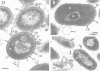
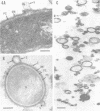
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abiko Y., Hayakawa M., Murai S., Takiguchi H. Glycylprolyl dipeptidylaminopeptidase from Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1985 Feb;64(2):106–111. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640020201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amano A., Tamagawa H., Shizukuishi S., Tsunemitsu A. Superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidases in oral anaerobic bacteria. J Osaka Univ Dent Sch. 1986 Dec;26:187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahn A. N. Microbial potential in the etiology of periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 1970 Nov;41(11):603–610. doi: 10.1902/jop.1970.41.11.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Evans R. T., Slots J., Genco R. J. Antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria from the human oral cavity. J Dent Res. 1985 Oct;64(10):1233–1244. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640101201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Slots J., Genco R. J., Evans R. T. Minimal inhibitory concentrations of various antimicrobial agents for human oral anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):420–424. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bom-van Noorloos A. A., Schipper C. A., van Steenbergen T. J., de Graaff J., Burger E. H. Bacteroides gingivalis activates mouse spleen cells to produce a factor that stimulates resorptive activity of osteoclasts in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 1986 Jul;21(4):440–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1986.tb01478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeau G., Mayrand D. Phenylacetic acid production by Bacteroides gingivalis from phenylalanine and phenylalanine-containing peptides. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Sep;29(9):1184–1189. doi: 10.1139/m83-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook I. Encapsulated anaerobic bacteria in synergistic infections. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):452–457. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.452-457.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Herrmann B. F., Höfling J. F., Sundqvist G. K. Degradation of the human proteinase inhibitors alpha-1-antitrypsin and alpha-2-macroglobulin by Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):644–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.644-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson J., Höfling J. F., Sundqvist G. K. Degradation of albumin, haemopexin, haptoglobin and transferrin, by black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Aug;18(1):39–46. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-1-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P., Bochacki V., Reynolds H. S., Beanan J., Tatakis D. N., Zambon J. J., Genco R. J. The use of monoclonal antibodies to detect Bacteroides gingivalis in biological samples. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):798–803. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.798-803.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courant P. R., Gibbons R. J. Biochemical and immunological heterogeneity of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Dec;12(12):1605–1613. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden B. I. Pigment production by Bacteroides species with reference to sub-classification. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):113–125. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden B. I. The isolation and identification of Bacteroides spp. from the normal human faecal flora. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):69–78. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duerden B. I. The isolation and identification of Bacteroides spp. from the normal human gingival flora. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):89–101. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius L., Dahlén G., Holm S. E., Möller A. J. Influence of combinations of oral bacteria on periapical tissues of monkeys. Scand J Dent Res. 1982 Jun;90(3):200–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1982.tb00728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank R. M. Bacterial penetration in the apical pocket wall of advanced human periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1980 Nov;15(6):563–573. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1980.tb00315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura S., Nakamura T. Isolation and characterization of a protease from Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):716–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.716-720.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Degradation of collagenous substrates by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:614–621. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.614-621.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS R. J., MACDONALD J. B. Hemin and vitamin K compounds as required factors for the cultivation of certain strains of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:164–170. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.164-170.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Houte J. V. Bacterial adherence in oral microbial ecology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:19–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Cytotoxic effects of culture supernatants of oral bacteria and various organic acids on Vero cells. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Mar;31(3):302–304. doi: 10.1139/m85-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Etudes d'infections mixtes anaérobies comportant Bacteroides gingivalis. Can J Microbiol. 1983 May;29(5):612–618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Functional characterization of extracellular vesicles produced by Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):111–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.111-117.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Nutritional relationships between oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):616–620. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.616-620.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier D., Mayrand D. Selected characteristics of pathogenic and nonpathogenic strains of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Apr;25(4):738–740. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.4.738-740.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo M. Bacteroides buccae and related taxa in necrotic root canal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Dec;24(6):940–944. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.6.940-944.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapasalo M., Ranta H., Ranta K., Shah H. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in human apical periodontitis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):149–153. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.149-153.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halhoul N., Colvin J. R. The ultrastructure of bacterial plaque attached to the gingiva of man. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Feb;20(2):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanazawa S., Nakada K., Ohmori Y., Miyoshi T., Amano S., Kitano S. Functional role of interleukin 1 in periodontal disease: induction of interleukin 1 production by Bacteroides gingivalis lipopolysaccharide in peritoneal macrophages from C3H/HeN and C3H/HeJ mice. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):262–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.262-270.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanazawa S., Saitoh K., Ohmori Y., Nishihara H., Fujiwara S., Kitano S. Production of monoclonal antibodies that recognize specific and cross-reactive antigens of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):285–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.285-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley P. S., Tipler L. S. An electron microscope survey of the surface structures and hydrophobicity of oral and non-oral species of the bacterial genus Bacteroides. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31(5):325–335. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Courant P. R., Arnold D. S. Conditions for the demonstration of collagenolytic activity in Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1967 Feb;12(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(67)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann E., Kaufman E. Collagenase activity in a particulate fraction from Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 23;194(2):612–615. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T. Biological activities of endotoxin from Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Apr;15(4):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstad T. The distribution of heptose and 2-keto-3-deoxy-octonate in Bacteroidaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):314–320. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt D. E., Jones J. V., Dowell V. R., Jr Selective medium for the isolation of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):441–445. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.441-445.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino Y., Hopps R. M. The bone-resorbing activities in tissue culture of lipopolysaccharides from the bacteria Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Bacteroides gingivalis and Capnocytophaga ochracea isolated from human mouths. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29(1):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Sisson P. R., Middleton R. L., Narang H. K., Codd A. A., Selkon J. B. Phagocytosis and killing of bacteria in aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):391–399. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingham H. R., Sisson P. R., Tharagonnet D., Selkon J. B., Codd A. A. Inhibition of phagocytosis in vitro by obligate anaerobes. Lancet. 1977 Dec 17;2(8051):1252–1254. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoshita E., Amano A., Hanioka T., Tamagawa H., Shizukuishi S., Tsunemitsu A. Isolation and some properties of exohemagglutinin from the culture medium of Bacteroides gingivalis 381. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):421–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.421-427.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara K., Takazoe I., Okuda K. Antibiotic susceptibilities of periodontopathic gram-negative bacteria. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1986 Aug;27(3):103–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek F. S., Coykendall A. L. Production of phenylacetic acid by strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides gingivalis (sp. nov.). J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Aug;12(2):288–290. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.2.288-290.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M. E., Smith H. O. Transformation in Haemophilus: a problem in membrane biology. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(2):89–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01868974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen P. R. The effects of bacterial sonicates on human keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 1981 May;16(3):323–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00981.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein P., van Steenbergen T. J., Bras J. M., de Graaff J. An experimentally induced phlegmonous abscess by a strain of Bacteroides gingivalis in guinea pigs and mice. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1981 Mar;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00399062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M. Degradation of immunoglobulins A2, A2, and G by suspected principal periodontal pathogens. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):757–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.757-765.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinder S. A., Holt S. C., Korman K. S. Penicillin resistance in the subgingival microbiota associated with adult periodontitis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jun;23(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.6.1127-1133.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Vesk M., Work E. Relation between excreted lipopolysaccharide complexes and surface structures of a lysine-limited culture of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(4):1206–1217. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.4.1206-1217.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Nishihara T., Fujiwara T., Nisizawa T., Okahashi N., Noguchi T., Hamada S. Biochemical and immunobiological properties of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from Bacteroides gingivalis and comparison with LPS from Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):638–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.638-647.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBach J. P., White D. C. Identification of ceramide phosphorylethanolamine and ceramide phosphorylglycerol in the lipids of an anaerobic bacterium. J Lipid Res. 1969 Sep;10(5):528–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. H., Listgarten M. A., Hammond B. F. Comparative ultrastructure of leukotoxic and non-leukotoxic strains of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1981 Jul;16(4):379–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laliberté M., Mayrand D. Characterization of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains isolated from animals. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;55(2):247–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01322.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr Determination of Bacteroides melaninogenicus serogroups by fluorescent antibody staining. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):561–567. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.561-567.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Ferguson K. P., Mayberry W. R. Characterization of Bacteroides gingivalis by direct fluorescent antibody staining and cellular fatty acid profiles. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Apr;28(4):367–374. doi: 10.1139/m82-056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambe D. W., Jr, Jerris R. C. Description of a polyvalent conjugate and a new serogroup of Bacteroides melaninogenicus by fluorescent antibody staining. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 May;3(5):506–512. doi: 10.1128/jcm.3.5.506-512.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larjava H., Uitto V. J., Eerola E., Haapasalo M. Inhibition of gingival fibroblast growth by Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):201–205. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.201-205.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. API ZYM system for identification of Bacteroides spp., Capnocytophaga spp., and spirochetes of oral origin. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Jan;15(1):97–102. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.1.97-102.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon B. E., Syed S. A., Loesche W. J. Rapid identification of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):345–346. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.345-346.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Keudell K. C., Milford A. F. Succinate as a growth factor for Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):175–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.175-178.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Milford A. F. Sensitivity of a Bacteroides melaninogenicus strain to monosaccharides: effect on enzyme induction. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):152–159. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.152-159.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev M., Milford A. F. Vitamin K stimulation of sphingolipid synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Oct 15;45(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90826-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liakoni H., Barber P., Newman H. N. Bacterial penetration of pocket soft tissues in chronic adult and juvenile periodontitis cases. An ultrastructural study. J Clin Periodontol. 1987 Jan;14(1):22–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1987.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Listgarten M. A., Lai C. H. Comparative ultrastructure of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Jul;14(4):332–340. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J., Paunio K. U., Woolfolk M. P., Hockett R. N. Collagenolytic activity of dental plaque associated with periodontal pathology. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):329–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.329-336.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., GIBBONS R. J. The relationship of indigenous bacteria to periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 1962 Jan-Feb;41:320–326. doi: 10.1177/00220345620410014201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD J. B., SUTTON R. M., KNOLL M. L., MADLENER E. M., GRAINGER R. M. The pathogenic components of an experimental fusospirochetal infection. J Infect Dis. 1956 Jan-Feb;98(1):15–20. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., THONARD J. C., SCHERP H. W. Studies on synergistic infections. I. Experimental infections with anaerobic streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1958 Jul-Aug;103(1):33–44. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Coleman S. E. Immunochemical differences between oral and nonoral strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):589–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.589-596.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Kasper D. L. Purification and immunochemical characterization of the outer membrane complex of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus. J Infect Dis. 1977 May;135(5):787–799. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.5.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Onderdonk A. B., Kasper D. L. Immunochemical and biologic studies of the lipopolysaccharide of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):72–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansheim B. J., Solstad C. A., Kasper D. L. Identification of a subspecies-specific capsular antigen from Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies asaccharolyticus by immunofluorescence and electron microscopy. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):736–741. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Bourgeau G., Grenier D., Lacroix J. M. Properties of oral asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Sep;30(9):1133–1136. doi: 10.1139/m84-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Bourgeau G. Production of phenylacetic acid by anaerobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):747–750. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.747-750.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., Grenier D. Detection of collagenase activity in oral bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Feb;31(2):134–138. doi: 10.1139/m85-026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D. Identification of clinical isolates of selected species of Bacteroides: production of phenylacetic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Aug;25(8):927–928. doi: 10.1139/m79-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C., Edwards T., Jensen S. Characterization of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and B. melaninogenicus oral isolates. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Oct;26(10):1178–1183. doi: 10.1139/m80-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand D., McBride B. C. Exological relationships of bacteria involved in a simple, mixed anaerobic infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.44-50.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee A. S., McDermid A. S., Baskerville A., Dowsett A. B., Ellwood D. C., Marsh P. D. Effect of hemin on the physiology and virulence of Bacteroides gingivalis W50. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.349-355.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikx F. H., de Jong M. H. Keratinolytic activity of cutaneous and oral bacteria. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):621–625. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.621-625.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar S. J., Goldstein E. G., Levine M. J., Hausmann E. Modulation of bone metabolism by two chemically distinct lipopolysaccharide fractions from Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):302–306. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.302-306.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Dextraze L., Mayrand D. Sensibilité au métronidazole, à la spiramycine et à leur association de bactéries à potentiel parodontopathique. J Biol Buccale. 1984 Mar;12(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P. G., Slots J., Reed M. J., Genco R. J. Identification of Bacteroides gingivalis by fluorescent antibody staining. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1981 Jul-Aug;132B(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouton C., Hammond P., Slots J., Genco R. J. Evaluation of Fluoretec-M for detection of oral strains of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jun;11(6):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.6.682-686.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair B. C., Mayberry W. R., Dziak R., Chen P. B., Levine M. J., Hausmann E. Biological effects of a purified lipopolysaccharide from Bacteroides gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1983 Jan;18(1):40–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1983.tb00333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito Y., Okuda K., Kato T., Takazoe I. Monoclonal antibodies against surface antigens of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):231–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.231-235.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namavar F., Verweij A. M., Bal M., van Steenbergen T. J., de Graaff J., MacLaren D. M. Effect of anaerobic bacteria on killing of Proteus mirabilis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):930–935. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.930-935.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. G. The role of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and other anaerobes in periodontal infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Mar-Apr;1(2):313–324. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson T., Carlsson J., Sundqvist G. Inactivation of key factors of the plasma proteinase cascade systems by Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1985 Nov;50(2):467–471. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.2.467-471.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitzan D., Sperry J. F., Wilkins T. D. Fibrinolytic activity of oral anaerobic bacteria. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(6):465–470. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notten F. J., Nieman F. H., Mikx F. H. Antibiotypes of Bacteroides gingivalis assessed by antimicrobial disks and multivariate analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1020–1024. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1020-1024.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Behling U. H., Hammond B., Lai C. H., Listgarten M., Pham P. H., Sanavi F. Release of toxic microvesicles by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):151–154. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.151-154.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Ohta K., Kato T., Takazoe I., Slots J. Antigenic characteristics and serological identification of 10 black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Jul;24(1):89–95. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.1.89-95.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Takazoe I. Antiphagocytic effects of the capsular structure of a pathogenic strain of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1973 Aug;14(3):99–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Takazoe I. Haemagglutinating activity of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1974 May;19(5):415–416. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Yamamoto A., Naito Y., Takazoe I., Slots J., Genco R. J. Purification and properties of hemagglutinin from culture supernatant of Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):659–665. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.659-665.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onderdonk A. B., Weinstein W. M., Sullivan N. M., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Experimental intra-abdominal abscesses in rats: quantitative bacteriology of infected animals. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1256–1259. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1256-1259.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Okuda K., Takazoe I. Purification and characterization of a thiol-protease from Bacteroides gingivalis strain 381. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1987 Jun;2(2):77–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1987.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pancholi V., Ayyagari A., Agarwal K. C. Role of haemagglutinating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus in clinical infections. Indian J Med Res. 1983 Mar;77:324–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent R., Mouton C., Lamonde L., Bouchard D. Human and animal serotypes of Bacteroides gingivalis defined by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):909–918. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.909-918.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peković D. D., Fillery E. D. Identification of bacteria in immunopathological mechanisms of human periodontal diseases. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Jul;19(4):329–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier T. P., Tonelli S. J., Holt S. C. Ultrastructure of gliding bacteria: scanning electron microscopy of Capnocytophaga sputigena, Capnocytophaga gingivalis, and Capnocytophaga ochracea. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1146–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1146-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poxton I. R., Brown R., Collee J. G. Detection of species-specific and cross-reactive cell-surface antigens of Bacteroides species by an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Med Microbiol. 1982 May;15(2):223–231. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEBURY T., CLARK A. R., ENGEL S. G., TERGIS F. Studies of fusospirochetal infection. I. Pathogenicity for guinea pigs of individual and combined cultures of spirochetes and other anaerobic bacteria derived from the human mouth. J Infect Dis. 1950 Nov-Dec;87(3):217–225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/87.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M. J., Slots J., Mouton C., Genco R. J. Antigenic studies of oral and nonoral black-pigmented Bacteroides strains. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):564–574. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.564-574.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza V., Sinclair P. R., White D. C., Cuorant P. R. Electron transport system of the protoheme-requiring anaerobe Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):665–671. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.665-671.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza V., Tucker A. N., White D. C. Lipids of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jan;101(1):84–91. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.1.84-91.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson P. B., Lantz M., Marucha P. T., Kornman K. S., Trummel C. L., Holt S. C. Collagenolytic activity associated with Bacteroides species and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1982 May;17(3):275–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01154.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeterink C. H., van Steenbergen T. J., de Graaff J. Histopathological changes in the hind foot of the mouse induced by black-pigmented Bacteroides strains. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Dec;20(3):355–361. doi: 10.1099/00222615-20-3-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeterink C. H., van Steenbergen T. J., de Jong W. F., de Graaff J. Histopathological effects in the palate of the rat induced by injection with different black-pigmented Bacteroides strains. J Periodontal Res. 1984 May;19(3):292–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb00820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotstein O. D., Pruett T. L., Simmons R. L. Mechanisms of microbial synergy in polymicrobial surgical infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Mar-Apr;7(2):151–170. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudek W., Haque R. U. Extracellular enzymes of the genus Bacteroides. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):458–460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.458-460.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAWYER S. J., MACDONALD J. B., GIBBONS R. J. Biochemical characteristics of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. A study of thirty-one strains. Arch Oral Biol. 1962 Nov-Dec;7:685–691. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(62)90117-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S. S., GIBBONS R. J., DALE A. C., BORTNICK L., ROSENTHAL E., MACDONALD J. B. The microbiota of the gingival crevice area of man. I. Total microscopic and viable counts and counts of specific organisms. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 May-Jun;8:275–280. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCRANSKY S. S., GIBBONS R. J. REQUIRED ROLE OF BACTEROIDES MELANINOGENICUS IN MIXED ANAEROBIC INFECTIONS. J Infect Dis. 1965 Jun;115:247–253. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglie R., Newman M. G., Carranza F. A., Jr, Pattison G. L. Bacterial invasion of gingiva in advanced periodontitis in humans. J Periodontol. 1982 Apr;53(4):217–222. doi: 10.1902/jop.1982.53.4.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Bonnett R., Mateen B., Williams R. A. The porphyrin pigmentation of subspecies of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):45–50. doi: 10.1042/bj1800045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Collins M. D. Fatty acid and isoprenoid quinone composition in the classification of Bacteroides melaninogenicus and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;48(1):75–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb05209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah H. N., Williams R. A., Bowden G. H., Hardie J. M. Comparison of the biochemical properties of Bacteroides melaninogenicus from human dental plaque and other sites. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;41(3):473–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G. L., Klempner M. S., Kasper D. L., Gorbach S. L. Alterations in opsonophagocytic killing by neutrophils of Bacteroides fragilis associated with animal and laboratory passage: effect of capsular polysaccharide. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jan;145(1):72–77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson L. G., Merrell B. R., Rouse R. F., Shklair I. L. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1986 Feb;65(2):95–97. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650021801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer R. E., Buckner B. A. Butyrate and propionate: important components of toxic dental plaque extracts. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.458-463.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren A., Hovmöller S., Farrants G., Ranta H., Haapasalo M., Ranta K., Lounatmaa K. Structures of two different surface layers found in six Bacteroides strains. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1278–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1278-1282.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Enzymatic characterization of some oral and nonoral gram-negative bacteria with the API ZYM system. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Sep;14(3):288–294. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.3.288-294.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides species, Capnocytophaga species, and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in human periodontal disease: virulence factors in colonization, survival, and tissue destruction. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):412–421. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Genco R. J. Direct hemagglutination technique for differentiating Bacteroides asaccharolyticus oral strains from nonoral strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Sep;10(3):371–373. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.3.371-373.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Gibbons R. J. Attachment of Bacteroides melaninogenicus subsp. asaccharolyticus to oral surfaces and its possible role in colonization of the mouth and of periodontal pockets. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):254–264. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.254-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Microflora in the healthy gingival sulcus in man. Scand J Dent Res. 1977 May;85(4):247–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1977.tb00560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J., Möenbo D., Langebaek J., Frandsen A. Microbiota of gingivitis in man. Scand J Dent Res. 1978 May;86(3):174–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1978.tb01929.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slots J. Subgingival microflora and periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):351–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socransky S. S., Dzink J. L., Smith C. M. Chemically defined medium for oral microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):303–305. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.303-305.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel C. A., Hayduk S. E., Minah G. E., Krywolap G. N. Black-pigmented Bacteroides from clinically characterized periodontal sites. J Periodontal Res. 1979 Sep;14(5):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1979.tb00234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen E. K., Hentges D. J. Hydrolytic enzymes of anaerobic bacteria isolated from human infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(2):153–156. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.2.153-156.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom A., Dyer J. K., Marsh C., Tribble J. L. Identification and characterization of species of the family Bacteriodaceae by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Dent Res. 1976 Mar-Apr;55(2):252–256. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550021501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suido H., Nakamura M., Mashimo P. A., Zambon J. J., Genco R. J. Arylaminopeptidase activities of oral bacteria. J Dent Res. 1986 Nov;65(11):1335–1340. doi: 10.1177/00220345860650111101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G. K., Carlsson J., Herrmann B. F., Höfling J. F., Vätäinen A. Degradation in vivo of the C3 protein of guinea-pig complement by a pathogenic strain of Bacteroides gingivalis. Scand J Dent Res. 1984 Feb;92(1):14–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1984.tb00854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G. K., Eckerbom M. I., Larsson A. P., Sjögren U. T. Capacity of anaerobic bacteria from necrotic dental pulps to induce purulent infections. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):685–693. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.685-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G., Carlsson J., Herrmann B., Tärnvik A. Degradation of human immunoglobulins G and M and complement factors C3 and C5 by black-pigmented Bacteroides. J Med Microbiol. 1985 Feb;19(1):85–94. doi: 10.1099/00222615-19-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G., Carlsson J., Hänström L. Collagenolytic activity of black-pigmented Bacteroides species. J Periodontal Res. 1987 Jul;22(4):300–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1987.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundqvist G., Johansson E. Bactericidal effect of pooled human serum on Bacteroides melaninogenicus, Bacteroides asaccharolyticus and Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Scand J Dent Res. 1982 Feb;90(1):29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1982.tb01521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to 23 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):736–752. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveen K., Hofstad T., Milner K. C. Lethality for mice and chick embryos, pyrogenicity in rabbits and ability to gelate lysate from amoebocytes of Limulus polyphemus by lipopolysaccharides from Bacteroides, Fusobacterium and Veillonella. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Dec;85B(6):388–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveen K., Skaug N. Bone resorption stimulated by lipopolysaccharides from Bacteroides, Fusobacterium and Veillonella, and by the lipid A and the polysaccharide part of Fusobacterium lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Dent Res. 1980 Dec;88(6):535–542. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1980.tb01264.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sveen K. The capacity of lipopolysaccharides from bacteroides, fusobacterium and veillonella to produce skin inflammation and the local and generalized Shwartzman reaction in rabbits. J Periodontal Res. 1977 Sep;12(5):340–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1977.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swindlehurst C. A., Shah H. N., Parr C. W., Williams R. A. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of polypeptides from Bacteroides melaninogenicus. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):319–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A. Characteristics of Bacteroides asaccharolyticus from dental plaques of beagle dogs. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):522–526. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.522-526.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Nakamura T. Experimental mixed infection by human gingival crevice material. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1971 May;12(2):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Nakamura T., Okuda K. Colonization of the subgingival area by Bacteroides gingivalis. J Dent Res. 1984 Mar;63(3):422–426. doi: 10.1177/00220345840630031201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takazoe I., Tanaka M., Homma T. A pathogenic strain of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Arch Oral Biol. 1971 Jul;16(7):817–822. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(71)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner A. C., Haffer C., Bratthall G. T., Visconti R. A., Socransky S. S. A study of the bacteria associated with advancing periodontitis in man. J Clin Periodontol. 1979 Oct;6(5):278–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051x.1979.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. S., Naidu Y. M., Pestka J. J. Ultrastructural localization of an extracellular protease in Pseudomonas fragi by using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):1038–1042. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.1038-1042.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda K., Otsuka M., Ishikawa Y., Sato M., Yamamoto Y., Nakamura R. Thiol-dependent collagenolytic activity in culture media of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Jul;19(4):372–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonzetich J., McBride B. C. Characterization of volatile sulphur production by pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of oral Bacteroides. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26(12):963–969. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90104-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J. J., van Kampen G. P., van Steenbergen T. J., Veldhuijzen J. P., de Graaff J. The effect of culture filtrates of oral strains of black-pigmented Bacteroides on the matrix production of chick embryo cartilage cells in vitro. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Jul;17(4):351–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J. J., van Steenbergen T. J., De Graaff J. Butyrate: a cytotoxin for Vero cells produced by Bacteroides gingivalis and Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1982;48(4):315–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00418285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy O. Pigment production in bacteroides. J Med Microbiol. 1969 Aug;2(3):309–315. doi: 10.1099/00222615-2-3-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui H., Kinouchi T., Wakano Y., Ohnishi Y. Purification and characterization of a protease from Bacteroides gingivalis 381. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):420–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.420-427.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren A., Gibbons R. J. Amino acid fermentation by Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(1):149–159. doi: 10.1007/BF02069017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Sebald M. Etude sérologique d'anaérobies gram-Bégatifs aspourlés, et particulièrement de Bacteroides convexus et Bacteriodes melaninogenicu. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1968 Sep;115(3):350–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N., Sweeley C. C. Characterization of the iso-branched sphinganines from the ceramide phospholipids of Bacteroides melaninogenicus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 17;187(4):527–532. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(69)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D., Mayrand D. Association of oral Bacteroides with gingivitis and adult periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 1981 May;16(3):259–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1981.tb00974.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. B., Dahlén G., Linde A. Fibrinogenolytic and fibrinolytic activity in oral microorganisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):759–767. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.759-767.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Linde A. Ability of oral bacteria to degrade fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):707–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.707-711.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G. D., Holt S. C. Characteristics of the outer membrane of selected oral Bacteroides species. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Mar;31(3):238–250. doi: 10.1139/m85-046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo D. D., Holt S. C., Leadbetter E. R. Ultrastructure of Bacteroides species: Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Bacteroides fragilis, Bacteroides melaninogenicus subspecies melaninogenicus, and B. melaninogenicus subspecies intermedius. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):534–546. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Takahashi M., Takamori K., Sasaki T. Ultrastructure of the outer membrane surface of black-pigmented Bacteroides isolated from human oral cavity. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 1982 Feb;23(1):47–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nishikata M., Suzuki T., Hoover C. I., Newbrun E. Characterization of a trypsin-like protease from the bacterium Bacteroides gingivalis isolated from human dental plaque. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29(7):559–564. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takahashi K., Nodasaka Y., Suzuki T. Purification and characterization of a novel type of fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):949–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.949-957.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Takasawa T., Yoneyama M., Yamaguchi T., Shiokawa H., Suzuki T. Fimbriae from the oral anaerobe Bacteroides gingivalis: physical, chemical, and immunological properties. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):730–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.730-734.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambon J. J., Reynolds H. S., Slots J. Black-pigmented Bacteroides spp. in the human oral cavity. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):198–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.198-203.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kampen G. P., van Steenbergen T. J., Schipper C. A., de Graaff J., Veldhuijzen J. P. Proteoglycan production by chick embryonic chondrocytes is inhibited by culture filtrate of Bacteroides gingivalis. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Sep;19(5):483–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., Kastelein P., Touw J. J., de Graaff J. Virulence of black-pigmented Bacteroides strains from periodontal pockets and other sites in experimentally induced skin lesions in mice. J Periodontal Res. 1982 Jan;17(1):41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., Namavar F., de Graaff J. Chemiluminescence of human leukocytes by black-pigmented Bacteroides strains from dental plaque and other sites. J Periodontal Res. 1985 Jan;20(1):58–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1985.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., dan Ouden M. D., Touw J. J., de Graaff J. Cytotoxic activity of Bacteroides gingivalis and Bacteroides asaccharolyticus. J Med Microbiol. 1982 May;15(2):253–258. doi: 10.1099/00222615-15-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steenbergen T. J., van Winkelhoff A. J., de Graaff J. Pathogenic synergy: mixed infections in the oral cavity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1984;50(5-6):789–798. doi: 10.1007/BF02386241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff A. J., Carlee A. W., de Graaff J. Bacteroides endodontalis and other black-pigmented Bacteroides species in odontogenic abscesses. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):494–497. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.494-497.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff A. J., Kippuw N., de Graaff J. Serological characterization of black-pigmented Bacteroides endodontalis. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):972–974. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.972-974.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff A. J., de Graaff J. Vancomycin as a selective agent for isolation of Bacteroides species. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1282–1284. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1282-1284.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Winkelhoff A. J., van Steenbergen T. J., Kippuw N., De Graaff J. Further characterization of Bacteroides endodontalis, an asaccharolytic black-pigmented Bacteroides species from the oral S cavity. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jul;22(1):75–79. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.1.75-79.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]