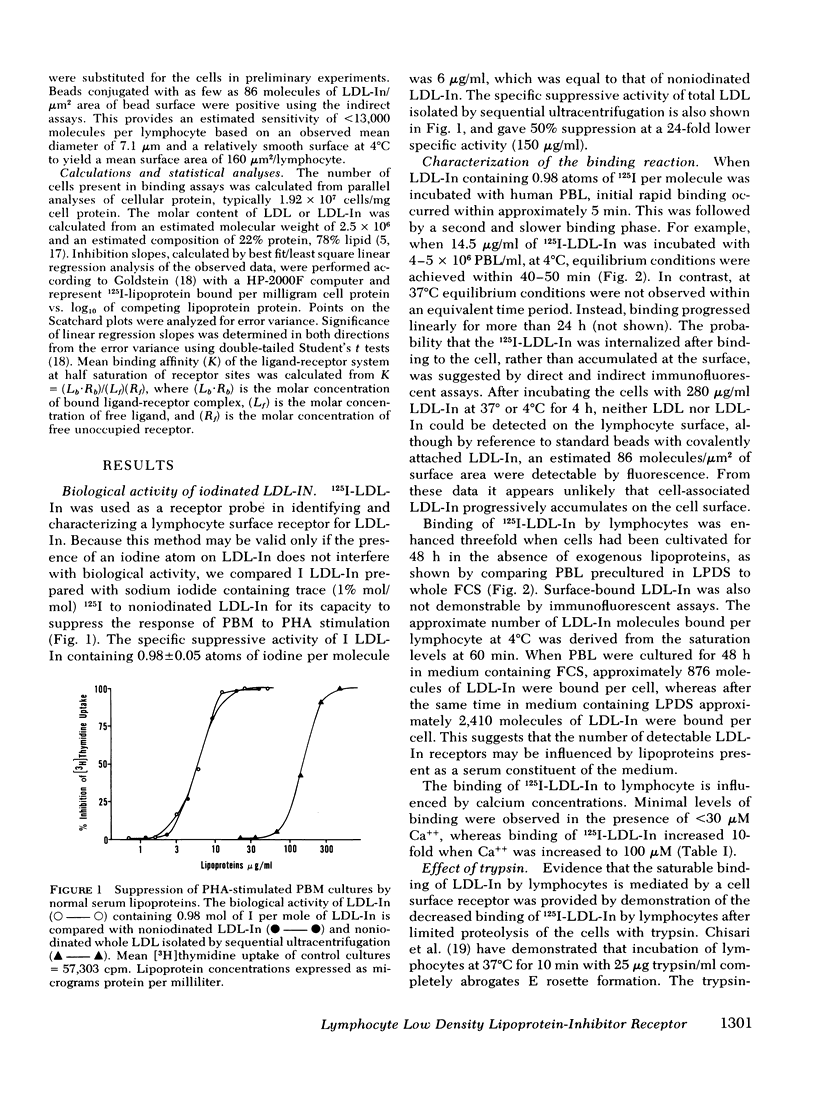
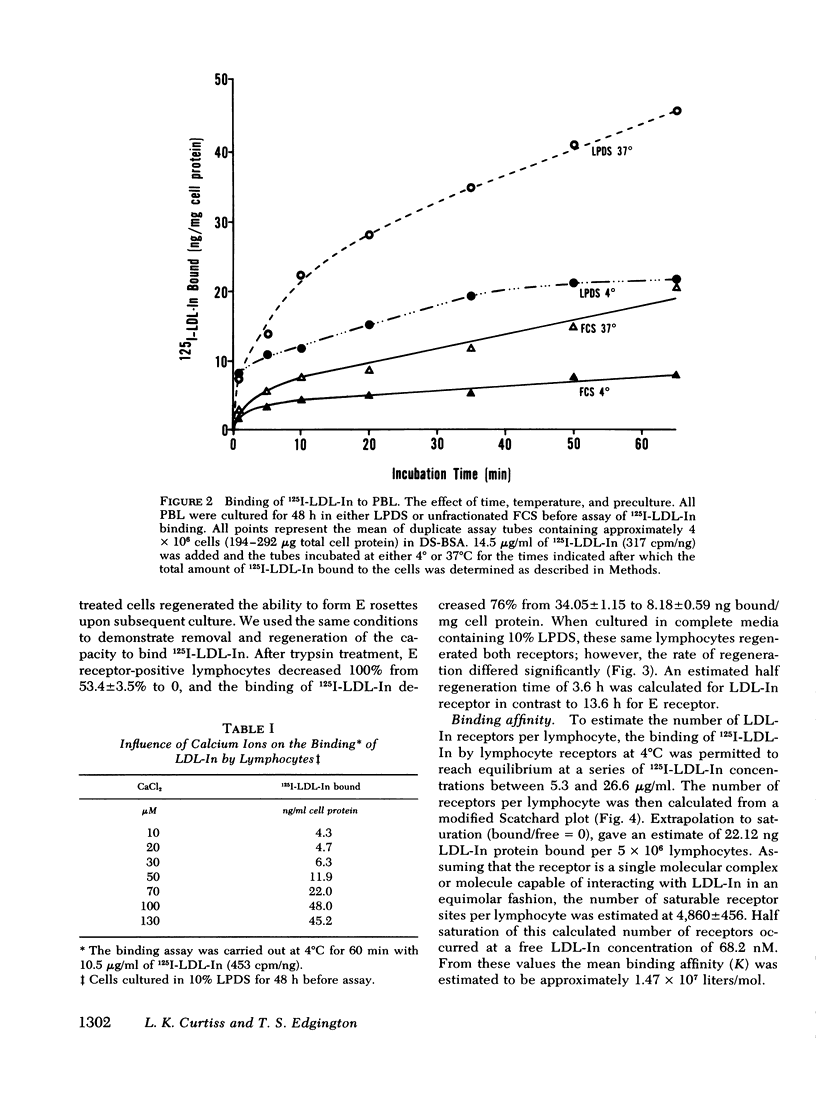
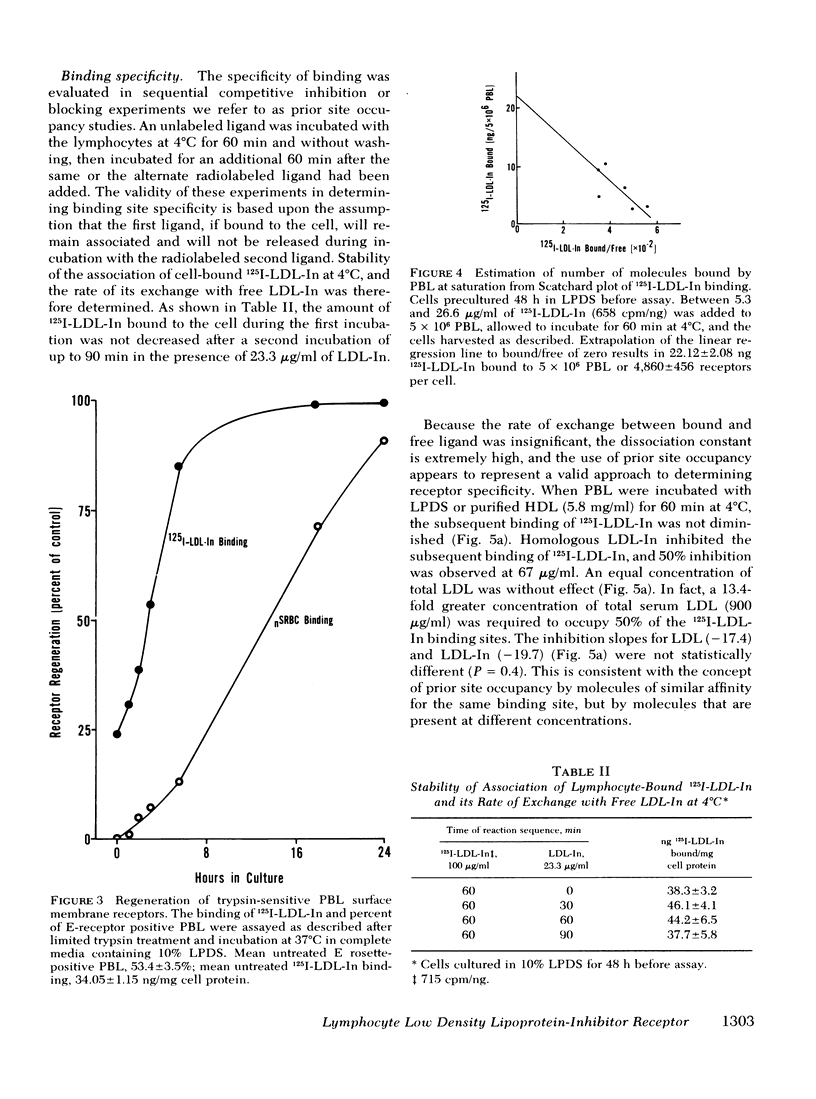
Abstract
The present study demonstrates the existence on human peripheral blood lymphocytes of a saturable cell surface receptor for low density lipoprotein inhibitor (LDL-In), a subset of normal human serum low density lipoprotein (LDL) that has been previously demonstrated to suppress selected lymphocyte functions in vivo and in vitro. The binding of radioiodinated LDL-In of demonstrable biological activity occurs rapidly and is quantitatively augmented by prior cultivation of the lymphocytes in lipoprotein-depleted serum, suggesting regulation of receptor density by lipoproteins in vivo. Binding is temperature dependent, facilitated by calcium ions, saturable at 4 degrees C within 40-60 min, and blocked by prior exposure to unlabeled LDL-In. The lymphocyte receptor is trypsin sensitive and regenerates in vitro with a t1/2 of 3.6 h. LDL-In receptors are calculated to have a maximum density of 4,860 +/- 460 per cell if uniformly distributed on all lymphocyte subsets. These receptors have an estimated average association constant of 1.47 X 10(7) liters/mol. When considered in context of the estimated concentration of LDL-In in blood, the receptors should be partially occupied in vivo by endogenous plasma LDL-In. Prior site occupancy inhibition experiments designed to analyze the specificity of LDL-In binding demonstrate that (a) LDL-In is 13.7-fold more effective than whole LDL in blocking the subsequent binding of 125I-LDL-In to cells; and that (b) LDL is 11-fold more effective than LDL-In in blocking the binding of 125I-LKL. This is consistent with the degree of contamination of each lipoprotein with the other lipoprotein. An independent identity of the LDL-In receptor is also supported by observations that in contrast to the previously described LDL receptor, synthesis and expression of the LDL-In receptor on lymphocytes are not suppressed by cultivation of the cells in the presence of 25-hydroxycholesterol and cholesterol. These findings suggest the existence of a previously undescribed and discrete receptor on lymphocytes for LDL-In, and that the modulation of lymphocyte function by LDL-In may be mediated by a specific cell surface receptor pathway.
Full text
PDF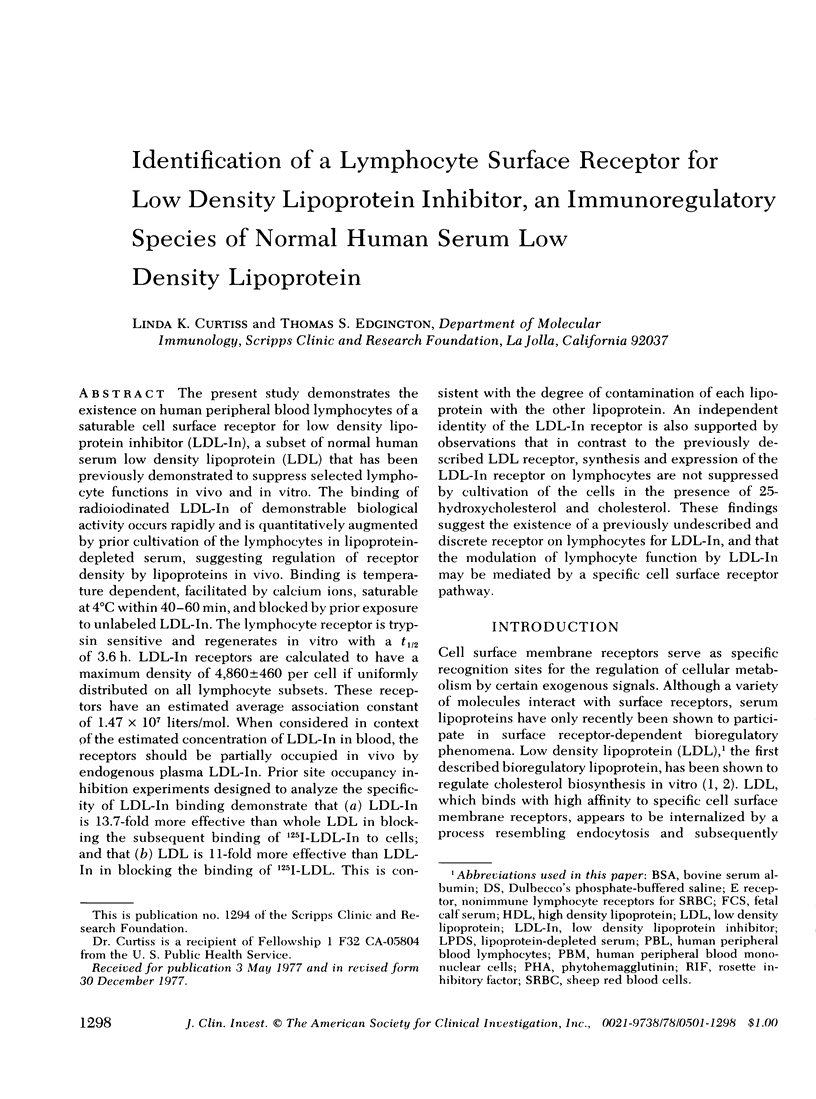






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bierman E. L., Stein O., Stein Y. Lipoprotein uptake and metabolism by rat aortic smooth muscle cells in tissue culture. Circ Res. 1974 Jul;35(1):136–150. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Receptor-mediated control of cholesterol metabolism. Science. 1976 Jan 16;191(4223):150–154. doi: 10.1126/science.174194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of the activity of the low density lipoprotein receptor in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Edgington T. S. Lymphocyte E rosette inhibitory factor: a regulatory serum lipoprotein. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1092–1107. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Gealy W. J., Edgington T. S. Recovery of soluble sheep erythrocyte receptor from the T lymphocyte surface by proteolytic cleavage. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1138–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Gerin J. L., Edgington T. S. Immunochemistry of the hepatitis B virus: 125I HB Ag ligand. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Routenberg J. A., Edgington T. S. Mechanisms responsible for defective human T-lymphocyte sheep erythrocyte rosette function associated with hepatitis B virus infections. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1227–1238. doi: 10.1172/JCI108391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Hollenberg M. D. Membrane receptors and hormone action. Adv Protein Chem. 1976;30:251–451. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60481-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., DeHeer D. H., Edgington T. S. In vivo suppression of the primary immune response by a species of low density serum lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):648–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Effect of LDL-In, a normal immunoregulatory human serum low density lipoprotein, on the interaction of macrophages with lymphocytes proliferating in response to mitogen and allogeneic stimulation. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):1966–1970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Regulatory serum lipoproteins: regulation of lymphocyte stimulation by a species of low density lipoprotein. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1452–1458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana S. E., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Specific, saturable, and high affinity binding of 125I-low density lipoprotein to glass beads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1369–1376. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90593-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Binding and degradation of low density lipoproteins by cultured human fibroblasts. Comparison of cells from a normal subject and from a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5153–5162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Kayden H. J., Goldstein J. L. Binding, internalization, and hydrolysis of low density lipoprotein in long-term lymphoid cell lines from a normal subject and a patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):444–455. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho Y. K., Brown S., Bilheimer D. W., Goldstein J. L. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor activity in freshly isolated human lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1976 Dec;58(6):1465–1474. doi: 10.1172/JCI108603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLOW L. S. SIMPLIFIED MYELOPEROXIDASE STAIN USING BENZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:215–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


