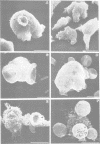
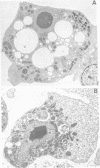
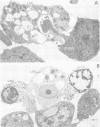
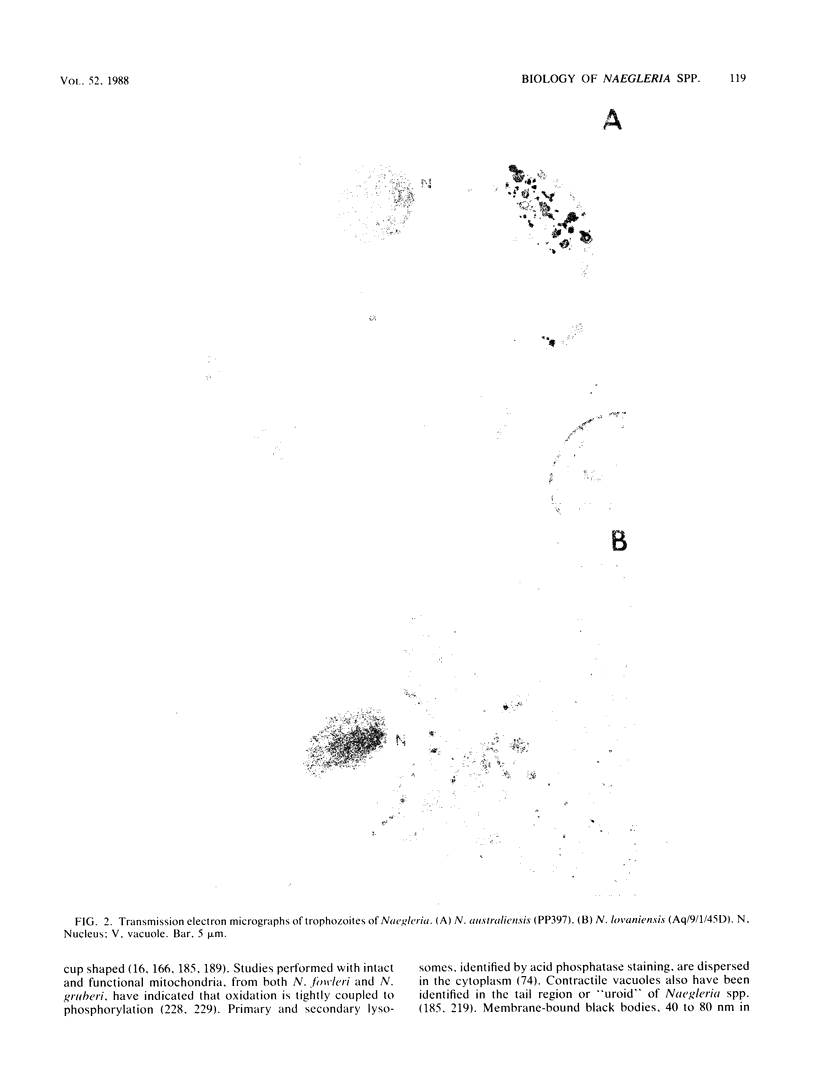
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso P., Zubiaur E. Phagocytic activity of three Naegleria strains in the presence of erythrocytes of various types. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):661–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K., Jamieson A. Agglutination test for the investigation of the genus Naegleria. Pathology. 1972 Oct;4(4):273–278. doi: 10.3109/00313027209068953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averner M., Fulton C. Carbon dioxide: signal for excystment of Naegleria gruberi. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Feb;42(2):245–255. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Band R. N., Balamuth W. Hemin replaces serum as a growth requirement for Naegleria. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):64–65. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.64-65.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biddick C. J., Rogers L. H., Brown T. J. Viability of pathogenic and nonpathogenic free-living amoebae in long-term storage at a range of temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):859–860. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.859-860.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Inhibition by amoeba-specific antiserum and by cytochalasin B of the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):355–362. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Observations by immunofluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy on the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1979 Aug;12(3):363–371. doi: 10.1099/00222615-12-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. Observations by light microscopy on the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri in mouse embryo-cell cultures. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Aug;11(3):249–259. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-3-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt C. G., Baro C., Knorr R. W. Naegleria (sp.) identified in amebic encephalitis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968 Nov;50(5):568–574. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/50.5.568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt C. G. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jun 30;274(26):1473–1476. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196606302742605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULBERTSON C. G., SMITH J. W., COHEN H. K., MINNER J. R. Experimental infection of mice and monkeys by Acanthamoeba. Am J Pathol. 1959 Jan-Feb;35(1):185–197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CULBERTSON C. G., SMITH J. W., MINNER J. R. Acanthamoeba: observations on animal pathogenicity. Science. 1958 Jun 27;127(3313):1506–1506. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3313.1506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariou M. L., Pernin P. First evidence for diploidy and genetic recombination in free-living amoebae of the genus naegleria on the basis of electrophoretic variation. Genetics. 1987 Feb;115(2):265–270. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Description of a Naegleria sp. isolated from two cases of primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis, and of the experimental pathological changes induced by it. J Pathol. 1970 Apr;100(4):217–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711000402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis. An appraisal of present knowledge. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1972;66(2):193–213. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(72)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. F. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis: clinical, pathological and epidemiological features of six fatal cases. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):1–25. doi: 10.1002/path.1700960102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L. Amoebic meningoencephalitis: axenic culture of Naegleria. Science. 1969 Feb 7;163(3867):576–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L., Kramár J. Antigenic relationships among several limax amoebae isolates assessed with the indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFAT). Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1973;20(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L. Naegleria fowleri: trimethoprim sensitivity. Science. 1980 Sep 26;209(4464):1541–1541. doi: 10.1126/science.7433975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerva L. Spontaneous occurrence of antibodies against pathogenic amoebae of the limax group in domestic animals. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1981;28(2):105–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. L., Healy G. R., McCabe L., Shumaker J. B., Schultz M. G. A strain of pathogenic Naegleria isolated from a human nasal swab. Health Lab Sci. 1975 Jan;12(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. L. Pathogenesis of pathogenic Naegleria amoeba. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1979;26(3):195–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. L. Resistance of pathogenic Naegleria to some common physical and chemical agents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):368–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.368-375.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary S. F., Marciano-Cabral F. Activated macrophages demonstrate direct cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, and enhanced binding of Naegleria fowleri amoebae. Cell Immunol. 1986 Mar;98(1):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90273-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary S. F., Marciano-Cabral F. Soluble amoebicidal factors mediate cytolysis of Naegleria fowleri by activated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1986 Aug;101(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M., Carchman R., Marciano-Cabral F. Movement of Naegleria fowleri stimulated by mammalian cells in vitro. J Protozool. 1986 Feb;33(1):10–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05547.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M., Marciano-Cabral F., Bradley S. G. Comparison of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi cultivated in the same nutrient medium. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corff S., Yuyama S. Cessation of nuclear DNA synthesis in differentiating Naegleria. J Protozool. 1976 Nov;23(4):587–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson C. G., Ensminger P. W., Overton W. M. Pathogenic Naegleria sp.--study of a strain isolated from human cerebrospinal fluid. J Protozool. 1968 May;15(2):353–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson C. G. The pathogenicity of soil amebas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:231–254. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Culbertson C. G. Immunoperoxidase staining of trophozoites in primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Lancet. 1976 Aug 28;2(7983):479–479. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A. Effect of disinfectants on pathogenic free-living amoebae: in axenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):62–66. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.62-66.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A., Moriarty K. M., Till D. Immunity to pathogenic free-living amoebae: role of cell-mediated immunity. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):408–410. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.408-410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A., Moriarty K. M., Till D. Immunity to pathogenic free-living amoebae: role of humoral antibody. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.401-407.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J., Keys E. A. Virulence of pathogenic free-living amebae. J Parasitol. 1978 Aug;64(4):744–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Brown T. J. Use of cell cultures as an indicator of pathogenicity of free-living amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cursons R. T., Keys E. A., Brown T. J., Learmonth J., Campbell C., Metcalf P. IgA and primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):223–224. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daggett P. M., Nerad T. A. The biochemical identification of vahlkampfiid amoebae. J Protozool. 1983 Feb;30(1):126–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb01045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das S., Saha A. K., Nerad T. A., Martinez A. J., Lamarco K. L., Basu A., Legler G., Glew R. H. Partial purification and characterization of Naegleria fowleri beta-glucosidase. J Protozool. 1987 Feb;34(1):68–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03134.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F., Aerts M., Martinez A. J. Naegleria australiensis: experimental meningoencephalitis in mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(5):712–716. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F., Dierickx P. J. Determination of acid phosphatase and leucine amino peptidase activity as an identification method for pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1982;76(6):773–775. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90104-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F. Isoenzyme patterns of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Naegleria spp. using agarose isoelectric focusing. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):319–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. F., Pernin P., Scaglia M., Michel R. A comparative study of 14 strains of Naegleria australiensis demonstrates the existence of a highly virulent subspecies: N. australiensis italica n. spp. J Protozool. 1984 May;31(2):324–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J., Van Dijck P., Van de Voorde H. The effect of thermal pollution on the distribution of Naegleria fowleri. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):7–13. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J., van de Voorde H. Differences in destruction of cysts of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria and Acanthamoeba by chlorine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):294–297. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.294-297.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre J. M., Oger C. Naegleria fowleri and heated aquatic environments: a possible mechanism. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1981 Dec;61(4):441–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempe S., Martinez A. J., Janitschke K. Subacute and chronic meningoencephalitis in mice after experimental infection with a strain of Naegleria fowleri originally isolated from a patient. Infection. 1982 Jan;10(1):5–8. doi: 10.1007/BF01640827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley P., Skeels M. R., Sogandares-Bernal F. Delayed type hypersensitivity in guinea pig infected subcutaneously with Naegleria fowleri Carter. Z Parasitenkd. 1976 Apr 30;49(2):133–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00382420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle A. D. Cellular and environmental variables determining numbers of flagella in temperature-shocked Naegleria. J Protozool. 1979 Nov;26(4):604–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle A. D., Fulton C. Development of the flagellar apparatus of Naegleria. J Cell Biol. 1966 Oct;31(1):43–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive D. G., Leclerc H., De Jonckheere J., Delattre J. M. Isolation of Naegleria fowleri from the cooling pond of an electric power plant in France. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jan-Feb;132A(1):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Schuster F. L. An infectious agent associated with amebas of the genus Naegleria. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):327–329. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Schuster F. L. Morphological response of cultured cells to Naegleria amoeba cytopathogenic material. J Cell Sci. 1985 Apr;75:1–16. doi: 10.1242/jcs.75.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Schuster F. L. The nature of a cytopathogenic material present in amebae of the genus Naegleria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 May;26(3):412–421. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. P., Rubin A. J., Sproul O. J. Inactivation of Naegleria gruberi cysts by chlorinated cyanurates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1157-1162.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Smyth C. Mitogenicity of Naegleria fowleri extract for murine T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1984 Mar;51(3):461–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Antibody induced capping and endocytosis of surface antigens in Naegleria fowleri. Int J Parasitol. 1979 Dec;9(6):599–601. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(79)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler M., Carter R. F. Acute pyogenic meningitis probably due to Acanthamoeba sp.: a preliminary report. Br Med J. 1965 Sep 25;2(5464):740–742. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5464.734-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke E. D., Mackiewicz J. S. Isolation of Acanthamoeba and Naegleria from the intestinal contents of freshwater fishes and their potential pathogenicity. J Parasitol. 1982 Feb;68(1):164–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulford D. E., Bradley S. G., Marciano-Cabral F. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri for cultured rat neuroblastoma cells. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):176–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulford D. E., Marciano-Cabral F. Cytolytic activity of Naegleria fowleri cell-free extract. J Protozool. 1986 Nov;33(4):498–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C. Cell differentiation in Naegleria gruberi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:597–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.003121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C., Cheng K. L., Lai E. Y. Two calmodulins in Naegleria flagellates: characterization, intracellular segregation, and programmed regulation of mRNA abundance during differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1671–1678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C., Dingle A. D. Basal bodies, but not centrioles, in Naegleria. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):826–836. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C., Guerrini A. M. Mitotic synchrony in Nalegleria amebae. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Aug;56(2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C., Lai E. Y., Lamoyi E., Sussman D. J. Naegleria actin elicits species-specific antibodies. J Protozool. 1986 Aug;33(3):322–327. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton C. Macromolecular syntheses during the quick-change act of Naegleria. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):192–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner P. R., Miller R. H., Marsh M. C. Studies of the rhizoplast from Naegleria gruberi. J Cell Sci. 1981 Feb;47:277–293. doi: 10.1242/jcs.47.1.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. L. Temperature tolerance of pathogenic and nonpathogenic free-living amoebas. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):869–870. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. L. The pathogenic amoeboflagellate Naegleria fowleri: environmental isolations, competitors, ecologic interactions, and the flagellate-empty habitat hypothesis. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavo dos Santos Neto Fatal primary amebic meningoencephalitis. A retrospective study in Richmond, Virginia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1970 Nov;54(5):737–742. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/54.5.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadaś E., Kasprzak W., Mazur T. Electrophoretic characterization of small free-living Amoebae. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1977 Mar;28(1):35–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Innate resistance of mice to experimental infection with Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):73–77. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.73-77.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty R. M., John D. T. Serum agglutination and immunoglobulin levels of mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1982 Feb;29(1):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1982.tb02892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook T. W., Boackle R. J., Parker B. W., Vesely J. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.58-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hysmith R. M., Franson R. C. Degradation of human myelin phospholipids by phospholipase-enriched culture media of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 14;712(3):698–701. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90300-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hysmith R. M., Franson R. C. Elevated levels of cellular and extracellular phospholipases from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 15;711(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A., Anderson K. A method for the isolation of Naegleria species from water samples. Pathology. 1973 Jan;5(1):55–58. doi: 10.3109/00313027309068969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. Effect of clotrimazole on Naegleria fowleri. J Clin Pathol. 1975 Jun;28(6):446–449. doi: 10.1136/jcp.28.6.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T., Cole T. B., Jr, Bruner R. A. Amebostomes of Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):12–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T., Cole T. B., Jr, Marciano-Cabral F. M. Sucker-like structures on the pathogenic amoeba Naegleria fowleri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):12–14. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.12-14.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T., De Jonckheere J. F. Isolation of Naegleria australiensis from an Oklahoma Lake. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):571–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John D. T. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis and the biology of Naegleria fowleri. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:101–123. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephson S. L., Weik R. R., John D. T. Concanavalin A-induced agglutination of Naegleria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Sep;26(5 Pt 1):856–858. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadlec V. The effects of some factors on the growth and morphology of Naegleria sp. and three strains of the genus Acanthamoeba. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1975;22(4):317–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilvington S., Mann P., Warhurst D. Differentiation between Naegleria fowleri and N. lovaniensis using isoenzyme electrophoresis of aspartate aminotransferase. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(4):562–563. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilvington S., White D. G. Rapid identification of thermophilic Naegleria, including Naegleria fowleri using API ZYM system. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Nov;38(11):1289–1292. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.11.1289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Preston T. M., Miller R. H. Cell-substrate interactions in amoeboid locomotion - a matched reflexion interference and transmission electron microscopy study. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 Aug;7(8):641–649. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. A., Preston T. M., Miller R. H., Grose C. The cell surface in amoeboid locomotion--studies on the role of cell-substrate adhesion. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1982 Sep;6(9):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(82)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston D., Warhurst D. C. Isolation of amoebae from the air. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Feb;2(1):27–36. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Fulton C. Programmed synthesis of tubulin for the flagella that develop during cell differentiation in Naegleria gruberi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2877–2881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. E., Noblet G. P. Seasonal distribution of thermotolerant free-living amoebae. I. Willard's Pond. J Protozool. 1986 Aug;33(3):422–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. E., Noblet G. P. Seasonal distribution of thermotolerant free-living amoebae. II. Lake Issaqueena. J Protozool. 1987 Feb;34(1):10–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03122.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyle D. E., Noblet G. P. Vertical distribution of potentially pathogenic free-living amoebae in freshwater lakes. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):99–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. Y., Walsh C., Wardell D., Fulton C. Programmed appearance of translatable flagellar tubulin mRNA during cell differentiation in Naegleria. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):867–878. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. E., Dingle A. D. Isolation, ultrastructure, and protein composition of the flagellar rootlet of Naegleria gruberi. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):424–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastovica A. J., Dingle A. D. Superprecipitation of an actomyosin-like complex isolated from Naegleria gruberi amoebae. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90686-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastovica A. J. Microfilaments in Naegleria fowleri amoebae. Z Parasitenkd. 1976 Oct 12;50(3):245–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02462969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lastovica A. J. Scanning electron microscopy of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Naegleria cysts. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Apr;4(2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90096-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawande R. V., Abraham S. N., John I., Egler L. J. Recovery of soil Amebas from the nasal passages of children during the dusty harmattan period in Zaria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Feb;71(2):201–203. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawande R. V., Macfarlane J. T., Weir W. R., Awunor-Renner C. A case of primary amebic meningoencephalitis in a Nigerian farmer. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Jan;29(1):21–25. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey D. M., McLaughlin J. A multicomponent hemolytic system in the pathogenic amoeba Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):731–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.731-736.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey D. M., McLaughlin J. Activation of a heat-stable cytolytic protein associated with the surface membrane of Naegleria fowleri. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):478–482. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.478-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey D. M., McLaughlin J. Subcellular distribution of hydrolases in Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1985 Nov;32(4):616–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra S. C., Krishna Prasad B. N., Agarwala S. C., Das S. R. Ultrastructural studies on experimental primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis (PAME) of mouse due to Naegleria aerobia and Hartmannella culbertsoni. Int J Parasitol. 1976 Dec;6(6):489–493. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(76)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J., Lee J. H., Shea D., Walsh C. J. New poly(A)+RNAs appear coordinately during the differentiation of Naegleria gruberi amebae into flagellates. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):353–361. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. M., Bradley S. G. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria gruberi for rat neuroblastoma cell cultures. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1139–1141. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1139-1141.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. M., Fulford D. E. Cytopathology of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria species for cultured rat neuroblastoma cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):1133–1137. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.1133-1137.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F. M., Patterson M., John D. T., Bradley S. G. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi for established mammalian cell cultures. J Parasitol. 1982 Dec;68(6):1110–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F., Cline M. L., Bradley S. G. Specificity of antibodies from human sera for Naegleria species. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):692–697. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.692-697.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F., Cline M. Chemotaxis by Naegleria fowleri for bacteria. J Protozool. 1987 May;34(2):127–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F., John D. T. Cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri for rat neuroblastoma cell cultures: scanning electron microscopy study. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1214–1217. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1214-1217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciano-Cabral F., Stanitski S., Radhakrishna V., Bradley S. G. Characterization of a neutral aminoacyl-peptide hydrolase from Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1987 May;34(2):146–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1987.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. H., Corff S. C., Yuyama S. DNA synthesis during growth and synchronous differentiation of Naegleria. Cytobios. 1982;33(129):29–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A. J. Acanthamoebiasis and immunosuppression. Case report. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1982 Sep;41(5):548–557. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198209000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez A. J., Nelson E. C., Jones M. M., Duma R. J., Rosenblum W. I. Experimental Naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. An electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1971 Nov;25(5):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez A. J. Is Acanthamoeba encephalitis an opportunistic infection? Neurology. 1980 Jun;30(6):567–574. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.6.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muldrow L. L., Tyndall R. L., Fliermans C. B. Application of flow cytometry to studies of pathogenic free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1258-1269.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerad T. A., Daggett P. M. Starch gel electrophoresis: an effective method for separation of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria strains. J Protozool. 1979 Nov;26(4):613–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerad T. A., Visvesvara G., Daggett P. M. Chemically defined media for the cultivation of Naegleria: pathogenic and high temperature tolerant species. J Protozool. 1983 May;30(2):383–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1983.tb02935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Arnold R. R. Equivalent mortality in normal and athymic mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1985 Oct;71(5):678–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Baker R. L., Miller R. D., Arnold R. R. Interactions between Naegleria fowleri and Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):449–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.449-452.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Wilhelm W. E. Effect of exogenous iron on the viability of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in serum. Experientia. 1981 Nov 15;37(11):1160–1162. doi: 10.1007/BF01989894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome A. L., Wilhelm W. E. Inhibition of Naegleria fowleri by microbial iron-chelating agents: ecological implications. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):665–668. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.665-668.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell W. D., Stevens A. R. Quantitative growth of Naegleria in axenic culture. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Apr;25(4):621–627. doi: 10.1128/am.25.4.621-627.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olomu N., Martinez A. J., Lamarco K. L., Nerad T. A., Saha A. K., Das S., Glew R. H. Demonstration of various acid hydrolases and preliminary characterization of acid phosphatase in Naegleria fowleri. J Protozool. 1986 Aug;33(3):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco G., Tulloch G. S. Microfilariae of Dirofilaria striata in a dog. J Parasitol. 1970 Apr;56(2):248–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page F. C. Taxonomic criteria for limax amoebae, with descriptions of 3 new species of Hartmannella and 3 of Vahlkampfia. J Protozool. 1967 Aug;14(3):499–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patras D., Andujar J. J. Meningoencephalitis due to Hartmannella (Acanthamoeba). Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Aug;46(2):226–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Woodworth T. W., Marciano-Cabral F., Bradley S. G. Ultrastructure of Naegleria fowleri enflagellation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):217–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.217-226.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernin P., Bouikhsain I., De Jonckheere J. F., Petavy A. F. Comparative protein patterns of three thermophilic nonpathogenic Naegleria isolates and two Naegleria fowleri strains by isoelectric focusing. Int J Parasitol. 1983 Feb;13(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(83)80059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernin P. Isoenzyme patterns of pathogenic and nonpathogenic thermophilic Naegleria strains by isoelectric focusing. Int J Parasitol. 1984 Oct;14(5):459–465. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(84)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. P. Naegleria: another pathogenic ameba studies in germfree guinea pigs. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1974 Sep;23(5):850–855. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1974.23.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle H. L., Bradley S. G., Harris L. S. Susceptibility of Naegleria fowleri to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):674–679. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. F., Marciano-Cabral F., Bradley D. W., Bradley S. G. Agglutination of Naegleria fowleri and Naegleria gruberi by antibodies in human serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):576–581. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.576-581.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly M. F., White K. L., Jr, Bradley S. G. Host resistance of mice to Naegleria fowleri infections. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):645–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.645-652.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan-Kelly B., Ferrante A., Thong Y. H. Activation of complement by Naegleria. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(3):333–336. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUSTER F. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE AMOEBO-FLAGELLATE, NAEGLERIA GRUBERI (SCHARDINGER). I. THE AMOEBOID AND FLAGELLATE STAGES. J Protozool. 1963 Aug;10:297–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1963.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUSTER F. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY OF THE AMOEBO-FLAGELLATE, NAEGLERIA GRUBERI (SCHARDINGER). II. THE CYST STAGE. J Protozool. 1963 Aug;10:313–320. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1963.tb01682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Clemente J. S. 5-Bromodeoxyuridine-induced formation of virus-like particles in Naegleria gruberi EGs. J Cell Sci. 1977 Aug;26:359–371. doi: 10.1242/jcs.26.1.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Dunnebacke T. H. Development and release of virus-like particles in naegleria gruberi EGS. Cytobiologie. 1976 Dec;14(1):131–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L. Intranuclear virus-like bodies in the amoeboflagellate Naegleria gruberi. J Protozool. 1969 Nov;16(4):724–727. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Rechthand E. In vitro effects of amphotericin B on growth and ultrastructure of the amoeboflagellates Naegleria gruberi and Naegleria fowleri. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):591–605. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Svihla G. Ribonucleoprotein-containing vesicles in cysts of Naegleria gruberi. J Protozool. 1968 Nov;15(4):752–758. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Twomey R. Calcium regulation of flagellation in Naegleria gruberi. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:311–326. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebek Z., Rosický B., Sixl W. The occurrence of babesiasis affecting small terrestrial mammals and the importance of this zoonosis in Europe. Folia Parasitol (Praha) 1977;24(3):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. S., Harmatz P., Visvesvara G. S., Cohen A., Edwards J., Turner J. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1982 Feb 11;306(6):346–348. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198202113060607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simione F. P., Jr, Daggett P. M. Freeze preservation of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria species. J Parasitol. 1976 Feb;62(1):49–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson C. F., Willaert E., Neal F. C., Stevens A. R., Young M. D. Experimental Naegleria fowleri meningoencephalitis in sheep: light and electron microscopic studies. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Jan;43(1):154–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B. N., Das S. R. Studies on pathogenic and non-pathogenic small free-living amoebae and the bearing of nuclear division on the classification of the order amoebida. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Oct 22;259(832):435–476. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smego R. A., Jr, Durack D. T. An experimental model for Naegleria fowleri-induced primary amebic meningoencephalitis in rabbits. J Parasitol. 1984 Feb;70(1):78–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., De Jonckheere J., Willaert E. Naegleria lovaniensis new species: isolation and identification of six thermophilic strains of a new species found in association with Naegleria fowleri. Int J Parasitol. 1980 Feb;10(1):51–64. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(80)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Gallup E. D., Willaert E. Evaluation of membrane-bound black bodies in trophozoites and cysts of Naegleria spp. J Invertebr Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(78)90110-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Stein S. Analyses of Pathogenic and nonpathogenic Acanthamoeba and Naegleria for lectin-induced agglutination. J Parasitol. 1977 Feb;63(1):151–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Lai E. Y., Fulton C. Rapid disappearance of translatable actin mRNA during cell differentiation in Naegleria. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7355–7360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman D. J., Sellers J. R., Flicker P., Lai E. Y., Cannon L. E., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Fulton C. Actin of Naegleria gruberi. Absence of N tau-methylhistidine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7349–7354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. W. Isolation and experimental infection of free-living amebae in freshwater fishes. J Parasitol. 1977 Apr;63(2):232–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tew J. G., Burmeister J., Greene E. J., Pflaumer S. K., Goldstein J. A radioimmunoassay for human antibody specific for microbial antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1977;14(3-4):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Carter R. F., Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B. Site of expression of immunity to Naegleria fowleri in immunized mice. Parasite Immunol. 1983 Jan;5(1):67–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A. Migration patterns of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria spp. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):177–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.177-180.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., O'Keefe D. E. Immunization with culture supernatant in experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1979;73(6):684–685. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(79)90021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A., Rowan-Kelly B., O'Keefe D. Immunization with live amoebae, amoebic lysate and culture supernatant in experimental Naegleria meningoencephalitis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(5):570–576. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thong Y. H., Ferrante A., Shepherd C., Rowan-Kelly B. Resistance of mice to Naegleria meningoencephalitis transferred by immune serum. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(6):650–652. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Domingue E. L. Cocultivation of Legionella pneumophila and free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):954–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.954-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VICKERMAN K. Patterns of cellular organisation in Limax amoebae. An electron microscope study. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Mar;26:497–519. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Callaway C. S. Light and electron microsopic observations on the pathogenesis of Naegleria fowleri in mouse brain and tissue culture. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):239–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Healy G. R. Comparative antigenic analysis of pathogenic and free-living Naegleria species by the gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis techniques. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):95–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.95-108.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Fulton C. Transcription during cell differentiation in Naegleria gruberi. Preferential synthesis of messenger RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 8;312(1):52–71. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. Synthesis and assembly of the cytoskeleton of Naegleria gruberi flagellates. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):449–456. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warhurst D. C., Carman J. A., Mann P. G. Survival of Naegleria fowleri cysts at 4 degrees C for eight months with retention of virulence. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(6):832–832. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R. R., John D. T. Agitated mass cultivation of Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):868–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R. R., John D. T. Cell and mitochondria respiration of Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1979 Oct;65(5):700–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R. R., John D. T. Cell size, macromolecular composition, and O2 consumption during agitated cultivation of Naegleria gruberi. J Protozool. 1977 Feb;24(1):196–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb05306.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weik R. R., John D. T. Macromolecular composition and nuclear number during growth of Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1978 Aug;64(4):746–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Amuso P. T., Chang S. L., Lewis A. L. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Naegleria from Florida lakes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):661–667. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.661-667.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman L. Y., Marciano-Cabral F. Susceptibility of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria spp. to complement-mediated lysis. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2442-2447.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willaert E., Jamieson A., Jadin J. B., Anderson K. Epidemiological and immunoelectrophoretic studies on human and environmental strains of Naegleria fowleri. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1974;54(4-5):333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willaert E. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis. A selected bibliography and tabular survey of cases. Ann Soc Belg Med Trop. 1974;54(4-5):429–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Karr S. L., Jr, Balamuth W. B. Experimental infections with pathogenic free-living amebae in laboratory primate hosts: I (A) A study on susceptibility to Naegleria fowleri. J Parasitol. 1975 Apr;61(2):199–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. M., Karr S. L., Jr, Chow C. K. Changes in the virulence of Naegleria fowleri maintained in vitro. J Parasitol. 1977 Oct;63(5):872–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth T. W., John D. T., Bradley S. G. Biological factors affecting enflagellation of Naegleria fowleri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):803–808. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.803-808.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth T. W., Keefe W. E., Bradley S. G. Characterization of proteins in flagellates and growing amebae of Naegleria fowleri. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1366-1374.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonckheere J., Voorde H. The distribution of Naegleria fowleri in man-made thermal waters. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):10–15. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]