Abstract
The assembly of a eucaryotic ribosome requires the synthesis of four ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA) molecules and more than 75 ribosomal proteins. It utilizes all three RNA polymerases; it requires the cooperation of the nucleus and the cytoplasm, the processing of RNA, and the specific interaction of RNA and protein molecules. It is carried out efficiently and is exquisitely sensitive to the needs of the cell. Our current understanding of this process in the genetically tractable yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is reviewed. The ribosomal RNA genes are arranged in a tandem array of 100 to 200 copies. This tandem array has led to unique ways of carrying out a number of functions. Replication is asymmetric and does not initiate from every autonomously replicating sequence. Recombination is suppressed. Transcription of the major ribosomal RNA appears to involve coupling between adjacent transcription units, which are separated by the 5S RNA transcription unit. Genes for many ribosomal proteins have been cloned and sequenced. Few are linked; most are duplicated; most have an intron. There is extensive homology between yeast ribosomal proteins and those of other species. Most, but not all, of the ribosomal protein genes have one or two sites that are essential for their transcription and that bind a common transcription factor. This factor binds also to many other places in the genome, including the telomeres. There is coordinated transcription of the ribosomal protein genes under a variety of conditions. However, the cell seems to possess no mechanism for regulating the transcription of individual ribosomal protein genes in response either to a deficiency or an excess of a particular ribosomal protein. A deficiency causes slow growth. Any excess ribosomal protein is degraded very rapidly, with a half-life of 1 to 5 min. Unlike most types of cells, yeast cells appear not to regulate the translation of ribosomal proteins. However, in the case of ribosomal protein L32, the protein itself causes a feedback inhibition of the splicing of the transcript of its own gene. The synthesis of ribosomes involves a massive transfer of material across the nuclear envelope in both directions. Nuclear localization signals have been identified for at least three ribosomal proteins; they are similar but not identical to those identified for the simian virus 40 T antigen. There is no information about how ribosomal subunits are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Rosbash M. Two genes for ribosomal protein 51 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae complement and contribute to the ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1871–1879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrew C., Hopper A. K., Hall B. D. A yeast mutant defective in the processing of 27S r-RNA precursor. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Feb 27;144(1):29–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00277300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a yeast nucleolar protein that is similar to a rat liver nucleolar protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):17–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. M., Platt T. Pol I transcription: which comes first, the end or the beginning? Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):839–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayev A., Georgiev O. I., Hadjiolov A. A., Nikolaev N., Skryabin K. G., Zakharyev V. M. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. 3. Precise mapping of the 18 S and 25 S rRNA genes and structure of the adjacent regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):789–799. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., DeGennaro L. J., Gelfand D. H., Bishop R. J., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Ribosomal RNA genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Physical map of the repeating unit and location of the regions coding for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S, and 25 S ribosomal RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8118–8125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Klaassen A. W., Planta R. J. Isolation of cloned ribosomal protein genes from the yeast Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Gene. 1981 Sep;14(4):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90160-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen G. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. High resolution mini-two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of yeast ribosomal proteins. A standard nomenclature for yeast ribosomal proteins. Mol Biol Rep. 1981 Nov 30;8(1):37–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00798383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Fragapane P., Annesi F., Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Amaldi F., Beccari E. Expression of two Xenopus laevis ribosomal protein genes in injected frog oocytes. A specific splicing block interferes with the L1 RNA maturation. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):987–1005. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90267-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill S. J., DiNardo S., Voelkel-Meiman K., Sternglanz R. Need for DNA topoisomerase activity as a swivel for DNA replication for transcription of ribosomal RNA. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):414–416. doi: 10.1038/326414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Geiduschek E. P. Modulation of yeast 5 S rRNA synthesis in vitro by ribosomal protein YL3. A possible regulatory loop. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):13953–13958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Lue N. F., Kornberg R. D. Connections between transcriptional activators, silencers, and telomeres as revealed by functional analysis of a yeast DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5086–5099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron S., Levin L., Zoller M., Wigler M. cAMP-independent control of sporulation, glycogen metabolism, and heat shock resistance in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90572-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Dietrich F. S., Fink G. R. Mitotic recombination in the rDNA of S. cerevisiae is suppressed by the combined action of DNA topoisomerases I and II. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
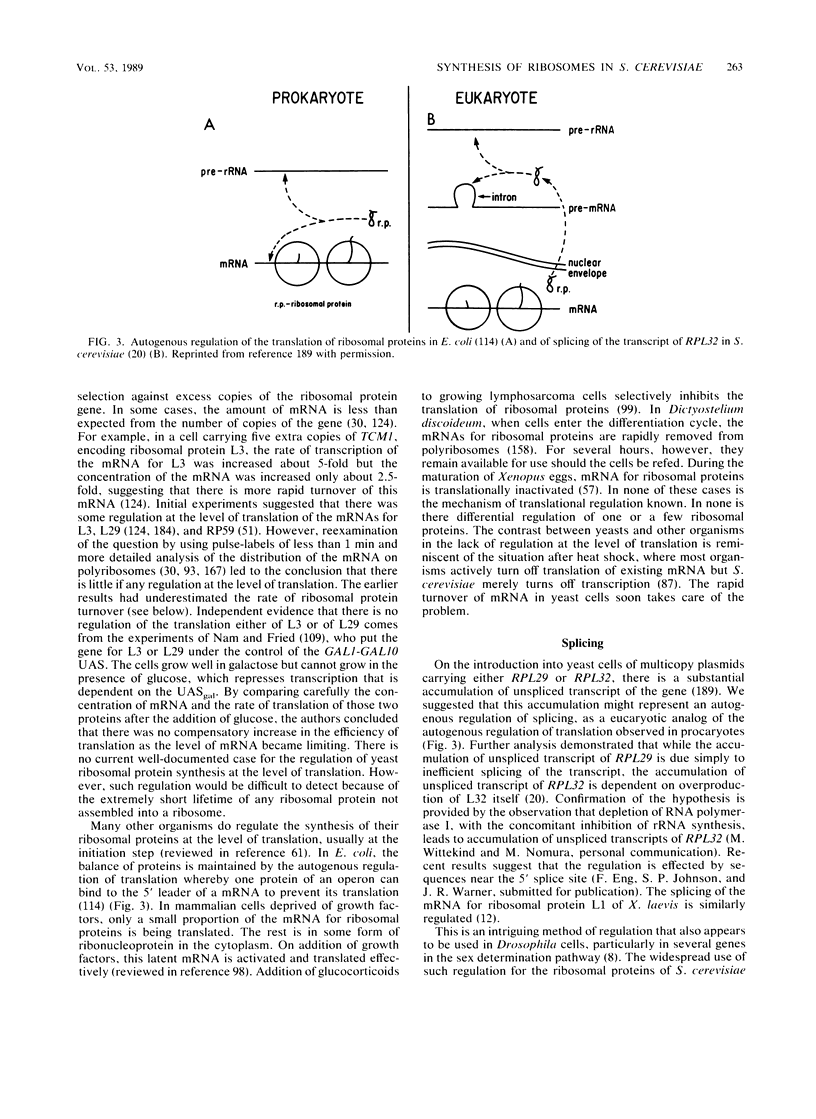
- Dabeva M. D., Post-Beittenmiller M. A., Warner J. R. Autogenous regulation of splicing of the transcript of a yeast ribosomal protein gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5854–5857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabeva M. D., Warner J. R. The yeast ribosomal protein L32 and its gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16055–16059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge P., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Terminal nucleotide sequences of 17-S ribosomal RNA and its immediate precursor 18-S RNA in yeast. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):361–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Winter R. F., Moss T. The ribosomal spacer in Xenopus laevis is transcribed as part of the primary ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6041–6051. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Transcriptional regulation of ribosomal proteins during a nutritional upshift in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2429–2435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Baradi T. T., Raué H. A., De Regt C. H., Planta R. J. Stepwise dissociation of yeast 60S ribosomal subunits by LiCl and identification of L25 as a primary 26S rRNA binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):393–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. The major promoter element of rRNA transcription in yeast lies 2 kb upstream. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90473-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian G. R., Hopper A. K. RRP1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene affecting rRNA processing and production of mature ribosomal subunits. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1571-1578.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming G., Belhumeur P., Skup D., Fried H. M. Functional substitution of mouse ribosomal protein L27' for yeast ribosomal protein L29 in yeast ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):217–221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Cloning of yeast gene for trichodermin resistance and ribosomal protein L3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):238–242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Molecular cloning and analysis of yeast gene for cycloheximide resistance and ribosomal protein L29. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3133–3148. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Warner J. R. Coordinate regulation of the synthesis of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1547–1551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein C., Warner J. R. Synthesis and turnover of ribosomal proteins in the absence of 60S subunit assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 9;157(3):327–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00268670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb S., Esposito R. E. A new role for a yeast transcriptional silencer gene, SIR2, in regulation of recombination in ribosomal DNA. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):771–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90681-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L. R., Mitlin J. A., Cannon M., Littlewood B., Carter C. J., Davies J. E. Ribosome structure, maturation of ribosomal RNA and drug sensitivity in temperature-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):384–391. doi: 10.1007/BF00330038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Abovich N., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Posttranscriptional regulation and assembly into ribosomes of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein-beta-galactosidase fusion. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3436–3442. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudenus R., Mariotte S., Moenne A., Ruet A., Memet S., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Thuriaux P. Conditional mutants of RPC160, the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase C in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Jul;119(3):517–526. doi: 10.1093/genetics/119.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil K. G., Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Constitutive transcription of yeast ribosomal protein gene TCM1 is promoted by uncommon cis- and trans-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4328–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Raué H. A., Vreken P., Wilms E., Planta R. J. Mild temperature shock affects transcription of yeast ribosomal protein genes as well as the stability of their mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7917–7929. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Woudt L. P., Nieuwint R. T., Wassenaar G. M., Groeneveld P., Planta R. J. Transcriptional control of yeast ribosomal protein synthesis during carbon-source upshift. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10133–10144. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himmelfarb H. J., Vassarotti A., Friesen J. D. Molecular cloning and biosynthetic regulation of cry1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):500–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00341453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan J. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Probing the conformation of 18S rRNA in yeast 40S ribosomal subunits with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3322–3330. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan J. J., Gutell R. R., Noller H. F. Probing the conformation of 26S rRNA in yeast 60S ribosomal subunits with kethoxal. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3330–3335. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Banks F. A yeast mutant which accumulates precursor tRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Cottrelle P., Cool M., Vignais M. L., Thiele D., Marck C., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3539–3547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison H. T., Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S. Temperature-sensitive yeast mutant defective in ribonucleic acid production. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):807–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.807-814.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. E., Wormington W. M. Translational inactivation of ribosomal protein mRNAs during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):598–605. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Otaka E., Matsui K. A. Primary structures of ribosomal protein YS25 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its counterparts from Schizosaccharomyces pombe and rat liver. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7418–7423. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T. Primary structure of yeast acidic ribosomal protein YP A1. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 19;114(1):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Wittmann-Liebold B. The primary structure of protein 44 from the large subunit of yeast ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 15;96(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemtland R., Maehlum E., Gabrielsen O. S., Oyen T. B. Regular distribution of length heterogeneities within non-transcribed spacer regions of cloned and genomic rDNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5145–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong A. Y., Clark M. W., Gilbert M., Oehm A., Campbell J. L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae SSB1 protein and its relationship to nucleolar RNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2947–2955. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Schaefer J. E., Laird C. D. A Drosophila rRNA gene located in euchromatin is active in transcription and nucleolus formation. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1745–1763. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil R. L., Roeder G. S. Cis-acting, recombination-stimulating activity in a fragment of the ribosomal DNA of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Musters W., Dekker A. F., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Deletion mapping of the yeast Pol I promoter. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):253–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00365621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., Oliemans J., Offenberg H., Dekker A. F., Piper P. W., Planta R. J., Klootwijk J. 3'-End formation of transcripts from the yeast rRNA operon. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2703–2710. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempers-Veenstra A. E., van Heerikhuizen H., Musters W., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. Transcription of an artificial ribosomal RNA gene in yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1377–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kief D. R., Warner J. R. Coordinate control of syntheses of ribosomal ribonucleic acid and ribosomal proteins during nutritional shift-up in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Warner J. R. Messenger RNA for ribosomal proteins in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Warner J. R. Mild temperature shock alters the transcription of a discrete class of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;3(3):457–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.3.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Geiduschek E. P. The 5' terminus of the precursor ribosomal RNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2679–2689. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., Verbeet M. P., Veldman G. M., de Regt V. C., van Heerikhuizen H., Bogerd J., Planta R. J. The in vivo and in vitro initiation site for transcription of the rRNA operon of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 10;12(3):1377–1390. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.3.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Planta R. J. The primary transcript of the ribosomal repeating unit in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):27–39. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Haber J. E., Rosbash M. Sporulation and rna2 lower ribosomal protein mRNA levels by different mechanisms in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1199–1204. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruiswijk T., Planta R. J., Krop J. M. The course of the assembly of ribosomal subunits in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 16;517(2):378–389. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroiwa T., Miyamura S., Kawano S., Hizume M., Tho-E A., Miyakawa I., Sando N. Cytological characterization of NOR in the bivalent of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jul;165(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90544-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. C., Thompson J. R., Woolford J. L., Jr Structure and expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CRY1 gene: a highly conserved ribosomal protein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1764–1775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., Van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequences upstream of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Curr Genet. 1985;9(4):273–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00419955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Hagendoorn M. J., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Structural comparison of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6685–6700. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Kraakman P., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The genes for yeast ribosomal proteins S24 and L46 are adjacent and divergently transcribed. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):701–709. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Witsenboer H. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast contains two functional genes coding for ribosomal protein S10. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5027–5039. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Schoppink P. J., Cornelissen M. T., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast ribosomal protein S33 is encoded by an unsplit gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7759–7768. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. Heat shock--a comparison of Drosophila and yeast. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1984 Nov;83 (Suppl):147–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D. Chromatin structure differs between coding and upstream flanking sequences of the yeast 35S ribosomal genes. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):927–934. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohr D., Ide G. I. In vitro initiation and termination of ribosomal RNA transcription in isolated yeast nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4668–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager W. H. Control of ribosomal protein gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 25;949(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maicas E., Pluthero F. G., Friesen J. D. The accumulation of three yeast ribosomal proteins under conditions of excess mRNA is determined primarily by fast protein decay. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):169–175. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin A. S., Skryabin K. G., Rubtsov P. M. Identification of ten additional nucleotides in the primary structure of yeast 18S rRNA. Gene. 1986;44(1):143–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann C., Buhler J. M., Treich I., Sentenac A. RPC40, a unique gene for a subunit shared between yeast RNA polymerases A and C. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Skryabin K. G., Gilbert W. Promotor region for yeast 5S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):643–645. doi: 10.1038/267643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon M. E., Stamenkovich D., Petes T. D. Tandemly arranged variant 5S ribosomal RNA genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):8001–8016. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.8001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Thompson E. A., Jr, Perry R. P. Glucocorticoids selectively inhibit translation of ribosomal protein mRNAs in P1798 lymphosarcoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2691–2699. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra G., Warner J. R. A yeast ribosomal protein gene whose intron is in the 5' leader. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9218–9224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of 38 kDa-type acidic ribosomal protein A0 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3573–3573. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of acidic ribosomal protein A1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3574–3574. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Tsurugi K. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence of acidic ribosomal protein A2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3575–3575. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar C. M., Woudt L. P., Jansen A. E., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Donovan D. M., Pearson N. J. Structure and organization of two linked ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7345–7358. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreland R. B., Nam H. G., Hereford L. M., Fried H. M. Identification of a nuclear localization signal of a yeast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6561–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murtif V. L., Rae P. M. In vivo transcription of rDNA spacers in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3221–3239. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musters W., Venema J., van der Linden G., van Heerikhuizen H., Klootwijk J., Planta R. J. A system for the analysis of yeast ribosomal DNA mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):551–559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Effects of progressive depletion of TCM1 or CYH2 mRNA on Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein accumulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1535–1544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S. Yeast chromosome replication and segregation. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):568–601. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.568-601.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwint R. T., Molenaar C. M., van Bommel J. H., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The gene for yeast ribosomal protein S31 contains an intron in the leader sequence. Curr Genet. 1985;10(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00418486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev N., Georgiev O. I., Venkov P. V., Hadjiolov A. A. The 37 S precursor to ribosomal RNA is the primary transcript of ribosomal RNA genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jan 25;127(3):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Higo K., Itoh T. Yeast ribosomal proteins. VIII. Isolation of two proteins and sequence characterization of twenty-four proteins from cytoplasmic ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(3):544–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00341461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Higo K., Itoh T. Yeast ribosomal proteins: VII. Cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(3):519–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00425772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Higo K., Osawa S. Isolation of seventeen proteins and amino-terminal amino acid sequences of eight proteins from cytoplasmic ribosomes of yeast. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 14;21(19):4545–4550. doi: 10.1021/bi00262a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Kobata K. Yeast ribosomal proteins. I. Characterization of cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 4;162(3):259–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00268851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Paietta J., Gallant J. A. Synthesis of guanosine tetraphosphate (magic spot I) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):314–322. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91410-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papciak S. M., Pearson N. J. Genetic mapping of two pairs of linked ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1987;11(6-7):445–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00384605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh V. S., Conrad-Webb H., Docherty R., Butow R. A. Interaction between the yeast mitochondrial and nuclear genomes influences the abundance of novel transcripts derived from the spacer region of the nuclear ribosomal DNA repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1897–1907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Yeast use translational control to compensate for extra copies of a ribosomal protein gene. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Botstein D. Simple Mendelian inheritance of the reiterated ribosomal DNA of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5091–5095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. W., Bellatin J. A., Lockheart A. Altered maturation of sequences at the 3' terminus of 5S gene transcripts in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant that lacks a RNA processing endonuclease. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):353–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planta R. J., Raué H. A. Control of ribosome biogenesis in yeast. Trends Genet. 1988 Mar;4(3):64–68. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90042-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presutti C., Lucioli A., Bozzoni I. Ribosomal protein L2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is homologous to ribosomal protein L1 in Xenopus laevis. Isolation and characterization of the genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6188–6192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quincey R. V., Arnold R. E. Transcription of a yeast ribosomal RNA minigene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 1;224(2):497–503. doi: 10.1042/bj2240497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman K. L., Rechsteiner M. Identification of the long ubiquitin extension as ribosomal protein S27a. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):438–440. doi: 10.1038/338438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacha M., Sáenz-Robles M. T., Vilella M. D., Ballesta J. P. Independent genes coding for three acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9094–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. D., Dixit A., Roufa D. J. Primary structure of human ribosomal protein S14 and the gene that encodes it. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2774–2783. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich B. E., Steitz J. A. Human acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins P0, P1, and P2: analysis of cDNA clones, in vitro synthesis, and assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4065–4074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosbash M., Harris P. K., Woolford J. L., Jr, Teem J. L. The effect of temperature-sensitive RNA mutants on the transcription products from cloned ribosomal protein genes of yeast. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):679–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg M. O., Moritz M., Woolford J. L., Jr Depletion of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein L16 causes a decrease in 60S ribosomal subunits and formation of half-mer polyribosomes. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):160–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotenberg M. O., Woolford J. L., Jr Tripartite upstream promoter element essential for expression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):674–687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubtsov P. M., Musakhanov M. M., Zakharyev V. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Bayev A. A. The structure of the yeast ribosomal RNA genes. I. The complete nucleotide sequence of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5779–5794. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Miller O. L., Jr Electron microscopic study of Saccharomyces cerevisiae rDNA chromatin replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1148–1157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Friesen J. D. Nucleotide sequence of the tcml gene (ribosomal protein L3) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.8-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R. Transcriptional elements of the yeast ribosomal protein gene CYH2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5690–5695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. Assembly of a yeast 5 S RNA gene transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11578–11584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. W., Sripati C. E., Warner J. R. Noncoordinated transcription in the absence of protein synthesis in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1344–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. W., Warner J. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in a mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective in ribosomal protein synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 May 3;161(2):221–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00274191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skryabin K. G., Eldarov M. A., Larionov V. L., Bayev A. A., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Veldman G. M., Planta R. J., Georgiev O. I., Hadjiolov A. A. Structure and function of the nontranscribed spacer regions of yeast rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2955–2968. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smitt W. W., Vlak J. M., Molenaar I., Rozijn T. H. Nucleolar function of the dense crescent in the yeast nucleus. A biochemical and ultrastructural study. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Aug;80(2):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Tower J. Transcription of cloned eukaryotic ribosomal RNA genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:801–830. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stateva L. I., Venkov P. V. Genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae SY 15 relaxed mutant. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):234–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00332752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steel L. F., Jacobson A. Translational control of ribosomal protein synthesis during early Dictyostelium discoideum development. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):965–972. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. E., Holland M. J. RNA polymerase I-dependent selective transcription of yeast ribosomal DNA. Identification of a new cellular ribosomal RNA precursor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3242–3250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. E., Yip M., Holland M. J. Characterization of an RNA polymerase I-dependent promoter within the spacer region of yeast ribosomal cistrons. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9905–9915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Unequal crossing over in the ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):426–430. doi: 10.1038/284426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáenz-Robles M. T., Vilella M. D., Pucciarelli G., Polo F., Remacha M., Ortíz B. L., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Ribosomal protein interactions in yeast. Protein L15 forms a complex with the acidic proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 15;177(3):531–537. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threadgill G. J., Conrad R. C., Cannon M., Craven G. R. A rapid and preparative method for the separation of yeast ribosomal proteins by using high-performance liquid chromatography. Biochem J. 1987 Jun 15;244(3):523–532. doi: 10.1042/bj2440523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D. A yeast small nuclear RNA is required for normal processing of pre-ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4169–4175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02763.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsay Y. F., Thompson J. R., Rotenberg M. O., Larkin J. C., Woolford J. L., Jr Ribosomal protein synthesis is not regulated at the translational level in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: balanced accumulation of ribosomal proteins L16 and rp59 is mediated by turnover of excess protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):664–676. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Warner J. R. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):227–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Warner J. R. The cytoplasmic maturation of a ribosomal precursor ribonucleic acid in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1412–1416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veinot-Drebot L. M., Singer R. A., Johnston G. C. Rapid initial cleavage of nascent pre-rRNA transcripts in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90382-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Jonge P., Leer R. J., Planta R. J. The transcription termination site of the ribosomal RNA operon in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5179–5192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., de Regt V. C., Planta R. J., Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P. The primary and secondary structure of yeast 26S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6935–6952. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Planta R. J. The nucleotide sequence of the intergenic region between the 5.8S and 26S rRNA genes of the yeast ribosomal RNA operon. Possible implications for the interaction between 5.8S and 26S rRNA and the processing of the primary transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4847–4862. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeet M. P., Klootwijk J., van Heerikhuizen H., Fontijn R. D., Vreugdenhil E., Planta R. J. A conserved sequence element is present around the transcription initiation site for RNA polymerase A in Saccharomycetoideae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1137–1148. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais M. L., Woudt L. P., Wassenaar G. M., Mager W. H., Sentenac A., Planta R. J. Specific binding of TUF factor to upstream activation sites of yeast ribosomal protein genes. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1451–1457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelkel-Meiman K., Keil R. L., Roeder G. S. Recombination-stimulating sequences in yeast ribosomal DNA correspond to sequences regulating transcription by RNA polymerase I. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1071–1079. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90714-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron C., Lacroute F. Effect of growth rate on the amounts of ribosomal and transfer ribonucleic acids in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):855–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.855-865.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron C. Synthesis of ribosomal and transfer ribonucleic acids in yeast during a nutritional shift-up. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):215–221. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley R. M., Johnston L. H., Williamson D. H., Oliver S. G. Replicon size of yeast ribosomal DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):260–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00332757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltschewa L., Georgiev O., Venkov P. Relaxed mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: proper maturation of ribosomal RNA in absence of protein synthesis. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. Distribution of newly formed ribosomal proteins in HeLa cell fractions. J Cell Biol. 1979 Mar;80(3):767–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;20:45–60. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)62008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The synthesis of eucaryotic ribosomal proteins in vitro. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. Yeast has a true stringent response. Nature. 1978 Sep 28;275(5678):338–339. doi: 10.1038/275338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. In the absence of ribosomal RNA synthesis, the ribosomal proteins of HeLa cells are synthesized normally and degraded rapidly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Johnson S. P. Molecular inventory control in ribosome biosynthesis. Microbiol Sci. 1986 Nov;3(11):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Udem S. A. Temperature sensitive mutations affecting ribosome synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 28;65(2):243–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90280-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Mager W. H., Beek J. G., Wassenaar G. M., Planta R. J. Structural and putative regulatory sequences of the gene encoding ribosomal protein L25 in Candida utilis. Curr Genet. 1987;12(3):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00436878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woudt L. P., Smit A. B., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Conserved sequence elements upstream of the gene encoding yeast ribosomal protein L25 are involved in transcription activation. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1037–1040. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi M., Nomura M. Deficiency in both type I and type II DNA topoisomerase activities differentially affect rRNA and ribosomal protein synthesis in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Curr Genet. 1988 Apr;13(4):305–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00424424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh Y. C., Traut R. R., Lee J. C. Protein topography of the 40 S ribosomal subunit from Saccharomyces cerevisiae as shown by chemical cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14148–14153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip M. T., Holland M. J. In vitro RNA processing generates mature 3' termini of yeast 35 and 25 S ribosomal RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4045–4051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorski J., Tollervey D., Fournier M. J. Characterization of an SNR gene locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that specifies both dispensible and essential small nuclear RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3282–3290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamb T. J., Petes T. D. Analysis of the junction between ribosomal RNA genes and single-copy chromosomal sequences in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S., Warner J. R. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phosphorylated and exchangeable proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T. T., Raué H. A., de Regt V. C., Verbree E. C., Planta R. J. Yeast ribosomal protein L25 binds to an evolutionary conserved site on yeast 26S and E. coli 23S rRNA. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2101–2107. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T. T., de Regt V. C., Einerhand S. W., Teixido J., Planta R. J., Ballesta J. P., Raué H. A. Ribosomal proteins EL11 from Escherichia coli and L15 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae bind to the same site in both yeast 26 S and mouse 28 S rRNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- elBaradi T. T., van der Sande C. A., Mager W. H., Raué H. A., Planta R. J. The cellular level of yeast ribosomal protein L25 is controlled principally by rapid degradation of excess protein. Curr Genet. 1986;10(10):733–739. doi: 10.1007/BF00405095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


