Abstract
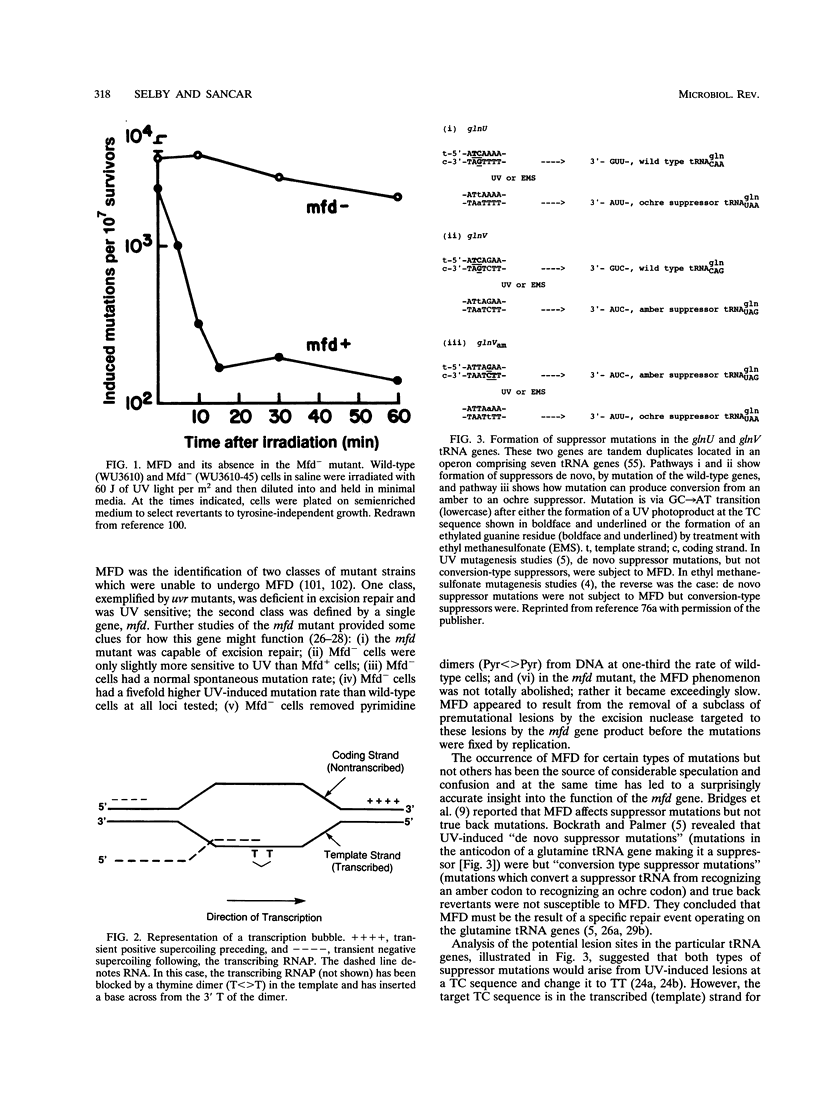
Mutation frequency decline is the rapid and irreversible decline in the suppressor mutation frequency of Escherichia coli cells if the cells are kept in nongrowth media immediately following the mutagenic treatment. The gene mfd, which is necessary for mutation frequency decline, encodes a protein of 130 kDa which couples transcription to excision repair by binding to RNA polymerase and to UvrA, which is the damage recognition subunit of the excision repair enzyme. Although current evidence suggests that transcription-repair coupling is the cause of the preferential repair of the transcribed strand of mRNA encoding genes as well as of suppressor tRNA genes, the decline occurs under stringent response conditions in which the tRNA genes are not efficiently transcribed. Thus, the mechanism of strand-specific repair is well understood, but some questions remain regarding the precise mechanism of mutation frequency decline.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. D., Kunz B. A. Site and strand specificity of UVB mutagenesis in the SUP4-o gene of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):9005–9009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.9005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrand J. E., Murray A. M. Benzpyrene groups bind preferentially to the DNA of active chromatin in human lung cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Mar 11;10(5):1547–1555. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedoyan J., Gupta R., Thoma F., Smerdon M. J. Transcription, nucleosome stability, and DNA repair in a yeast minichromosome. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5996–6005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockrath R. C., Palmer J. E. Differential repair of premutational UV-lesions at tRNA genes in E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 14;156(2):133–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00283485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockrath R., Barlow A., Engstrom J. Mutation frequency decline in Escherichia coli B/r after mutagenesis with ethyl methanesulfonate. Mutat Res. 1987 May;183(3):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodell W. J. Nonuniform distribution of DNA repair in chromatin after treatment with methyl methanesulfonate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Aug;4(8):2619–2628. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.8.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. DNA repair in an active gene: removal of pyrimidine dimers from the DHFR gene of CHO cells is much more efficient than in the genome overall. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):359–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Goldfarb A. Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges B. A., Dennis R. E., Munson R. J. Differential induction and repair of ultraviolet damage leading to true revesions and external suppressor mutations of an ochre codon in Escherichia coli B-r WP2. Genetics. 1967 Dec;57(4):897–908. doi: 10.1093/genetics/57.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers A. M., Mucha J., Grunberger D. DNA strand-specific mutations induced by (+/-)-3 alpha,4 beta-dihydroxy- 1 alpha,2 alpha-epoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[c]phenanthrene in the dihydrofolate reductase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Maher V. M., McCormick J. J. Effect of excision repair by diploid human fibroblasts on the kinds and locations of mutations induced by (+/-)-7 beta,8 alpha-dihydroxy-9 alpha,10 alpha-epoxy-7,8,9,10- tetrahydrobenzo[a]pyrene in the coding region of the HPRT gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8680–8684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Bogenhagen D. F. Effects of DNA lesions on transcription elongation by T7 RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5849–5855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Matsumoto Y., Shibutani S., Bogenhagen D. F. Acetylaminofluorene and aminofluorene adducts inhibit in vitro transcription of a Xenopus 5S RNA gene only when located on the coding strand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9583–9587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christians F. C., Hanawalt P. C. Inhibition of transcription and strand-specific DNA repair by alpha-amanitin in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutat Res. 1992 Aug;274(2):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. General initiation factors for RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:161–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda Y., Job C., Anin M. F., Leng M., Job D. Spectrum of DNA--platinum adduct recognition by prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 24;32(33):8582–8588. doi: 10.1021/bi00084a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corda Y., Job C., Anin M. F., Leng M., Job D. Transcription by eucaryotic and procaryotic RNA polymerases of DNA modified at a d(GG) or a d(AG) site by the antitumor drug cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II). Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):222–230. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMEREC M., CAHN E. Studies of mutability in nutritionally deficient strains of Escherichia coli. I. Genetic analysis of five auxotrophic strains. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jan;65(1):27–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.1.27-36.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doudney C. O., Haas F. L. MODIFICATION OF ULTRAVIOLET-INDUCED MUTATION FREQUENCY AND SURVIVAL IN BACTERIA BY POST-IRRADIATION TR000EATMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 May;44(5):390–401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.5.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
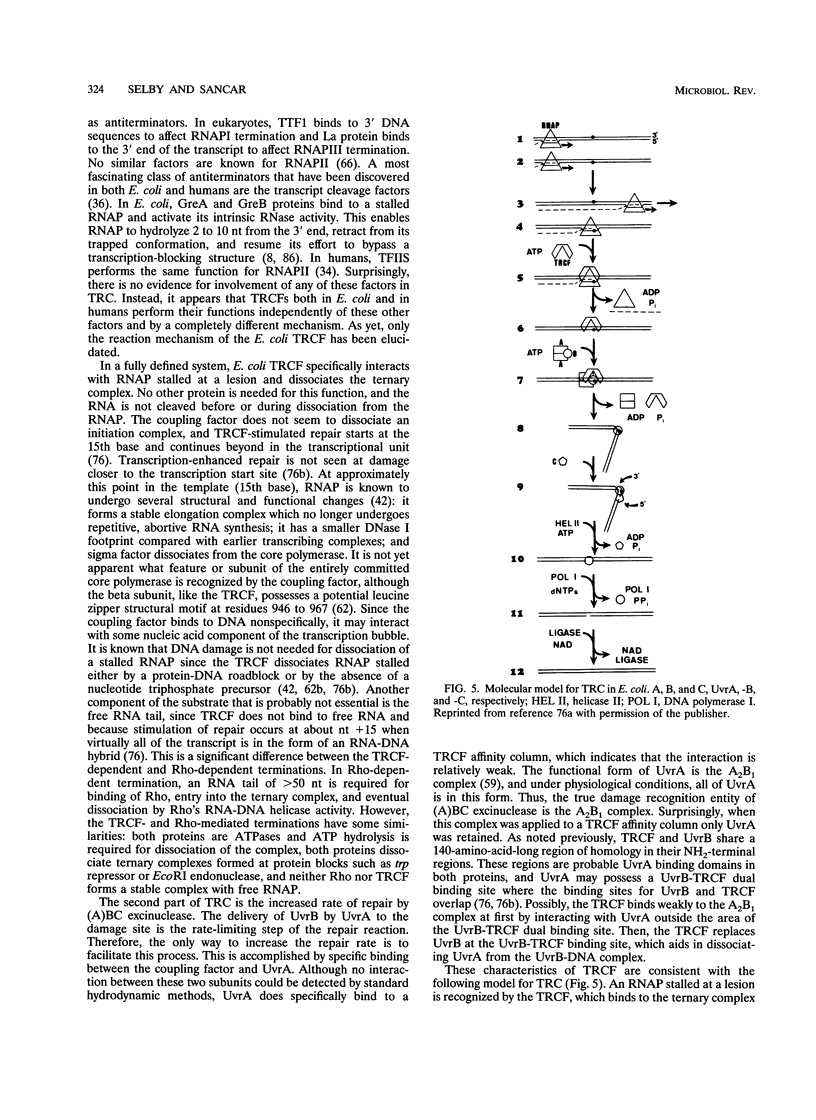
- Drapkin R., Sancar A., Reinberg D. Where transcription meets repair. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dröge P. Transcription-driven site-specific DNA recombination in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2759–2763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;2(3):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom J. E., Bockrath R. C. Mutation frequency decline in a rel strain of E. coli coli B/r. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00267222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engstrom J., Larsen S., Rogers S., Bockrath R. UV-mutagenesis at a cloned target sequence: converted suppressor mutation is insensitive to mutation frequency decline regardless of the gene orientation. Mutat Res. 1984 Nov-Dec;132(5-6):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fix D., Bockrath R. Targeted mutation at cytosine-containing pyrimidine dimers: studies of Escherichia coli B/r with acetophenone and 313-nm light. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4446–4449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fix D., Bockrath R. Thermal resistance to photoreactivation of specific mutations potentiated in E. coli B/r ung by ultraviolet light. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00422759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamper H. B., Hearst J. E. A topological model for transcription based on unwinding angle analysis of E. coli RNA polymerase binary, initiation and ternary complexes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):81–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey N., Witkin E. M., Brash D. E. Ultraviolet photoproducts at the ochre suppressor mutation site in the glnU gene of Escherichia coli: relevance to "mutation frequency decline". Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Nov;219(3):359–364. doi: 10.1007/BF00259607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet light-induced responses of an mfd mutant of Escherichia coli B/r having a slow rate of dimer excision. Mutat Res. 1975 Jun;28(3):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90229-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulyas K. D., Donahue T. F. SSL2, a suppressor of a stem-loop mutation in the HIS4 leader encodes the yeast homolog of human ERCC-3. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90621-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haak R. A., Bockrath R. C. Letter: Pyrimidine dimer excision and mutation frequency decline. Radiat Res. 1975 Jan;61(1):164–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H. Nucleotide excision repair. II: From yeast to mammals. Trends Genet. 1993 Jun;9(6):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90121-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar G. B., Holbrook S. R., Sancar A. Mechanism of damage recognition by Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13188–13197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Nakamura T., Maki H., Sekiguchi M. Roles of transcription and repair in alkylation mutagenesis. Mutat Res. 1994 May;314(3):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(94)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izban M. G., Luse D. S. The RNA polymerase II ternary complex cleaves the nascent transcript in a 3'----5' direction in the presence of elongation factor SII. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1342–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. K., Yeung A. T. Repair of 4,5',8-trimethylpsoralen monoadducts and cross-links by the Escherichia coli UvrABC endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8410–8414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. RNA polymerase marching backward. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):944–945. doi: 10.1126/science.7679800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Takao M., Oikawa A., Yasui A. Increased UV sensitivity of Escherichia coli cells after introduction of foreign photolyase genes. Mutat Res. 1990 Jul;236(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler D. R., Awadallah S. S., Glickman B. W. Sites of preferential induction of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in the nontranscribed strand of lacI correspond with sites of UV-induced mutation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11766–11773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Claassen L., Grossman L., Liu L. F. ATP-dependent partitioning of the DNA template into supercoiled domains by Escherichia coli UvrAB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krummel B., Chamberlin M. J. RNA chain initiation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Structural transitions of the enzyme in early ternary complexes. Biochemistry. 1989 Sep 19;28(19):7829–7842. doi: 10.1021/bi00445a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunala S., Brash D. E. Excision repair at individual bases of the Escherichia coli lacI gene: relation to mutation hot spots and transcription coupling activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11031–11035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kölsch E., Starlinger P. A difference in the photoreactivation of UV-damage between genes in the repressed and genes in the de-repressed state. Z Vererbungsl. 1965;96(4):304–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00895046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leadon S. A., Lawrence D. A. Strand-selective repair of DNA damage in the yeast GAL7 gene requires RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23175–23182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Phillips A. M., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. Active site of (A)BC excinuclease. II. Binding, bending, and catalysis mutants of UvrB reveal a direct role in 3' and an indirect role in 5' incision. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17693–17700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7024–7027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. G., Sharples G. J. Dissociation of synthetic Holliday junctions by E. coli RecG protein. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi P., Carraway M., Marinus M. G. Analysis of forward mutations induced by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in the bacteriophage P22 mnt repressor gene. J Bacteriol. 1986 Apr;166(1):34–37. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.1.34-37.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne L. V. Inhibitors of DNA synthesis (aphidicolin and araC/HU) prevent the recovery of RNA synthesis after UV-irradiation. Mutat Res. 1984 May-Jun;131(5-6):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(84)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne L. V., Lehmann A. R. Failure of RNA synthesis to recover after UV irradiation: an early defect in cells from individuals with Cockayne's syndrome and xeroderma pigmentosum. Cancer Res. 1982 Apr;42(4):1473–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Hanawalt P. C. Induction of the Escherichia coli lactose operon selectively increases repair of its transcribed DNA strand. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):95–98. doi: 10.1038/342095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Spivak G., Hanawalt P. C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalke H., Bremer H. RNA synthesis in Escherichia coli after irradiation with ultraviolet light. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr 14;41(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munn M. M., Rupp W. D. Interaction of the UvrABC endonuclease with DNA containing a psoralen monoadduct or cross-link. Differential effects of superhelical density and comparison of preincision complexes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24748–24756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Ozeki H., Shimura Y. Organization and structure of an E. coli tRNA operon containing seven tRNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose K., Nikaido O. Transcriptionally active and inactive genes are similarly modified by chemical carcinogens or X-ray in normal human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 5;781(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh E. Y., Grossman L. Helicase properties of the Escherichia coli UvrAB protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3638–3642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oller A. R., Fijalkowska I. J., Dunn R. L., Schaaper R. M. Transcription-repair coupling determines the strandedness of ultraviolet mutagenesis in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):11036–11040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.11036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren D. K., Sancar A. Formation and enzymatic properties of the UvrB.DNA complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15796–15803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren D. K., Sancar A. The (A)BC excinuclease of Escherichia coli has only the UvrB and UvrC subunits in the incision complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5237–5241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren D. K., Selby C. P., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. Post-incision steps of nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli. Disassembly of the UvrBC-DNA complex by helicase II and DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):780–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov Y. A., Monastyrskaya G. S., Gubanov V. V., Guryev S. O., Chertov OYu, Modyanov N. N., Grinkevich V. A., Makarova I. A., Marchenko T. V., Polovnikova I. N. The primary structure of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nucleotide sequence of the rpoB gene and amino-acid sequence of the beta-subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):621–629. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Guzder S. N., Koken M. H., Jaspers-Dekker I., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. RAD25 (SSL2), the yeast homolog of the human xeroderma pigmentosum group B DNA repair gene, is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11416–11420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavco P. A., Steege D. A. Elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase is blocked in vitro by a site-specific DNA binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9960–9969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Thompson L. H., Sancar A. Excision repair in man and the molecular basis of xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:605–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Hutchinson F. Effect of the direction of DNA replication on mutagenesis by N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine in adapted cells of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):446–449. doi: 10.1007/BF00328137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Transcription termination. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(1):1–30. doi: 10.3109/10409239309082571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. K., Crosby R. M., Richardson F. C., Skopek T. R. DNA base changes induced following in vivo exposure of unadapted, adapted or ada- Escherichia coli to N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):526–532. doi: 10.1007/BF00331159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SETLOW R. B., SWENSON P. A., CARRIER W. L. THYMINE DIMERS AND INHIBITION OF DNA SYNTHESIS BY ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATION OF CELLS. Science. 1963 Dec 13;142(3598):1464–1466. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3598.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STENT G. S., BRENNER S. A genetic locus for the regulation of ribonucleic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Dec 15;47:2005–2014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.12.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage E., Drobetsky E. A., Moustacchi E. 8-Methoxypsoralen induced mutations are highly targeted at crosslinkable sites of photoaddition on the non-transcribed strand of a mammalian chromosomal gene. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):397–402. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05671.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Franklin K. A., Sancar G. B. Escherichia coli DNA photolyase stimulates uvrABC excision nuclease in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7397–7401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hearst J. E. Molecular matchmakers. Science. 1993 Mar 5;259(5100):1415–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.8451638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. A novel repair enzyme: UVRABC excision nuclease of Escherichia coli cuts a DNA strand on both sides of the damaged region. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar G. B., Smith F. W. Interactions between yeast photolyase and nucleotide excision repair proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Escherichia coli. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4767–4776. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbier W., Hercules K. Gene and transcription unit mapping by radiation effects. Annu Rev Genet. 1978;12:329–363. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.12.120178.001553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauerbier W., Millette R. L., Hackett P. B., Jr The effects of ultraviolet irradiation on the transcription of T4 DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;209(2):368–386. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90735-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Gene- and strand-specific repair in vitro: partial purification of a transcription-repair coupling factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Molecular mechanism of transcription-repair coupling. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8465200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Transcription preferentially inhibits nucleotide excision repair of the template DNA strand in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21330–21336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Transcription-repair coupling and mutation frequency decline. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7509–7514. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7509-7514.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Witkin E. M., Sancar A. Escherichia coli mfd mutant deficient in "mutation frequency decline" lacks strand-specific repair: in vitro complementation with purified coupling factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11574–11578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. Interaction of T7 RNA polymerase with DNA in an elongation complex arrested at a specific psoralen adduct site. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):527–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. The effects of covalent additions of a psoralen on transcription by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6843–6854. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghat-Ullah, Sancar A. Substrate overlap and functional competition between human nucleotide excision repair and Escherichia coli photolyase and (a)BC excision nuclease. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5711–5718. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibghatullah, Husain I., Carlton W., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision repair in vitro: repair of pyrimidine dimers, psoralen and cisplatin adducts by HeLa cell-free extract. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4471–4484. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon M. J., Thoma F. Site-specific DNA repair at the nucleosome level in a yeast minichromosome. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90479-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt C. K., Milan S. C., Chamberlin M. J. Spontaneous cleavage of RNA in ternary complexes of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and its significance for the mechanism of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7983–7987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. S., Patrick M. H. Repair of UV damage in Escherichia coli under non-growth conditions. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 Sep;26(3):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb07481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang M. S., Patrick M. H. The role of DNA polymerase I in liquid holding recovery of UV-irradiated Escherichia coli. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 Sep;26(3):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., Landsvater R. M., Wiegant J., van der Ploeg M., Viel G., Buys C. H., Hoeijmakers J. H. Localization of the nucleotide excision repair gene ERCC6 to human chromosome 10q11-q21. Genomics. 1992 Apr;12(4):745–749. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90304-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B., Gamper H., Holbrook S. R., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. Action mechanism of ABC excision nuclease on a DNA substrate containing a psoralen crosslink at a defined position. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8077–8081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veaute X., Fuchs R. P. Greater susceptibility to mutations in lagging strand of DNA replication in Escherichia coli than in leading strand. Science. 1993 Jul 30;261(5121):598–600. doi: 10.1126/science.8342022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema J., Mullenders L. H., Natarajan A. T., van Zeeland A. A., Mayne L. V. The genetic defect in Cockayne syndrome is associated with a defect in repair of UV-induced DNA damage in transcriptionally active DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4707–4711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. M., Wauthier E. L. Differential introduction of DNA damage and repair in mammalian genes transcribed by RNA polymerases I and II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2245–2252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrieling H., Van Rooijen M. L., Groen N. A., Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W., Lohman P. H., van Zeeland A. A. DNA strand specificity for UV-induced mutations in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1277–1283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WITKIN E. M. Time, temperature, and protein synthesis: a study of ultraviolet-induced mutation in bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1956;21:123–140. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1956.021.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. B., Pierce J., Case R., Tang M. S. Recognition of the DNA helix stabilizing anthramycin-N2 guanine adduct by UVRABC nuclease. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):939–947. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Radiation-induced mutations and their repair. Science. 1966 Jun 3;152(3727):1345–1353. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3727.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M., Theil E. C. THE EFFECT OF POSTTREATMENT WITH OHLORAMPHENICOL VARIOUS ULTRAVIOLET-INDUCED MUTATIONS IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Feb;46(2):226–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.2.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet-induced mutation and DNA repair. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:487–514. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon H., Miller S. P., Pabich E. K., Donahue T. F. SSL1, a suppressor of a HIS4 5'-UTR stem-loop mutation, is essential for translation initiation and affects UV resistance in yeast. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12B):2463–2477. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12b.2463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou W., Doetsch P. W. Effects of abasic sites and DNA single-strand breaks on prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6601–6605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Cock J. G., Klink E. C., Ferro W., Lohman P. H., Eeken J. C. Neither enhanced removal of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers nor strand-specific repair is found after transcription induction of the beta 3-tubulin gene in a Drosophila embryonic cell line Kc. Mutat Res. 1992 Nov;293(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(92)90003-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Cock J. G., Klink E. C., Ferro W., Lohman P. H., Eeken J. C. Repair of UV-induced pyrimidine dimers in the individual genes Gart, Notch and white from Drosophila melanogaster cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 25;19(12):3289–3294. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.12.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Cock J. G., van Hoffen A., Wijnands J., Molenaar G., Lohman P. H., Eeken J. C. Repair of UV-induced (6-4)photoproducts measured in individual genes in the Drosophila embryonic Kc cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Sep 25;20(18):4789–4793. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.18.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



