Abstract
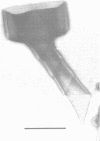
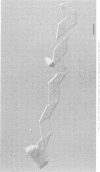
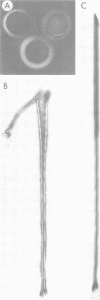
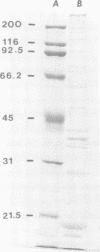
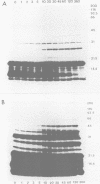
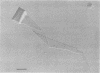
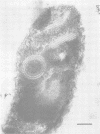
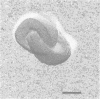
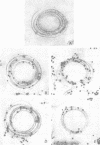
Until 10 years ago, R bodies were known only as diagnostic features by which endosymbionts of paramecia were identified as kappa particles. They were thought to be limited to the cytoplasm of two species in the Paramecium aurelia species complex. Now, R bodies have been found in free-living bacteria and other Paramecium species. The organisms now known to form R bodies include the cytoplasmic kappa endosymbionts of P. biaurelia and P. tetraurelia, the macronuclear kappa endosymbionts of P. caudatum, Pseudomonas avenae (a free-living plant pathogen), Pseudomonas taeniospiralis (a hydrogen-oxidizing soil microorganism), Rhodospirillum centenum (a photosynthetic bacterium), and a soil bacterium, EPS-5028, which is probably a pseudomonad. R bodies themselves fall into five distinct groups, distinguished by size, the morphology of the R-body ribbons, and the unrolling behavior of wound R bodies. In recent years, the inherent difficulties in studying the organization and assembly of R bodies by the obligate endosymbiont kappa, have been alleviated by cloning and expressing genetic determinants for these R bodies (type 51) in Escherichia coli. Type 51 R-body synthesis requires three low-molecular-mass polypeptides. One of these is modified posttranslationally, giving rise to 12 polypeptide species, which are the major structural subunits of the R body. R bodies are encoded in kappa species by extrachromosomal elements. Type 51 R bodies, produced in Caedibacter taeniospiralis, are encoded by a plasmid, whereas bacteriophage genomes probably control R-body synthesis in other kappa species. However, there is no evidence that either bacteriophages or plasmids are present in P. avenae or P. taeniospiralis. No sequence homology was detected between type 51 R-body-encoding DNA and DNA from any R-body-producing species, except C. varicaedens 1038. The evolutionary relatedness of different types of R bodies remains unknown.
Full text
PDF





































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON E. A cytological study of Chilomonas paramecium with particular reference to the so-called trichocysts. J Protozool. 1962 Nov;9:380–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1962.tb02640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus B., Purvis J., Stock D., Westley B. R., Samson A. C., Routledge E. G., Carpenter F. H., Horne C. H. NCL-5D3: a new monoclonal antibody recognizing low molecular weight cytokeratins effective for immunohistochemistry using fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. J Pathol. 1987 Dec;153(4):377–384. doi: 10.1002/path.1711530411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTZEL H. M., Jr, PAGLIARA A. The effect of biochemical inhibitors upon the killer-sensitive system in Paramecium aurelia. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Sep;27:382–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. Studies on the RNA of the mate-killer particles of Paramecium. Heredity (Edinb) 1970 Nov;25(4):657–662. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1970.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balsley M. Dependence of the kappa particles of stock 7 of Paramecium aurelia on a single gene. Genetics. 1967 May;56(1):125–131. doi: 10.1093/genetics/56.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale G. H., Jurand A. Three different types of mate-killer (mu) particle in Paramecium aurelia (syngen 1). J Cell Sci. 1966 Mar;1(1):31–34. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao P. K. Kappa Concentration per Cell in Relation to the Life Cycle, Genotype and Mating Type in Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Feb;39(2):103–113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPPELL R. V. Mutation of the killer cytoplasmic factor in Paramecium aurelia. Heredity (Edinb) 1950 Aug;4(2):165–187. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1950.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIPPELL R. V. The fine structure of kappa in killer stock 51 of Paramecium aurelia; preliminary observations. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jan 25;4(1):125–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOYLE B., SETLOW R. The action of ultraviolet light on paramecin and the chemical nature of paramecin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Oct;22(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90217-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Multiple methylation in processing of sensory signals during bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilts J. A. Chromosomal and extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid from four bacterial endosymbionts derived from stock 51 of Paramecium tetraurelia. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):888–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.888-894.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilts J. A. Covalently closed, circular DNA in kappa endosymbionts of Paramecium. Genet Res. 1976 Apr;27(2):161–170. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilts J. A., Quackenbush R. L. A mutation in the R body-coding sequence destroys expression of the killer trait in P. tetraurelia. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):641–643. doi: 10.1126/science.3008334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson I. The endosymbionts of Paramecium. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1974;3(3):243–273. doi: 10.3109/10408417409108752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson I. Transplantation of killer endosymbionts in paramecium. Nature. 1973 Jan 12;241(5385):127–129. doi: 10.1038/241127a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grim J. N., Staehelin L. A. The ejectisomes of the flagellate Chilomonas paramecium: visualization by freeze-fracture and isolation techniques. J Protozool. 1984 May;31(2):259–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb02957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., GETTNER M. E. Fine structure of kappa in Paramecium aurelia. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jan 25;4(1):122–124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding J. J. Nonenzymatic covalent posttranslational modification of proteins in vivo. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:247–334. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann K. Extrusive organelles in protists. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;52:197–276. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60757-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W., Casjens S. R. Protein fusion: a novel reaction in bacteriophage lambda head assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurand A., Rudman B. M., Preer J. R., Jr Prelethal effects of killing action by stock 7 of Paramecium aurelia. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jul;177(3):365–387. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401770311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanabrocki J. A., Lalucat J., Cox B. J., Quackenbush R. L. Comparative study of refractile (R) bodies and their genetic determinants: relationship of type 51 R bodies to R bodies produced by Pseudomonas taeniospiralis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1019–1022. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1019-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
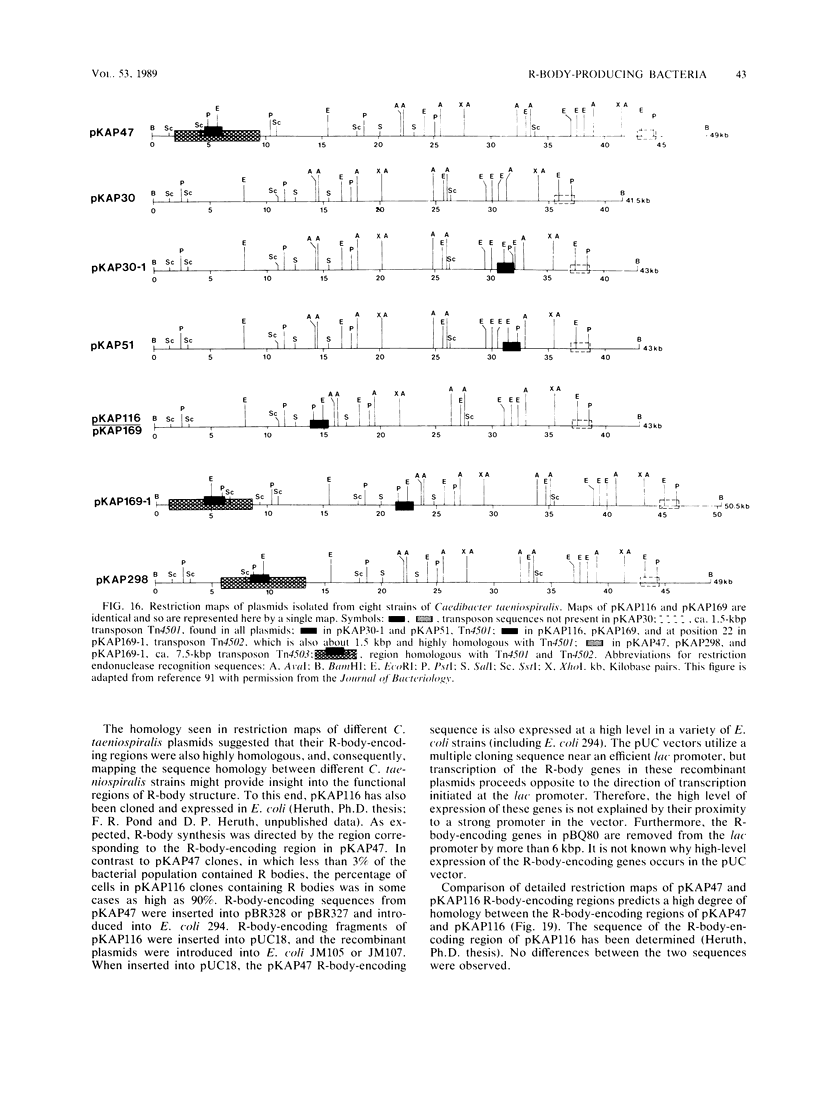
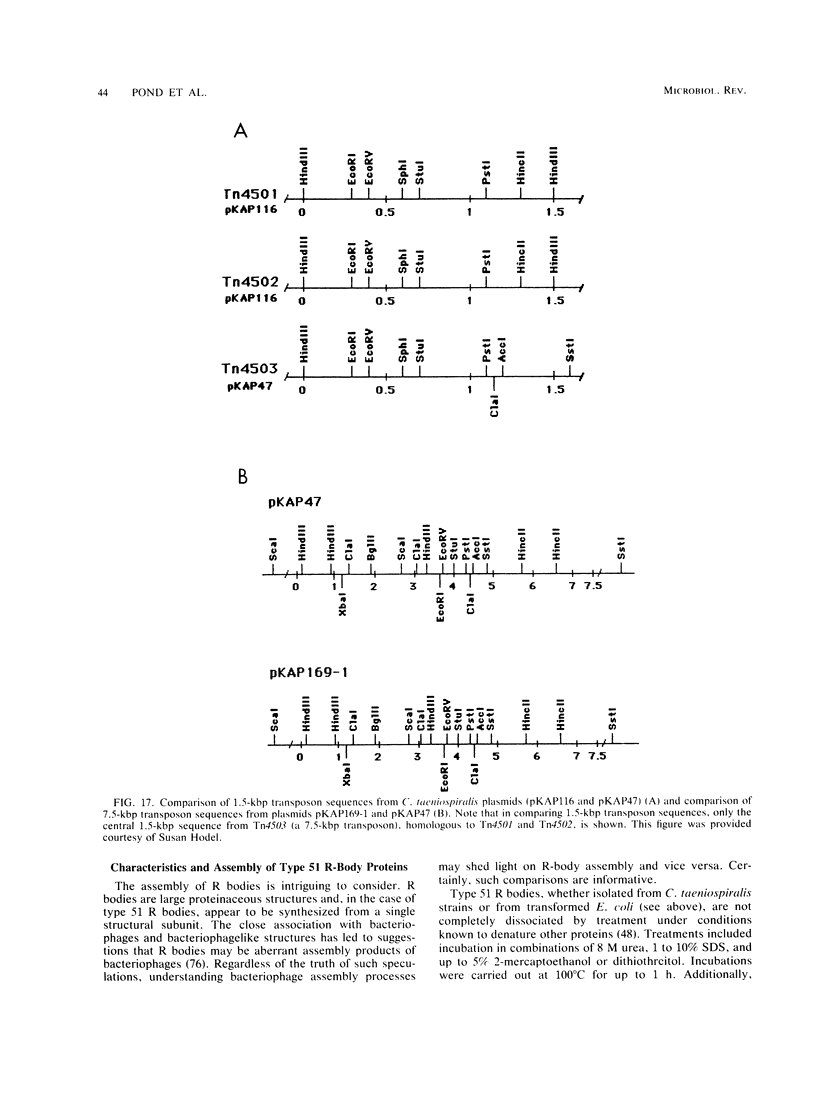
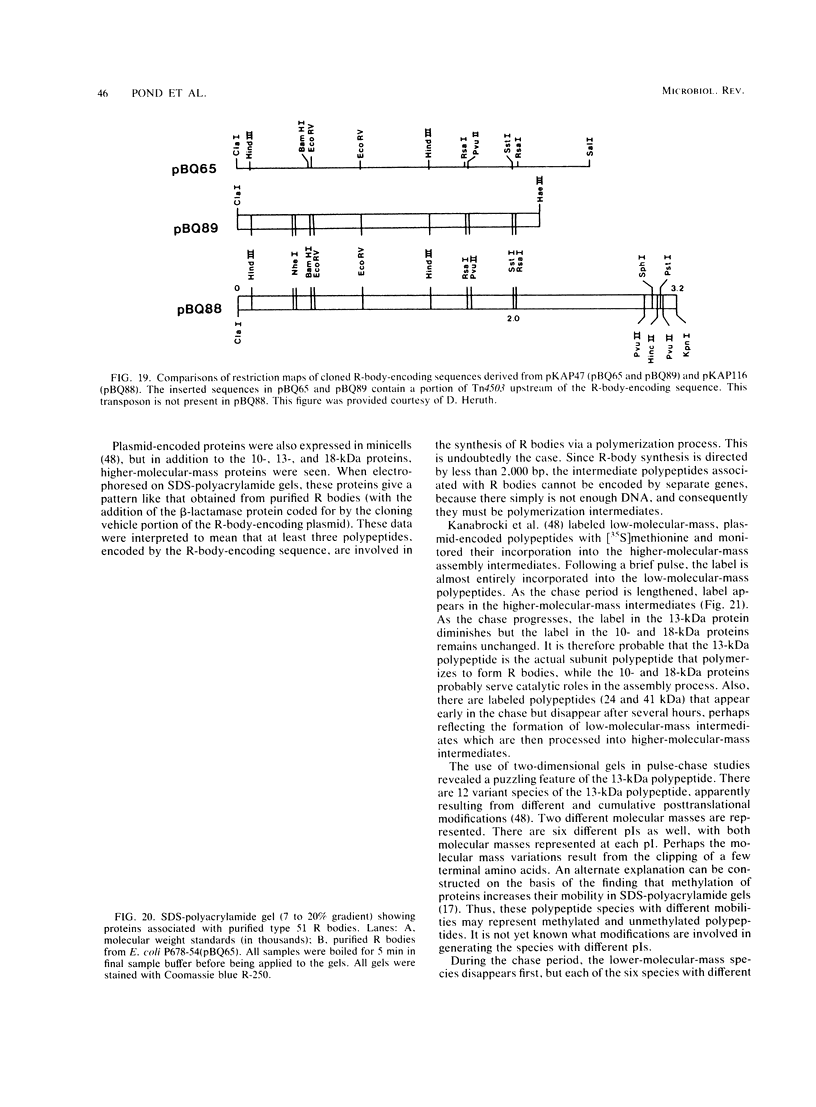
- Kanabrocki J. A., Quackenbush R. L., Pond F. R. Organization and expression of genetic determinants for synthesis and assembly of type 51 R bodies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):40–48. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.40-48.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsura I., Hendrix R. W. Length determination in bacteriophage lambda tails. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):691–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koizumi S. Microinjection and transfer of cytoplasm in Paramecium. Experiments on the transfer of kappa particles into cells at different stages. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Sep;88(1):74–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90619-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalucat J., Mayer F. "Spiral bodies"--intracytoplasmic membraneous structures in a hydrogen oxidizing bacterium. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1978;18(7):517–521. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630180708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. The Diverse Mate-Killers of Paramecium Aurelia, Variety 8: Their Interrelations and Genetic Basis. Genetics. 1953 Nov;38(6):561–578. doi: 10.1093/genetics/38.6.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulis L. Symbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic organelles; criteria for proof. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):21–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrall S., Greenwood A. D. A comparison of the periodic substructure of the trichocysts of the Cryptophyceae and Prasinophyceae. Biosystems. 1980;12(1-2):71–83. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(80)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREER J. R., Jr Microscopically visible bodies in the cytoplasm of the "killer" strains of Paramecium aurelia. Genetics. 1950 May;35(3):344–362. doi: 10.1093/genetics/35.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREER J. R., Jr, STARK P. Cytological observations on the cytoplasmic factor "kappa" in Paramecium aurelia. Exp Cell Res. 1953 Dec;5(2):478–491. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(53)90234-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Hufnagel L. A., Preer L. B. Structure and behavior of R bodies from killer paramecia. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Apr;15(1):131–143. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Jurand A. The relation between virus-like particles and R bodies of Paramecium aurelia. Genet Res. 1968 Dec;12(3):331–340. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Jurand A. Kappa and other endosymbionts in Paramecium aurelia. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):113–163. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.113-163.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B., Rudman B., Jurand A. Isolation and composition of bacteriophage-like particles from kappa of killer Paramecia. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):202–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00433105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr, Preer L. B. Virus-like bodies in killer paramecia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1774–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Jr The hereditary symbionts of Paramecium aurelia. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):125–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer J. R., Siegel R. W., Stark P. S. The Relationship between Kappa and Paramecin in Paramecium Aurelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Dec;39(12):1228–1233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.12.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preer L. B., Jurand A., Preer J. R., Jr, Rudman B. M. The classes of kappa in Paramecium aurelia. J Cell Sci. 1972 Sep;11(2):581–600. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.2.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L., Burbach J. A. Cloning and expression of DNA sequences associated with the killer trait of Paramecium tetraurelia stock 47. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):250–254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L., Cox B. J., Kanabrocki J. A. Extrachromosomal elements of extrachromosomal elements of Paramecium and their extrachromosomal elements. Basic Life Sci. 1986;40:265–278. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5251-8_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L., Dilts J. A., Cox B. J. Transposonlike elements in Caedibacter taeniospiralis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):349–352. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.349-352.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L., Dilts J. A., Maser R. L. Physical map of a plasmid from Caedibacter taeniospiralis 51. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):939–942. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.939-942.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L. Phylogenetic relationships of bacterial endosymbionts of Paramecium aurelia: polynucleotide sequence relationships of 51 kappa and its mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):895–900. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.895-900.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quackenbush R. L. Plasmids from bacterial endosymbionts of hump-killer paramecia. Plasmid. 1983 May;9(3):298–306. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH-SONNEBORN J. E., VANWAGTENDONK W. J. PURIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF KAPPA OF STOCK 51, PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:50–59. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLDO A. T. Axenic culture of Paramecium-some observations on the growth behavior and nutritional requirements of a particle-bearing strain of Paramecium aurelia 299 lambda. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jun 29;108:380–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. J., Görtz H. D., Pond F. R., Quackenbush R. L. Characterization of Caedibacter endonucleobionts from the macronucleus of Paramecium caudatum and the identification of a mutant with blocked R-body synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Jan;174(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster A. M., Burbank D. E., Meister B., Skrdla M. P., Meints R. H., Hattman S., Swinton D., Van Etten J. L. Characterization of viruses infecting a eukaryotic Chlorella-like green alga. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):170–177. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L. The gullet and trichocysts of Cyathomonas truncata. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Feb;49(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90178-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. Gene and Cytoplasm: I. The Determination and Inheritance of the Killer Character in Variety 4 of Paramecium Aurelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1943 Dec;29(11):329–338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.29.11.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M., Gibson I., Schneller M. V. Killer Particles and Metagons of Paramecium Grown in Didinium. Science. 1964 May 1;144(3618):567–568. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3618.567-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamburini P. P., Masson H. A., Bains S. K., Makowski R. J., Morris B., Gibson G. G. Multiple forms of hepatic cytochrome P-450. Purification, characterisation and comparison of a novel clofibrate-induced isozyme with other major forms of cytochrome P-450. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):235–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. J. Problems in the development of an explicit hypothetical phylogeny of the lower eukaryotes. Biosystems. 1978 Apr;10(1-2):67–89. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANWAGTENDONK W. J., CLARK J. A., GODOY G. A. THE BIOLOGICAL STATUS OF LAMBDA AND RELATED PARTICLES IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Nov;50:835–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.5.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J. L., Burbank D. E., Schuster A. M., Meints R. H. Lytic viruses infecting a Chlorella-like alga. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J. L., Meints R. H., Kuczmarski D., Burbank D. E., Lee K. Viruses of symbiotic Chlorella-like algae isolated from Paramecium bursaria and Hydra viridis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3867–3871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J. L., Van Etten C. H., Johnson J. K., Burbank D. E. A survey for viruses from fresh water that infect a eucaryotic chlorella-like green alga. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1326–1328. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1326-1328.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDMAYER D. J. A NONKILLER RESISTANT KAPPA AND ITS BEARING ON THE INTERPRETATION OF KAPPA IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Genetics. 1965 Apr;51:613–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]