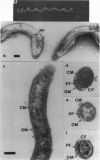
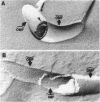
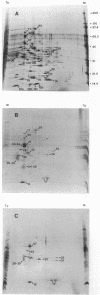
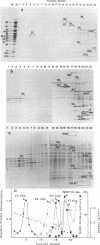
Abstract
Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum, the spirochete that causes syphilis, is unusual in a number of respects, including its small genome size, inability to grow under standard in vitro culture conditions, microaerophilism, apparent paucity of outer membrane proteins, structurally complex periplasmic flagella, and ability to evade the host immune responses and cause disease over a period of years to decades. Many of these attributes are related ultimately to its protein content. Our knowledge of the activities, structure, and immunogenicity of its proteins has been expanded by the application of recombinant DNA, hybridoma, and structural fractionation techniques. The purpose of this monograph is to summarize and correlate this new information by using two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, monoclonal antibody reactivity, sequence data, and other properties as the bases of polypeptide identification. The protein profiles of the T. pallidum subspecies causing syphilis, yaws, and endemic syphilis are virtually indistinguishable but differ considerably from those of other treponemal species. Among the most abundant polypeptides are a group of lipoproteins of unknown function that appear to be important in the immune response during syphilitic infection. The periplasmic flagella of T. pallidum and other spirochetes are unique with regard to their protein content and ultrastructure, as well as their periplasmic location. They are composed of three core proteins (homologous to the other members of the eubacterial flagellin family) and a single, unrelated sheath protein; the functional significance of this arrangement is not understood at present. Although the bacterium contains the chaperonins GroEL and DnaK, these proteins are not under the control of the heat shock regulon as they are in most organisms. Studies of the immunogenicity of T. pallidum proteins indicate that many may be useful for immunodiagnosis and immunoprotection. Future goals in T. pallidum polypeptide research include continued elucidation of their structural locations and functional activities, identification and characterization of the low-abundance outer membrane proteins, further study of the immunoprotective and immunodiagnostic potential of T. pallidum proteins, and clarification of the roles of treponemal proteins in pathogenesis.
Full text
PDF

























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins D. R., Purcell B. K., Mitra M. M., Norgard M. V., Radolf J. D. Lipid modification of the 17-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum determines macrophage activation as well as amphiphilicity. Infect Immun. 1993 Apr;61(4):1202–1210. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.4.1202-1210.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Analysis of serum IgG against Treponema pallidum protein antigens in experimentally infected rabbits. Br J Vener Dis. 1981 Oct;57(5):302–308. doi: 10.1136/sti.57.5.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface characterization of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):814–823. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.814-823.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderete J. F., Freeman-Shade L., Baseman J. B. Immunodiagnostic test for detection of serum antibody to Treponema pallidum (syphilis): fibronectin as a capture vehicle for treponemal adhesins. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Nov 28;84(1-2):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90443-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
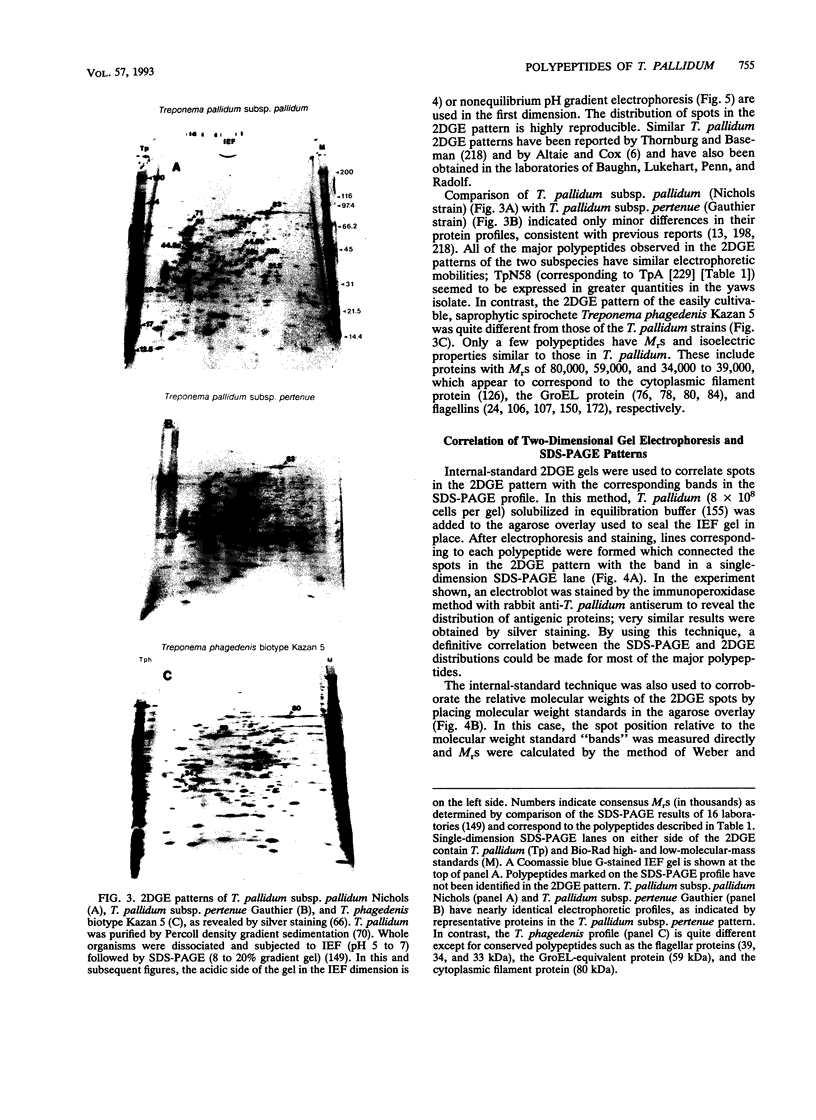
- Altaie S. S., Cox D. L. Identification of T. pallidum polypeptides: a comparative study between the protein profiles of in vitro cultivated and in vivo propagated Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Appl Theor Electrophor. 1991;1(6):291–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin F. E., Barbieri J. T., Corin R. E., Grigas K. E., Cox C. D. Distribution of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities among Treponema pallidum and other spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):372–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.372-379.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M. J., Cockayne A., Penn C. W. Monoclonal antibodies directed against surface-associated polypeptides of Treponema pallidum define a biologically active antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1793–1803. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M. J., Cockayne A., Penn C. W. Production of murine monoclonal antibodies to the major axial filament polypeptide of Treponema pallidum. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jul;133(7):1805–1813. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-7-1805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey M. J., Thomas C. M., Cockayne A., Strugnell R. A., Penn C. W. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Sep;135(9):2365–2378. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-9-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Fohn M. J., Lukehart S. A. Development of cellular immunity to individual soluble antigens of Treponema pallidum during experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4363–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Hook E. W., 3rd, Bonin P., Handsfield H. H., Lukehart S. A. Antigens of Treponema pallidum recognized by IgG and IgM antibodies during syphilis in humans. J Infect Dis. 1985 Feb;151(2):264–272. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.2.264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Antigenic cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and other pathogenic members of the family Spirochaetaceae. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):116–121. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.116-121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Molecular basis of immunological cross-reactivity between Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.634-638.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Hayes E. C. Molecular characterization of receptor binding proteins and immunogens of virulent Treponema pallidum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E. Antibody-independent interactions of fibronectin, C1q, and human neutrophils with Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.456-464.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E., Musher D. M. Radioimmunoassays for the detection of antibodies to treponemal polypeptide antigens in serum. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jun;21(6):922–929. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.6.922-929.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baughn R. E. Role of fibronectin in the pathogenesis of syphilis. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jul-Aug;9 (Suppl 4):S372–S385. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.supplement_4.s372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic and structural characterization of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) endoflagella. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):168–175. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.168-175.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Giladi M., Champion C. I., Haake D. A., Chikami G. K., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Identification of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum genes encoding signal peptides and membrane-spanning sequences using a novel alkaline phosphatase expression vector. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2405–2415. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. The antigenic interrelationship between the endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum Nichols strain. I. Treponemicidal activity of cross-reactive endoflagellar antibodies against T. pallidum. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2973–2979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco D. R., Walker E. M., Haake D. A., Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Complement activation limits the rate of in vitro treponemicidal activity and correlates with antibody-mediated aggregation of Treponema pallidum rare outer membrane protein. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1914–1921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein L. A., Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Immunization of rabbits with recombinant Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D alters the course of experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2415–2421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Biochemical and cytological analysis of the complex periplasmic flagella from Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4023–4032. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4023-4032.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahamsha B., Greenberg E. P. Cloning and sequence analysis of flaA, a gene encoding a Spirochaeta aurantia flagellar filament surface antigen. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1692–1697. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1692-1697.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMBERLAND M. C., TURNER T. B. The rate of multiplication of Treponema pallidum in normal and immune rabbits. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1949 May;33(3):201–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Brandt M. E., Erwin A. L., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Major integral membrane protein immunogens of Treponema pallidum are proteolipids. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2872-2877.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., DeOgny L., Slaughter C., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Acylation of the 47-kilodalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum determines its hydrophobicity. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2878–2885. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2878-2885.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain N. R., Radolf J. D., Hsu P. L., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Genetic and physicochemical characterization of the recombinant DNA-derived 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):71–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.71-78.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Borenstein L. A., Lovett M. A., Blanco D. R. Immunization with Treponema pallidum endoflagella alters the course of experimental rabbit syphilis. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):3158–3161. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.3158-3161.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion C. I., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A., Blanco D. R. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of two class B endoflagellar genes of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum encoding the 34.5- and 31.0-kilodalton proteins. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1697–1704. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1697-1704.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne A., Bailey M. J., Penn C. W. Analysis of sheath and core structures of the axial filament of Treponema pallidum. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Jun;133(6):1397–1407. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-6-1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne A., Sanger R., Ivic A., Strugnell R. A., MacDougall J. H., Russell R. R., Penn C. W. Antigenic and structural analysis of Treponema denticola. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Dec;135(12):3209–3218. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-12-3209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne A., Strugnell R. A., Bailey M. J., Penn C. W. Comparative antigenic analysis of Treponema pallidum laboratory and street strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Aug;135(8):2241–2247. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-8-2241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Chang P., McDowall A. W., Radolf J. D. The outer membrane, not a coat of host proteins, limits antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1076-1083.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. L., Riley B., Chang P., Sayahtaheri S., Tassell S., Hevelone J. Effects of molecular oxygen, oxidation-reduction potential, and antioxidants upon in vitro replication of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):3063–3072. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.3063-3072.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Identification of Treponema pallidum penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5298–5300. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5298-5300.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham T. M., Walker E. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Selective release of the Treponema pallidum outer membrane and associated polypeptides with Triton X-114. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5789–5796. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5789-5796.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Ray P. H., Leong J., Benedict C. D., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and purification of a recombinant Treponema pallidum basic membrane protein antigen expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1106–1115. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1106-1115.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Chang J. Y., Shaper J. H., Glazer A. N. Amino acid sequence of flagellin of Bacillus subtilis 168. III. Tryptic peptides, N-bromosuccinimide peptides, and the complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 10;251(3):705–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dettori G., Grillo R., Mora G., Cavalli A., Alinovi A., Chezzi C., Sanna A. Evaluation of Western immunoblotting technique in the serological diagnosis of human syphilitic infections. Eur J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;5(1):22–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00145040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Lovett M. A. Properties of an ordered ring structure formed by recombinant Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):732–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.732-739.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Radolf J. D., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Native surface association of a recombinant 38-kilodalton Treponema pallidum antigen isolated from the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):586–593. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.586-593.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehniger T. E., Walfield A. M., Cunningham T. M., Radolf J. D., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Purification and characterization of a cloned protease-resistant Treponema pallidum-specific antigen. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.598-607.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Cultivation of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue culture. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):908–915. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.908-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Cox D. L., Moeckli R. A. Further studies on replication of virulent Treponema pallidum in tissue cultures of Sf1Ep cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):449–455. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.449-455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Gannon E. M. Further evidence for hyaluronidase activity of Treponema pallidum. Can J Microbiol. 1983 Nov;29(11):1507–1513. doi: 10.1139/m83-232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A. Interactions of fibronectin with Treponema pallidum. Genitourin Med. 1985 Jun;61(3):147–155. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.3.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Oakes S. G. Morphological destruction of cultured cells by the attachment of Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Feb;58(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A. The hyaluronidase associated with Treponema pallidum facilitates treponemal dissemination. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1023–1028. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1023-1028.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J. Syphilis vaccine: up-regulation of immunogenicity by cyclophosphamide, Ribi adjuvant, and indomethacin confers significant protection against challenge infection in rabbits. Vaccine. 1991 Apr;9(4):266–272. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90110-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fohn M. J., Wignall S., Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A. Specificity of antibodies from patients with pinta for antigens of Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):32–37. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardini F. C., Hobbs M. M., Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Complementation of an Escherichia coli proC mutation by a gene cloned from Treponema pallidum. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2996–3002. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2996-3002.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Bishop N. H., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1973–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Fehniger T. E., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1287–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Molecular characterization of common treponemal antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):825–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.825-828.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanff P. A., Norris S. J., Lovett M. A., Miller J. N. Purification of Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, by Percoll density gradient centrifugation. Sex Transm Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;11(4):275–286. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B., Pedersen P. E., Schouls L. M., Severin E., van Embden J. D. Genetic characterization and partial sequence determination of a Treponema pallidum operon expressing two immunogenic membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1227–1237. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1227-1237.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. DNA sequence analysis suggests that expression of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is controlled by an alternative sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6422–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensel U., Wellensiek H. J., Bhakdi S. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoblotting as a serological tool in the diagnosis of syphilitic infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.82-87.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Cockayne A., Schouls L. M., van Emden J. D. Immunochemical characterization and purification of Treponema pallidum antigen TpD expressed by Escherichia coli K12. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):237–244. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Knudsen J. D., Axelsen N. H. Cloning and expression of treponema pallidum common antigen (Tp-4) in Escherichia coli K12. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):587–596. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Petersen C. S., Axelsen N. H. Purified flagella from Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter does not induce protective immunity against experimental syphilis in rabbits. Sex Transm Dis. 1985 Jul-Sep;12(3):124–127. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198507000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Petersen C. S., Pedersen N. S., Høiby N., Axelsen N. H. Immunological cross-reaction between antigen Tp-4 of Treponema pallidum and an antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1984 Aug;92(4):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb02818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindersson P., Thomas D., Stamm L., Penn C., Norris S., Joens L. A. Interaction of spirochetes with the host. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):629–639. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Fujita H., Yamaguchi S., Iino T. Regions of Salmonella typhimurium flagellin essential for its polymerization and excretion. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):291–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.291-296.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd Syphilis and HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):530–534. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H., Birch-Andersen A. Electron microscopy of endoflagella and microtubules in Treponema reiter. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(1):37–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. Further observations on the ultrastructure of Treponema pallidum nichols. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(2):297–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. S., Cook R. G., Norris S. J. Isolation and characterization of a Treponema pallidum major 60-kilodalton protein resembling the groEL protein of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2862–2870. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2862-2870.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Chamberlain N. R., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Zhang L. Q., Slaughter C. A., Radolf J. D., Sell S., Norgard M. V. Sequence analysis of the 47-kilodalton major integral membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Jan;57(1):196–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.1.196-203.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Qin M., Norris S. J., Sell S. Isolation and characterization of recombinant Escherichia coli clones secreting a 24-kilodalton antigen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1135–1143. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1135-1143.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard C. L., Gherardini F. C., Bassford P. J., Jr, Stamm L. V. Molecular cloning and characterization of a 35.5-kilodalton lipoprotein of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1521–1528. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1521-1528.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijsselmuiden O. E., Schouls L. M., Stolz E., Aelbers G. N., Agterberg C. M., Top J., van Embden J. D. Sensitivity and specificity of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using the recombinant DNA-derived Treponema pallidum protein TmpA for serodiagnosis of syphilis and the potential use of TmpA for assessing the effect of antibiotic therapy. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):152–157. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.152-157.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijsselmuiden O. E., Top J., Stolz E., van Eijk R. V. Development and evaluation of a monoclonal antibody inhibition enzyme linked immunosorbent assay to diagnose syphilis. Genitourin Med. 1989 Oct;65(5):308–315. doi: 10.1136/sti.65.5.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs R. D., Hanke J. H., Guzman-Verduzco L. M., Newport G., Agabian N., Norgard M. V., Lukehart S. A., Radolf J. D. Molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis of the 37-kilodalton endoflagellar sheath protein gene of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3403–3411. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3403-3411.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs R. D., Radolf J. D. Expression in Escherichia coli of the 37-kilodalton endoflagellar sheath protein of Treponema pallidum by use of the polymerase chain reaction and a T7 expression system. Infect Immun. 1990 Jul;58(7):2025–2034. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.7.2025-2034.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito F., Hunter E. F., George R. W., Pope V., Larsen S. A. Specific immunofluorescent staining of pathogenic treponemes with a monoclonal antibody. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Apr;30(4):831–838. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.4.831-838.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Marchitto K. S., Miller J. N., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody with hemagglutination, immobilization, and neutralization activities defines an immunodominant, 47,000 mol wt, surface-exposed immunogen of Treponema pallidum (Nichols). J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1404–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Canale-Parola E. Axial fibrils of anaerobic spirochetes: ultrastructure and chemical characteristics. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;81(2):146–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00412325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelson J. S., Adler B., Chapman A. J., Faine S. Identification of leptospiral flagellar antigens by gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):47–53. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Sellwood R., Lemcke R. M., Burrows M. R., Lysons R. J. Analysis of the axial filaments of Treponema hyodysenteriae by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jun;135(6):1625–1632. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-6-1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman M. B., de Leeuw O. S., van der Zeijst B. M., Kusters J. G. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of a Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae gene encoding a periplasmic flagellar sheath protein. Infect Immun. 1992 Jul;60(7):2920–2925. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.7.2920-2925.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G., Asaka J., Fujiwara T., Fujiwara T., Node K., Kondo E. Nucleotide sequence of the hag gene encoding flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1479–1483. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1479-1483.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwajima G. Construction of a minimum-size functional flagellin of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3305–3309. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3305-3309.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaVallie E. R., Stahl M. L. Cloning of the flagellin gene from Bacillus subtilis and complementation studies of an in vitro-derived deletion mutation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3085–3094. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3085-3094.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis L. L., Taber L. H., Baughn R. E. Evaluation of immunoglobulin M western blot analysis in the diagnosis of congenital syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):296–302. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.296-302.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Antiserum to the 33,000-dalton periplasmic-flagellum protein of "Treponema phagedenis" reacts with other treponemes and Spirochaeta aurantia. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):1030–1032. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.1030-1032.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Charon N. W. Treponema phagedenis has at least two proteins residing together on its periplasmic flagella. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):105–112. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.105-112.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberger R. J., Slivienski L. L., Yelton D. B., Charon N. W. Molecular genetic analysis of a class B periplasmic-flagellum gene of Treponema phagedenis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6404–6410. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6404-6410.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan S. M., Trust T. J., Guerry P. Evidence for posttranslational modification and gene duplication of Campylobacter flagellin. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3031–3038. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3031-3038.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Gubish E. R., Jr Identification of Treponema pallidum antigens: comparison with a nonpathogenic treponeme. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Baker-Zander S. A., Sell S. Characterization of the humoral immune response of the rabbit to antigens of Treponema pallidum after experimental infection and therapy. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Jan-Mar;13(1):9–15. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198601000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A. Prospects for development of a treponemal vaccine. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7 (Suppl 2):S305–S313. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7-supplement_2.s305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukehart S. A., Tam M. R., Hom J., Baker-Zander S. A., Holmes K. K., Nowinski R. C. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Treponema pallidum. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):462–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.462-473.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Terminal electron transport in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):885–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.885-890.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., DeRosier D. J. Bacterial flagellar structure and function. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Apr;34(4):442–451. doi: 10.1139/m88-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Jones S. A., Schell R. F., Holmans P. L., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody analysis of specific antigenic similarities among pathogenic Treponema pallidum subspecies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):660–666. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.660-666.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Selland-Grossling C. K., Norgard M. V. Molecular specificities of monoclonal antibodies directed against virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1986 Jan;51(1):168–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.1.168-176.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marra C. M. Syphilis and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Semin Neurol. 1992 Mar;12(1):43–50. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1041156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. H., Savage D. C. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and taxonomic implications of the flagellin gene of Roseburia cecicola. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2612–2617. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2612-2617.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda K., Kawata T. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic fibrils from treponemes. Microbiol Immunol. 1989;33(8):619–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1989.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R. M., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetic relationship between Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue, two noncultivable human pathogens. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):427–429. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.427-429.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R. M., Fieldsteel A. H., Harris D. L. Genetics of Treponema: characterization of Treponema hyodysenteriae and its relationship to Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):736–739. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.736-739.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. N. Immunity in experimental syphilis. VI. Successful vaccination of rabbits with Treponema pallidum, Nichols strain, attenuated by -irradiation. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1206–1215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirel D. B., Chamberlin M. J. The Bacillus subtilis flagellin gene (hag) is transcribed by the sigma 28 form of RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3095–3101. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3095-3101.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison M., Rood J. I., Faine S., Adler B. Molecular analysis of a Leptospira borgpetersenii gene encoding an endoflagellar subunit protein. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jul;137(7):1529–1536. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-7-1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison-Plummer J., Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of serum antibody to outer membrane proteins of Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Apr;59(2):75–79. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.2.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Identification of glycosylated protein antigens of Treponema pallidum and Treponema phagedenis. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Jul;259(4):468–476. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular analysis of immunoglobulins M and G immune response to protein antigens of Treponema pallidum in human syphilis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):127–132. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.127-132.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Molecular characterization of glycoprotein antigens on surface of Treponema pallidum: comparison with nonpathogenic Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter. Infect Immun. 1984 Dec;46(3):867–869. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.3.867-869.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis M., Müller F. Monoclonal antibodies to immunodominant surface-exposed protein antigens of Treponema pallidum. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;4(5):473–477. doi: 10.1007/BF02014427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M. Syphilis, neurosyphilis, penicillin, and AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jun;163(6):1201–1206. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.6.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Yamashita I., Vonderviszt F. Structure of the core and central channel of bacterial flagella. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):648–654. doi: 10.1038/342648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauman R. K., Holt S. C., Cox C. D. Purification, ultrastructure, and composition of axial filaments from Leptospira. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):264–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.264-280.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Cockayne A., Schouls L. M., Meloen R. H., Stolz E., van Embden J. D. A new attempt to distinguish serologically the subspecies of Treponema pallidum causing syphilis and yaws. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1600–1607. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1600-1607.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Hermans P. W., Paul A. N., Schouls L. M., van der Sluis J. J., van Embden J. D. Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum (Nichols) and Treponema pallidum subspecies pertenue (CDC 2575) differ in at least one nucleotide: comparison of two homologous antigens. Microb Pathog. 1989 Jan;6(1):29–42. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noordhoek G. T., Wieles B., van der Sluis J. J., van Embden J. D. Polymerase chain reaction and synthetic DNA probes: a means of distinguishing the causative agents of syphilis and yaws? Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):2011–2013. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.2011-2013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Chamberlain N. R., Swancutt M. A., Goldberg M. S. Cloning and expression of the major 47-kilodalton surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):500–506. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.500-506.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Miller J. N. Cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) antigen genes in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):435–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.435-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgard M. V., Selland C. K., Kettman J. R., Miller J. N. Sensitivity and specificity of monoclonal antibodies directed against antigenic determinants of Treponema pallidum Nichols in the diagnosis of syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Oct;20(4):711–717. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.4.711-717.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Charon N. W., Cook R. G., Fuentes M. D., Limberger R. J. Antigenic relatedness and N-terminal sequence homology define two classes of periplasmic flagellar proteins of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum and Treponema phagedenis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4072–4082. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4072-4082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Edmondson D. G. Factors affecting the multiplication and subculture of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum in a tissue culture system. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):534–539. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.534-539.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Edmondson D. G. Serum requirement for the multiplication of Treponema pallidum in a tissue-culture system: association of growth-promoting activity with the protein fraction. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):207–213. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Sell S. Antigenic complexity of Treponema pallidum: antigenicity and surface localization of major polypeptides. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2686–2692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes S. G., Repesh L. A., Pozos R. S., Fitzgerald T. J. Electrophysiological dysfunction and cellular disruption of sensory neurones during incubation with Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Aug;58(4):220–227. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.4.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen L., Hindersson P. Cloning and sequencing of a Treponema pallidum gene encoding a 31.3-kilodalton endoflagellar subunit (FlaB2). Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2166–2172. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2166-2172.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parales J., Jr, Greenberg E. P. Analysis of the Spirochaeta aurantia flaA gene and transcript. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Feb 1;106(3):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parales J., Jr, Greenberg E. P. N-terminal amino acid sequences and amino acid compositions of the Spirochaeta aurantia flagellar filament polypeptides. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1357–1359. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1357-1359.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paster B. J., Dewhirst F. E., Weisburg W. G., Tordoff L. A., Fraser G. J., Hespell R. B., Stanton T. B., Zablen L., Mandelco L., Woese C. R. Phylogenetic analysis of the spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(19):6101–6109. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.19.6101-6109.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Axelsen N. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of immunoglobulin M antibody against the Reiter treponeme flagellum in syphilis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Oct;16(4):608–614. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.4.608-614.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Axelsen N. H. Ribonucleic acid antigen from the Reiter treponeme used in an ELISA for antibodies in syphilis. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Nov;16(5):431–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. S., Petersen C. S., Vejtorp M., Axelsen N. H. Serodiagnosis of syphilis by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for IgG antibodies against the Reiter treponeme flagellum. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Apr;15(4):341–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bailey M. J., Cockayne A. The axial filament antigen of Treponema pallidum. Immunology. 1985 Apr;54(4):635–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Bassford P. J., Yelton D. B., Dunn J., Nelson D. R., Fukunaga M., Stanek G. Genetic approaches to cell biology and metabolism of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):605–613. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Cockayne A., Bailey M. J. The outer membrane of Treponema pallidum: biological significance and biochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Sep;131(9):2349–2357. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-9-2349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W., Rhodes J. G. Surface-associated antigens of Treponema pallidum concealed by an inert outer layer. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penn C. W. The eighth C. L. Oakley lecture. Pathogenicity and immunobiology of Treponema pallidum. J Med Microbiol. 1987 Aug;24(1):1–9. doi: 10.1099/00222615-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Cloning structural genes for Treponema pallidum immunogens and characterisation of recombinant treponemal surface protein, P2 (P2 star). Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):289–296. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Isolation of a Treponema pallidum gene encoding immunodominant outer envelope protein P6, which reacts with sera from patients at different stages of syphilis. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1160–1170. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Molecular cloning of Treponema pallidum outer envelope fibronectin binding proteins, P1 and P2. Genitourin Med. 1987 Dec;63(6):355–360. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.6.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell B. K., Chamberlain N. R., Goldberg M. S., Andrews L. P., Robinson E. J., Norgard M. V., Radolf J. D. Molecular cloning and characterization of the 15-kilodalton major immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3708–3714. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3708-3714.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell B. K., Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D. Lipid modification of the 15 kiloDalton major membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1371–1379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Antigenic interrelationship between endoflagella of Treponema phagedenis biotype Reiter and Treponema pallidum (Nichols): molecular characterization of endoflagellar proteins. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):626–634. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Borenstein L. A., Kim J. Y., Fehniger T. E., Lovett M. A. Role of disulfide bonds in the oligomeric structure and protease resistance of recombinant and native Treponema pallidum surface antigen 4D. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1365–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1365-1371.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Chamberlain N. R., Clausell A., Norgard M. V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Feb;56(2):490–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.2.490-498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Fehniger T. E., Silverblatt F. J., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. The surface of virulent Treponema pallidum: resistance to antibody binding in the absence of complement and surface association of recombinant antigen 4D. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):579–585. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.579-585.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Lernhardt E. B., Fehniger T. E., Lovett M. A. Serodiagnosis of syphilis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with purified recombinant Treponema pallidum antigen 4D. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jun;153(6):1023–1027. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.6.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Moomaw C., Slaughter C. A., Norgard M. V. Penicillin-binding proteins and peptidoglycan of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1248-1254.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Brandt M. E., Isaacs R. D., Thompson P. A., Beutler B. Lipoproteins of Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum activate cachectin/tumor necrosis factor synthesis. Analysis using a CAT reporter construct. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1968–1974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Pathogen specificity of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum integral membrane proteins identified by phase partitioning with Triton X-114. Infect Immun. 1988 Jul;56(7):1825–1828. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.7.1825-1828.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V., Schulz W. W. Outer membrane ultrastructure explains the limited antigenicity of virulent Treponema pallidum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2051–2055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley B. S., Oppenheimer-Marks N., Hansen E. J., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Virulent Treponema pallidum activates human vascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):484–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riviere G. R., Thomas D. D., Cobb C. M. In vitro model of Treponema pallidum invasiveness. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2267–2271. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2267-2271.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers G. C., Laird W. J., Coates S. R., Mack D. H., Huston M., Sninsky J. J. Serological characterization and gene localization of an Escherichia coli-expressed 37-kilodalton Treponema pallidum antigen. Infect Immun. 1986 Jul;53(1):16–25. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.1.16-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint Girons I., Norris S. J., Göbel U., Meyer J., Walker E. M., Zuerner R. Genome structure of spirochetes. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Cox C. D. Catabolism of glucose and fatty acids by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.60-68.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouls L. M., Ijsselmuiden O. E., Weel J., van Embden J. D. Overproduction and purification of Treponema pallidum recombinant-DNA-derived proteins TmpA and TmpB and their potential use in serodiagnosis of syphilis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2612–2623. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2612-2623.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouls L. M., Mout R., Dekker J., van Embden J. D. Characterization of lipid-modified immunogenic proteins of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog. 1989 Sep;7(3):175–188. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schouls L. M., van der Heide H. G., van Embden J. D. Characterization of the 35-kilodalton Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum recombinant lipoprotein TmpC and antibody response to lipidated and nonlipidated T. pallidum antigens. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3536–3546. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3536-3546.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Norris S. J. The biology, pathology, and immunology of syphilis. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;24:203–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Milward F., Lefebvre R., Schouls L., Fikrig E., Wasmoen T., Stover K., Menefee B., Robinson J. Spirochetes: vaccines, animal models and diagnostics. Res Microbiol. 1992 Jul-Aug;143(6):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(92)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Bassford P. J., Jr Cellular and extracellular protein antigens of Treponema pallidum synthesized during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):799–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.799-807.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Folds J. D., Bassford P. J., Jr Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1238–1241. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1238-1241.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Gherardini F. C., Parrish E. A., Moomaw C. R. Heat shock response of spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1991 Apr;59(4):1572–1575. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.4.1572-1575.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Hodinka R. L., Wyrick P. B., Bassford P. J., Jr Changes in the cell surface properties of Treponema pallidum that occur during in vitro incubation of freshly extracted organisms. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2255–2261. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2255-2261.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Kerner T. C., Jr, Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Identification and preliminary characterization of Treponema pallidum protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):709–721. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.709-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamm L. V., Parrish E. A., Gherardini F. C. Cloning of the recA gene from a free-living leptospire and distribution of RecA-like protein among spirochetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.183-189.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner B., Wong G. H., Graves S. Susceptibility of Treponema pallidum to the toxic products of oxygen reduction and the non-treponemal nature of its catalase. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Feb;60(1):14–22. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R. A., Handley C. J., Drummond L. P., Faine S. Characterization of the proteoglycans synthesized by rabbit testis in response to infection by Treponema pallidum. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):216–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R. A., Handley C. J., Drummond L., Faine S., Lowther D. A., Graves S. R. Polyanions in syphilis: evidence that glycoproteins and macromolecules resembling glycosaminoglycans are synthesised by host tissues in response to infection with Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1984 Apr;60(2):75–82. doi: 10.1136/sti.60.2.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R. A., Maskell D., Fairweather N., Pickard D., Cockayne A., Penn C., Dougan G. Stable expression of foreign antigens from the chromosome of Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strains. Gene. 1990 Mar 30;88(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90059-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R. A., Williams W. F., Drummond L., Pedersen J. S., Toh B. H., Faine S. Development of increased serum immunoblot reactivity against a 45,000-dalton polypeptide of Treponema pallidum (Nichols) correlates with establishment of chancre immunity in syphilitic rabbits. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):957–960. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.957-960.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strugnell R., Cockayne A., Penn C. W. Molecular and antigenic analysis of treponemes. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1990;17(4):231–250. doi: 10.3109/10408419009105727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. The 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum is a lipoprotein. Infect Immun. 1990 Feb;58(2):384–392. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.2.384-392.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Riley B. S., Radolf J. D., Norgard M. V. Molecular characterization of the pathogen-specific, 34-kilodalton membrane immunogen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Nov;57(11):3314–3323. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.11.3314-3323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swancutt M. A., Twehous D. A., Norgard M. V. Monoclonal antibody selection and analysis of a recombinant DNA-derived surface immunogen of Treponema pallidum expressed in Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):110–119. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.110-119.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez P. J., McCracken G. H., Jr, Wendel G. D., Olsen K., Threlkeld N., Norgard M. V. Molecular analysis of the fetal IgM response to Treponema pallidum antigens: implications for improved serodiagnosis of congenital syphilis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Mar;159(3):508–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.3.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Fogelman A. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Interactions of Treponema pallidum with endothelial cell monolayers. Eur J Epidemiol. 1989 Mar;5(1):15–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00145039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Navab M., Haake D. A., Fogelman A. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Treponema pallidum invades intercellular junctions of endothelial cell monolayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Baseman J. B. Comparison of major protein antigens and protein profiles of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):623–627. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.623-627.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., Morrison-Plummer J., Baseman J. B. Monoclonal antibodies to Treponema pallidum: recognition of a major polypeptide antigen. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueba G. A., Bolin C. A., Zuerner R. L. Characterization of the periplasmic flagellum proteins of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4761–4768. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4761-4768.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfield A. M., Hanff P. A., Lovett M. A. Expression of Treponema pallidum antigens in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):522–523. doi: 10.1126/science.7041257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfield A. M., Roche E. S., Zounes M. C., Kirkpatrick H., Wild M. A., Textor G., Tsai P. K., Richardson C. Primary structure of an oligomeric antigen of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):633–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.633-635.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Arnett J. K., Heath J. D., Norris S. J. Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum has a single, circular chromosome with a size of approximately 900 kilobase pairs. Infect Immun. 1991 Jul;59(7):2476–2479. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.7.2476-2479.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Borenstein L. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Analysis of outer membrane ultrastructure of pathogenic Treponema and Borrelia species by freeze-fracture electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5585–5588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5585-5588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker E. M., Zampighi G. A., Blanco D. R., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Demonstration of rare protein in the outer membrane of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by freeze-fracture analysis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5005–5011. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5005-5011.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Moter S. E., Simon M. M., Ebnet K., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. The Borrelia burgdorferi flagellum-associated 41-kilodalton antigen (flagellin): molecular cloning, expression, and amplification of the gene. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1711-1719.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
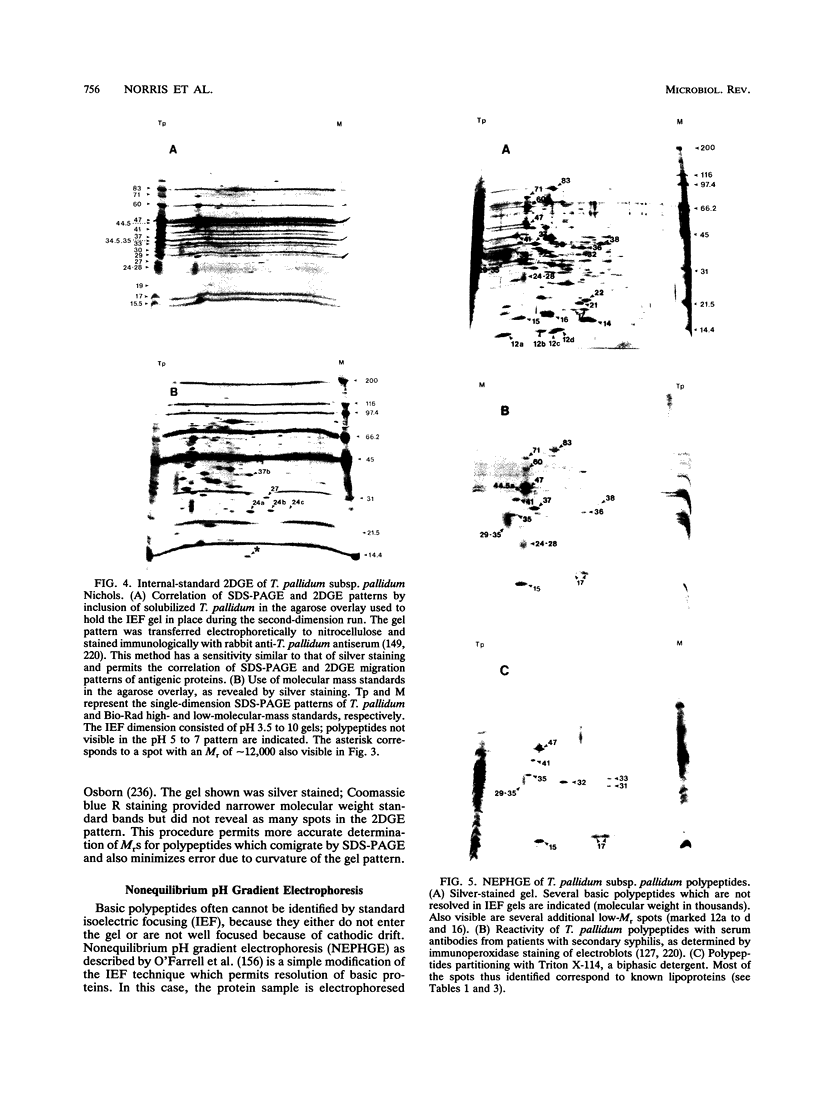
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei L. N., Joys T. M. Covalent structure of three phase-1 flagellar filament proteins of Salmonella. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90397-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel L. M., Brandt M. E., Norgard M. V. Analysis of the N-terminal region of the 47-kilodalton integral membrane lipoprotein of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1992 Apr;60(4):1568–1576. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.4.1568-1576.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Miller J. N., Urquhart A. W., Wicher V. Treponema pallidum-immobilizing antibodies in guinea pig experimental syphilis. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2900–2902. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2900-2902.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Schouls L. M., Wicher V., Van Embden J. D., Nakeeb S. S. Immunization of guinea pigs with recombinant TmpB antigen induces protection against challenge infection with Treponema pallidum Nichols. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4343–4348. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4343-4348.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., Wos S. M., Wicher V. Kinetics of antibody response to polypeptides of pathogenic and nonpathogenic treponemes in experimental syphilis. Sex Transm Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;13(4):251–257. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198610000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher K., van Embden J. D., Schouls L. M., Zabek J., Jakubowski A., Wicher V. Immunogenicity of three recombinant Treponema pallidum antigens examined in guinea pigs. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89(2-3):128–135. doi: 10.1159/000234935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher V., Zabek J., Wicher K. Pathogen-specific humoral response in Treponema pallidum-infected humans, rabbits, and guinea pigs. J Infect Dis. 1991 Apr;163(4):830–836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieland F., Paul G., Sumper M. Halobacterial flagellins are sulfated glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15180–15185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wos S. M., Wicher K. Antigenic evidence for host origin of exudative fluids in lesions of Treponema pallidum-infected rabbits. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):228–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.228-233.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Tokunaga M. Biogenesis of lipoproteins in bacteria. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;125:127–157. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71251-7_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton D. B., Limberger R. J., Curci K., Malinosky-Rummell F., Slivienski L., Schouls L. M., van Embden J. D., Charon N. W. Treponema phagedenis encodes and expresses homologs of the Treponema pallidum TmpA and TmpB proteins. Infect Immun. 1991 Oct;59(10):3685–3693. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.10.3685-3693.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vrije G. J., Batenburg A. M., Killian J. A., de Kruijff B. Lipid involvement in protein translocation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):143–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02024.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Embden J. D., van der Donk H. J., van Eijk R. V., van der Heide H. G., de Jong J. A., van Olderen M. F., Osterhaus A. B., Schouls L. M. Molecular cloning and expression of Treponema pallidum DNA in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.187-196.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Donk H. J., van Embden J. D., de Jong A., van Olderen M. F., Osterhaus A. D. Monoclonal antibodies to Treponema pallidum. Dev Biol Stand. 1984;57:107–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluis J. J., ten Kate F. J., Vuzevski V. D., Stolz E. Light and electron microscopy of rabbit testes infected with Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain): nature of deposited mucopolysaccharides and localisation of treponemes. Genitourin Med. 1987 Oct;63(5):297–304. doi: 10.1136/sti.63.5.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sluis J. J., van Dijk G., Boer M., Stolz E., van Joost T. Mucopolysaccharides in suspensions of Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit testes. Genitourin Med. 1985 Feb;61(1):7–12. doi: 10.1136/sti.61.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]