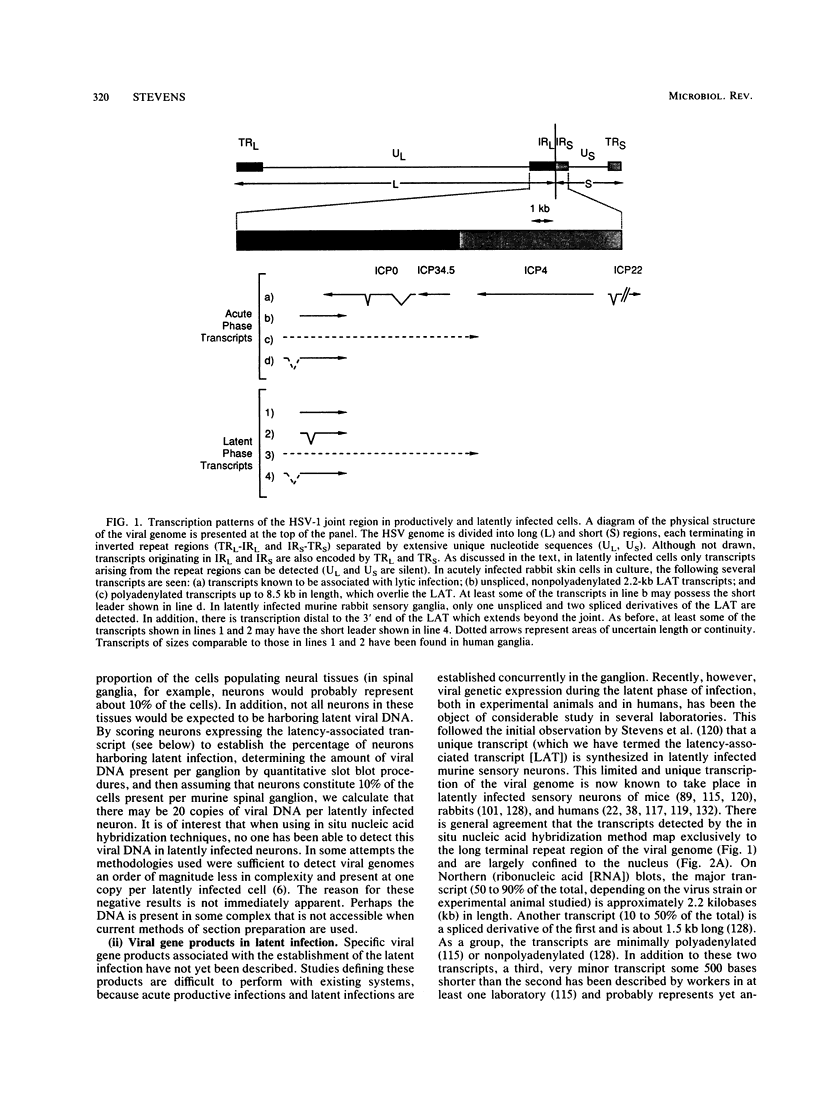
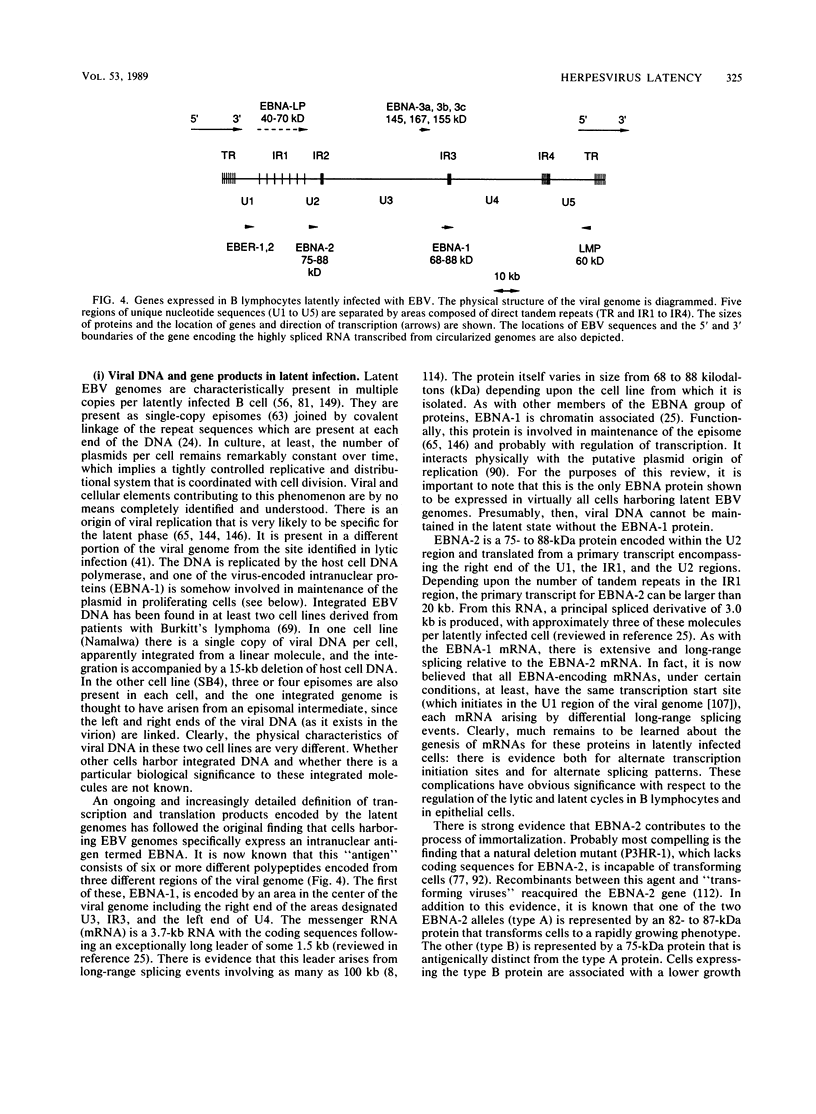
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abghari S. Z., Stulting R. D. Recovery of herpes simplex virus from ocular tissues of latently infected inbred mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Feb;29(2):239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Latency comes of age for herpesviruses. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):787–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Stowring L., Figus A., Montgomery C. K., Haase A. T., Vyas G. N. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes, bile duct epithelium, and vascular elements by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6685–6688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Brison O., Perricaudet M. An Epstein-Barr virus transcription unit is at least 84 kilobases long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2611–2620. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M. Epstein-Barr virus mRNAs produced by alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7103–7114. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera C. V., Wohlenberg C., Openshaw H., Rey-Mendez M., Puga A., Notkins A. L. Herpes simplex virus DNA sequences in the CNS of latently infected mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):288–290. doi: 10.1038/288288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter V. C., Rice P. L., Tevethia S. S. Intratypic and intertypic specificity of lymphocytes involved in the recognition of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):116–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.116-126.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. W. Acquisition of donor strains of cytomegalovirus by renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 29;314(22):1418–1423. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605293142205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. W. Cytomegalovirus infection and reinfection transmitted by heart transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1987 May;155(5):1054–1056. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.5.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements G. B., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Herpes simplex virus type 2 establishes latency in the mouse footpad. J Gen Virol. 1988 Feb;69(Pt 2):375–383. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-2-375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Bastone V. B., Stevens J. G. Evidence that neurons harbor latent herpes simplex virus. Infect Immun. 1974 May;9(5):946–951. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.5.946-951.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Latent herpetic infections following experimental viraemia. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):75–80. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M. L., Stevens J. G. Pathogenesis of herpetic neuritis and ganglionitis in mice: evidence for intra-axonal transport of infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):272–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.272-288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. D., Batra S. K., Brown S. M. Recovery of herpes simplex virus from the corneas of experimentally infected rabbits. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):2013–2017. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. D., Brown S. M. Herpes simplex virus type 1 latency in rabbit corneal cells in vitro: reactivation and recombination following intratypic superinfection of long term cultures. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):813–824. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey L., Spear P. G. Infections with herpes simplex viruses (2). N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 20;314(12):749–757. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603203141205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Jenson H., Seibl R., Wolf H., Miller G. Polymorphic proteins encoded within BZLF1 of defective and standard Epstein-Barr viruses disrupt latency. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3672–3679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3672-3679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Latent herpes simplex virus in human trigeminal ganglia. Detection of an immediate early gene "anti-sense" transcript by in situ hybridization. N Engl J Med. 1987 Dec 3;317(23):1427–1432. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198712033172302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Beisel C., Hummel M., King W., Fennewald S., Cheung A., Heller M., Raab-Traub N., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus (B95-8) DNA VII: molecular cloning and detailed mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshmane S. L., Fraser N. W. During latency, herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA is associated with nucleosomes in a chromatin structure. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):943–947. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.943-947.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ernberg I., Uno M., Ono Y., Klein G., Lerner R. A. An Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-determined nuclear antigen (EBNA5) partly encoded by the transformation-associated Bam WYH region of EBV DNA: preferential expression in lymphoblastoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6641–6645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing R. G., Sewankambo N., Serwadda D., Honess R., Crawford D., Jarrett R., Griffin B. E. Isolation of human lymphotropic herpesviruses from Uganda. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–390. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92403-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Minson A. C., Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Detection of herpes simplex virus-specific DNA sequences in latently infected mice and in humans. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.446-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggioni A., Zompetta C., Grimaldi S., Barile G., Frati L., Lazdins J. Calcium modulation activates Epstein-Barr virus genome in latently infected cells. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1554–1556. doi: 10.1126/science.3012779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser N. W., Lawrence W. C., Wroblewska Z., Gilden D. H., Koprowski H. Herpes simplex type 1 DNA in human brain tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6461–6465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Anti-glycoprotein D antibodies that permit adsorption but block infection by herpes simplex virus 1 prevent virion-cell fusion at the cell surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Lucas S., Nonoyama M., Perlin E., Goldstein L. I. Oral excretion of Epstein-Barr virus by healthy subjects and patients with infectious mononucleosis. Lancet. 1972 Nov 11;2(7785):988–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Rozenman Y., Murray R., Devlin M., Vafai A. Detection of varicella-zoster virus nucleic acid in neurons of normal human thoracic ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):377–380. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Vafai A., Shtram Y., Becker Y., Devlin M., Wellish M. Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):478–480. doi: 10.1038/306478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnann J. W., Jr, Ahlmén J., Svalander C., Olding L., Oldstone M. B., Nelson J. A. Inflammatory cells in transplanted kidneys are infected by human cytomegalovirus. Am J Pathol. 1988 Aug;132(2):239–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon Y. J., Johnson B., Romanowski E., Araullo-Cruz T. RNA complementary to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 gene demonstrated in neurons of human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1832–1835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1832-1835.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan J. S., Greenspan D., Lennette E. T., Abrams D. I., Conant M. A., Petersen V., Freese U. K. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral "hairy" leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 19;313(25):1564–1571. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512193132502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E., Jenson H., Countryman J., Heston L., Gradoville L., Miller G. Transfection of a rearranged viral DNA fragment, WZhet, stably converts latent Epstein-Barr viral infection to productive infection in lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Hummel M., Cole T., Kieff E. A membrane protein encoded by Epstein-Barr virus in latent growth-transforming infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7207–7211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Fennewald S., Kieff E. A third viral nuclear protein in lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Wang F., Bushman E. W., Kieff E. Definitive identification of a member of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 3 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Katsuki T. Colonies of EBNA-positive cells in soft agar from peripheral leukocytes of infectious mononucleosis patients. Int J Cancer. 1978 Apr 15;21(4):426–431. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley E. A., Thorley-Lawson D. A. B cell activation and the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus latency. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2059–2075. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W., Ecker J. R., Tenser R. B. Varicella-zoster virus RNA in human trigeminal ganglia. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):814–816. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javier R. T., Stevens J. G., Dissette V. B., Wagner E. K. A herpes simplex virus transcript abundant in latently infected neurons is dispensable for establishment of the latent state. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):254–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90169-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings S. R., Lippe P. A., Pauza K. J., Spear P. G., Pereira L., Tevethia S. S. Kinetics of expression of herpes simplex virus type 1-specific glycoprotein species on the surfaces of infected murine, simian, and human cells: flow cytometric analysis. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):104–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.104-112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Rowe D. T., Bodescot M., Nicolas J. C., Farrell P. J., Perricaudet M. Mapping of the gene coding for Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen EBNA3 and its transient overexpression in a human cell line by using an adenovirus expression vector. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3340–3344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3340-3344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. C., Mar V. L. Spontaneous activation of latent cytomegalovirus from murine spleen explants. Role of lymphocytes and macrophages in release and replication of virus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):762–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI110672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs S. F., Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Schachter F., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Genomic analysis of the human B-lymphotropic virus (HBLV). Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):601–603. doi: 10.1126/science.3020691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallin B., Dillner J., Ernberg I., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Rosén A., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. Four virally determined nuclear antigens are expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1499–1503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki T., Hinuma Y., Saito T., Yamamoto J., Hirashima Y., Sudoh H., Deguchi M., Motokawa M. Simultaneous presence of EBNA-positive and colony-forming cells in peripheral blood of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jun 15;23(6):746–750. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai Y., Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Reassociation kinetics for Epstein-Barr virus DNA: nonhomology to mammalian DNA and homology of viral DNA in various diseases. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1006-1012.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Al-Saadi S. A., Clements G. B. Reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus from dissociated identified dorsal root ganglion cells in culture. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jul;64(Pt 7):1629–1635. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-7-1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensson K., Lycke E., Sjöstrand J. Spread of herpes simplex virus in peripheral nerves. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;17(1):44–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00684740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Gangarosa L. P., Burch K. D., deBack J., Hill J. M. Induction of ocular herpes simplex virus shedding by iontophoresis of epinephrine into rabbit cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1981 Sep;21(3):442–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Gangarosa L. P., Sr, Green K., Hill J. M. Kinetics of ocular herpes simplex virus shedding induced by epinephrine iontophoresis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982 Jun;22(6):818–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Adams A., Bjursell G., Bornkamm G. W., Kaschka-Dierich C., Jehn U. Covalently closed circular duplex DNA of Epstein-Barr virus in a human lymphoid cell line. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):511–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Pellett P., Stewart J., Goldsmith C., Sanderlin K., Black J., Warfield D., Feorino P. Characteristics of human herpesvirus-6. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jun;157(6):1271–1273. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.6.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupton S., Levine A. J. Mapping genetic elements of Epstein-Barr virus that facilitate extrachromosomal persistence of Epstein-Barr virus-derived plasmids in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2533–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusso P., Markham P. D., Tschachler E., di Marzo Veronese F., Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Pahwa S., Krohn K., Gallo R. C. In vitro cellular tropism of human B-lymphotropic virus (human herpesvirus-6). J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1659–1670. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Kristensson K., Svennerholm B., Vahlne A., Ziegler R. Uptake and transport of herpes simplex virus in neurites of rat dorsal root ganglia cells in culture. J Gen Virol. 1984 Jan;65(Pt 1):55–64. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-1-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Courtney R. J., Fowler G., Rouse B. T. Herpes simplex virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2265–2273. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2265-2273.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLennan J. L., Darby G. Herpes simplex virus latency: the cellular location of virus in dorsal root ganglia and the fate of the infected cell following virus activation. J Gen Virol. 1980 Dec;51(Pt 2):233–243. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-51-2-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellerick D. M., Fraser N. W. Physical state of the latent herpes simplex virus genome in a mouse model system: evidence suggesting an episomal state. Virology. 1987 Jun;158(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. A., Wiley C. A., Spector D. H. Pathogenesis of murine cytomegalovirus infection: identification of infected cells in the spleen during acute and latent infections. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):987–997. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.987-997.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Niederman J. C., Andrews L. L. Prolonged oropharyngeal excretion of Epstein-Barr virus after infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1973 Feb 1;288(5):229–232. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197302012880503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Rabson M., Heston L. Epstein-Barr virus with heterogeneous DNA disrupts latency. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):174–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.174-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. J., Misko I. S., Burrows S. R., Burman K., McCarthy R., Sculley T. B. Cytotoxic T-cell clones discriminate between A- and B-type Epstein-Barr virus transformants. Nature. 1988 Feb 25;331(6158):719–721. doi: 10.1038/331719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Wang D., Young L. S., Wang F., Rowe M., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell recognition of transfectants expressing the virus-coded latent membrane protein LMP. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3747–3755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3747-3755.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Young L. S., Calender A., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and of cytotoxic T-cell recognition in B-cell lines infected with transforming (B95.8) or nontransforming (P3HR1) virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):894–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.894-901.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama M., Pagano J. S. Detection of Epstein-Barr viral genome in nonproductive cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 22;233(38):103–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio233103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North J. R., Morgan A. J., Thompson J. L., Epstein M. A. Purified Epstein-Barr virus Mr 340,000 glycoprotein induces potent virus-neutralizing antibodies when incorporated in liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7504–7508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olding L. B., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Pathogenesis of of cytomegalovirus infection. I. Activation of virus from bone marrow-derived lymphocytes by in vitro allogenic reaction. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):561–572. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Immunoglobulin G(Fc)-binding receptors on virions of herpes simplex virus type 1 and transfer of these receptors to the cell surface by infection. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.512-520.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., McGeoch D. J. The DNA sequences of the long repeat region and adjoining parts of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2831–2846. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Kieff E. A sixth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3B) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2173–2178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2173-2178.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Sample J., Wang F., Kieff E. A fifth Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein (EBNA3C) is expressed in latently infected growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1330–1338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1330-1338.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Notkins A. L. Continued expression of a poly(A)+ transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1700–1703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1700-1703.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragona G., Ernberg I., Klein G. Induction and biological characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) carried by the Jijoye lymphoma line. Virology. 1980 Mar;101(2):553–557. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90473-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Finerty S., Epstein M. A. Mechanism of the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus genome-containing lymphoid cell lines from infectious mononucleosis patients: studies with phosphonoacetate. Int J Cancer. 1977 Dec 15;20(6):861–868. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Jarvis J. E., Crawford D. H., Epstein M. A. Observations on the type of infection by Epstein-Barr virus in peripheral lymphoid cells of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Int J Cancer. 1974 Dec 15;14(6):704–715. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricksten A., Kallin B., Alexander H., Dillner J., Fåhraeus R., Klein G., Lerner R., Rymo L. BamHI E region of the Epstein-Barr virus genome encodes three transformation-associated nuclear proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):995–999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Fraser N. W. Detection of HSV-1 genome in central nervous system of latently infected mice. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):523–525. doi: 10.1038/302523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA contains two copies of the virion DNA joint region. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):849–852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.849-852.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock D. L., Nesburn A. B., Ghiasi H., Ong J., Lewis T. L., Lokensgard J. R., Wechsler S. L. Detection of latency-related viral RNAs in trigeminal ganglia of rabbits latently infected with herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3820–3826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3820-3826.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Sears A. E. An inquiry into the mechanisms of herpes simplex virus latency. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:543–571. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Preston C. M. An in vitro latency system for herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):397–403. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J., Stow N. D., Stow E. C., Preston C. M. Herpes simplex virus genes involved in latency in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3009–3018. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Ablashi D. V., Markham P. D., Josephs S. F., Sturzenegger S., Kaplan M., Halligan G., Biberfeld P., Wong-Staal F., Kramarsky B. Isolation of a new virus, HBLV, in patients with lymphoproliferative disorders. Science. 1986 Oct 31;234(4776):596–601. doi: 10.1126/science.2876520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Davis D. S., Young L. S., Hutt-Fletcher L., Tedder T. F., Rickinson A. B. Human epithelial cell expression of an Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):805–811. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Hanes R. A., Pagano J. S. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oropharyngeal epithelial cells. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 10;310(19):1225–1230. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405103101905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Vesterinen E. H., Nedrud J. G., Raab-Traub N., Walton L. A., Pagano J. S. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus in human epithelial cells infected in vitro. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):480–483. doi: 10.1038/306480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Farley J., Strominger J. L., Fresen K. O., Cho M. S., zur Hausen H. Transformation by Epstein-Barr virus requires DNA sequences in the region of BamHI fragments Y and H. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):286–297. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.286-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Pfitzner A., Strominger J. L. An Epstein-Barr virus transcript from a latently infected, growth-transformed B-cell line encodes a highly repetitive polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9298–9302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Detection of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcripts during latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3841–3847. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3841-3847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spivack J. G., Fraser N. W. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) latency-associated transcripts and transcripts affected by the deletion in avirulent mutant HFEM: evidence for a new class of HSV-1 genes. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3281–3287. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3281-3287.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner I., Spivack J. G., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd, Lavi E., Fraser N. W. Latent herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3493–3496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3493-3496.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Haarr L., Porter D. D., Cook M. L., Wagner E. K. Prominence of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in trigeminal ganglia from seropositive humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):117–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G. Latent characteristics of selected herpesviruses. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;26:227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Briggs M., Cameron C. H., Honess R., Robertson D., Whittle H. A novel lymphotropic herpesvirus. Lancet. 1987 Aug 15;2(8555):390–392. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92404-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Israelsohn E. S. Generation of specific cytotoxic T cells with a fragment of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded p63/latent membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5384–5388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtinen L. W., Saltzman R., Jordan M. C., Haase A. T. Interactions of human cytomegalovirus with leukocytes in vivo: analysis by in situ hybridization. Microb Pathog. 1987 Oct;3(4):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Murray R. S., Wellish M., Devlin M., Gilden D. H. Expression of varicella-zoster virus and herpes simplex virus in normal human trigeminal ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2362–2366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G., Feldman L. T., Dobson A. T., Zhang Y. F., Flanagan W. M., Stevens J. G. Physical characterization of the herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript in neurons. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1194–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1194-1202.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. K., Flanagan W. M., Devi-Rao G., Zhang Y. F., Hill J. M., Anderson K. P., Stevens J. G. The herpes simplex virus latency-associated transcript is spliced during the latent phase of infection. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4577–4585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4577-4585.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Petti L., Braun D., Seung S., Kieff E. A bicistronic Epstein-Barr virus mRNA encodes two nuclear proteins in latently infected, growth-transformed lymphocytes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):945–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.945-954.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Brown S. M., Wroblewska Z., Gilden D., Koprowski H., Subak-Sharpe J. Isolation of latent herpes simplex virus from the superior cervical and vagus ganglions of human beings. N Engl J Med. 1978 May 11;298(19):1068–1069. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197805112981907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Nesburn A. B., Watson R., Slanina S., Ghiasi H. Fine mapping of the major latency-related RNA of herpes simplex virus type 1 in humans. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):3101–3106. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-3101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B. L., Isom H. C., Rapp F. Repression and activation of the genome of herpes simplex viruses in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B. L., Scheck A. C., De Clercq E., Rapp F. High efficiency latency and activation of herpes simplex virus in human cells. Science. 1982 Sep 17;217(4565):1145–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.6180477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B. L., Ziegler R. J., Sneve M., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus latency and reactivation in isolated rat sensory neurons. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Scheck A. C., Ziegler R. J., De Clercq E., Rapp F. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus genome during in vitro latency in human diploid fibroblasts and rat sensory neurons. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):205–213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.205-213.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigdahl B., Smith C. A., Traglia H. M., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus latency in isolated human neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6217–6221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. L., Johnson E. M., Jr Characterization of nerve growth factor-dependent herpes simplex virus latency in neurons in vitro. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):393–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.393-399.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. L., Johnson E. M., Jr Nerve growth factor deprivation results in the reactivation of latent herpes simplex virus in vitro. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2311–2315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2311-2315.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Okuno T., Shiraki K., Takahashi M., Kondo T., Asano Y., Kurata T. Identification of human herpesvirus-6 as a causal agent for exanthem subitum. Lancet. 1988 May 14;1(8594):1065–1067. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Ogan P., Rowe M., Wood M., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus-infected B cells persist in the circulation of acyclovir-treated virus carriers. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jan 15;43(1):67–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Q. Y., Rickinson A. B., Epstein M. A. A re-examination of the Epstein-Barr virus carrier state in healthy seropositive individuals. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jan 15;35(1):35–42. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Clark D., Sixbey J. W., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human pharyngeal epithelia. Lancet. 1986 Feb 1;1(8475):240–242. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90776-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Dawson C. W., Clark D., Rupani H., Busson P., Tursz T., Johnson A., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Gen Virol. 1988 May;69(Pt 5):1051–1065. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H., Schulte-Holthausen H., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G., Clifford P., Santesson L. EBV DNA in biopsies of Burkitt tumours and anaplastic carcinomas of the nasopharynx. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/2281056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]