Abstract
The fate of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) constituents was determined in the isolated perfused rat heart. VLDL was labeled with [14C]palmitate, 32P-phospholipids, [3H] cholesterol, and 125I-apolipoprotein C (apoC). Perfusions were performed with an albumin-containing buffer and without plasma. Radioactivity was followed in fractions of d < 1.019, d 1.019-1.04, d 1.04-1.21, and d > 1.21 g/ml, prepared by ultracentrifugation.
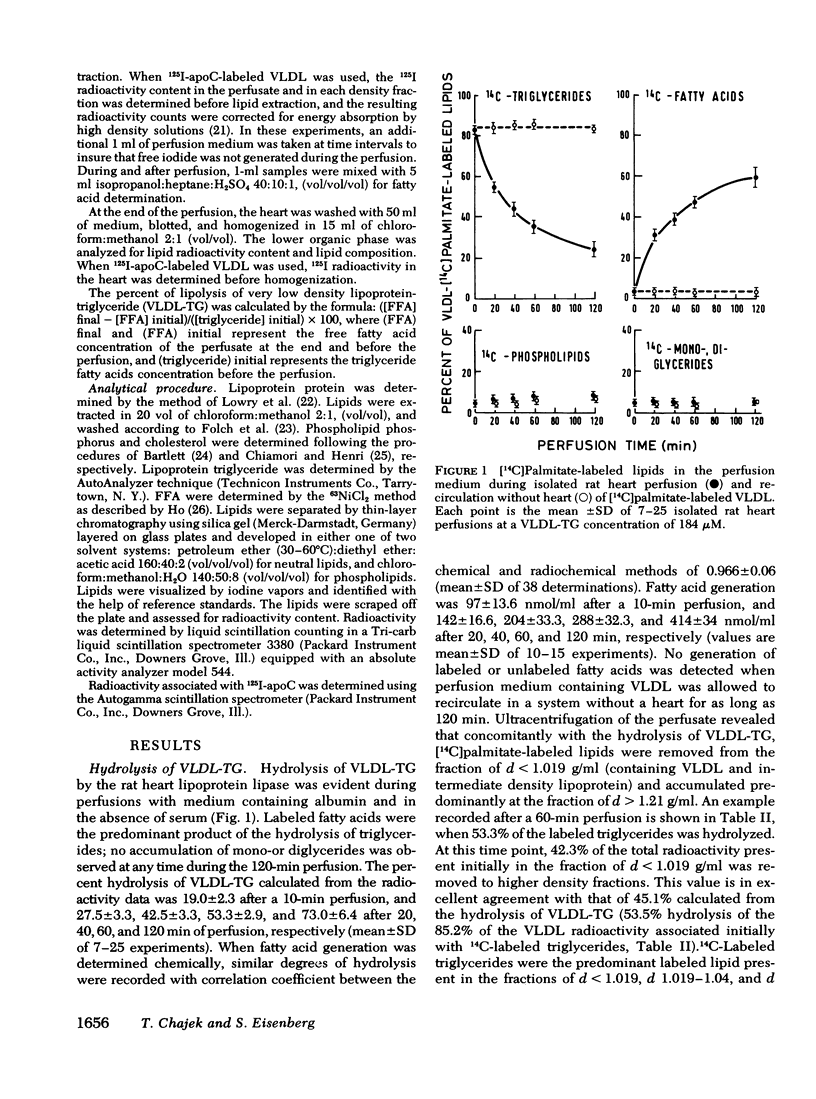
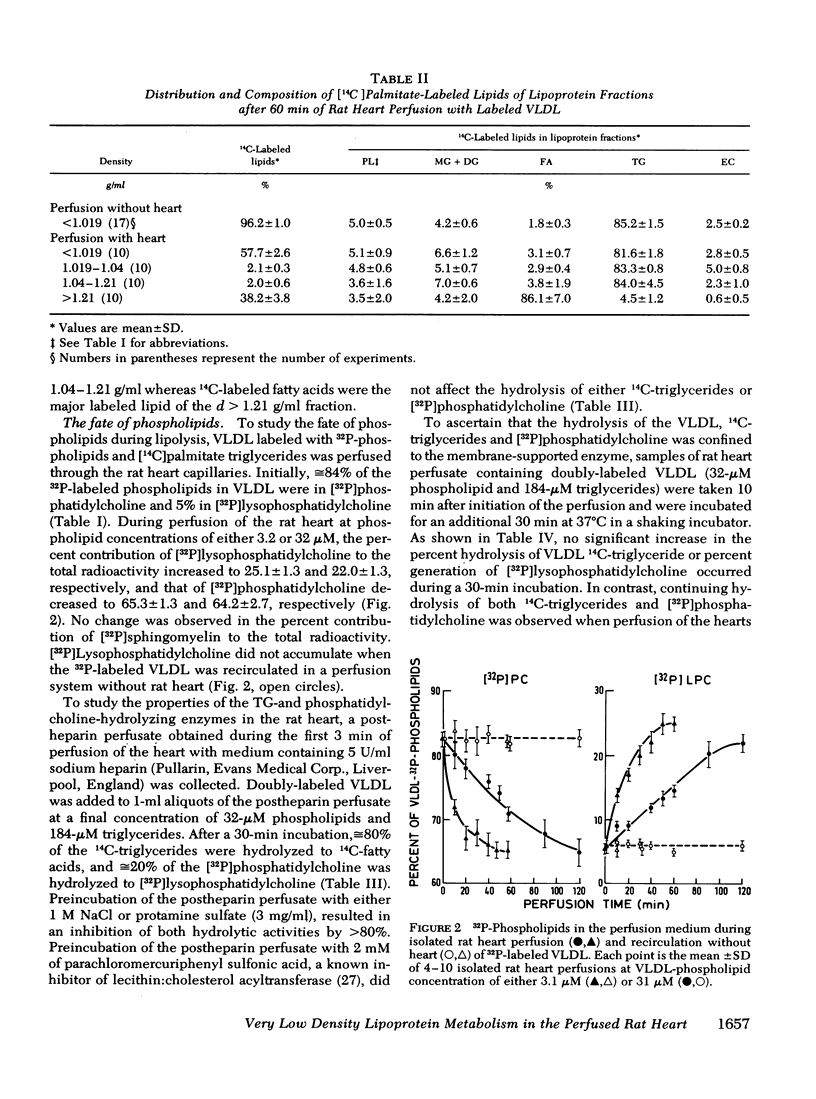
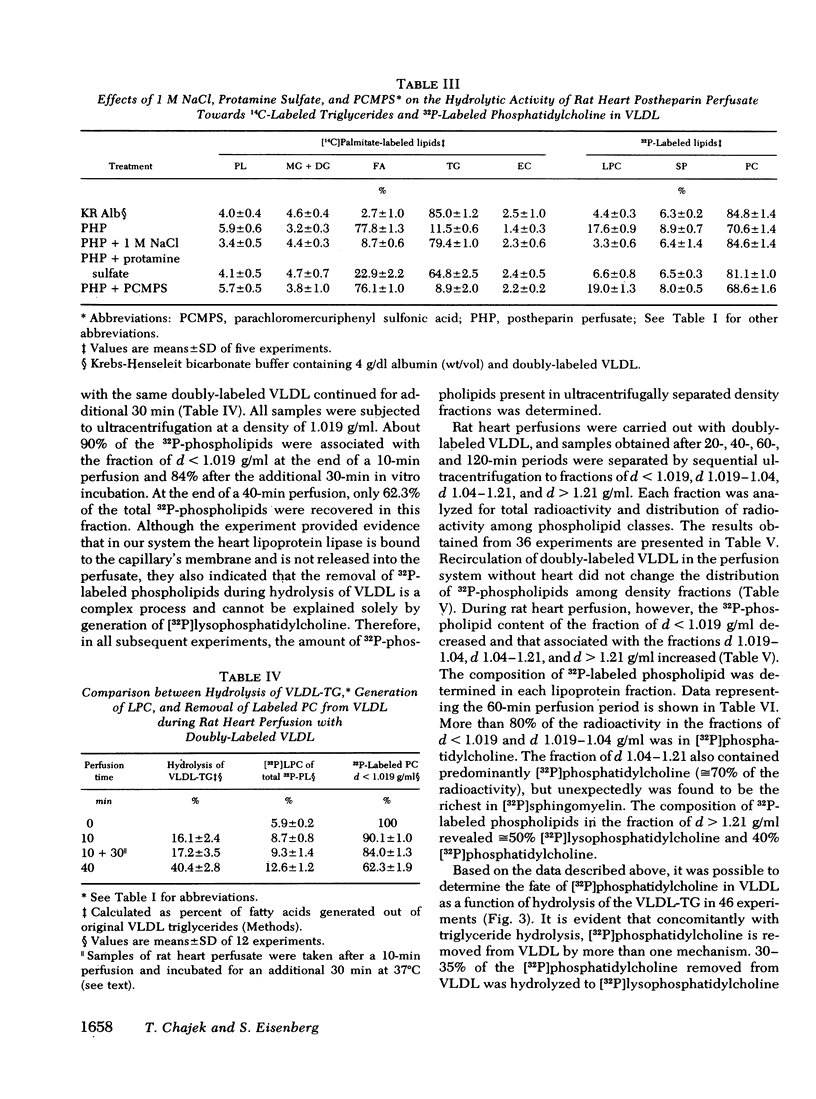
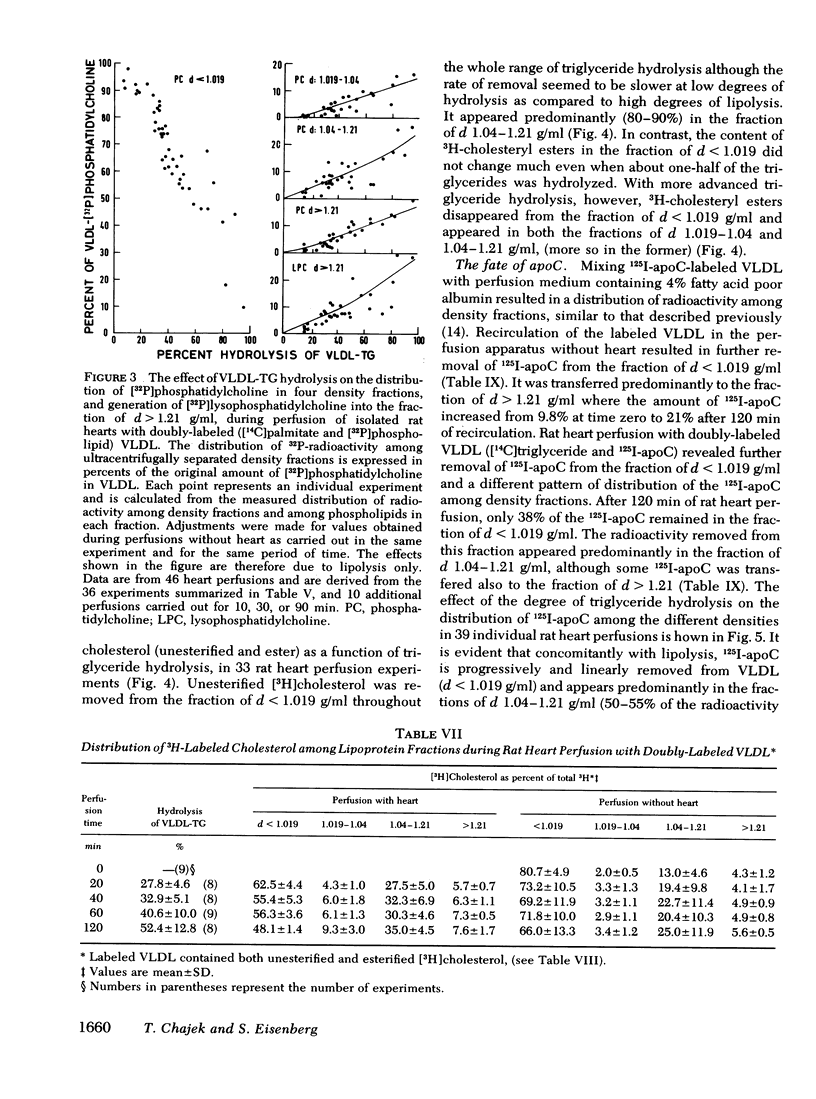
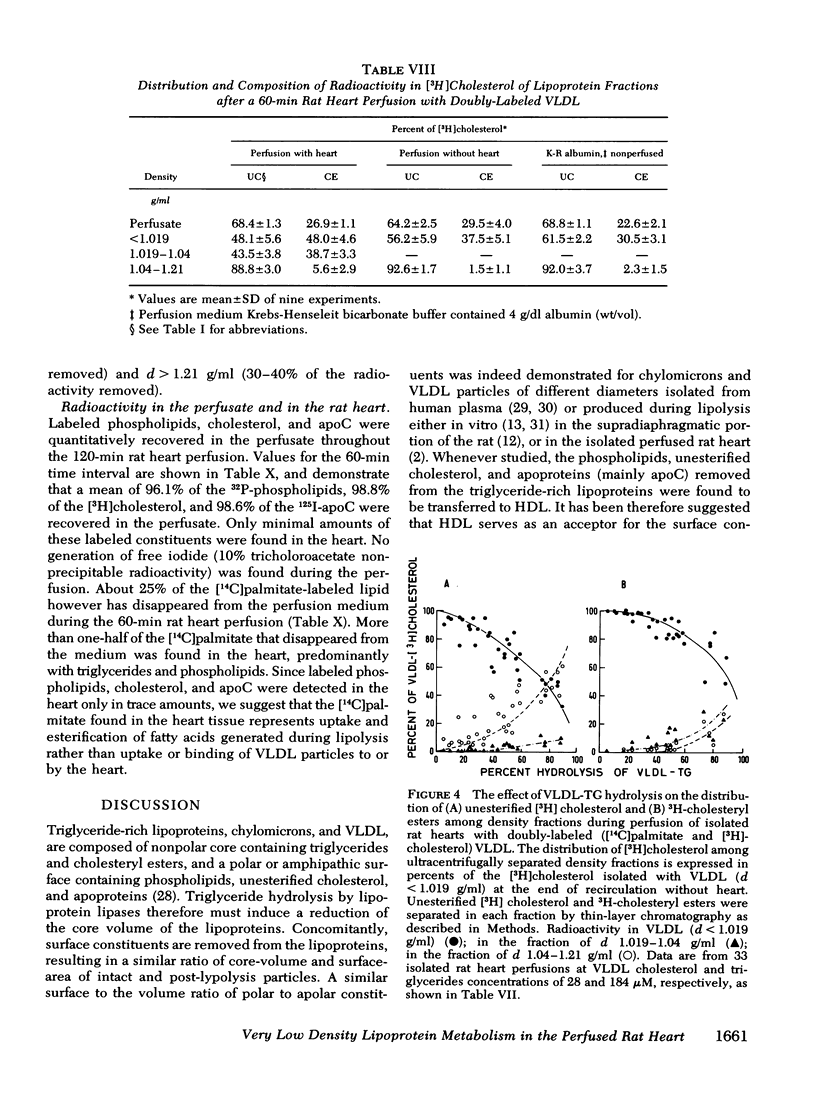
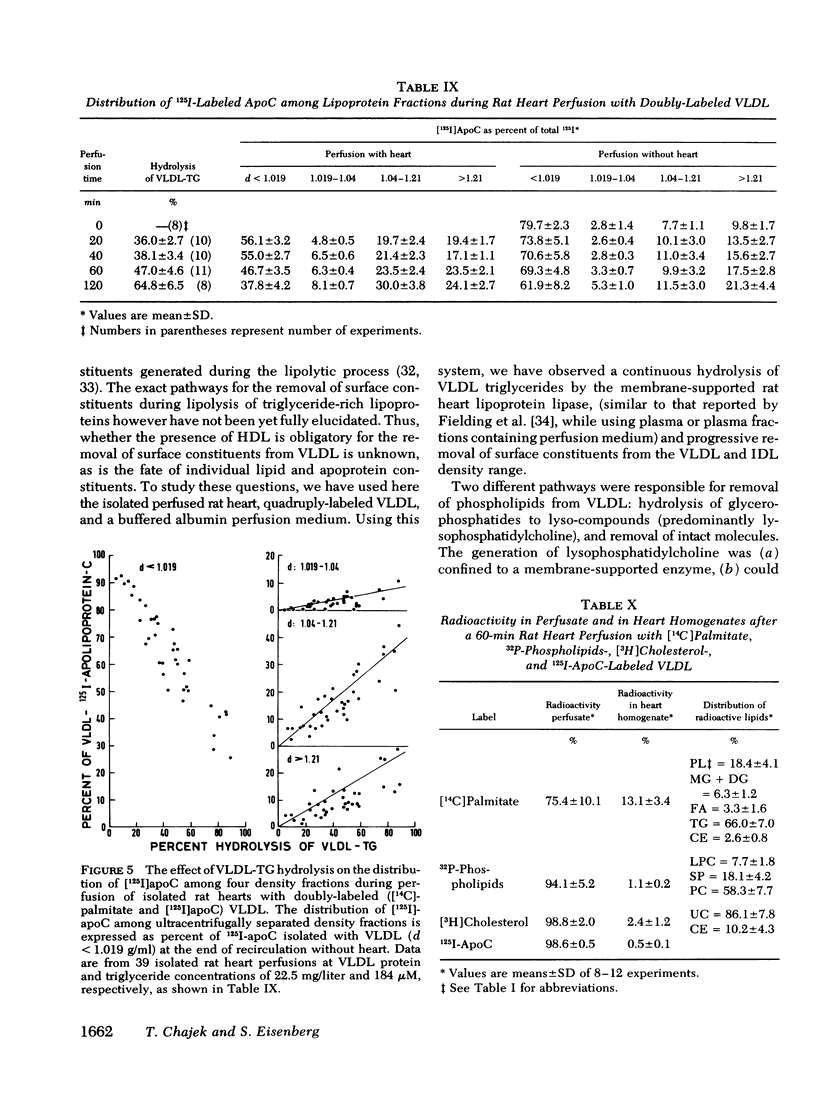
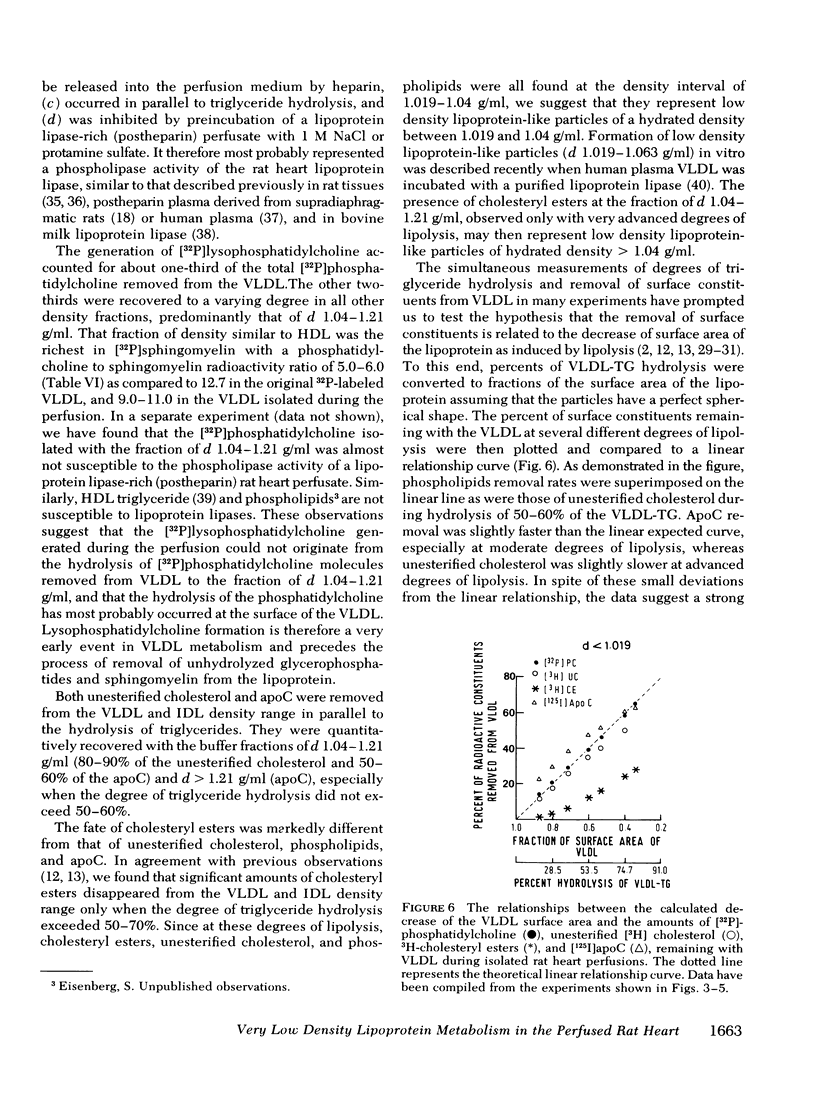
VLDL triglycerides were progressively hydrolyzed to fatty acids (10-120-min perfusions). Concomitantly, phospholipids, cholesterol (predominantly unesterified), and apoC were removed from the VLDL to all other fractions. About 30-35% of the phosphatidylcholine was hydrolized to lysophosphatidylcholine and was recovered at d > 1.21 g/ml. The phosphatidylcholine-and triglyceride-hydrolyzing activities were confined to membrane supported enzyme(s). The other 60-65% of the phosphatidylcholine was removed unhydrolyzed and was found in fractions of d 1.019-1.04 (10-15%), d 1.04-1.21 (25-30%), and d > 1.21 g/ml (15-20%). [32P]Sphingomyelin accumulated at the fraction of d 1.04-1.21 g/ml. Unesterified cholesterol was found in the fraction of d 1.04-1.21 g/ml. ApoC was recovered predominantly in fractions of d 1.04-1.21 (50-60%) and d > 1.21 g/ml (30-40%). Cholesteryl esters were associated with VLDL during the hydrolysis of 50-70% of the triglycerides, but with advanced lipolysis, appeared in higher densities, mainly d 1.019-1.04 g/ml.
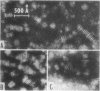
The fraction of d 1.04-1.21 g/ml, (containing phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, unesterified cholesterol, and apoC) contained by negative staining, many disk-like structures.
The study demonstrated that removal of surface constituents (phospholipids, unesterified cholesterol, and apoC) during lipolysis of VLDL is an intrinsic feature of the lipolytic process, and is independent of the presence of plasma. It also indicated that surface constituents may be removed in a particulated form.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assmann G., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Forte T. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein in Tangier Diesase. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):242–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilheimer D. W., Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. The metabolism of very low density lipoprotein proteins. I. Preliminary in vitro and in vivo observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 21;260(2):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIAMORI N., HENRY R. J. Study of the ferric chloride method for determination of total cholesterol and cholesterol esters. Am J Clin Pathol. 1959 Apr;31(4):305–309. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/31.4.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Bilheimer D. W., Levy R. I., Lindgren F. T. On the metabolic conversion of human plasma very low density lipoprotein to low density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):361–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90138-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1975;13:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Interaction of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein with lipoprotein lipase-rich (postheparin) plasma. J Lipid Res. 1975 Sep;16(5):341–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Metabolism of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. I. Fate in circulation of the whole lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):378–390. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Rachmilewitz D. Metabolism of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein. II. Fate in circulation of apoprotein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):391–405. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Schurr D. Phospholipid removal during degradation of rat plasma very low density lipoprotein in vitro. J Lipid Res. 1976 Nov;17(6):578–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Stein O., Stein Y. Radioiodinated lipoproteins: absorption of 125I radioactivity by high density solutions. J Lipid Res. 1975 Nov;16(6):468–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Higgins J. M. Lipoprotein lipase: comparative properties of the membrane-supported and solubilized enzyme species. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4324–4330. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase: evidence for high- and low-affinity enzyme sites. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 24;15(4):879–884. doi: 10.1021/bi00649a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P. E., Shore V. G., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Isolation and characterization of a second enzyme species from postheparin plasma. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1896–1900. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fixler D. E., Watson J. T., Wheeler J. M., Willerson J. T. Effect of hypertonic mannitol and isoproterenol on regional coronary flow following right ventriculotomy. Circulation. 1976 Jul;54(1):26–31. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.54.1.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Gong E., Nichols A. V. Interaction by sonication of C-apolipoproteins with lipid: an electron microscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Feb 25;337(2):169–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90199-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T., Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: structure of low and high density lipoproteins as revealed by elctron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1971 May;50(5):1141–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI106586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOMSET J. A. The mechanism of the plasma cholesterol esterification reaction: plasma fatty acid transferase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Nov 19;65:128–135. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glangeaud M. C., Eisenberg S., Olivecrona T. Very low density lipoprotein. Dissociation of apolipoprotein C during lipoprotein lipase induced lipolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glomset J. A., Norum K. R., Nichols A. V., King W. C., Mitchell C. D., Applegate K. R., Gong E. L., Gjone E. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: effects of dietary manipulation. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1975;142:3–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Blaurock A. E., Sata T. Cholestasis: lamellar structure of the abnormal human serum lipoprotein. Science. 1971 Apr 30;172(3982):475–478. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3982.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamosh M., Hamosh P. Lipoprotein lipase in rat lung. The effect of fasting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 24;380(1):132–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(75)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kashyap M. L. Interchange of apolipoproteins between chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins during alimentary lipemia in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jan;52(1):32–38. doi: 10.1172/JCI107171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Lipoproteins and lipid transport. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;63:37–59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3258-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. M., Fielding C. J. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of formation of triglyceride-rich remnant particles from very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2288–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho R. J. Radiochemical assay of long-chain fatty acids using 63Ni as tracer. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90337-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff H. F., Morrisett J. D., Gotto A. M., Jr Interaction of phosphatidylcholine and apolipoprotein-alanine: electron microscopic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 8;296(3):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa J. C., Levy R. I., Brown W. V., Fredrickson D. S. Changes in high-density lipoprotein protein composition after heparin-induced lipolysis. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):785–791. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossow W. J., Lindgren F. T., Murchio J. C., Stevens G. R., Jensen L. C. Particle size and protein content of six fractions of the Sf 20 plasma lipoproteins isolated by density gradient centrifugation. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):68–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., HENDERSON M. J., REGEN D. M., PARK C. R. Regulation of glucose uptake in muscle. I. The effects of insulin and anoxia on glucose transport and phosphorylation in the isolated, perfused heart of normal rats. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjos O. D., Faergeman O., Hamilton R. L., Havel R. J. Characterization of remnants produced during the metabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins of blood plasma and intestinal lymph in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep;56(3):603–615. doi: 10.1172/JCI108130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipid-protein interactions in the plasma lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 9;472(2):93–133. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norum K. R., Glomset J. A., Nichols A. V., Forte T., Albers J. J., King W. C., Mitchell C. D., Applegate K. R., Gong E. L., Cabana V. Plasma lipoproteins in familial lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase deficiency: effects of incubation with lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase in vitro. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1975;142:31–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykälistö O. J., Vogel W. C., Bierman E. L. The tissue distribution of triacylglycerol lipase, monoacylglycerol lipase and phospholipase A in fed and fasted rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 18;369(2):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quarfordt S. H., Oelschlaeger H., Krigbaum W. R. Liquid crystalline lipid in the plasma of humans with biliary obstruction. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):1979–1988. doi: 10.1172/JCI107004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redgrave T. G. Formation of cholesteryl ester-rich particulate lipid during metabolism of chylomicrons. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):465–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI106255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN O., STEIN Y. METABOLISM OF FATTY ACIDS IN THE ISOLATED PERFUSED RAT HEART. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Oct 22;70:517–530. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90790-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scow R. O., Egelrud T. Hydrolysis of chylomicron phosphatidylcholine in vitro by lipoprotein lipase, phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 22;431(3):538–549. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M. H., Sata T., Havel R. J. The significance of lipoprotein lipase in rat skeletal muscles. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve F. J., Zieve L. Post-heparin phospholipase and post-heparin lipase have different tissue origins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 28;47(6):1480–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90239-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]