Abstract
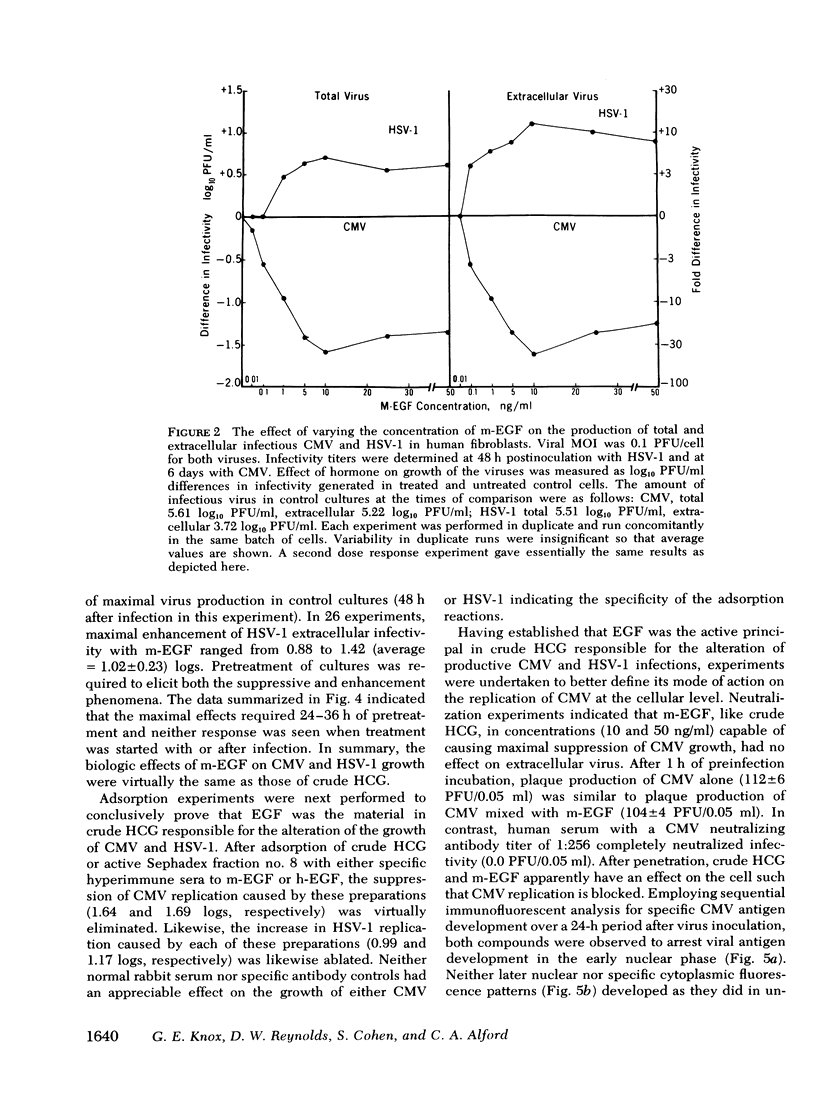
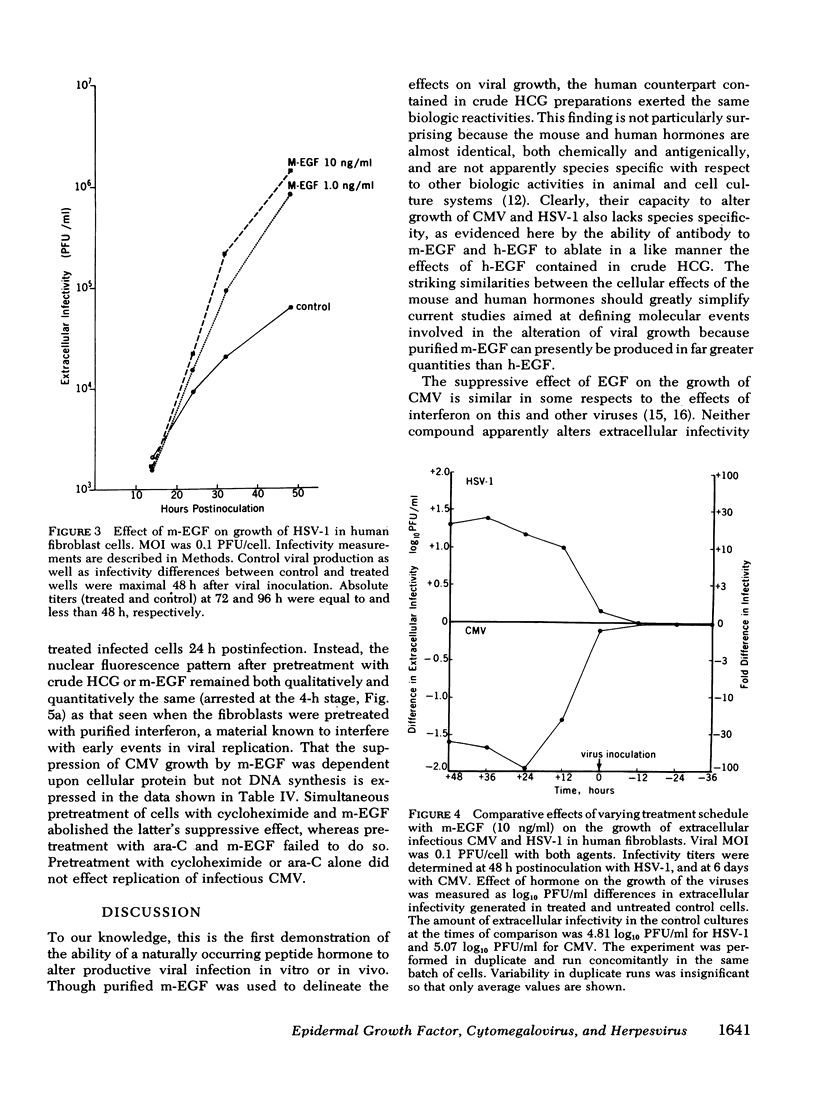
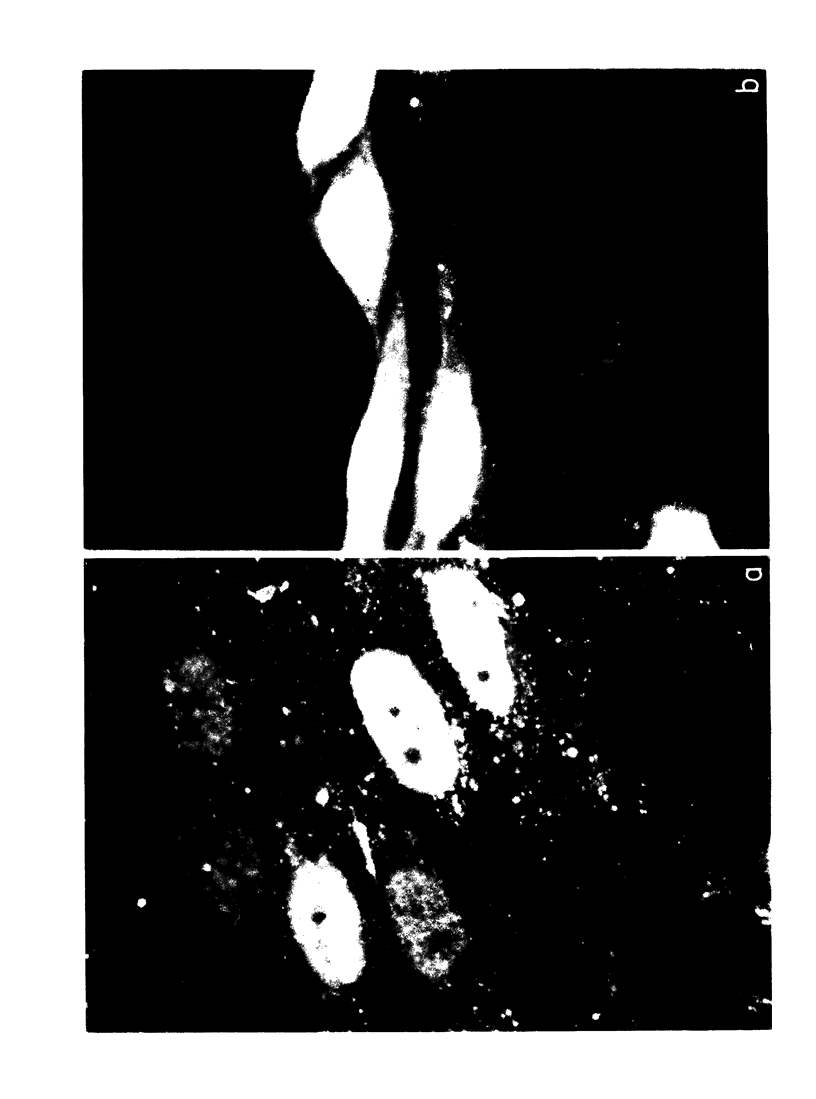
Pretreatment (12-48 h) of human fibroblasts with crude, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) was found to suppress cytomegalovirus infection and enhance productive herpes simplex type 1 (HSV) infection in vitro. Maximal effect on virus replication occurred at the time of maximal infectivity of control cultures (48 h and 6 days after viral innoculation for HSV and cytomegalovirus, respectively). The alteration in viral growth was not due to the HCG itself, but rather to epidermal growth factor, a contaminant of crude HCG. The effect of epidermal growth factor on viral infectivity was shown to be a cell-mediated event requiring protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell J. L., Stites D. P., Fudenberg H. H. Human chorionic gonadotropin: effects of crude and purified preparations on lymphocyte responses to phytohemagglutinin and allogenenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1249–1253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Lembach K. J., Morrison M. M., Cohen S. Characterization of the binding of 125-I-labeled epidermal growth factor to human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4297–4304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G. Human epidermal growth factor: isolation and chemical and biological properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1317–1321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geder L. Evidence for early nuclear antigens in cytomegalovirus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Aug;32(2):315–319. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-2-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Zimmerman J., St Jeor S., Rapp F. Demonstration of a cellular inhibitor of Epstein-Barr and cytomegalovirus synthesis. Virology. 1975 Mar;64(1):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90103-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Rousseau W. E., Noble G. R., Steward J. A., Chin T. D. Association of cervical cytomegaloviruses with venereal disease. N Engl J Med. 1973 May 3;288(18):932–934. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197305032881803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loke Y. W., Pepys M. B. Effects of human chorionic gonadotropin preparations on complement in vitro. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Jan 1;121(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(75)90971-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery R., Youngblood L., Medearis D. N., Jr Recovery of cytomegalovirus from the cervix in pregnancy. Pediatrics. 1972 Apr;49(4):524–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numazaki Y., Yano N., Morizuka T., Takai S., Ishida N. Primary infection with human cytomegalovirus: virus isolation from healthy infants and pregnant women. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Apr;91(4):410–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Jeor S., Rapp F. Cytomegalovirus replication in cells pretreated with 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):986–990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.986-990.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Reynolds D., Tsiantos A., Fuccillo D. A., Smith R., Tiller M., Alford C. A., Jr Cervical cytomegalovirus excretion in pregnant and nonpregnant women: suppression in early gestation. J Infect Dis. 1975 May;131(5):522–527. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.5.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey R. H., Cohen S., Orth D. N. Epidermal growth factor: identification of a new hormone in human urine. Science. 1975 Sep 5;189(4205):800–802. doi: 10.1126/science.1172293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulchinsky D., Hobel C. J. Plasma human chorionic gonadotropin, estrone, estradiol, estriol, progesterone, and 17 alpha-hydroxyprogesterone in human pregnancy. 3. Early normal pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1973 Dec 1;117(7):884–893. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(73)90057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. B., French L. Plaque assay of cytomegalovirus strains of human origin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):253–258. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]