Abstract
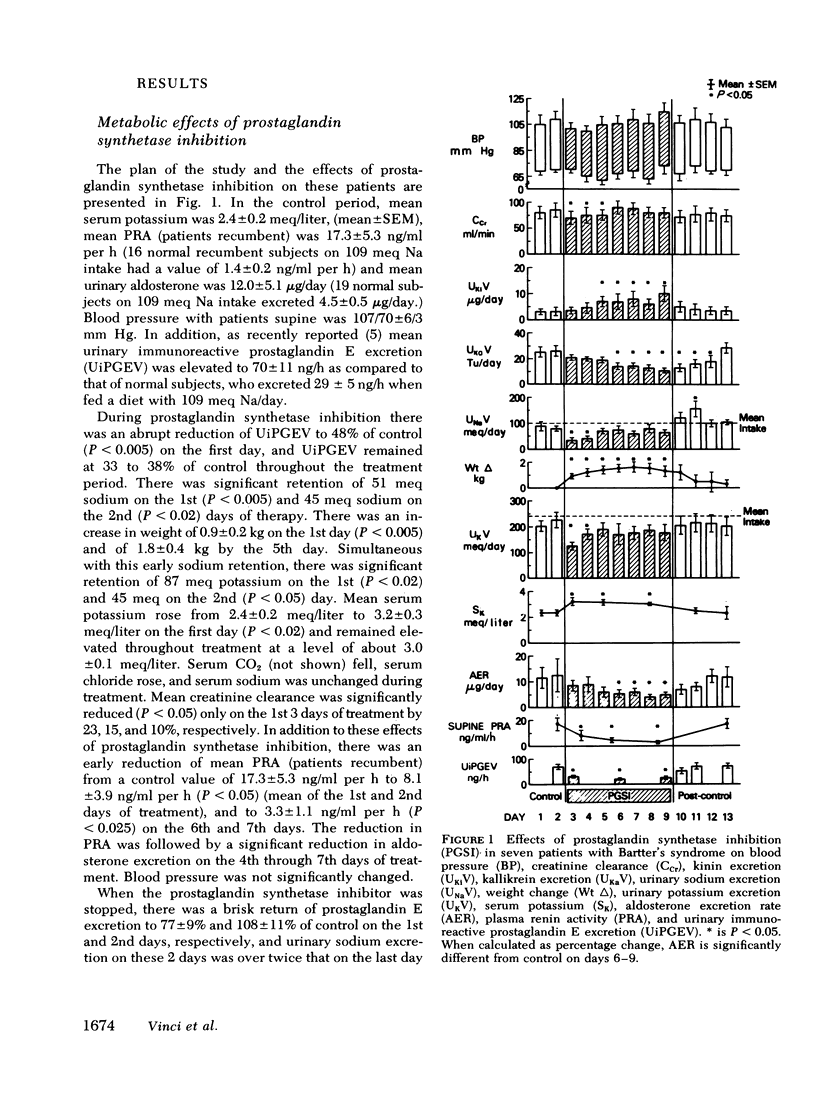
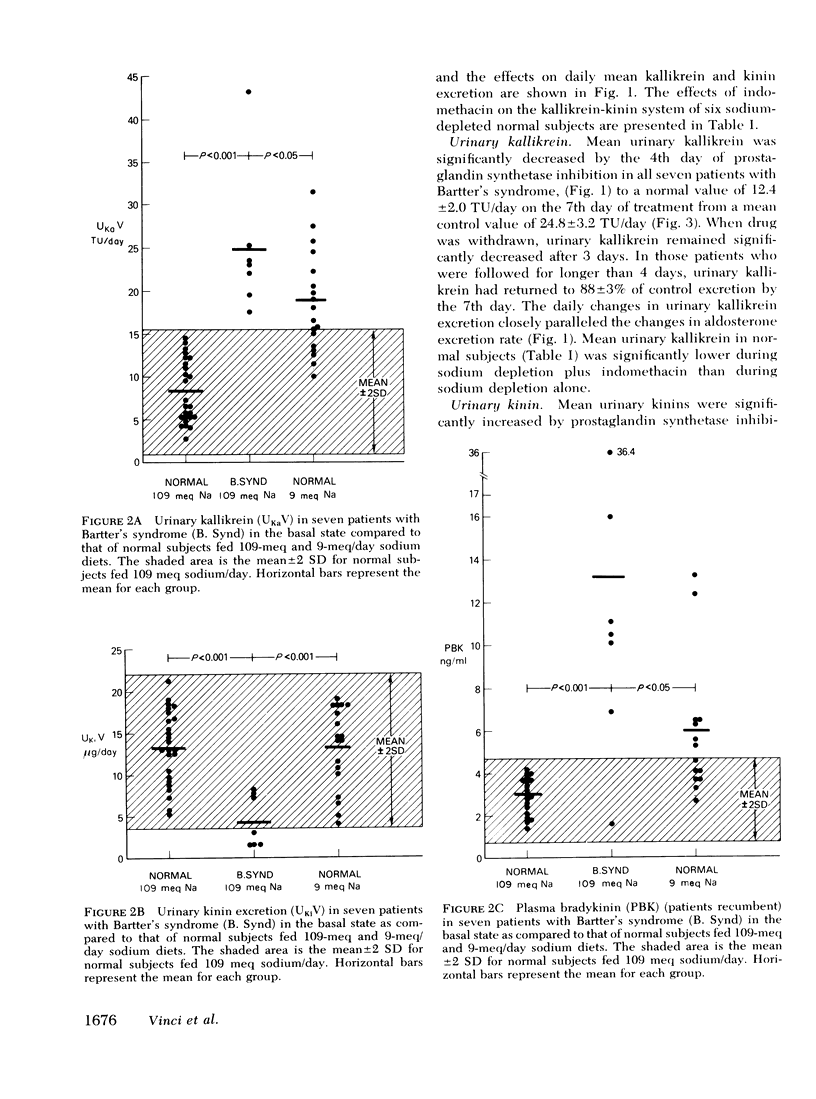
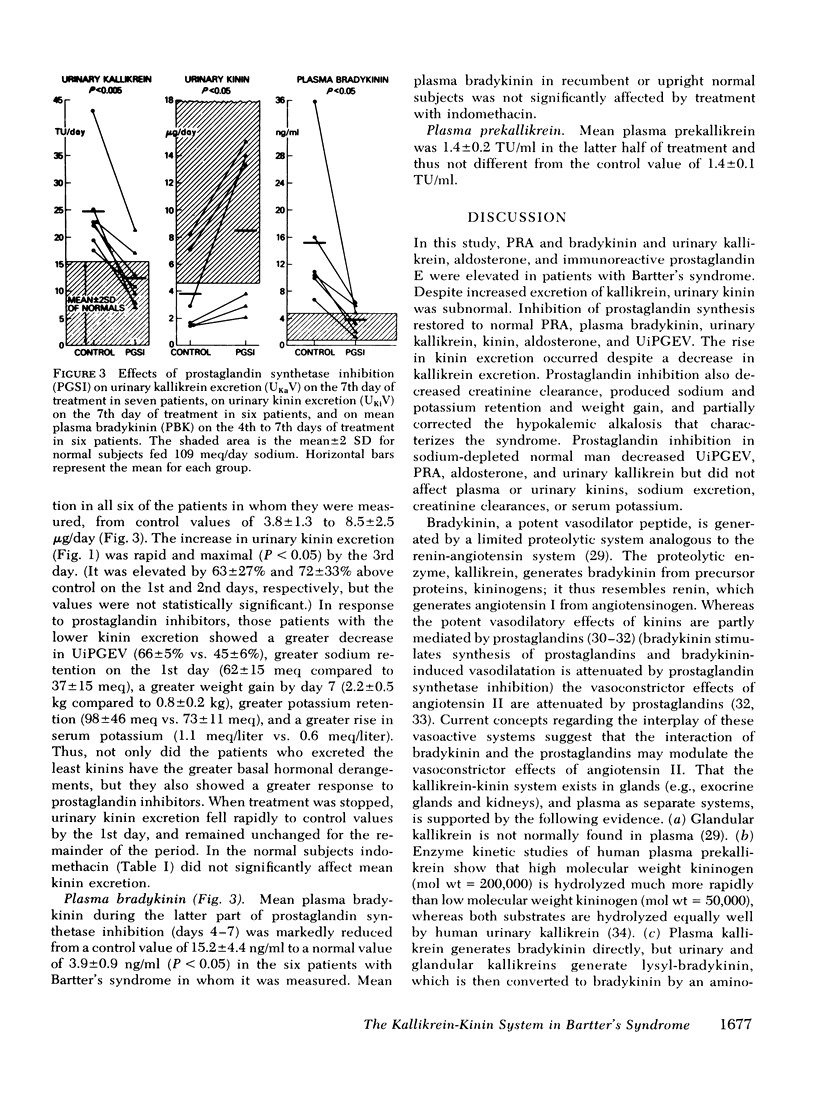
The kallikrein-kinin system was characterized in seven patients with Bartter's syndrome on constant metabolic regimens before, during, and after treatment with prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors. Patients with Bartter's syndrome had high values for plasma bradykinin, plasma renin activity (PRA), urinary kallikrein, urinary immunoreactive prostaglandin E excretion, and urinary aldosterone; urinary kinins were subnormal and plasma prekallikrein was normal. Treatment with indomethacin or ibuprofen which decreased urinary immunoreactive prostaglandin E excretion by 67%, decreased mean PRA (patients recumbent) from 17.3±5.3 (S.E.M.) ng/ml per h to 3.3±1.1 ng/ml per h, mean plasma bradykinin (patients recumbent) from 15.4±4.4 ng/ml to 3.9±0.9 ng/ml, mean urinary kallikrein excretion from 24.8±3.2 tosyl-arginine-methyl ester units (TU)/day to 12.4±2.0 TU/day, but increased mean urinary kinin excretion from 3.8±1.3 μg/day to 8.5±2.5 μg/day. Plasma prekallikrein remained unchanged at 1.4 TU/ml. Thus, with prostaglandin synthetase inhibition, values for urinary kallikrein and kinin and plasma bradykinin returned to normal pari passu with changes in PRA, in aldosterone, and in prostaglandin E. The results suggest that, in Bartter's syndrome, prostaglandins mediate the low urinary kinins and the high plasma bradykinin, and that urinary kallikrein, which is aldosterone dependent, does not control kinin excretion. The high plasma bradykinin may be a cause of the pressor hyporesponsiveness to angiotensin II which characterizes the syndrome.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. W., Vane J. R. Intrarenal prostaglandin release attenuates the renal vasoconstrictor activity of angiotensin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Mar;184(3):678–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alabaster V. A., Bakhle Y. S. The bradykininase activities of extracts of dog lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Apr;47(4):799–807. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTTER F. C., PRONOVE P., GILL J. R., Jr, MACCARDLE R. C. Hyperplasia of the juxtaglomerular complex with hyperaldosteronism and hypokalemic alkalosis. A new syndrome. Am J Med. 1962 Dec;33:811–828. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(62)90214-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACK D. A. K., MILNE M. D. Experimental potassium depletion in man. Clin Sci. 1952 Nov;11(4):397–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaven V. H., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. A sensitive isotopic procedure for the assay of esterase activity: measurement of human urinary kallikrein. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 Mar;32(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden R. E., Gill J. R., Jr, Radfar N., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R. Prostaglandin synthetase inhibitors in Bartter's syndrome. Effect on immunoreactive prostaglandin E excretion. JAMA. 1978 Jan 9;239(2):117–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L. Postglomerular vascular protein concentration: evidence for a causal role in governing fluid reabsorption and glomerulotublar balance by the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):336–349. doi: 10.1172/JCI106501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Scicli A. G. Renal kallikrein: its localization and possible role in renal function. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):194–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorer F. E., Kahn J. R., Lentz K. E., Levine M., Skeggs L. T. Hydrolysis of bradykinin by angiotensin-converting enzyme. Circ Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):824–827. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.6.824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichman M. P., Telfer N., Zia P., Speckart P., Golub M., Rude R. Role of prostaglandins in the pathogenesis of Bartter's syndrome. Am J Med. 1976 May 31;60(6):785–797. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. R., Jr, Frölich J. C., Bowden R. E., Taylor A. A., Keiser H. R., Seyberth H. W., Oates J. A., Bartter F. C. Bartter's syndrome: a disorder characterized by high urinary prostaglandins and a dependence of hyperreninemia on prostaglandin synthesis. Am J Med. 1976 Jul;61(1):43–51. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halushka P. V., Wohltmann H., Privitera P. J., Hurwitz G., Margolius H. S. Bartter's syndrome: urinary prostaglandin E-like material and kallikrein; indomethacin effects. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):281–286. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Keiser H. R., Pisano J. J. Origin and content of methionyl-lysyl-bradykinin, lysyl-bradykinin and bradykinin in human urine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Nov 15;25(22):2499–2503. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen S. Substrates for plasma kinin-forming enzymes in human, dog and rabbit plasmas. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Feb;26(2):403–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01920.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khuri R. N., Strieder W. N., Giebisch G. Effects of flow rate and potassium intake on distal tubular potassium transfer. Am J Physiol. 1975 Apr;228(4):1249–1261. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.228.4.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechi A., Covi G., Lechi C., Mantero F., Scuro L. A. Urinary kallikrein excretion in Bartter's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1175–1178. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALNIC G., KLOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF RENAL POTASSIUM EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:674–686. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Geller R. G., Alexander R. W., Gill J. R., Jr, Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in normal man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):812–819. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Relationships among urinary kallikrein, mineralocorticoids and human hypertensive disease. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):203–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolius H. S., Horwitz D., Pisano J. J., Keiser H. R. Urinary kallikrein excretion in hypertensive man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium-retaining steroids. Circ Res. 1974 Dec;35(6):820–825. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.6.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martino J. A., Earley L. E. Demonstraton of a role of physical factors as determinants of the natriuretic response to volume expansion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Dec;46(12):1963–1978. doi: 10.1172/JCI105686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C. Bartter's syndrome results from an imbalance of vasoactive hormones. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):369–372. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Itskovitz H. D., Terragno A., Wong P. Y. Modulation and mediation of the action of the renal kallikrein-kinin system by prostaglandins. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGiff J. C., Terragno N. A., Malik K. U., Lonigro A. J. Release of a prostaglandin E-like substance from canine kidney by bradykinin. Circ Res. 1972 Jul;31(1):36–43. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.1.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messina E. J., Weiner R., Kaley G. Inhibition of bradykinin vasodilation and potentiation of norepinephrine and angiotensin vasoconstriction by inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis in skeletal muscle of the rat. Circ Res. 1975 Oct;37(4):430–437. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.4.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Colina-Chourio J. Interaction of mineralocorticoids, renal prostaglandins and the renal kallikrein-kinin system. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):189–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasjletti A., Colina-Chourio J., McGiff J. C. Disappearance of bradykinin in the renal circulation of dogs. Effects of kininase inhibition. Circ Res. 1975 Jul;37(1):59–65. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Marshall G. R., Sobel B. E. Hormone interactions in the isolated rabbit heart. Synthesis and coronary vasomotor effects of prostaglandins, angiotensin, and bradykinin. Circ Res. 1975 Dec;37(6):802–808. doi: 10.1161/01.res.37.6.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby L., Flamenbaum W., Lentz R., Ramwell P. Prostaglandins and aspirin therapy in Bartter's syndrome. Lancet. 1976 Sep 18;2(7986):604–606. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90669-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nustad K., Vaaje K., Pierce J. V. Synthesis of kallikreins by rat kidney slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Feb;53(2):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oparil S., Carone F. A., Pullman T. N., Nakamura S. Inhibition of proximal tubular hydrolysis and reabsorption of bradykinin by peptides. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):743–748. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, VANGIESEN G., KIIL F., SELDIN D. W. INFLUENCE OF EXPANSION OF EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME ON TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM INDEPENDENT OF CHANGES IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE AND ALDOSTERONE ACTIVITY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:341–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI104919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Bühler F. R., Laragh J. H., Manning E. L., Brunner H. R. Aldosterone excretion. Physiological variations in man measured by radioimmunoassay or double-isotope dilution. Circ Res. 1972 Sep;31(3):367–378. doi: 10.1161/01.res.31.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B., Kokko J. P. Inhibition of sodium transport by prostaglandin E2 across the isolated, perfused rabbit collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1099–1104. doi: 10.1172/JCI108733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayasu H., Aso Y., Nakauchi K., Kawabe K. A case of Bartter's syndrome with surgical treatment followed for four years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Jun;32(6):842–845. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-6-842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talamo R. C., Haber E., Austen K. F. A radioimmunoassay for bradykinin in plasma and synovial fluid. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Nov;74(5):816–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terragno D. A., Crowshaw K., Terragno N. A., McGiff J. C. Prostaglandin synthesis by bovine mesenteric arteries and veins. Circ Res. 1975 Jun;36(6 Suppl 1):76–80. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.6.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trygstad C. W., Mangos J. A., Bloodworth J. M., Jr, Lobeck C. C. A sibship with Bartter's syndrome: failure of total adrenalectomy to correct the potassium wasting. Pediatrics. 1969 Aug;44(2):234–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verberckmoes R., van Damme B B., Clement J., Amery A., Michielsen P. Bartter's syndrome with hyperplasia of renomedullary cells: successful treatment with indomethacin. Kidney Int. 1976 Mar;9(3):302–307. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman R. M., Keiser H. R. Prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by rabbit renomedullary interstitial cells in tissue culture. Mechanism of stimulation by angiotensin II, bradykinin, and arginine vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2069–2071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


