Abstract
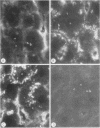
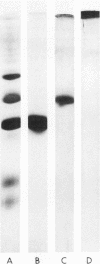
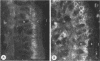
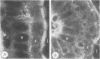
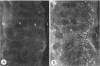
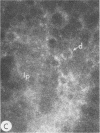
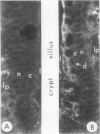
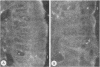
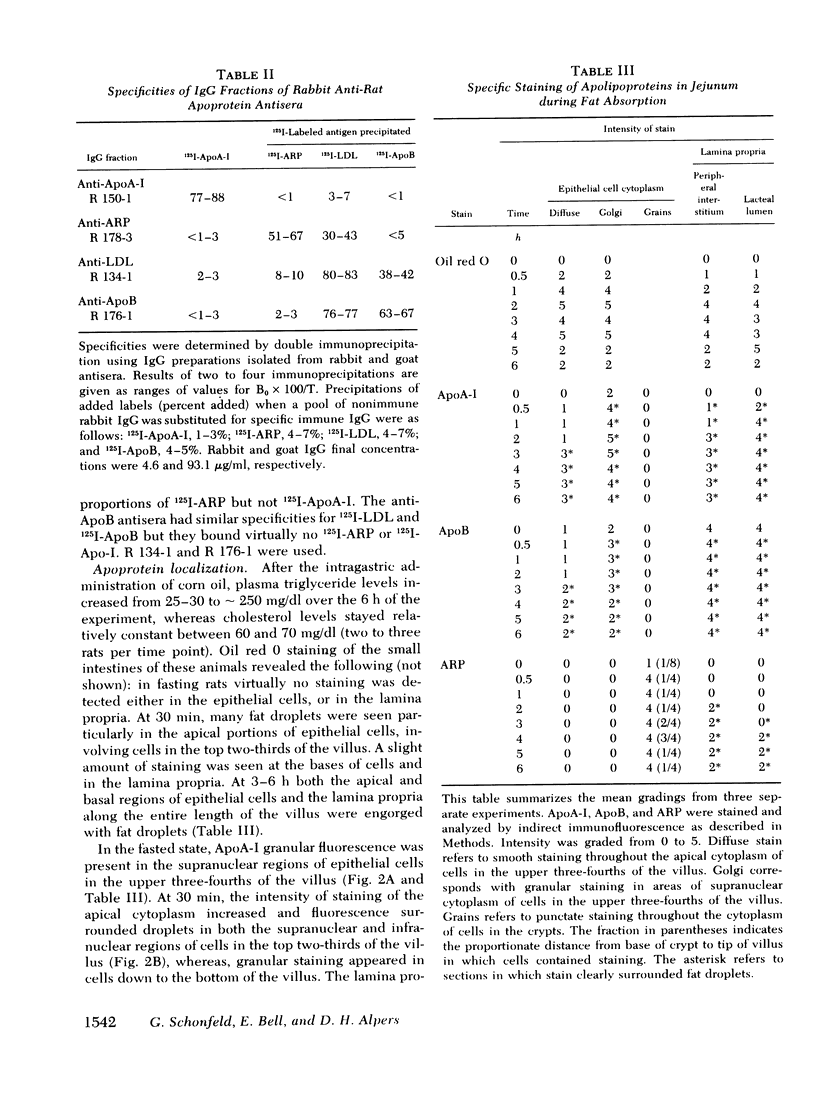
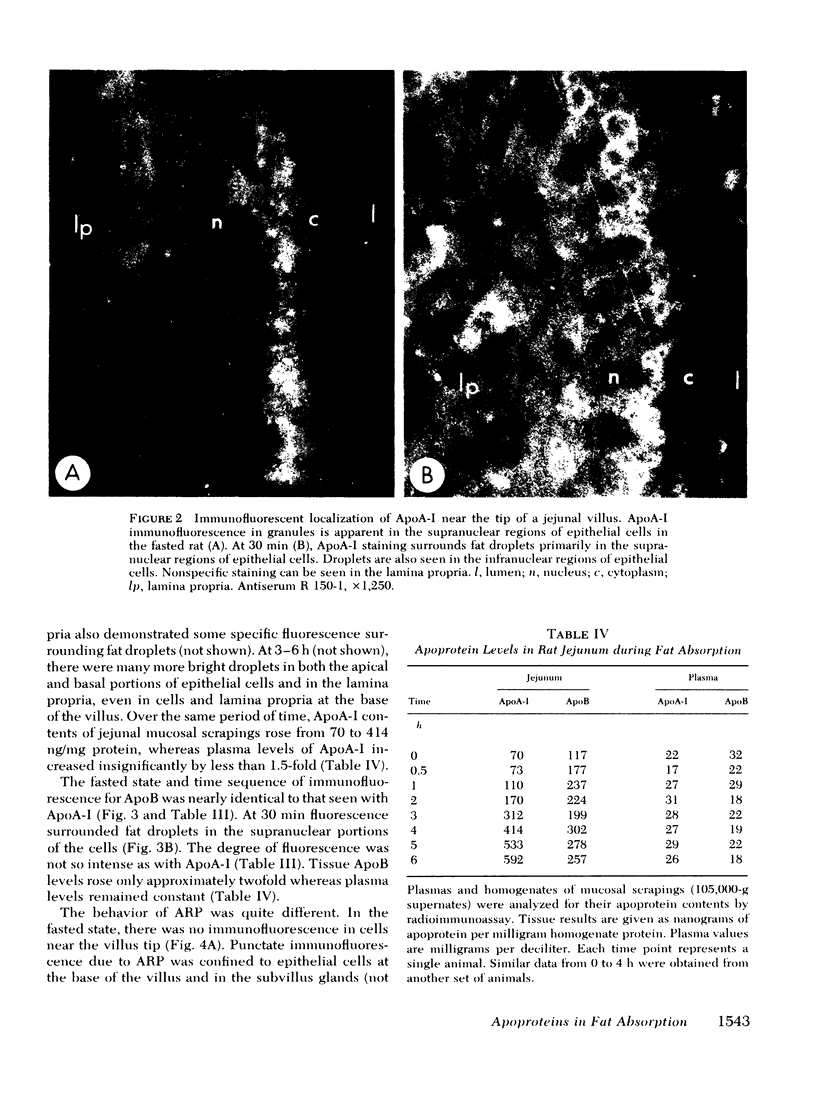
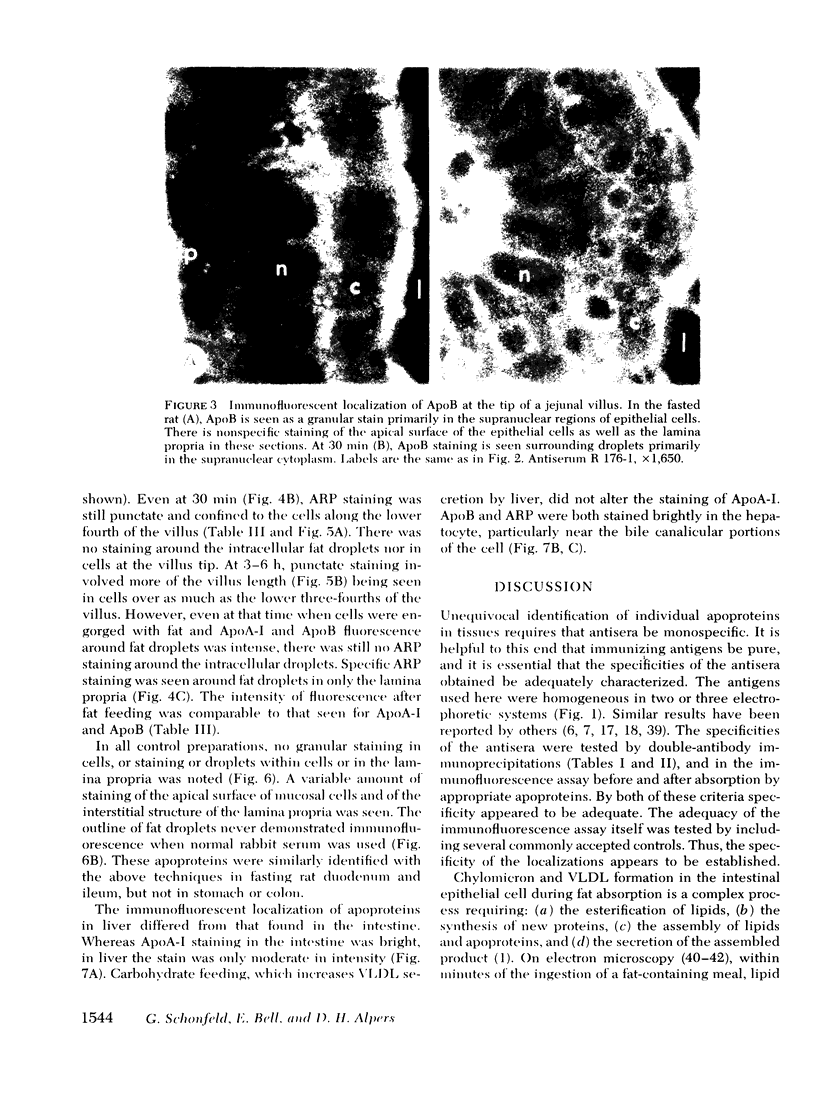
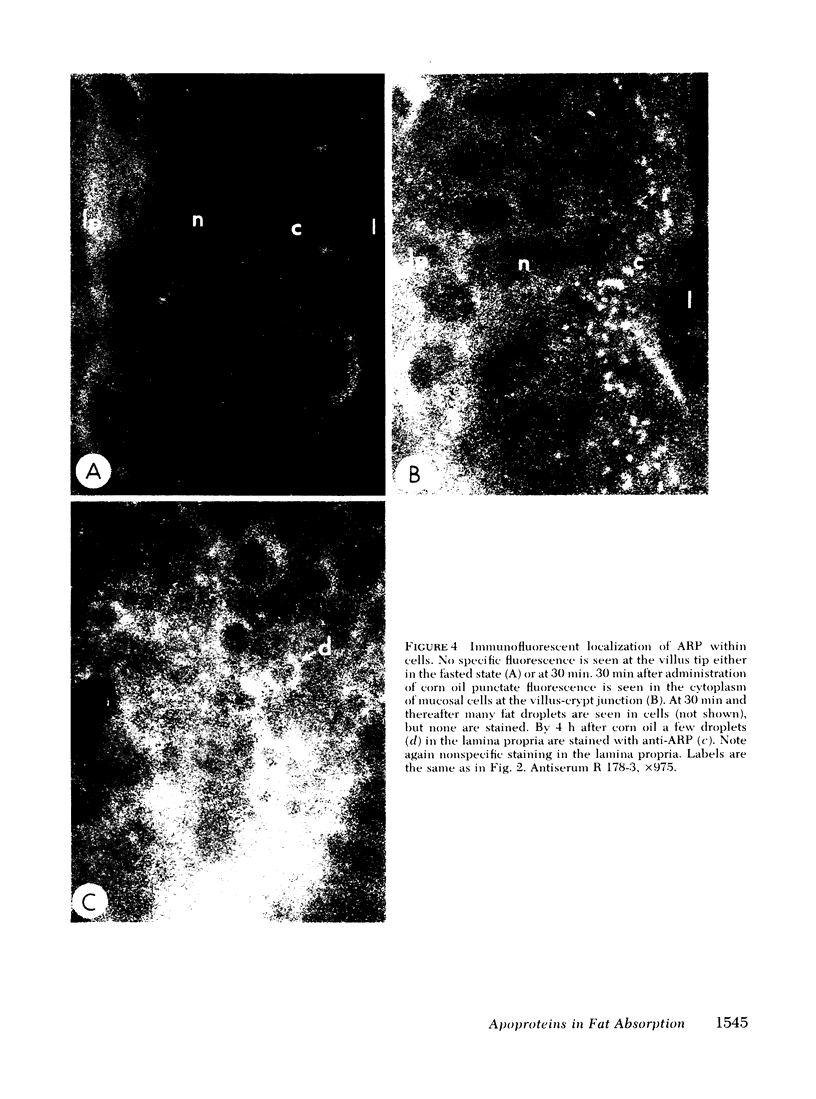
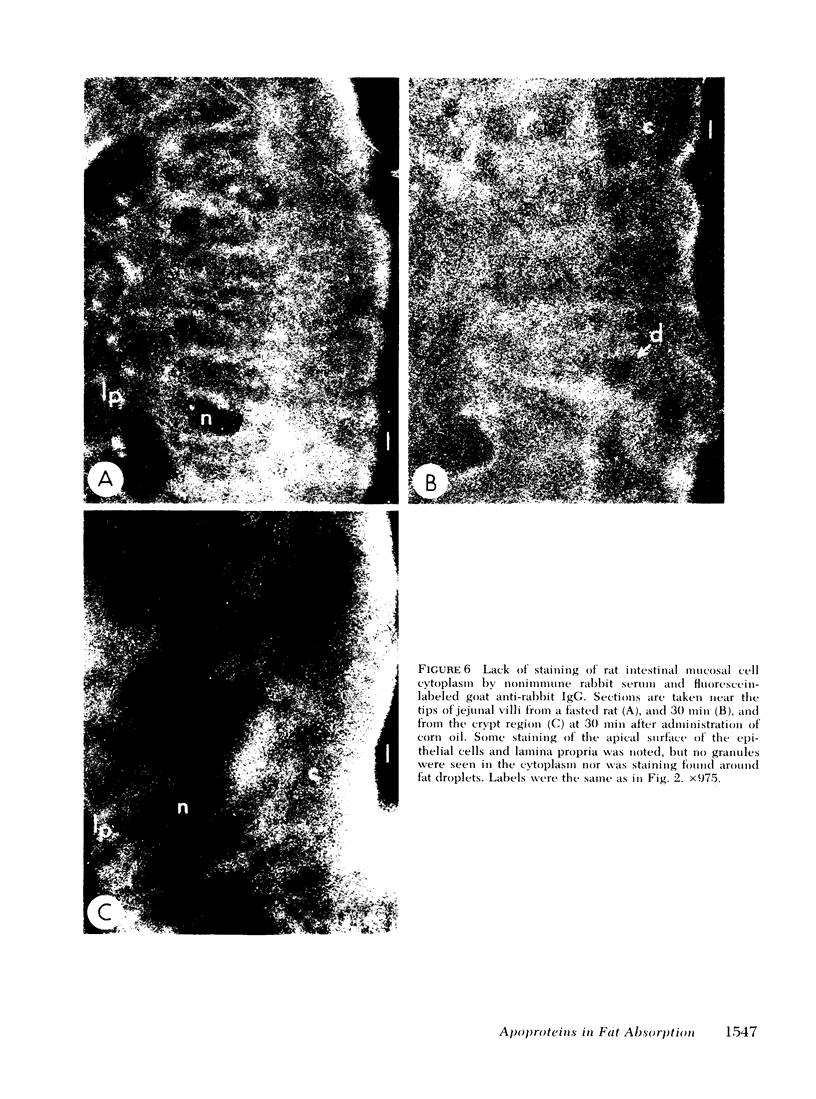
To compare the roles of apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I, B, and E (or arginine-rich apoprotein, ARP) in the intracellular production of intestinal chylomicrons (and/or VLDL), these apoproteins were localized in rat intestinal mucosa by the light microscope method of indirect immunofluorescence. In addition, tissue levels of ApoA-I and ApoB were measured during fat absorption by radioimmunoassay. Antisera were produced using ApoA-I isolated from rat plasma high density lipoprotein, and ApoB and ARP from plasma VLDL by column chromatography. The apoproteins yielded single bands on polyacrylamide disc gel electrophoresis in urea and in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anti-apoprotein antisera were produced in rabbits. These antisera appeared to be monospecific on double-antibody immunoprecipitation of 125I-labeled apoproteins. In fasted animals granular staining of ApoA-I was noted in the supranuclear (Golgi) regions of epithelial cells in the top third of the villus. At 30 min, when fat droplets were seen in the supranuclear cytoplasm of the cells along the top two-thirds of the villus, intense ApoA-I staining surrounded droplets in the cytoplasm. At later times when epithelial cells and lamina propria both contained fat droplets, bright ApoA-I stain surrounded many droplets in the supranuclear cytoplasm of cells and in the lamina propria. Over the same period of time, tissue levels of ApoA-I rose 10-fold. The distribution and time-course of ApoB staining was nearly identical with that of ApoA-I. Concomitantly, tissue ApoB levels doubled. By contrast, in fasting rat intestine, staining of ARP was sparse, punctate, and confined to the lower quarter of the villus. After fat feeding, stained droplets were seen only in the lamina propria near the base of the villus even though abundant ARP was found in cells along most of this length of the villus. Stain was never seen to surround any droplets inside cells. Thus, ApoA-I and ApoB appeared to participate in the intracellular assemply of lipoproteins in gut, whereas ARP did not, although ARP was found within mucosal cells. Liver and intestine differed in their stainable contents of ApoA-I and ARP. Whereas intestine stained heavily for ApoA-I and lightly for ARP, liver stained heavily for ARP and lightly for ApoA-I. Both organs stained for ApoB. These findings suggest that there may be some quantitative "specialization" of the two organs which secrete lipoproteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alaupovic P., Furman R. H., Falor W. H., Sullivan M. L., Walraven S. L., Olson A. C. Isolation and characterization of human chyle chylomicrons and lipoproteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Nov 21;149(2):791–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb53836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell C. E., Jr, Seetharam S., McDaniel R. C. Endodermally-derived and neural crest-derived differentiation antigens expressed by a human lung tumor. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1236–1243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bersot T. P., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Interaction of swine lipoproteins with the low density lipoprotein receptor in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2395–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardell R. R., Jr, Badenhausen S., Porter K. R. Intestinal triglyceride absorption in the rat. An electron microscopical study. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):123–155. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton R. P., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay of beta lipoprotein-protein of rat serum. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1387–1396. doi: 10.1172/JCI106104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Imaizumi K. Radioimmunoassay of arginine-rich apolipoprotein of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):144–155. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90114-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felker T. E., Fainaru M., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Secretion of the arginine-rich and A-I apolipoproteins by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E. A protein cofactor of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 25;46(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90776-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangl A., Ockner R. K. Intestinal metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):167–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidez L. I., Swaney J. B., Murnane S. Analysis of rat serum apolipoproteins by isoelectric focusing. I. Studies on the middle molecular weight subunits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jan;18(1):59–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H. The intestine as a source of apolipoprotein A1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2569–2573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Khorana J., Kilgore A. Localization of apolipoprotein B in intestinal epithelial cells. Science. 1976 Sep 24;193(4259):1254–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.183265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Fielding C. J., Olivecrona T., Shore V. G., Fielding P. E., Egelrud T. Cofactor activity of protein components of human very low density lipoproteins in the hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipoproteins lipase from different sources. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 24;12(9):1828–1833. doi: 10.1021/bi00733a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. I., Stein J., Dannacker D., Narcessian P. Biosynthesis of low density lipoprotein by cell-free preparations of rat intestinal mucosa. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5281–5288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga S., Bolis L., Scanu A. M. Isolation and characterization of subunit polypeptides from apoproteins of rat serum lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 25;236(2):416–430. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees R. S., Ahrens E. H., Jr Fat transport in abetalipoproteinemia. The effects of repeated infusions of beta-lipoprotein-rich plasma. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 5;280(23):1261–1266. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906052802302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. B. Apoproteins of the lipoproteins in a nonrecirculating perfusate of rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):85–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: origin, composition, and role in lipid transport in the fasting state. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2079–2088. doi: 10.1172/JCI106174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., KARLIN L. J. An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. II. The pathway of fat absorption. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. L., Ghiselli G. C., Torreggiani D., Sirtori C. R. Very low density lipoproteins in normal and cholesterol-fed rabbits: lipid and protein composition and metabolism. Part 1. Chemical composition of very low density lipoproteins in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. 1976 Jan-Feb;23(1):73–83. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(76)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke J. A., Skinner E. R. The biosynthesis of rat serum apolipoproteins by liver and intestinal mucosa. Biochem Soc Trans. 1976;4(6):1144–1145. doi: 10.1042/bst0041144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabesin S. M., Frase S. Electron microscopic studies of the assembly, intracellular transport, and secretion of chylomicrons by rat intestine. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jul;18(4):496–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Frick M. S., Bailey A. P. Measurement of apolipoprotein A-I in rat high density lipoprotein and in rat plasma by radioimmunoassay. J Lipid Res. 1976 Jan;17(1):25–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Lees R. S., George P. K., Pfleger B. Assay of total plasma apolipoprotein B concentration in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1458–1467. doi: 10.1172/JCI107694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Weidman S. W., Witztum J. L., Bowen R. M. Alterations in levels and interrelations of plasma apolipoproteins induced by diet. Metabolism. 1976 Mar;25(3):261–275. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(76)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptides by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: further data concerning resolving power and general considerations. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V. G., Shore B., Hart R. G. Changes in apolipoproteins and properties of rabbit very low density lipoproteins on induction of cholesteremia. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 9;13(8):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00705a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar A. K., Garner C. W., Baker H. N., Sparrow J. T., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Smith L. C. Effect of the human plasma apolipoproteins and phosphatidylcholine acyl donor on the activity of lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul 15;14(14):3057–3064. doi: 10.1021/bi00685a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Gidez L. I. Analysis of rat serum apolipoproteins by isoelectric focusing. II. Studies on the low molecular weight subunits. J Lipid Res. 1977 Jan;18(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Reese H., Eder H. A. Polypeptide composition of rat high density lipoprotein: characterization by SDS-gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jul 24;59(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windmueller H. G., Lindgren F. T., Lossow W. J., Levy R. I. On the nature of circulating lipoproteins of intestinal origin in the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]