. T., Caen J. P. Specific roles for platelet surface glycoproteins in platelet function. Nature. 1975 Jun 26;255(5511):720–722. doi: 10.1038/255720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet membrane defects in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. Evidence for decreased amounts of two major glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):535–545. doi: 10.1172/JCI108805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Agin P. P. Platelet plasma membrane glycoproteins. Evidence for the presence of nonequivalent disulfide bonds using nonreduced-reduced two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2121–2126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. R., Jenkins C. S., Lüscher E. F., Larrieu M. Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membranes. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):599–600. doi: 10.1038/257599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsak B. Effects of thrombin, chymotrypsin and aggregated gamma-globulins on the proteins of the human platelet membrane. Thromb Haemost. 1977 Jun 30;37(3):396–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R. Immunoreactions involving platelets. I. A steric and kinetic model for formation of a complex from a human antibody, quinidine as a haptene, and platelets; and for fixation of complement by the complex. J Exp Med. 1958 May 1;107(5):665–690. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHULMAN N. R., MARDER V. J., HILLER M. C., COLLIER E. M. PLATELET AND LEUKOCYTE ISOANTIGENS AND THEIR ANTIBODIES: SEROLOGIC PHYSIOLOGIC AND CLINICAL STUDIES. Prog Hematol. 1964;4:222–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt P. J., Lostumbo M. M., English C. T., Hunter O. B., Jr Aberrant U blood group accompanying Rh-null. Transfusion. 1967 Jan-Feb;7(1):33–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1967.tb04827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman N. R., Aster R. H., Leitner A., Hiller M. C. IMMUNOREACTIONS INVOLVING PLATELETS. V. POST-TRANSFUSION PURPURA DUE TO A COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIBODY AGAINST A GENETICALLY CONTROLLED PLATELET ANTIGEN. A PROPOSED MECHANISM FOR THROMBOCYTOPENIA AND ITS RELEVANCE IN "AUTOIMMUNITY". J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40(9):1597–1620. doi: 10.1172/JCI104383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DER WEERDT C. M., VEENHOVEN-VONRIESZ L. E., NIJENHUIS L. E., VAN LOGHEM J. THE ZW BLOOD GROUP SYSTEM IN PLATELETS. Vox Sang. 1963 Sep-Oct;8:513–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1963.tb04179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN LOGHEM JJ J., DORFMEIJER H., VAN HART M., SCHREUDER F. Serological and genetical studies on a platelet antigen (Zw). Vox Sang. 1959 Apr;4(2):161–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1959.tb04032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Kochwa S. Studies of platelet function and proteins in 3 patients with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):153–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


