Abstract
The identification, cloning, and characterization of protein toxins from various species of bacilli have demonstrated the existence of mosquitocidal toxins with different structures, mechanisms of action, and host ranges. A start has been made in understanding the polypeptide determinants of toxicity and insecticidal activity, and the purification of toxins from recombinant organisms may lead to the elucidation of their X-ray crystal structures and the cloning of brush border membrane receptors. The results of cloning mosquitocidal toxins in heterologous microorganisms show the potential of expanding the range of susceptible mosquito species by combining several toxins of different host specificity in one cell. Toxins have been expressed in new microorganisms with the potential for increasing potency by persisting at the larval feeding zone. The powerful tools of bacterial genetics are being applied to engineer genetically stable, persistent toxin expression and expand the insecticidal host ranges of Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus thuringiensis strains. These techniques, together with modern formulation technology, should eventually lead to the construction of mosquitocidal microorganisms which are effective enough to have a real impact on mosquito-borne diseases.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad W., Ellar D. J. Directed mutagenesis of selected regions of a Bacillus thuringiensis entomocidal protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Mar 1;56(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90132-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktories K., Bärmann M., Ohishi I., Tsuyama S., Jakobs K. H., Habermann E. Botulinum C2 toxin ADP-ribosylates actin. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):390–392. doi: 10.1038/322390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albertini A. M., Galizzi A. Amplification of a chromosomal region in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1203–1211. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1203-1211.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander B., Priest F. G. Numerical classification and identification of Bacillus sphaericus including some strains pathogenic for mosquito larvae. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Feb;136(2):367–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-2-367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly C., Mulla M. S., Federici B. A. Ingestion, dissolution, and proteolysis of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin by mosquito larvae. J Invertebr Pathol. 1989 Jan;53(1):12–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(89)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aly C., Mulla M. S., Schnetter W., Xu B. Z. Floating bait formulations increase effectiveness of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis against Anopheles larvae. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 1987 Dec;3(4):583–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angsuthanasombat C., Chungjatupornchai W., Kertbundit S., Luxananil P., Settasatian C., Wilairat P., Panyim S. Cloning and expression of 130-kd mosquito-larvicidal delta-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis var. Israelensis in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):384–389. doi: 10.1007/BF00328128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angsuthanasombat C., Panyim S. Biosynthesis of 130-kilodalton mosquito larvicide in the cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum PR-6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2428–2430. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2428-2430.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Beckman W., Dunn P. Bacillus thuringiensis and related insect pathogens. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.1-24.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Han E. S., McGaughey W., Johnson D. The solubility of inclusion proteins from Bacillus thuringiensis is dependent upon protoxin composition and is a factor in toxicity to insects. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):981–986. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.981-986.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar E., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Rahamim E., Keynan A., Sandler N. Cloning and expression of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis delta-endotoxin DNA in B. sphaericus. J Invertebr Pathol. 1991 Mar;57(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(91)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. T., Rhodes C. S., Ferber D. M., Jenkins B., Kuhl S. A., Ely B. Construction of a genetic map for Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):889–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.889-896.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann L., Baumann P. Expression in Bacillus subtilis of the 51- and 42-kilodalton mosquitocidal toxin genes of Bacillus sphaericus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):252–253. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.252-253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Baumann P. Sequence analysis of the mosquitocidal toxin genes encoding 51.4- and 41.9-kilodalton proteins from Bacillus sphaericus 2362 and 2297. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2045–2050. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2045-2050.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Baumann L., Bowditch R. D., Broadwell A. H. Cloning of the gene for the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus 2362: evidence for a family of related sequences. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4061–4067. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4061-4067.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Clark M. A., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H. Bacillus sphaericus as a mosquito pathogen: properties of the organism and its toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):425–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.425-436.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann P., Unterman B. M., Baumann L., Broadwell A. H., Abbene S. J., Bowditch R. D. Purification of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus and evidence for high-molecular-weight precursors. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):738–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.738-747.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C., Hindley J. Bacillus sphaericus strain 2362: identification and nucleotide sequence of the 41.9 kDa toxin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5891–5891. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C., Hindley J., Ehrhardt A. F., Grounds T., de Souza I., Davidson E. W. Genetic determinants of host ranges of Bacillus sphaericus mosquito larvicidal toxins. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(2):510–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.2.510-518.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C., Jackson-Yap J., Oei C., Hindley J. Nucleotide sequence of two toxin genes from Bacillus sphaericus IAB59: sequence comparisons between five highly toxinogenic strains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7516–7516. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgouin C., Delécluse A., Ribier J., Klier A., Rapoport G. A Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis gene encoding a 125-kilodalton larvicidal polypeptide is associated with inverted repeat sequences. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3575–3583. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3575-3583.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgouin C., Delécluse A., de la Torre F., Szulmajster J. Transfer of the toxin protein genes of Bacillus sphaericus into Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and their expression. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):340–344. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.340-344.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Baumann L., Baumann P. The 42- and 51-kilodalton mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus sphaericus 2362: construction of recombinants with enhanced expression and in vivo studies of processing and toxicity. J Bacteriol. 1990 May;172(5):2217–2223. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.5.2217-2223.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Baumann P. Proteolysis in the gut of mosquito larvae results in further activation of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1333–1337. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1333-1337.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell A. H., Clark M. A., Baumann L., Baumann P. Construction by site-directed mutagenesis of a 39-kilodalton mosquitocidal protein similar to the larva-processed toxin of Bacillus sphaericus 2362. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4032–4036. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4032-4036.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruand C., Ehrlich S. D., Jannière L. Unidirectional theta replication of the structurally stable Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pAM beta 1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2171–2177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke W. F., McDonald K. O., Davidson E. W. Effect of UV Light on Spore Viability and Mosquito Larvicidal Activity of Bacillus sphaericus 1593. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Oct;46(4):954–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.4.954-956.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzby J. S., Porter R. D., Stevens S. E., Jr Expression of the Escherichia coli lacZ gene on a plasmid vector in a cyanobacterium. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):805–807. doi: 10.1126/science.2997920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caramori T., Albertini A. M., Galizzi A. In vivo generation of hybrids between two Bacillus thuringiensis insect-toxin-encoding genes. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90101-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Dai S. M., Frutos R., Federici B. A., Gill S. S. Properties of a 72-kilodalton mosquitocidal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. morrisoni PG-14 expressed in B. thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki by using the shuttle vector pHT3101. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):507–512. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.507-512.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles J. F., Kalfon A., Bourgouin C., de Barjac H. Bacillus sphaericus asporogenous mutants: morphology, protein pattern and larvicidal activity. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Mar-Apr;139(2):243–259. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung P. Y., Hammock B. D. Micro-lipid-droplet encapsulation of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis delta-endotoxin for control of mosquito larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):984–988. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.984-988.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilcott C. N., Ellar D. J. Comparative toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis crystal proteins in vivo and in vitro. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Sep;134(9):2551–2558. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-9-2551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chungjatupornchai W., Höfte H., Seurinck J., Angsuthanasombat C., Vaeck M. Common features of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins specific for Diptera and Lepidoptera. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):9–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplak W., Burnette W. N., Mar V. L., Kaljot K. T., Morris C. F., Chen K. K., Sato H., Keith J. M. Identification of a region in the S1 subunit of pertussis toxin that is required for enzymatic activity and that contributes to the formation of a neutralizing antigenic determinant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4667–4671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. A., Baumann P. Deletion analysis of the 51-kilodalton protein of the Bacillus sphaericus 2362 binary mosquitocidal toxin: construction of derivatives equivalent to the larva-processed toxin. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6759–6763. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6759-6763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Fourth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Intervirology. 1982;17(1-3):1–199. doi: 10.1159/000149278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convents D., Cherlet M., Van Damme J., Lasters I., Lauwereys M. Two structural domains as a general fold of the toxic fragment of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Feb 14;195(3):631–635. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Convents D., Houssier C., Lasters I., Lauwereys M. The Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. Evidence for a two domain structure of the minimal toxic fragment. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crickmore N., Nicholls C., Earp D. J., Hodgman T. C., Ellar D. J. The construction of Bacillus thuringiensis strains expressing novel entomocidal delta-endotoxin combinations. Biochem J. 1990 Aug 15;270(1):133–136. doi: 10.1042/bj2700133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouzet J., Lévy-Schil S., Cauchois L., Cameron B. Construction of a broad-host-range non-mobilizable stable vector carrying RP4 par-region. Gene. 1992 Jan 2;110(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90451-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W. Binding of the Bacillus sphaericus (Eubacteriales: Bacillaceae) toxin to midgut cells of mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae: relationship to host range. J Med Entomol. 1988 May;25(3):151–157. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.3.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W. Effects of Bacillus sphaericus 1593 and 2362 spore/crystal toxin on cultured mosquito cells. J Invertebr Pathol. 1986 Jan;47(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W., Oei C., Meyer M., Bieber A. L., Hindley J., Berry C. Interaction of the Bacillus sphaericus mosquito larvicidal proteins. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Dec;36(12):870–878. doi: 10.1139/m90-151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W., Urbina M., Payne J., Mulla M. S., Darwazeh H., Dulmage H. T., Correa J. A. Fate of Bacillus sphaericus 1593 and 2362 spores used as larvicides in the aquatic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):125–129. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.125-129.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. W. Variation in binding of Bacillus sphaericus toxin and wheat germ agglutinin to larval midgut cells of six species of mosquitoes. J Invertebr Pathol. 1989 Mar;53(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(89)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delécluse A., Bourgouin C., Klier A., Rapoport G. Specificity of action on mosquito larvae of Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis toxins encoded by two different genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):42–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00340177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delécluse A., Charles J. F., Klier A., Rapoport G. Deletion by in vivo recombination shows that the 28-kilodalton cytolytic polypeptide from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis is not essential for mosquitocidal activity. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3374–3381. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3374-3381.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenighini M., Montecucco C., Ripka W. C., Rappuoli R. Computer modelling of the NAD binding site of ADP-ribosylating toxins: active-site structure and mechanism of NAD binding. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):23–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01822.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan W. P., Dankocsik C., Gilbert M. P. Molecular characterization of a gene encoding a 72-kilodalton mosquito-toxic crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4732–4738. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4732-4738.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D., Bruand C., Sozhamannan S., Dabert P., Gros M. F., Jannière L., Gruss A. Plasmid replication and structural stability in Bacillus subtilis. Res Microbiol. 1991 Sep-Oct;142(7-8):869–873. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90067-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B. Genetics of Caulobacter crescentus. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:372–384. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04019-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferré J., Real M. D., Van Rie J., Jansens S., Peferoen M. Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticide in a field population of Plutella xylostella is due to a change in a midgut membrane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foo A. E., Yap H. H. Comparative bioassays of Bacillus thuringiensis H-14 formulations against four species of mosquitoes in Malaysia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1982 Jun;13(2):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garczynski S. F., Crim J. W., Adang M. J. Identification of putative insect brush border membrane-binding molecules specific to Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin by protein blot analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):2816–2820. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.2816-2820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garduno F., Thorne L., Walfield A. M., Pollock T. J. Structural relatedness between mosquitocidal endotoxins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):277–279. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.277-279.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge A. Z., Shivarova N. I., Dean D. H. Location of the Bombyx mori specificity domain on a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4037–4041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Langner A., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Bujard H. Cloning and analysis of strong promoters is made possible by the downstream placement of a RNA termination signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4936–4940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlitz M., Hrabak O., Schwab H. Partitioning of broad-host-range plasmid RP4 is a complex system involving site-specific recombination. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6194–6203. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6194-6203.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. S., Cowles E. A., Pietrantonio P. V. The mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis endotoxins. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37:615–636. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman I. F., Arnold J., Carlton B. C. Selection for resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies israelensis in field and laboratory populations of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. J Invertebr Pathol. 1986 May;47(3):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(86)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould F., Martinez-Ramirez A., Anderson A., Ferre J., Silva F. J., Moar W. J. Broad-spectrum resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in Heliothis virescens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7986–7990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss A., Ehrlich S. D. The family of highly interrelated single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):231–241. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.231-241.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerineau M., Alexander B., Priest F. G. Isolation and identification of Bacillus sphaericus strains pathogenic for mosquito larvae. J Invertebr Pathol. 1991 May;57(3):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(91)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Ellar D. J. Analysis of the molecular basis of insecticidal specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal delta-endotoxin. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 15;248(1):197–201. doi: 10.1042/bj2480197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Ellar D. J. Characterization of the toxicity and cytopathic specificity of a cloned Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein using insect cell culture. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):59–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Smith G. P., Ellar D. J. Delineation of the toxin coding fragments and an insect-specificity region of a dual toxicity Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider M. Z., Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Cloning and heterologous expression of an insecticidal delta-endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis var. aizawai IC1 toxic to both lepidoptera and diptera. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haima P., Bron S., Venema G. The effect of restriction on shotgun cloning and plasmid stability in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00329663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood C. R. Bacillus subtilis and its relatives: molecular biological and industrial workhorses. Trends Biotechnol. 1992 Jul;10(7):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(92)90233-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R. Genetic systems in cyanobacteria. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:418–430. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04022-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Berry C. Bacillus sphaericus strain 2297: nucleotide sequence of 41.9 kDa toxin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4168–4168. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Berry C. Identification, cloning and sequence analysis of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593 41.9 kD larvicidal toxin gene. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):187–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis in Bacillus subtilis. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:305–320. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Vanderbruggen H., Höfte H., Van Rie J., Jansens S., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins is correlated with the presence of high-affinity binding sites in the brush border membrane of target insect midguts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7844–7848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honée G., Vriezen W., Visser B. A Translation Fusion Product of Two Different Insecticidal Crystal Protein Genes of Bacillus thuringiensis Exhibits an Enlarged Insecticidal Spectrum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):823–825. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.823-825.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfte H., Whiteley H. R. Insecticidal crystal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):242–255. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.242-255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra J. E., Federici B. A. Isolation of a relatively nontoxic 65-kilodalton protein inclusion from the parasporal body of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.527-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannière L., Bruand C., Ehrlich S. D. Structurally stable Bacillus subtilis cloning vectors. Gene. 1990 Mar 1;87(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90495-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Recombination between short repeated sequences is more frequent in plasmids than in the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Nov;210(1):116–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00337766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannière L., Niaudet B., Pierre E., Ehrlich S. D. Stable gene amplification in the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1985;40(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalfon A., Charles J. F., Bourgouin C., de Barjac H. Sporulation of Bacillus sphaericus 2297: an electron microscope study of crystal-like inclusion biogenesis and toxicity to mosquito larvae. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Apr;130(4):893–900. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-4-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. H., Ellar D. J. Characterization and partial purification of a plasma membrane receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki lepidopteran-specific delta-endotoxin. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:89–101. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. H., Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Lectin-like binding of Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki lepidopteran-specific toxin is an initial step in insecticidal action. FEBS Lett. 1984 Mar 26;168(2):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80245-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koni P. A., Ellar D. J. Cloning and characterization of a novel Bacillus thuringiensis cytolytic delta-endotoxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):319–327. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C. J., Thomas A. A., van der Ende A., van Leen R. W., Borrias W. E., van den Hondel C. A., van Arkel G. A. A host-vector system for gene cloning in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans R2. Plasmid. 1983 Sep;10(2):156–163. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey L. A., Undeen A. H. Effect of formulation, concentration, and application time on the efficacy of Bacillus thuringiensis (H-14) against black fly (Diptera: Simuliidae) larvae under natural conditions. J Econ Entomol. 1984 Apr;77(2):412–418. doi: 10.1093/jee/77.2.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey L. A., Undeen A. H. Microbial control of black flies and mosquitoes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1986;31:265–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.31.010186.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecadet M. M., Chaufaux J., Ribier J., Lereclus D. Construction of Novel Bacillus thuringiensis Strains with Different Insecticidal Activities by Transduction and Transformation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):840–849. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.840-849.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lereclus D., Vallade M., Chaufaux J., Arantes O., Rambaud S. Expansion of insecticidal host range of Bacillus thuringiensis by in vivo genetic recombination. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Apr;10(4):418–421. doi: 10.1038/nbt0492-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Lockman H., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Falkow S. Recombinant DNA risk assessment studies in humans: efficacy of poorly mobilizable plasmids in biologic containment. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):699–709. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. D., Carroll J., Ellar D. J. Crystal structure of insecticidal delta-endotoxin from Bacillus thuringiensis at 2.5 A resolution. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):815–821. doi: 10.1038/353815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. W., Hindley J., Porter A. G., Priest F. G. New high-toxicity mosquitocidal strains of Bacillus sphaericus lacking a 100-kilodalton-toxin gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3470–3473. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3470-3473.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis J., Jayaraman K., Szulmajster J. Biocide gene(s) and biocidal activity in different strains of Bacillus sphaericus. Expression of the gene(s) in E. coli maxicells. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):23–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00332718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martens J. W., Honée G., Zuidema D., van Lent J. W., Visser B., Vlak J. M. Insecticidal activity of a bacterial crystal protein expressed by a recombinant baculovirus in insect cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2764–2770. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2764-2770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaughey W. H. Insect Resistance to the Biological Insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):193–195. doi: 10.1126/science.229.4709.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean K. M., Whiteley H. R. Expression in Escherichia coli of a cloned crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1017-1023.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medynski D. Genetic approaches to protein structure and function: point mutations as modifiers of protein function. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Sep;10(9):1002–1006. doi: 10.1038/nbt0992-1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt R. W., Dadd R. H., Walker E. D. Feeding behavior, natural food, and nutritional relationships of larval mosquitoes. Annu Rev Entomol. 1992;37:349–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.37.010192.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merryweather A. T., Weyer U., Harris M. P., Hirst M., Booth T., Possee R. D. Construction of genetically engineered baculovirus insecticides containing the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-73 delta endotoxin. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1535–1544. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H. The challenge of malaria. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):36–37. doi: 10.1126/science.1621092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat A. S. Research on biological pest control moves ahead. Science. 1991 Apr 12;252(5003):211–212. doi: 10.1126/science.2011760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Stevens S. E., Jr Cloning and expression of the cryIVD gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis in the cyanobacterium Agmenellum quadruplicatum PR-6 and its resulting larvicidal activity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1650–1655. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1650-1655.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P., Yousten A. A., Davidson E. W. Comparative studies of the mosquito-larval toxin of Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1 and 1593. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Nov;25(11):1227–1231. doi: 10.1139/m79-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P., Yousten A. A. Toxic activity of Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1 for mosquito larvae. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1047–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1047-1053.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narasu M. L., Gopinathan K. P. Purification of larvicidal protein from Bacillus sphaericus 1593. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):756–761. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80237-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niaudet B., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D. Recombination between repeated DNA sequences occurs more often in plasmids than in the chromosome of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(1):46–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00327921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas L., Nielsen-Leroux C., Charles J. F., Delécluse A. Respective role of the 42- and 51-kDa components of the Bacillus sphaericus toxin overexpressed in Bacillus thuringiensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Feb 1;106(3):275–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05976.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen-Leroux C., Charles J. F. Binding of Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin to a specific receptor on midgut brush-border membranes from mosquito larvae. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Dec 1;210(2):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogimori K., Tamura M., Yajima M., Ito K., Nakamura T., Kajikawa N., Maruyama Y., Ui M. Dual mechanisms involved in development of diverse biological activities of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, as revealed by chemical modification of lysine residues in the toxin molecule. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 28;801(2):232–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton N. B., Orzech K. A., Burke W. F., Jr Construction and characterization of plasmid vectors for cloning in the entomocidal organism Bacillus sphaericus 1593. Plasmid. 1985 May;13(3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Plasmid incompatibility. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):381–395. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.381-395.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Hynes R. H., Bender R. A. Recombination deficient mutant of Caulobacter crescentus. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(2):275–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00383006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oei C., Hindley J., Berry C. An analysis of the genes encoding the 51.4- and 41.9-kDa toxins of Bacillus sphaericus 2297 by deletion mutagenesis: the construction of fusion proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90315-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oei C., Hindley J., Berry C. Binding of purified Bacillus sphaericus binary toxin and its deletion derivatives to Culex quinquefasciatus gut: elucidation of functional binding domains. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jul;138(7):1515–1526. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-7-1515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohana B., Margalit J., Barak Z. Fate of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis under Simulated Field Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Apr;53(4):828–831. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.4.828-831.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padua L. E., Federici B. A. Development of mutants of the mosquitocidal bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies morrisoni (PG-14) toxic to lepidopterous or dipterous insects. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90293-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang Y., Frutos R., Federici B. A. Synthesis and toxicity of full-length and truncated bacterial CryIVD mosquitocidal proteins expressed in lepidopteran cells using a baculovirus vector. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):89–101. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao-intara M., Angsuthanasombat C., Panyim S. The mosquito larvicidal activity of 130 kDa delta-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis resides in the 72 kDa amino-terminal fragment. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):294–300. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Davidson E. W. Insecticidal activity of the crystalline parasporal inclusions and other components of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593 spore complex. J Invertebr Pathol. 1984 May;43(3):383–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(84)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereyra-Alférez B., Bravo A., Quintero R., Soberón X. The delta-endotoxin protein family displays a hydrophobic motif that might be implicated in toxicity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(15):2095–2098. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01382.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Joliff G., Mesas J. M., Klier A., Rapoport G., Ehrlich S. D. Hypersecretion of a cellulase from Clostridium thermocellum in Bacillus subtilis by induction of chromosomal DNA amplification. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jun;8(6):559–563. doi: 10.1038/nbt0690-559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Ross E. J., Nickerson K. W. Immunological relationships among proteins making up the Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis crystalline toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):644–649. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.644-649.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poindexter J. S. The caulobacters: ubiquitous unusual bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Mar;45(1):123–179. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.1.123-179.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport G., Klier A. Gene expression using Bacillus. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1990 Oct;1(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(90)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnik E., LaPorte D. C. Introduction of single-copy sequences into the chromosome of Escherichia coli: application to gene and operon fusions. Gene. 1991 Oct 30;107(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90292-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Burioni R., Helinski D. R. Genetic characterization of the stabilizing functions of a region of broad-host-range plasmid RK2. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6204–6216. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6204-6216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Tomczak K., Ortega J. P., Whiteley H. R. Specificity-determining regions of a lepidopteran-specific insecticidal protein produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):20923–20930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenlein P. V., Gallman L. M., Ely B. Use of transmissible plasmids as cloning vectors in Caulobacter crescentus. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):321–329. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. M., Chamberlain C., Davidson E. W. Resistance to the Bacillus sphaericus toxin in cultured mosquito cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1989 Oct;25(10):887–891. doi: 10.1007/BF02624000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebo P., Bennardo T., de la Torre F., Szulmajster J. Delineation of the minimal portion of the Bacillus sphaericus 1593M toxin required for the expression of larvicidal activity. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):161–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyler R. W., Jr, Yousten A. A., Burke W. F., Jr Plasmid stability in Bacillus sphaericus 2362 during recycling in mosquito larvae. J Invertebr Pathol. 1991 Nov;58(3):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(91)90181-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgarrella F., Szulmajster J. Purification and characterization of the larvicidal toxin of Bacillus sphaericus 1593M. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 30;143(3):901–907. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatzman A. R. Gene expression using gram-negative bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1990 Oct;1(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(90)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R. Homologous recombination in procaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):1–28. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.1-28.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinfield T. J., Jannière L., Ehrlich S. D., Minton N. P. Characterization of a region of the Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pAM beta 1 which enhances the segregational stability of pAM beta 1-derived cloning vectors in Bacillus subtilis. Plasmid. 1991 Nov;26(3):209–221. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(91)90044-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabashnik B. E. Evaluation of synergism among Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3343–3346. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3343-3346.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandeau de Marsac N., de la Torre F., Szulmajster J. Expression of the larvicidal gene of Bacillus sphaericus 1593M in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans R2. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):396–398. doi: 10.1007/BF00329671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
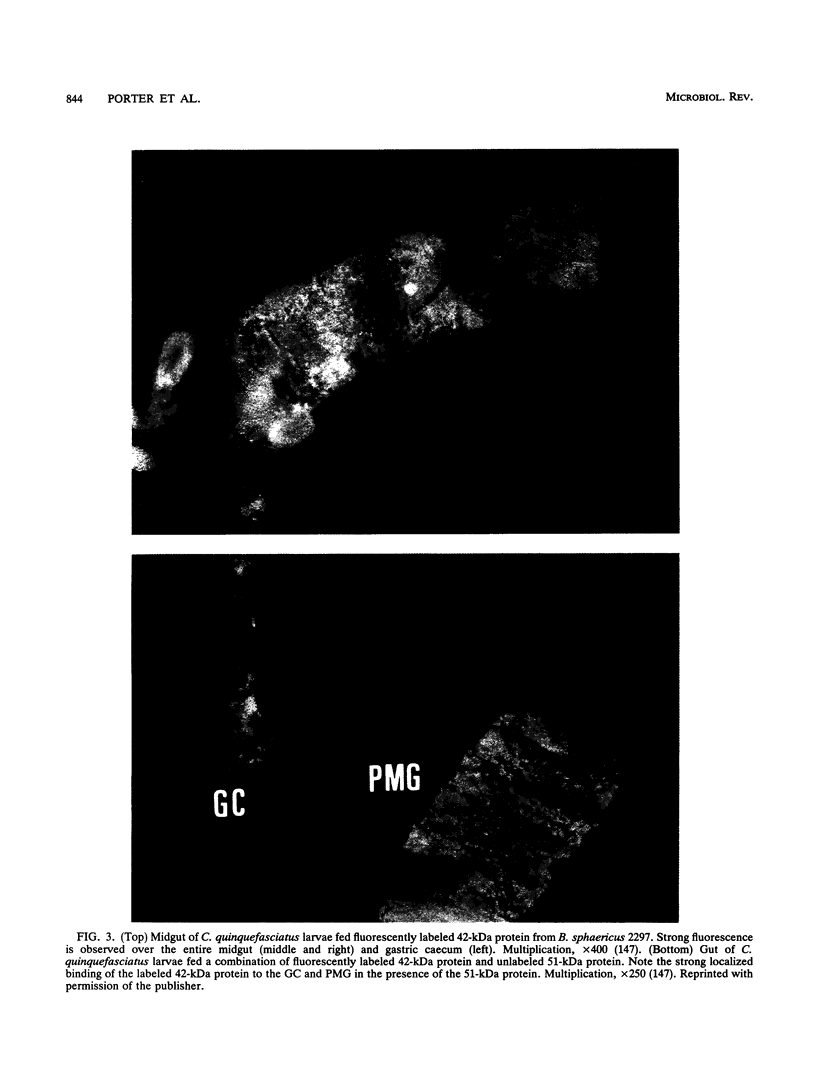
- Thanabalu T., Berry C., Hindley J. Cytotoxicity and ADP-ribosylating activity of the mosquitocidal toxin from Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1: possible roles of the 27- and 70-kilodalton peptides. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2314–2320. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2314-2320.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanabalu T., Hindley J., Berry C. Proteolytic processing of the mosquitocidal toxin from Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5051–5056. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5051-5056.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanabalu T., Hindley J., Brenner S., Oei C., Berry C. Expression of the mosquitocidal toxins of Bacillus sphaericus and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis by recombinant Caulobacter crescentus, a vehicle for biological control of aquatic insect larvae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):905–910. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.905-910.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanabalu T., Hindley J., Jackson-Yap J., Berry C. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of a gene encoding a 100-kilodalton mosquitocidal toxin from Bacillus sphaericus SSII-1. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2776–2785. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2776-2785.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Meyer R., Helinski D. R. Regions of broad-host-range plasmid RK2 which are essential for replication and maintenance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):213–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.213-222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A. Incompatibility group P plasmids: genetics, evolution, and use in genetic manipulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:77–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne L., Garduno F., Thompson T., Decker D., Zounes M., Wild M., Walfield A. M., Pollock T. J. Structural similarity between the lepidoptera- and diptera-specific insecticidal endotoxin genes of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. "kurstaki" and "israelensis". J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):801–811. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.801-811.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisrisook M., Pantuwatana S., Bhumiratana A., Panbangred W. Molecular cloning of the 130-kilodalton mosquitocidal delta-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis in Bacillus sphaericus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1710–1716. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1710-1716.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Receptors on the brush border membrane of the insect midgut as determinants of the specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1378–1385. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1378-1385.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., Jansens S., Höfte H., Degheele D., Van Mellaert H. Specificity of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins. Importance of specific receptors on the brush border membrane of the mid-gut of target insects. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Rie J., McGaughey W. H., Johnson D. E., Barnett B. D., Van Mellaert H. Mechanism of insect resistance to the microbial insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):72–74. doi: 10.1126/science.2294593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vellanoweth R. L., Rabinowitz J. C. The influence of ribosome-binding-site elements on translational efficiency in Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli in vivo. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(9):1105–1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Dullemans A. M., van Workum M. E., Visser B. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of the Mr 28 000 crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8207–8217. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis delta-endotoxin. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the transcripts in Bacillus thuringiensis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J., Chilcott C. N. Single amino acid changes in the Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis delta-endotoxin affect the toxicity and expression of the protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Cloning and expression of two homologous genes of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis which encode 130-kilodalton mosquitocidal proteins. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.727-735.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Nucleotide sequence of a Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis gene encoding a 130 kDa delta-endotoxin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7195–7195. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J., Todd J. A. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the insecticidal delta-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80772-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ridley A. R., Ellar D. J., Todd J. A. Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis delta-endotoxin. Cloning and expression of the toxin in sporogenic and asporogenic strains of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):13–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90418-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., Schnepf H. E. The molecular biology of parasporal crystal body formation in Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:549–576. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widner W. R., Whiteley H. R. Location of the dipteran specificity region in a lepidopteran-dipteran crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):2826–2832. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.2826-2832.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. R., Thomas C. M. Active partitioning of bacterial plasmids. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):1–16. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfersberger M. G. The toxicity of two Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins to gypsy moth larvae is inversely related to the affinity of binding sites on midgut brush border membranes for the toxins. Experientia. 1990 May 15;46(5):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF01954236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., Aronson A. I. Localized mutagenesis defines regions of the Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin involved in toxicity and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2311–2317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X. C., Lee W., Tran L., Wong S. L. Engineering a Bacillus subtilis expression-secretion system with a strain deficient in six extracellular proteases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4952–4958. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4952-4958.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Ehrlich S. D. Stability of reiterated sequences in the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2653–2656. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2653-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Gene amplification in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1613–1621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousten A. A., Davidson E. W. Ultrastructural Analysis of Spores and Parasporal Crystals Formed by Bacillus sphaericus 2297. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1449–1455. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1449-1455.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Torre F., Bennardo T., Sebo P., Szulmajster J. On the respective roles of the two proteins encoded by the Bacillus sphaericus 1593M toxin genes expressed in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Nov 15;164(3):1417–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Laan J. C., Gerritse G., Mulleners L. J., van der Hoek R. A., Quax W. J. Cloning, characterization, and multiple chromosomal integration of a Bacillus alkaline protease gene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):901–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.901-909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]