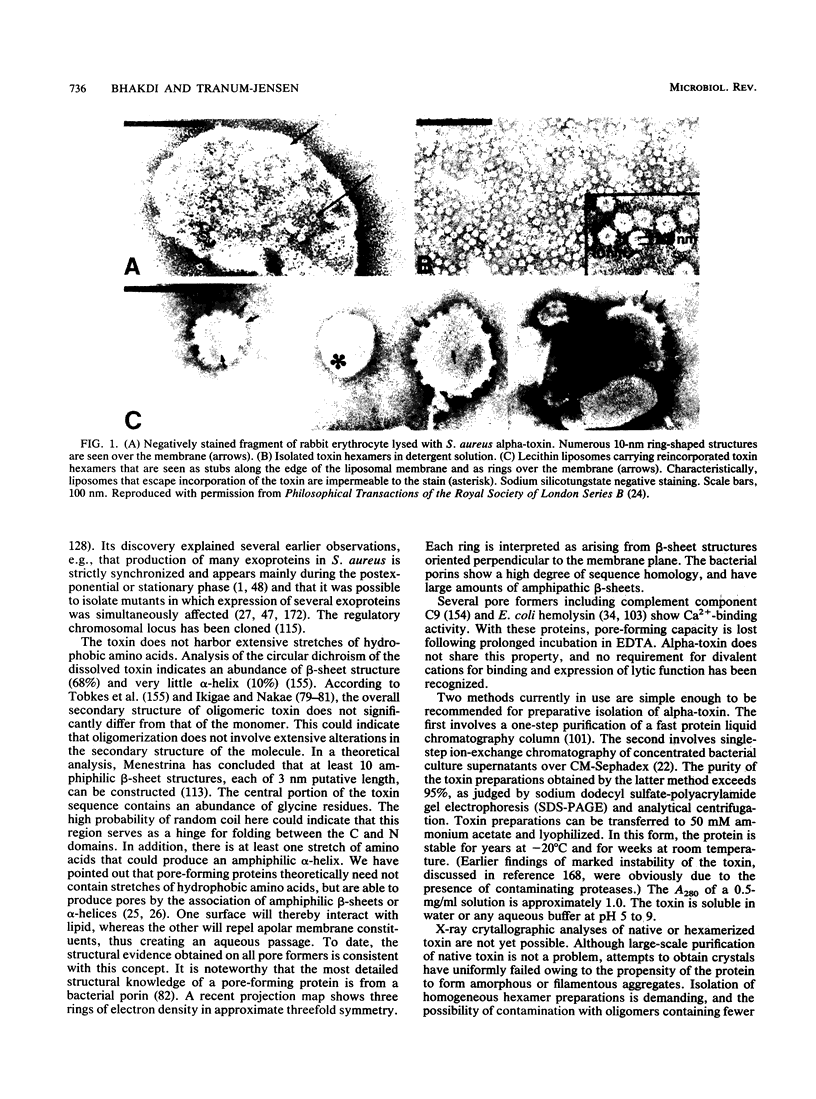
Abstract
Alpha-toxin, the major cytotoxic agent elaborated by Staphylococcus aureus, was the first bacterial exotoxin to be identified as a pore former. The protein is secreted as a single-chain, water-soluble molecule of Mr 33,000. At low concentrations (less than 100 nM), the toxin binds to as yet unidentified, high-affinity acceptor sites that have been detected on a variety of cells including rabbit erythrocytes, human platelets, monocytes and endothelial cells. At high concentrations, the toxin additionally binds via nonspecific absorption to lipid bilayers; it can thus damage both cells lacking significant numbers of the acceptor and protein-free artificial lipid bilayers. Membrane damage occurs in both cases after membrane-bound toxin molecules collide via lateral diffusion to form ring-structured hexamers. The latter insert spontaneously into the lipid bilayer to form discrete transmembrane pores of effective diameter 1 to 2 nm. A hypothetical model is advanced in which the pore is lined by amphiphilic beta-sheets, one surface of which interacts with lipids whereas the other repels apolar membrane constitutents to force open an aqueous passage. The detrimental effects of alpha-toxin are due not only to the death of susceptible targets, but also to the presence of secondary cellular reactions that can be triggered via Ca2+ influx through the pores. Well-studied phenomena include the stimulation of arachidonic acid metabolism, triggering of granule exocytosis, and contractile dysfunction. Such processes cause profound long-range disturbances such as development of pulmonary edema and promotion of blood coagulation.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas-ali B., Coleman G. The characteristics of extracellular protein secretion by Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46) and their relationship to the regulation of alpha-toxin formation. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Apr;99(2):277–282. doi: 10.1099/00221287-99-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adlam C., Ward P. D., McCartney A. C., Arbuthnott J. P., Thorley C. M. Effect immunization with highly purified alpha- and beta-toxins on staphylococcal mastitis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):250–256. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.250-256.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bhakdi S., Gratzl M. Minimal requirements for exocytosis. A study using PC 12 cells permeabilized with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12730–12734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahnert-Hilger G., Bräutigam M., Gratzl M. Ca2+-stimulated catecholamine release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized PC12 cells: biochemical evidence for exocytosis and its modulation by protein kinase C and G proteins. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7842–7848. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Bernheimer A. W. Physical states of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1170-1177.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Billcliffe B. Lipid-induced polymerization of staphylococcal -toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):309–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvand M., Bhakdi S., Dahlbäck B., Preissner K. T. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin attack on human platelets promotes assembly of the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14377–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. EFFECT OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND OTHER BACTERIAL TOXINS ON PLATELETS IN VITRO. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:209–223. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. Isolation and composition of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:455–468. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Ahnert-Hilger G., Gratzl M. Characterization of hormone and protein release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized chromaffin cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5777–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford C. L., Alder G. M., Menestrina G., Micklem K. J., Murphy J. J., Pasternak C. A. Membrane damage by hemolytic viruses, toxins, complement, and other cytotoxic agents. A common mechanism blocked by divalent cations. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9300–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmonte G., Cescatti L., Ferrari B., Nicolussi T., Ropele M., Menestrina G. Pore formation by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin in lipid bilayers. Dependence upon temperature and toxin concentration. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(6):349–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00262320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Kim K. S., Remsen C. C., Antanavage J., Watson S. W. Factors affecting interaction of staphylococcal alpha toxin with membranes. Infect Immun. 1972 Oct;6(4):636–642. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.4.636-642.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Fassbender W., Hugo F., Carreno M. P., Berstecher C., Malasit P., Kazatchkine M. D. Relative inefficiency of terminal complement activation. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3117–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Greulich S., Muhly M., Eberspächer B., Becker H., Thiele A., Hugo F. Potent leukocidal action of Escherichia coli hemolysin mediated by permeabilization of target cell membranes. J Exp Med. 1989 Mar 1;169(3):737–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
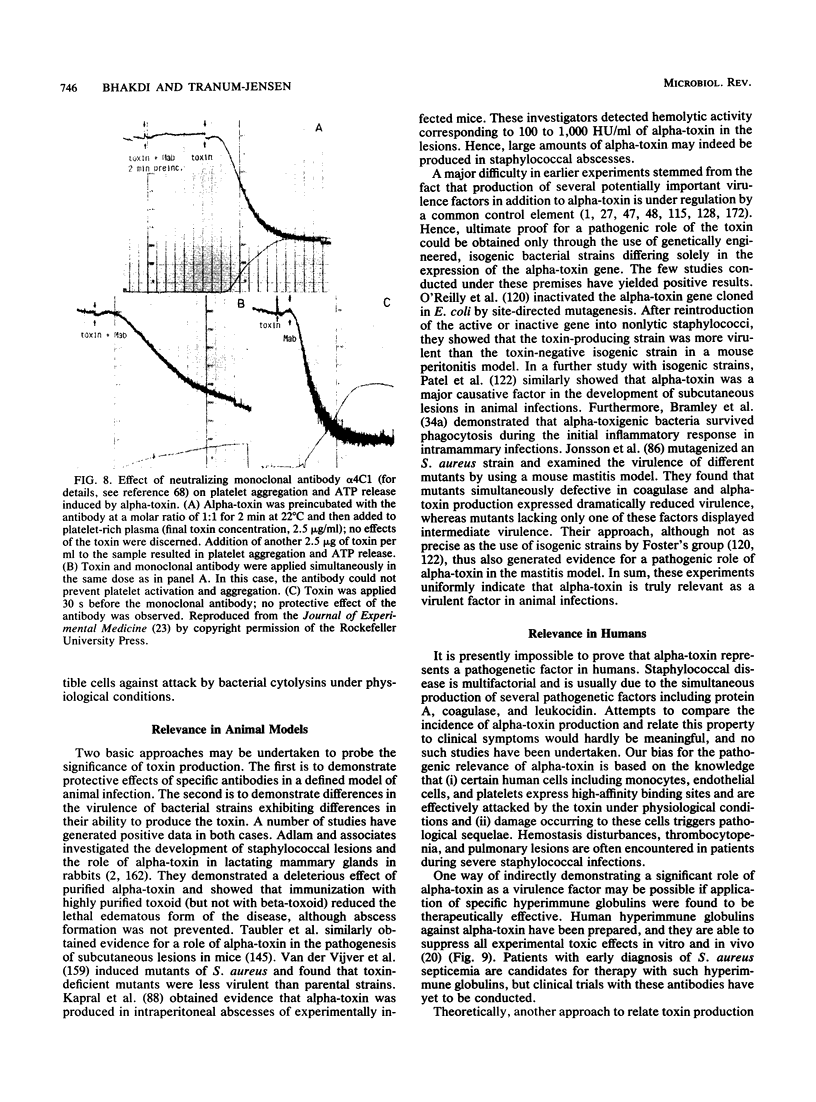
- Bhakdi S., Mannhardt U., Muhly M., Hugo F., Ronneberger H., Hungerer K. D. Human hyperimmune globulin protects against the cytotoxic action of staphylococcal alpha-toxin in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):3214–3220. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.3214-3220.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Füssle R. Correlation between toxin binding and hemolytic activity in membrane damage by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):318–323. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.318-323.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Korom S., Hugo F. Release of interleukin-1 beta associated with potent cytocidal action of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on human monocytes. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3512–3519. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3512-3519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Muhly M., Mannhardt U., Hugo F., Klapettek K., Mueller-Eckhardt C., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha toxin promotes blood coagulation via attack on human platelets. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):527–542. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to cell membranes by pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Prog Allergy. 1988;40:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Mechanism of complement cytolysis and the concept of channel-forming proteins. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Sep 6;306(1129):311–324. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Utermann G., Füssle R. Binding and partial inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin by human plasma low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5899–5904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Appelgren L. E., Thelestam M. Distribution of 3H-labeled staphylococcal alpha-toxin and a toxin fragment in mice. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1906–1913. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1906-1913.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Bergman T., Thelestam M., Jörnvall H. Characterization of domain borders and of a naturally occurring major fragment of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jan 26;211(2):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81422-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Sjögren A. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. Toxicon. 1988;26(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Thelestam M. A staphylococcal alpha-toxin fragment. Its characterization and use for mapping biologically-active regions of alpha-toxin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1986 Aug;94(4):277–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Thelestam M. Early events in the action of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on the plasma membrane of adrenocortical Y1 tumor cells. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):636–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.636-640.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomqvist L., Thelestam M. Oligomerization of 3H-labelled staphylococcal alpha-toxin and fragments on adrenocortical Y1 tumour cells. Microb Pathog. 1988 Mar;4(3):223–229. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm D. F., Welch R. A., Snyder I. S. Domains of Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) involved in binding of calcium and erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1959–1964. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1959-1964.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramley A. J., Patel A. H., O'Reilly M., Foster R., Foster T. J. Roles of alpha-toxin and beta-toxin in virulence of Staphylococcus aureus for the mouse mammary gland. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2489–2494. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2489-2494.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Pattee P. A. Identification of a chromosomal determinant of alpha-toxin production in Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):36–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.36-42.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckelew A. R., Jr, Colacicco G. Lipid monolayers. Interactions with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER L. Z., MADOFF M. A., WEINSTEIN L. HEMOLYSIS OF RABBIT ERYTHROCYTES BY PURIFIED STAPHYLOCOCCAL ALPHA-TOXIN. II. EFFECTS OF INHIBITORS ON THE HEMOLYTIC SEQUENCE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jan;87:136–144. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.1.136-144.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Characterization of detergent-solubilized iodine-125-labeled alpha-toxin bound to rabbit erythrocytes and mouse diaphragm muscle. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):232–236. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Iodination of a tyrosyl residue in staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2342–2348. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Studies on the binding of staphylococcal 125I-labeled alpha-toxin to rabbit erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2348–2355. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cescatti L., Pederzolli C., Menestrina G. Modification of lysine residues of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: effects on its channel-forming properties. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jan;119(1):53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF01868540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F., Lazarovici P. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. 1. Effect on protein phosphorylation in myelin. Toxicon. 1987;25(6):631–636. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(87)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyne M., De Azavedo J., Carlson E., Arbuthnott J. Production of gamma-hemolysin and lack of production of alpha-hemolysin by Staphylococcus aureus strains associated with toxic shock syndrome. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):535–539. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.535-539.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colacicco G., Buckelew A. R., Jr Lipid monolayers: influence of lipid film and urea on the surface activity of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Lipids. 1971 Aug;6(8):546–553. doi: 10.1007/BF02531134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G., Abbas-Ali B. Comparison of the patterns of increased in alpha-toxin and total extracellular protein by Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46) grown in media supporting widely differing growth characteristics. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):278–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.278-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman G. Pleiotropic compensation in the regulation of extracellular protein formation by a low alpha-toxin-producing variant of Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46). J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Jan;122(1):11–15. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper L. Z., Madoff M. A., Weinstein L. Heat stability and species range of purified staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1686–1692. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1686-1692.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelwejn Z., Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Brain bioelectrical activity in staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin intoxication. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1968 Sep;13(2):133–145. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(68)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson A., Granström M., Möllby R., Strandvik B. Antibodies to staphylococcal teichoic acid and alpha toxin in patients with cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1986 Jan;75(1):139–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1986.tb10170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fader R. C., Hals P. J., Koo F. C. Staphylococcal toxins: screening of burn wound isolates and evidence for alpha-haemolysin production in the burn wound. Burns Incl Therm Inj. 1987 Dec;13(6):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0305-4179(87)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairweather N., Kennedy S., Foster T. J., Kehoe M., Dougan G. Expression of a cloned Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin determinant in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1112–1117. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1112-1117.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forlani L., Bernheimer A. W., Chiancone E. Ultracentrifugal analysis of staphylococcal alpha toxin. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):138–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.138-142.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forti S., Menestrina G. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin increases the permeability of lipid vesicles by cholesterol- and pH-dependent assembly of oligomeric channels. Eur J Biochem. 1989 May 15;181(3):767–773. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Bernheimer A. W. Interaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with artificial and natural membranes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1153–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1153-1168.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Effects of staphylococcal -toxin on the structure of erythrocyte membranes: a biochemical and freeze-etching study. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):321–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P. Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmacol Ther. 1982;19(1):55–106. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(82)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell C. G., Peterson P. K., Schmeling D. J., Quie P. G. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on phagocytosis of staphylococci by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):975–980. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.975-980.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell C. G., Peterson P. K., Townsend K., Quie P. G., Kim Y. Biological effects of the interaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with human serum. Infect Immun. 1982 Dec;38(3):981–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.3.981-985.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant N. J., Aunis D., Bader M. F. Morphology and secretory activity of digitonin- and alpha-toxin-permeabilized chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1987 Dec;23(3):1143–1155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. S., Kehoe M. Primary sequence of the alpha-toxin gene from Staphylococcus aureus wood 46. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):615–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.615-618.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Alouf J. E., Siffert O., Baleux F. Reaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with peptide-induced antibodies. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3856–3862. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3856-3862.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Bondurant M. Susceptibility to staphylococcal alpha-toxin of Friend virus-infected murine erythroblasts during differentiation. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):114–118. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.114-118.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Boquet P., Duflot E., Alouf J. E., Montecucco C., Papini E. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: a study of membrane penetration and pore formation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14978–14984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Burt A. M., Robinson J. P., Blankenship M., Harshman D. L. Disruption of myelin sheaths in mouse brain in vitro and in vivo by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Toxicon. 1985;23(5):801–806. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(85)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Sugg N. Effect of calcium ions on staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):37–40. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.37-40.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman S., Sugg N., Gametchu B., Harrison R. W. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: a structure-function study using a monoclonal antibody. Toxicon. 1986;24(4):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(86)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon D. A., Hladky S. B. Ion transport across thin lipid membranes: a critical discussion of mechanisms in selected systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1972 May;5(2):187–282. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert T. E., Fackrell H. B. Inhibition of staphylococcal alpha-toxin by covalent modification of an arginine residue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 18;916(3):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90188-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J. Aggregation of IgE receptors induces degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells permeabilized with alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugo F., Sinner A., Reichwein J., Bhakdi S. Quantitation of monomeric and oligomeric forms of membrane-bound staphylococcal alpha-toxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2933–2939. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2933-2939.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikigai H., Nakae T. Assembly of the alpha-toxin-hexamer of Staphylococcus aureus in the liposome membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2156–2160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikigai H., Nakae T. Conformational alteration in alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus concomitant with the transformation of the water-soluble monomer to the membrane oligomer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jul 16;130(1):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90398-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikigai H., Nakae T. Interaction of the alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus with the liposome membrane. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2150–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Downing K. H., Walian P. J. Structure of PhoE porin in projection at 3.5 A resolution. J Struct Biol. 1990 Mar;103(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(90)90086-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Korbecki M., Zak C. Histochemical demonstration of changes in enzymatic activity of KB cells produced by staphylococcal alpha and beta hemolysins. J Infect Dis. 1965 Dec;115(5):421–428. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.5.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeljaszewicz J., Szmigielski S., Zak C. Distribution of 131-I-labelled staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin in the rabbit. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1969;209(3):310–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julander I. G., Granström M., Hedström S. A., Möllby R. The role of antibodies against alpha-toxin and teichoic acid in the diagnosis of staphylococcal infections. Infection. 1983 Mar-Apr;11(2):77–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01641071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapral F. A., Godwin J. R., Dye E. S. Formation of intraperitoneal abscesses by Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.204-211.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I. Inhibitory effect of a lethal toxic fragment of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 11;570(2):388–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Naiki M. Ganglioside and rabbit erythrocyte membrane receptor for staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):289–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.289-291.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Sakoda K., Saito M., Suzuki Y. Effects of lectins on the hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes by straphylococcal alpha toxin. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(9):517–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1977.tb00317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Sakoda K., Saito M., Suzuki Y., Watanabe M. Inhibitory effect of flavin mononucleotide on the hemolysis of rabbit erythrocytes by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):696–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.696-697.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Watanabe M. Chemical studies on staphylococcal alpha-toxin and its fragments. Toxicon. 1980;18(3):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(80)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Watanabe M., Kumazawa N. H. Inhibition of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):286–288. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.286-288.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Duncan J., Foster T., Fairweather N., Dougan G. Cloning, expression, and mapping of the Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin determinant in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1105-1111.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C. Antibiotic interaction with model membranes. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1970;10:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.10.040170.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovici P., Chan K. F. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. 2. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity in PC12 cells. Toxicon. 1987;25(6):637–647. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(87)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. Y., Birkbeck T. H. Effect of phenethyl alcohol on Staphylococcus aureus alpha-lysin production. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):112–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.112-117.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind I., Ahnert-Hilger G., Fuchs G., Gratzl M. Purification of alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus and application to cell permeabilization. Anal Biochem. 1987 Jul;164(1):84–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90371-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Vogel M., Goebel W. Mutations affecting activity and transport of haemolysin in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Feb;206(2):238–245. doi: 10.1007/BF00333579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maharaj I., Fackrell H. B. Rabbit erythrocyte band 3: a receptor for staphylococcal alpha toxin. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Apr;26(4):524–531. doi: 10.1139/m80-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar M., Maheswaran S. K., Frommes S. P., Lindorfer R. K. Platelet damaging factor, a fifth activity of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):224–231. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.224-231.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. M. Mechanism of cytolysis by complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2954–2958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorek N., Bar-Tana J. Lipid synthesis in permeabilized cultured rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4450–4455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Cellular signalling in programmed cell death (apoptosis). Immunol Today. 1990 Apr;11(4):120–121. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90048-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen B. F., Arion W. J. Permeabilization of rat hepatocytes with Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1922–1929. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee M. P., Kreger A., Leake E. S., Harshman S. Toxicity of staphylococcal alpha toxin for rabbit alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.439-444.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNiven A. C., Owen P., Arbuthnott J. P. Multiple forms of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Med Microbiol. 1972 Feb;5(1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/00222615-5-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G. Ionic channels formed by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: voltage-dependent inhibition by divalent and trivalent cations. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(2):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01869935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morfeldt E., Janzon L., Arvidson S., Löfdahl S. Cloning of a chromosomal locus (exp) which regulates the expression of several exoprotein genes in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Mar;211(3):435–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00425697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M., Kreiswirth B., Foster T. J. Cryptic alpha-toxin gene in toxic shock syndrome and septicaemia strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1947–1955. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly M., de Azavedo J. C., Kennedy S., Foster T. J. Inactivation of the alpha-haemolysin gene of Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4 by site-directed mutagenesis and studies on the expression of its haemolysins. Microb Pathog. 1986 Apr;1(2):125–138. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(86)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson A., Kavéus U., Hacksell I., Thelestam M., Hebert H. Crystalline layers and three-dimensional structure of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90162-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson A., Kavéus U., Thelestam M., Hebert H. The projection structure of alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus in human platelet membranes as analyzed by electron microscopy and image processing. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Aug;100(2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(88)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel A. H., Nowlan P., Weavers E. D., Foster T. Virulence of protein A-deficient and alpha-toxin-deficient mutants of Staphylococcus aureus isolated by allele replacement. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3103–3110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3103-3110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattee P. A. Chromosomal map location of the alpha-hemolysin structural gene in Staphylococcus aureus NCTC 8325. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):593–596. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.593-596.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederzolli C., Cescatti L., Menestrina G. Chemical modification of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin by diethylpyrocarbonate: role of histidines in its membrane-damaging properties. J Membr Biol. 1991 Jan;119(1):41–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01868539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrini B., Möllby R. Activation of human lymphocytes in vitro by membrane-damaging toxins from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):952–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.952-956.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phimister G. M., Freer J. H. Binding of 125I-alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus to erythrocytes. J Med Microbiol. 1984 Oct;18(2):197–204. doi: 10.1099/00222615-18-2-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. J., Barnwell P., Werner A. S. Detoxification of staphylococcal alpha toxin by hydrocortisone and methylprednisolone. J Med Microbiol. 1978 Feb;11(1):67–73. doi: 10.1099/00222615-11-1-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P., Kreiswirth B., O'Reilly M., Schlievert P., Gruss A., Novick R. P. Regulation of exoprotein gene expression in Staphylococcus aureus by agar. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jan;202(1):58–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00330517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichwein J., Hugo F., Roth M., Sinner A., Bhakdi S. Quantitative analysis of the binding and oligomerization of staphylococcal alpha-toxin in target erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):2940–2944. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.2940-2944.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogolsky M. Nonenteric toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Sep;43(3):320–360. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.3.320-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL I., COHEN S. ACTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL TOXIN ON HUMAN PLATELETS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Dec;114:488–502. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.5.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Haest C. W., Plasa G., Deuticke B. Bacterial cytotoxins, amphotericin B and local anesthetics enhance transbilayer mobility of phospholipids in erythrocyte membranes. Consequences for phospholipid asymmetry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 13;855(3):325–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrezenmeier H., Ahnert-Hilger G., Fleischer B. Inactivation of a T cell receptor-associated GTP-binding protein by antibody-induced modulation of the T cell receptor/CD3 complex. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):817–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
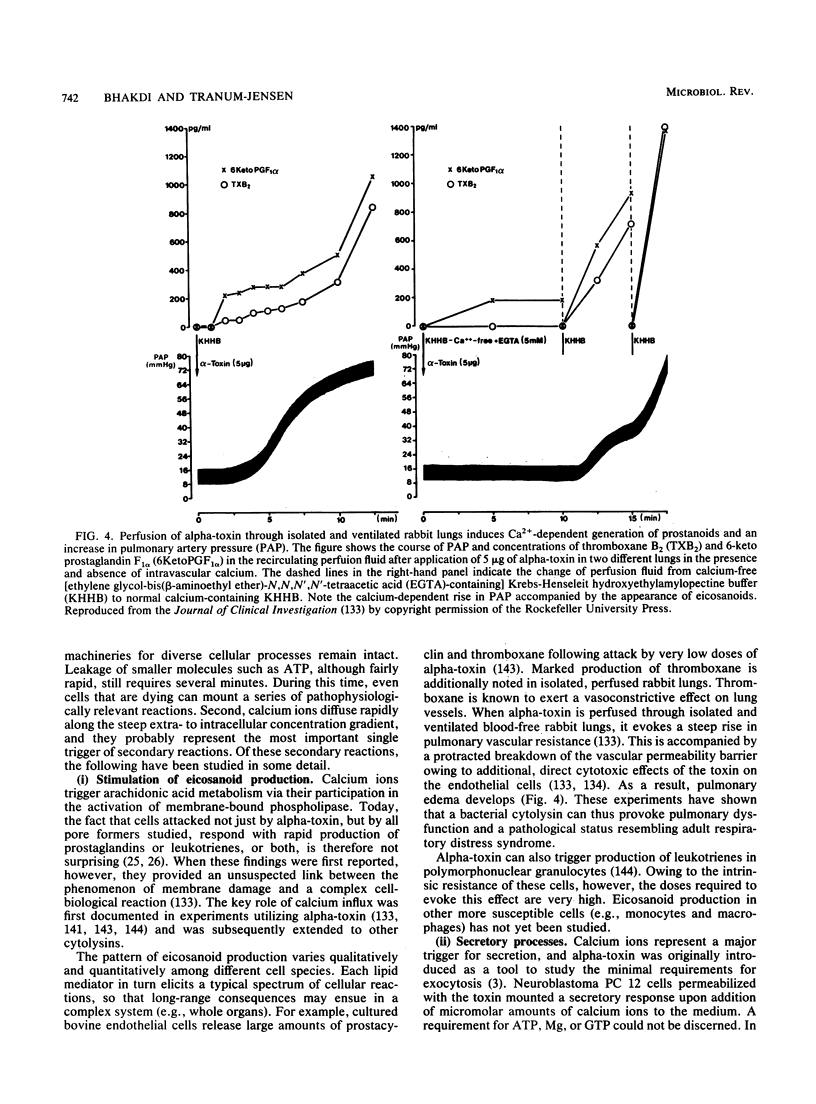
- Seeger W., Bauer M., Bhakdi S. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin elicits hypertension in isolated rabbit lungs. Evidence for thromboxane formation and the role of extracellular calcium. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):849–858. doi: 10.1172/JCI111502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Birkemeyer R. G., Ermert L., Suttorp N., Bhakdi S., Duncker H. R. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced vascular leakage in isolated perfused rabbit lungs. Lab Invest. 1990 Sep;63(3):341–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seydel U., Schröder G., Brandenburg K. Reconstitution of the lipid matrix of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria as asymmetric planar bilayer. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jul;109(2):95–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01870848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Physical and chemical studies on staphylococcal -toxins A and B . Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Harshman S. Purification and properties of two forms of staphylococcal toxin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jul 3;12(14):2672–2677. doi: 10.1021/bi00738a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Habben E. Effect of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on intracellular Ca2+ in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2228–2234. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2228-2234.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Hessz T., Seeger W., Wilke A., Koob R., Lutz F., Drenckhahn D. Bacterial exotoxins and endothelial permeability for water and albumin in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C368–C376. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Dewein E., Bhakdi S., Roka L. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced PGI2 production in endothelial cells: role of calcium. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C127–C134. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp N., Seeger W., Zucker-Reimann J., Roka L., Bhakdi S. Mechanism of leukotriene generation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes by staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):104–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.104-110.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmigielski S., Blankenship M., Robinson J. P., Harshman S. Injury of myelin sheaths in isolated rabbit vagus nerves by alpha-toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxicon. 1979;17(4):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUBLER J. H., KAPRAL F. A., MUDD S. ROLE OF ALPHA-TOXIN IN LESION FORMATION BY STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS ON SUTURES SUBCUTANEOUSLY IMPLANTED IN MICE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:51–57. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.51-57.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A. P., EGNER W. The site of action of the Staphylococcus alpha toxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Jan 1;113:67–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.113.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAL A., EGNER W. Local effect of staphylococcal toxin; studies on blood vessels with particular reference to phenomenon dermonecrosis. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954 May;57(5):392–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Blomqvist L. Staphylococcal alpha toxin--recent advances. Toxicon. 1988;26(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(88)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Jolivet-Reynaud C., Alouf J. E. Photolabeling of staphylococcal alpha-toxin from within rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):444–449. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90326-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Determination of toxin-induced leakage of different-size nucleotides through the plasma membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):640–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.640-648.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Survival of cultured cells after functional and structural disorganization of plasma membrane by bacterial haemolysins and phospholipases. Toxicon. 1983;21(6):805–815. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(83)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thielens N. M., Lohner K., Esser A. F. Human complement protein C9 is a calcium binding protein. Structural and functional implications. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6665–6670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobkes N., Wallace B. A., Bayley H. Secondary structure and assembly mechanism of an oligomeric channel protein. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1915–1920. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Christianson K. K., Iandolo J. J. Transport and processing of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):524–528. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.524-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vann J. M., Proctor R. A. Cytotoxic effects of ingested Staphylococcus aureus on bovine endothelial cells: role of S. aureus alpha-hemolysin. Microb Pathog. 1988 Jun;4(6):443–453. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel F., Blanckaert N. Endogenous esterification of bilirubin by liver microsomes. Evidence for an intramicrosomal pool of UDP-glucose and lumenal orientation of bilirubin UDP-glycosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4616–4623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. D., Adlam C., McCartney A. C., Arbuthnott J. P., Thorley C. M. A histopathological study of the effects of highly purified staphlococcal alpha and beta toxins on the lactating mammary gland and skin of the rabbit. J Comp Pathol. 1979 Apr;89(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(79)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Kato I. Purification and some properties of a lethal toxic fragment of staphylococcal alpha-toxin by tryptic digestion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 21;535(2):388–400. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Tomita T., Yasuda T. Membrane-damaging action of staphylococcal alpha-toxin on phospholipid-cholesterol liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 23;898(3):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Sessa G., Bernheimer A. W. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: effects on artificial lipid spherules. Science. 1966 Nov 11;154(3750):772–774. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3750.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmer T., Ando B., Sims P. J. Complement C5b-9-stimulated platelet secretion is associated with a Ca2+-initiated activation of cellular protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13674–13681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmer T., Esmon C. T., Sims P. J. On the mechanism by which complement proteins C5b-9 increase platelet prothrombinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14587–14592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D., Fackrell H. B. Trypsin-mediated activation of the alpha-haemolysin of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):29–38. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M., Caird J. D. Further observations on the mode of action of the alpha toxin of Staphylococcus aureus "Wood-46". Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jul;18(7):987–992. doi: 10.1139/m72-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman G. M. The hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Dec;39(4):317–344. doi: 10.1128/br.39.4.317-344.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurzel M., Bernheimer A. W., Zweifach B. W. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin-induced contraction of isolated arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1966 Feb;210(2):360–364. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.2.360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Merwe P. A., Millar R. P., Wakefield I. K., Davidson J. S. Mechanisms of luteinizing-hormone exocytosis in Staphylococcus aureus-alpha-toxin-permeabilized sheep gonadotropes. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):901–908. doi: 10.1042/bj2640901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Vijver J. C., van Es-Boon M. M., Michel M. F. A study of virulence factors with induced mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol. 1975 May;8(2):279–287. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-2-279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]