Abstract
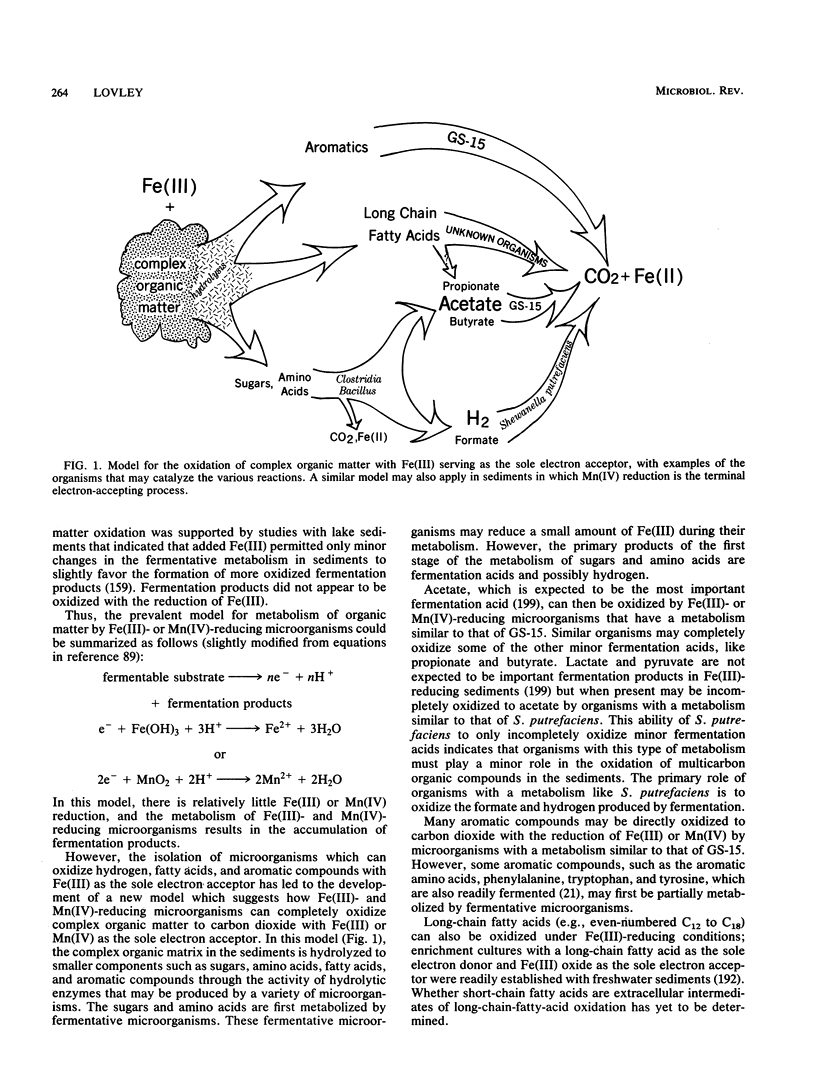
The oxidation of organic matter coupled to the reduction of Fe(III) or Mn(IV) is one of the most important biogeochemical reactions in aquatic sediments, soils, and groundwater. This process, which may have been the first globally significant mechanism for the oxidation of organic matter to carbon dioxide, plays an important role in the oxidation of natural and contaminant organic compounds in a variety of environments and contributes to other phenomena of widespread significance such as the release of metals and nutrients into water supplies, the magnetization of sediments, and the corrosion of metal. Until recently, much of the Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction in sedimentary environments was considered to be the result of nonenzymatic processes. However, microorganisms which can effectively couple the oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of Fe(III) or Mn(IV) have recently been discovered. With Fe(III) or Mn(IV) as the sole electron acceptor, these organisms can completely oxidize fatty acids, hydrogen, or a variety of monoaromatic compounds. This metabolism provides energy to support growth. Sugars and amino acids can be completely oxidized by the cooperative activity of fermentative microorganisms and hydrogen- and fatty-acid-oxidizing Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reducers. This provides a microbial mechanism for the oxidation of the complex assemblage of sedimentary organic matter in Fe(III)- or Mn(IV)-reducing environments. The available evidence indicates that this enzymatic reduction of Fe(III) or Mn(IV) accounts for most of the oxidation of organic matter coupled to reduction of Fe(III) and Mn(IV) in sedimentary environments. Little is known about the diversity and ecology of the microorganisms responsible for Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction, and only preliminary studies have been conducted on the physiology and biochemistry of this process.
Full text
PDF



























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold R. G., DiChristina T. J., Hoffmann M. R. Inhibitor studies of dissimilative Fe(III) reduction by Pseudomonas sp. strain 200 ("Pseudomonas ferrireductans") Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):281–289. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.281-289.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold R. G., Hoffmann M. R., Dichristina T. J., Picardal F. W. Regulation of Dissimilatory Fe(III) Reduction Activity in Shewanella putrefaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2811–2817. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2811-2817.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROMFIELD S. M. Reduction of ferric compounds by soil bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Aug;11(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker H. A. Amino acid degradation by anaerobic bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:23–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baur M. E., Hayes J. M., Studley S. A., Walter M. R. Millimeter-scale variations of stable isotope abundances in carbonates from banded iron-formations in the Hamersley Group of Western Australia. Econ Geol. 1985;80:270–282. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.80.2.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P. E., Mills A. L., Herman J. S. Biogeochemical Conditions Favoring Magnetite Formation during Anaerobic Iron Reduction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2610–2616. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2610-2616.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisschop A., Boonstra J., Sips H. J., Konings W. N. Respiratory chain linked ferricy anide reduction drives active transport in membrane vesicles from Bacillus subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P. Magnetotactic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:217–238. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra J., Sips H. J., Konings W. N. Active transport by membrane vesicles from anaerobically grown Escherichia coli energized by electron transfer to ferricyanide and chlorate. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):35–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Gustafson J. Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):567–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.567-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdige D. J., Nealson K. H. Microbial manganese reduction by enrichment cultures from coastal marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):491–497. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.491-497.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield D. E. Reactive iron in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 1989;53:619–632. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champine J. E., Goodwin S. Acetate catabolism in the dissimilatory iron-reducing isolate GS-15. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2704–2706. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2704-2706.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle F. H., Lovley D. R. Rates of microbial metabolism in deep coastal plain aquifers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1865–1874. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1865-1874.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. R., Dorotinsky C., Macy M., Hay R. Cell identity resolved. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):106–106. doi: 10.1038/340106b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dachman A. H., Nichols J. B., Patrick D. H., Lichtenstein J. E. Natural history of the obstructed rabbit appendix: observations with radiography, sonography, and CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Feb;148(2):281–284. doi: 10.2214/ajr.148.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey H. A., Jr, Lascelles J. Reduction of iron and synthesis of protoheme by Spirillum itersonii and other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):815–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.815-820.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Castro A. F., Ehrlich H. L. Reduction of iron oxide minerals by a marine Bacillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(3):317–327. doi: 10.1007/BF02069033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of Manganese Nodules: I. Bacterial Action on Manganese in Nodule Enrichments. Appl Microbiol. 1963 Jan;11(1):15–19. doi: 10.1128/am.11.1.15-19.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich H. L., Yang S. H., Mainwaring J. D., Jr Bacteriology of manganese nodules. VI. Fate of copper, nickel, cobalt, and iron during bacterial and chemical reduction of the manganese (IV). Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1973;13(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fassbinder J. W., Stanjek H., Vali H. Occurrence of magnetic bacteria in soil. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):161–163. doi: 10.1038/343161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. J., Dodge C. J. Anaerobic microbial dissolution of transition and heavy metal oxides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):1009–1014. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.1009-1014.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel R. B., Blakemore R. P. Magnetite and magnetotaxis in microorganisms. Bioelectromagnetics. 1989;10(3):223–237. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250100303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNNER H. B., ALEXANDER M. ANAEROBIC GROWTH OF FUSARIUM OXYSPORUM. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1309–1316. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1309-1316.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines C. G., Lodge J. S., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Ferrisiderophore reductase activity associated with an aromatic biosynthetic enzyme complex in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.527-533.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiorse W. C., Ehrlich H. L. Effects of seawater cations and temperature on manganese dioxide-reductase activity in a marine Bacillus. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Nov;28(5):785–792. doi: 10.1128/am.28.5.785-792.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiorse W. C., Ehrlich H. L. Electron transport components of the MnO2 reductase system and the location of the terminal reductase in a marine Bacillus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):977–985. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.977-985.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorby Y. A., Beveridge T. J., Blakemore R. P. Characterization of the bacterial magnetosome membrane. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):834–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.834-841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorby Y. A., Lovley D. R. Electron Transport in the Dissimilatory Iron Reducer, GS-15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):867–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.867-870.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J., Burke K. A. Reduction of ferric iron by L-lactate and DL-glycerol-3-phosphate in membrane preparations from Staphylococcus aureus and interactions with the nitrate reductase system. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):585–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.585-589.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Lonergan D. J. Anaerobic Oxidation of Toluene, Phenol, and p-Cresol by the Dissimilatory Iron-Reducing Organism, GS-15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1858–1864. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1858-1864.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Availability of ferric iron for microbial reduction in bottom sediments of the freshwater tidal potomac river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):751–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.751-757.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Competitive mechanisms for inhibition of sulfate reduction and methane production in the zone of ferric iron reduction in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2636–2641. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2636-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J., Lonergan D. J. Hydrogen and Formate Oxidation Coupled to Dissimilatory Reduction of Iron or Manganese by Alteromonas putrefaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):700–706. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.700-706.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):683–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.683-689.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Rapid assay for microbially reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jul;53(7):1536–1540. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.7.1536-1540.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Requirement for a Microbial Consortium To Completely Oxidize Glucose in Fe(III)-Reducing Sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3234–3236. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3234-3236.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Wolin M. J. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):985–987. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.985-987.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Bacterial manganese reduction and growth with manganese oxide as the sole electron acceptor. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1319–1321. doi: 10.1126/science.240.4857.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers C. R., Nealson K. H. Respiration-linked proton translocation coupled to anaerobic reduction of manganese(IV) and iron(III) in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6232–6238. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6232-6238.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obuekwe C. O., Westlake D. W., Cook F. D. Effect of nitrate on reduction of ferric iron by a bacterium isolated from crude oil. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jul;27(7):692–697. doi: 10.1139/m81-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obuekwe C. O., Westlake D. W., Cook F. D., William Costerton J. Surface changes in mild steel coupons from the action of corrosion-causing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):766–774. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.766-774.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obuekwe C. O., Westlake D. W. Effects of medium composition on cell pigmentation, cytochrome content, and ferric iron reduction in a Pseudomonas sp. isolated from crude oil. Can J Microbiol. 1982 Aug;28(8):989–992. doi: 10.1139/m82-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Bacterial mechanisms of gley formation in artificially submerged soil. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):103–103. doi: 10.1038/225103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Evaluation of iron-reducing bacteria in soil and the physiological mechanism of iron-reduction in Aerobacter aerogenes. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1968;8(5):441–443. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630080512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Selection, characterization and iron-reducing capacity of nitrate reductaseless (nit-) mutants of iron-reducing bacteria. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1970;10(1):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C., Von Klopotek A. Enzymatic reduction of iron oxide by fungi. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):41–43. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.41-43.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N. Metabolic diversity among the dissimilatory sulfate-reducing bacteria. Albert Jan Kluyver memorial lecture. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989 Aug;56(2):127–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00399977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short K. A., Blakemore R. P. Iron respiration-driven proton translocation in aerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):729–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.729-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Mizunashi W., Inagaki K., Tano T. Purification and some properties of sulfur:ferric ion oxidoreductase from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4916–4922. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4916-4922.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio Tsuyoshi, Wada Kimihito, Mori Manami, Inagaki Kenji, Tano Tatsuo. Synthesis of an Iron-Oxidizing System during Growth of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans on Sulfur-Basal Salts Medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):150–152. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.150-152.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic, marine sediment and interaction with reduction of nitrate and sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):319–324. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.319-324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Möller-Zinkhan D., Spormann A. M. Biochemistry of acetate catabolism in anaerobic chemotrophic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:43–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules. IV. Induction of an MnO2-reductase system in a marine bacillus. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):966–972. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.966-972.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Ehrlich H. L. Bacteriology of manganese nodules: III. Reduction of MnO(2) by two strains of nodule bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1968 May;16(5):695–702. doi: 10.1128/am.16.5.695-702.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tugel J. B., Hines M. E., Jones G. E. Microbial iron reduction by enrichment cultures isolated from estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1167–1172. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1167-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turekian K. K., Bertine K. K. Deposition of molybdenum and uranium along the major ocean ridge systems. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):250–251. doi: 10.1038/229250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C., Brimblecombe P. Iron and sulfur in the pre-biologic ocean. Precambrian Res. 1985;28:205–222. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(85)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C. Suboxic diagenesis in banded iron formations. Nature. 1984 May 24;309:340–342. doi: 10.1038/309340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. C. Was the Archaean biosphere upside down? Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329:710–712. doi: 10.1038/329710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vrind J. P., Boogerd F. C., de Vrind-de Jong E. W. Manganese reduction by a marine Bacillus species. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):30–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.30-34.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


