Abstract
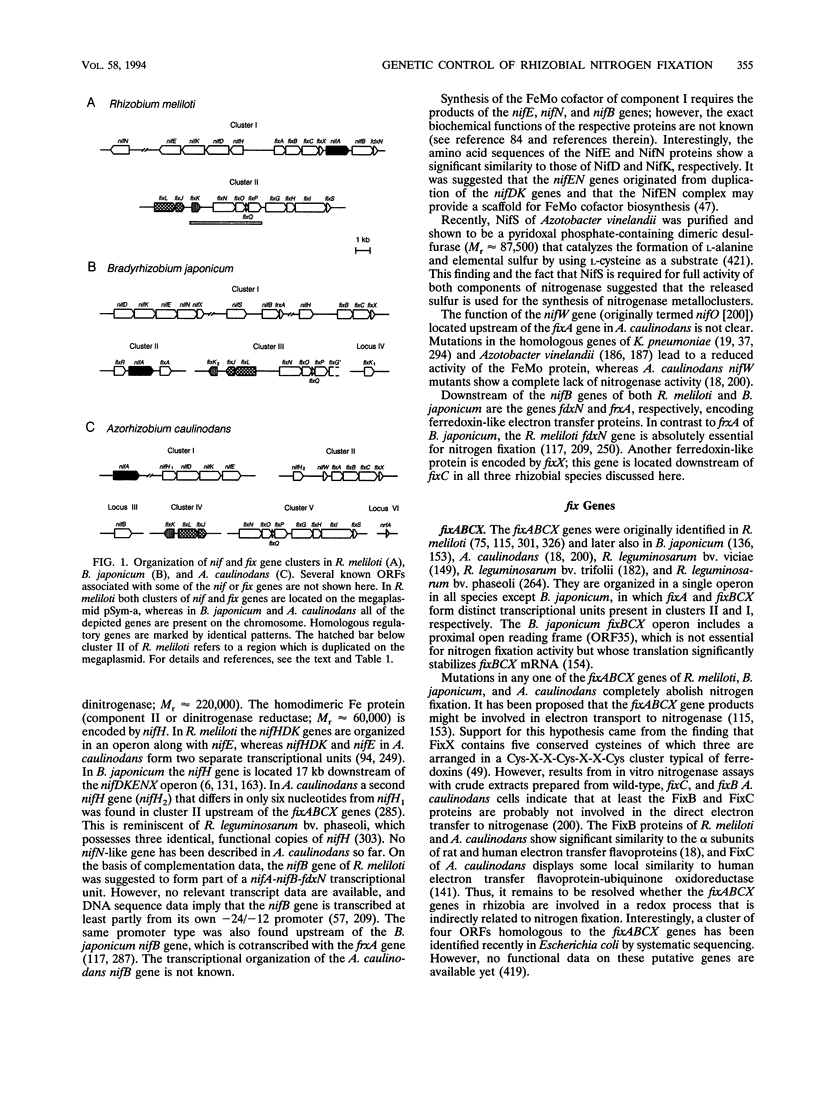
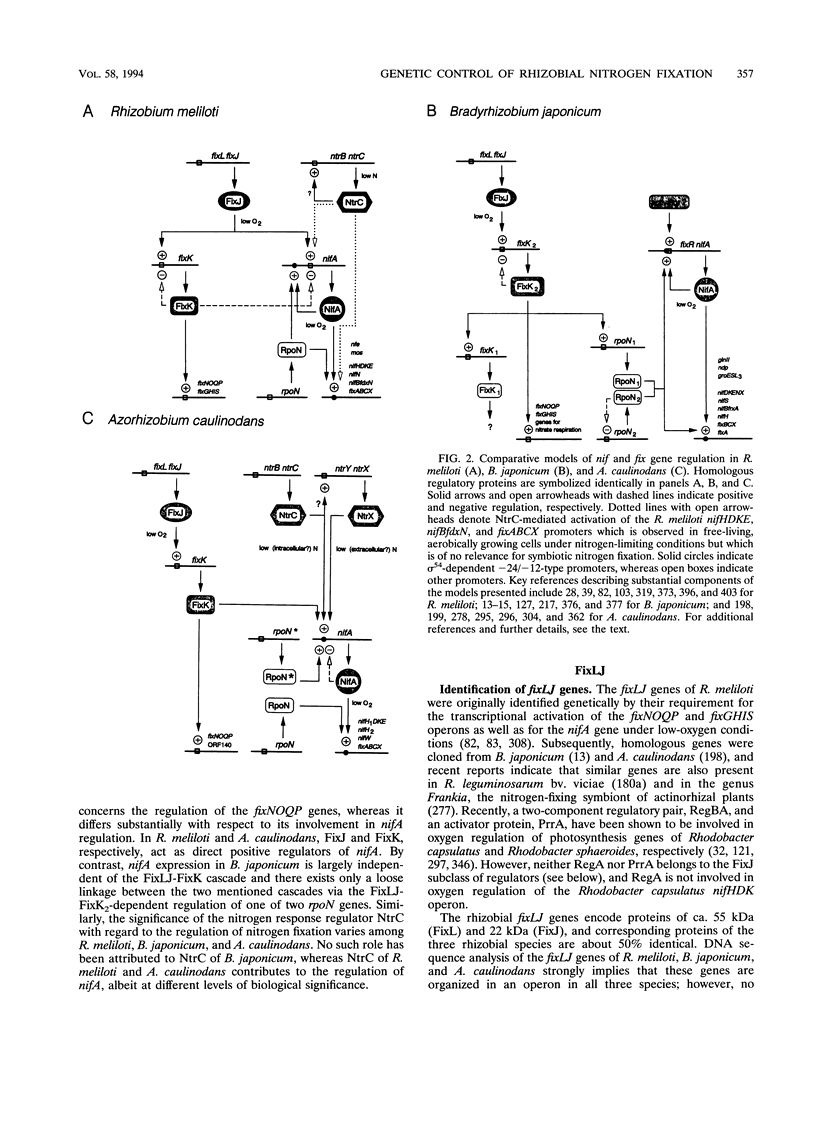
This review presents a comparison between the complex genetic regulatory networks that control nitrogen fixation in three representative rhizobial species, Rhizobium meliloti, Bradyrhizobium japonicum, and Azorhizobium caulinodans. Transcription of nitrogen fixation genes (nif and fix genes) in these bacteria is induced primarily by low-oxygen conditions. Low-oxygen sensing and transmission of this signal to the level of nif and fix gene expression involve at least five regulatory proteins, FixL, FixJ, FixK, NifA, and RpoN (sigma 54). The characteristic features of these proteins and their functions within species-specific regulatory pathways are described. Oxygen interferes with the activities of two transcriptional activators, FixJ and NifA. FixJ activity is modulated via phosphorylation-dephosphorylation by the cognate sensor hemoprotein FixL. In addition to the oxygen responsiveness of the NifA protein, synthesis of NifA is oxygen regulated at the level of transcription. This type of control includes FixLJ in R. meliloti and FixLJ-FixK in A. caulinodans or is brought about by autoregulation in B. japonicum. NifA, in concert with sigma 54 RNA polymerase, activates transcription from -24/-12-type promoters associated with nif and fix genes and additional genes that are not directly involved in nitrogen fixation. The FixK proteins constitute a subgroup of the Crp-Fnr family of bacterial regulators. Although the involvement of FixLJ and FixK in nifA regulation is remarkably different in the three rhizobial species discussed here, they constitute a regulatory cascade that uniformly controls the expression of genes (fixNOQP) encoding a distinct cytochrome oxidase complex probably required for bacterial respiration under low-oxygen conditions. In B. japonicum, the FixLJ-FixK cascade also controls genes for nitrate respiration and for one of two sigma 54 proteins.
Full text
PDF



























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams T. H., Chelm B. K. The nifH and nifDK promoter regions from Rhizobium japonicum share structural homologies with each other and with nitrogen-regulated promoters from other organisms. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(4):392–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agron P. G., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Mutational analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti nifA promoter. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):4120–4129. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.4120-4129.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agron P. G., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Oxygen regulation of nifA transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3506–3510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar O. M., Kapp D., Pühler A. Characterization of a Rhizobium meliloti fixation gene (fixF) located near the common nodulation region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):245–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.245-254.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar O. M., Reiländer H., Arnold W., Pühler A. Rhizobium meliloti nifN (fixF) gene is part of an operon regulated by a nifA-dependent promoter and codes for a polypeptide homologous to the nifK gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5393–5400. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5393-5400.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar O. M., Taormino J., Thöny B., Ramseier T., Hennecke H., Szalay A. A. The nifEN genes participating in FeMo cofactor biosynthesis and genes encoding dinitrogenase are part of the same operon in Bradyrhizobium species. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00262436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Huala E., Ausubel F. M. Prokaryotic signal transduction mediated by sensor and regulator protein pairs. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:311–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albright L. M., Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Identification of a gene linked to Rhizobium meliloti ntrA whose product is homologous to a family to ATP-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1932–1941. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1932-1941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Morales A., Betancourt-Alvarez M., Kaluza K., Hennecke H. Activation of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifH and nifDK operons is dependent on promoter-upstream DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4207–4227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Morales A., Hennecke H. Expression of Rhizobium japonicum nifH and nifDK operons can be activated by the Klebsiella pneumonia nifA protein but not by the product of ntrC. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(2):306–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00330273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. The regulatory status of the fixL- and fixJ-like genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum may be different from that in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):38–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00282640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthamatten D., Scherb B., Hennecke H. Characterization of a fixLJ-regulated Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene sharing similarity with the Escherichia coli fnr and Rhizobium meliloti fixK genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2111–2120. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2111-2120.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleby C. A., James P., Hennecke H. Characterization of three soluble c-type cytochromes isolated from soybean root nodule bacteroids of Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain CC705. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90344-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricó B., Miller J. F., Roy C., Stibitz S., Monack D., Falkow S., Gross R., Rappuoli R. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6671–6675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arigoni F., Kaminski P. A., Hennecke H., Elmerich C. Nucleotide sequence of the fixABC region of Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571: similarity of the fixB product with eukaryotic flavoproteins, characterization of fixX, and identification of nifW. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):514–520. doi: 10.1007/BF00261695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold W., Rump A., Klipp W., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Nucleotide sequence of a 24,206-base-pair DNA fragment carrying the entire nitrogen fixation gene cluster of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 5;203(3):715–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Dixon R. The prokaryotic enhancer binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity which is phosphorylation and DNA dependent. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin S., Henderson N., Dixon R. Characterisation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogen-fixation regulatory proteins NIFA and NIFL in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):353–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E. Similarities between legume-rhizobium communication and steroid-mediated intercellular communication in vertebrates. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Jun;38(6):541–547. doi: 10.1139/m92-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannan J. D., Moran M. J., MacInnes J. I., Soltes G. A., Friedman R. L. Cloning and characterization of btr, a Bordetella pertussis gene encoding an FNR-like transcriptional regulator. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7228–7235. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7228-7235.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Daveran-Mingot M. L., David M., Jacobs J., Garnerone A. M., Kahn D. fixK, a gene homologous with fnr and crp from Escherichia coli, regulates nitrogen fixation genes both positively and negatively in Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batut J., Santero E., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein FIXJ from Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5914–5917. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5914-5917.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer C., Buggy J., Mosley C. Control of photosystem genes in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Trends Genet. 1993 Feb;9(2):56–60. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90188-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J., Craig E. A. Heat-shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):11–23. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-79502-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett L. T., Cannon F., Dean D. R. Nucleotide sequence and mutagenesis of the nifA gene from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):315–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger D. K., Narberhaus F., Kustu S. The isolated catalytic domain of NIFA, a bacterial enhancer-binding protein, activates transcription in vitro: activation is inhibited by NIFL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):103–107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J. L., Williams M. K., Cannon F. C. Expression and functional analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti nifA gene. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J., Cannon M., Buchanan-Wollaston V., Ally A., Setterquist R., Dean D., Cannon F. The nucleotide sequence of the nifT, nifY, nifX and nifW genes of K. pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9860–9860. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beynon J., Cannon M., Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon F. The nif promoters of Klebsiella pneumoniae have a characteristic primary structure. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90399-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco G., Drummond M., Woodley P., Kennedy C. Sequence and molecular analysis of the nifL gene of Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):869–879. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01745.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur D., Lamb J. W., Johnston A. W. Identification of two classes of Rhizobium phaseoli genes required for melanin synthesis, one of which is required for nitrogen fixation and activates the transcription of the other. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):155–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00331503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botsford J. L., Harman J. G. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):100–122. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.100-122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourret R. B., Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. Signal transduction pathways involving protein phosphorylation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewin N. J. Development of the legume root nodule. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:191–226. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigle K. E., Weiss M. C., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Products of the iron-molybdenum cofactor-specific biosynthetic genes, nifE and nifN, are structurally homologous to the products of the nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein genes, nifD and nifK. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1547–1553. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1547-1553.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Shapiro L. A temporally controlled sigma-factor is required for polar morphogenesis and normal cell division in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2395–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi M., Guerlesquin F. Structure, function and evolution of bacterial ferredoxins. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1988 Apr-Jun;4(2):155–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1988.tb02741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan-Wollaston V., Cannon M. C., Beynon J. L., Cannon F. C. Role of the nifA gene product in the regulation of nif expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):776–778. doi: 10.1038/294776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W. Mutations in the RNA polymerase recognition sequence of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter permitting transcriptional activation in the absence of NifA binding to upstream activator sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2597–2612. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W. Specific binding of the transcription factor sigma-54 to promoter DNA. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):422–424. doi: 10.1038/358422a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Mutational analysis of upstream sequences required for transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifH promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9945–9956. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck M., Cannon W., Woodcock J. Transcriptional activation of the Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase promoter may involve DNA loop formation. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Sep;1(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Klingensmith J. A., Gibbons S. L., Ausubel F. M. Conservation of structure and location of Rhizobium meliloti and Klebsiella pneumoniae nifB genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1120–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1120-1126.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Szeto W. W., Lemley P. V., Orme-Johnson W. H., Ausubel F. M. Nitrogen fixation specific regulatory genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti share homology with the general nitrogen regulatory gene ntrC of K. pneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4539–4555. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkardt B., Schillik D., Pühler A. Physical characterization of Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmids. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burris R. H., Roberts G. P. Biological nitrogen fixation. Annu Rev Nutr. 1993;13:317–335. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.13.070193.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bánfalvi Z., Sakanyan V., Koncz C., Kiss A., Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Location of nodulation and nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):318–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00272925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero S., Gardan R., Glaser P., Schweizer J., Rapoport G., Debarbouille M. RocR, a novel regulatory protein controlling arginine utilization in Bacillus subtilis, belongs to the NtrC/NifA family of transcriptional activators. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1234–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1234-1241.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Buck M. Central domain of the positive control protein NifA and its role in transcriptional activation. J Mol Biol. 1992 May 20;225(2):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90921-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Charlton W., Buck M. Organization and function of binding sites for the transcriptional activator NifA in the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifE and nifU promoters. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):915–931. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90363-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Claverie-Martin F., Austin S., Buck M. Core RNA polymerase assists binding of the transcription factor sigma 54 to promoter DNA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(2):287–298. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon W., Claverie-Martin F., Austin S., Buck M. Identification of a DNA-contacting surface in the transcription factor sigma-54. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(2):227–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00303.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson T. A., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Characterization of the gene encoding glutamine synthetase I (glnA) from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.698-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson T. A., Martin G. B., Chelm B. K. Differential transcription of the two glutamine synthetase genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5861–5866. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5861-5866.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño I., Bastarrachea F. glnF-lacZ fusions in Escherichia coli: studies on glnF expression and its chromosomal orientation. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):228–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00332751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler M. S. The gene encoding cAMP receptor protein is required for competence development in Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1626–1630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastain C. J., Brusca J. S., Ramasubramanian T. S., Wei T. F., Golden J. W. A sequence-specific DNA-binding factor (VF1) from Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 vegetative cells binds to three adjacent sites in the xisA upstream region. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5044–5051. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5044-5051.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherfils J., Gibrat J. F., Levin J., Batut J., Kahn D. Model-building of Fnr and FixK DNA-binding domains suggests a basis for specific DNA recognition. J Mol Recognit. 1989 Nov;2(3):114–121. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbeau A., Vignais P. M. Use of hupS::lacZ gene fusion to study regulation of hydrogenase expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus: stimulation by H2. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4258–4264. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4258-4264.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna-Romano S., Arnold W., Schlüter A., Boistard P., Pühler A., Priefer U. B. An Fnr-like protein encoded in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae shows structural and functional homology to Rhizobium meliloti FixK. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):138–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00315806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook S. D., Thomas K. A., Harding A. F., Collins C. L., Haddad R. J., Jr, Milicic M., Fischer W. L. The in vivo performance of 250 internal fixation devices: a follow-up study. Biomaterials. 1987 May;8(3):177–184. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(87)90060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppard J. R., Merrick M. J. Cassette mutagenesis implicates a helix-turn-helix motif in promoter recognition by the novel RNA polymerase sigma factor sigma 54. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1309–1317. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin D., Barran L., Ditta G. Organization and expression of Rhizobium meliloti nitrogen fixation genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Gicquel-Sanzey B. Cloning and sequence of the crp gene of Escherichia coli K 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1363–1378. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cossart P., Groisman E. A., Serre M. C., Casadaban M. J., Gicquel-Sanzey B. crp genes of Shigella flexneri, Salmonella typhimurium, and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):639–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.639-646.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig N. L., Nash H. A. E. coli integration host factor binds to specific sites in DNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):707–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90478-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubo M. T., Buendia-Claveria A. M., Beringer J. E., Ruiz-Sainz J. E. Melanin production by Rhizobium strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1812–1817. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1812-1817.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen P. J., Foster-Hartnett D., Gabbert K. K., Kranz R. G. Structure and expression of the alternative sigma factor, RpoN, in Rhodobacter capsulatus; physiological relevance of an autoactivated nifU2-rpoN superoperon. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jan;11(1):51–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H., Zumft W. G. Anaerobic control of denitrification in Pseudomonas stutzeri escapes mutagenesis of an fnr-like gene. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7236–7246. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7236-7246.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Daveran M. L., Batut J., Dedieu A., Domergue O., Ghai J., Hertig C., Boistard P., Kahn D. Cascade regulation of nif gene expression in Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):671–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Domergue O., Pognonec P., Kahn D. Transcription patterns of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic plasmid pSym: identification of nifA-independent fix genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2239–2244. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2239-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. R., Bolin J. T., Zheng L. Nitrogenase metalloclusters: structures, organization, and synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6737–6744. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6737-6744.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Amábile-Cuevas C. F. Redox redux: the control of oxidative stress responses. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):837–839. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B. Regulation of bacterial oxidative stress genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:315–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dispensa M., Thomas C. T., Kim M. K., Perrotta J. A., Gibson J., Harwood C. S. Anaerobic growth of Rhodopseudomonas palustris on 4-hydroxybenzoate is dependent on AadR, a member of the cyclic AMP receptor protein family of transcriptional regulators. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5803–5813. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5803-5813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Virts E., Palomares A., Kim C. H. The nifA gene of Rhizobium meliloti is oxygen regulated. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3217–3223. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3217-3223.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Henderson N. C., Austin S. DNA supercoiling and aerobic regulation of transcription from the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifLA promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9933–9946. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic S. P., Ridge R. W., Chen H. C., Redmond J. W., Batley M., Rolfe B. G. Induction of pathogenic-like responses in the legume Macroptilium atropurpureum by a transposon-induced mutant of the fast-growing, broad-host-range Rhizobium strain NGR234. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1848–1857. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1848-1857.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Nees D. W., Raymond C. K., Loroch A. I., Ludwig R. A. Characterization of three genomic loci encoding Rhizobium sp. strain ORS571 N2 fixation genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jan;165(1):72–81. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.1.72-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus B. L., Elmerich C., Dommergues Y. R. Free-living Rhizobium strain able to grow on n(2) as the sole nitrogen source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):711–713. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.711-713.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M. H., Contreras A., Mitchenall L. A. The function of isolated domains and chimaeric proteins constructed from the transcriptional activators NifA and NtrC of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond M., Whitty P., Wootton J. Sequence and domain relationships of ntrC and nifA from Klebsiella pneumoniae: homologies to other regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):441–447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04230.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusha I., Kondorosi A. Genes at different regulatory levels are required for the ammonia control of nodulation in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Sep;240(3):435–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00280398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylan T., Ielpi L., Stanfield S., Kashyap L., Douglas C., Yanofsky M., Nester E., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for nodule development are related to chromosomal virulence genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dénarié J., Cullimore J. Lipo-oligosaccharide nodulation factors: a minireview new class of signaling molecules mediating recognition and morphogenesis. Cell. 1993 Sep 24;74(6):951–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90717-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dénarié J., Debellé F., Rosenberg C. Signaling and host range variation in nodulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:497–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earl C. D., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Genetic and structural analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti fixA, fixB, fixC, and fixX genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1127–1136. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1127-1136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling S., Noti J. D., Hennecke H. Identification of a new Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene (frxA) encoding a ferredoxinlike protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1999–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1999-2001.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiglmeier K., Honoré N., Iuchi S., Lin E. C., Cole S. T. Molecular genetic analysis of FNR-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):869–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eraso J. M., Kaplan S. prrA, a putative response regulator involved in oxygen regulation of photosynthesis gene expression in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1994 Jan;176(1):32–43. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.1.32-43.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):1–33. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.1-33.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estabrook E. M., Sengupta-Gopalan C. Differential expression of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase during soybean nodule development. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):299–308. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D., Jones R., Woodley P., Robson R. Further analysis of nitrogen fixation (nif) genes in Azotobacter chroococcum: identification and expression in Klebsiella pneumoniae of nifS, nifV, nifM, and nifB genes and localization of nifE/N-, nifU-, nifA- and fixABC-like genes. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Apr;134(4):931–942. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-4-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H M, Hennecke H. Direct response of Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA-mediated nif gene regulation to cellular oxygen status. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):621–626. doi: 10.1007/BF00331174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Alvarez-Morales A., Hennecke H. The pleiotropic nature of symbiotic regulatory mutants: Bradyrhizobium japonicum nifA gene is involved in control of nif gene expression and formation of determinate symbiosis. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1165–1173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Babst M., Kaspar T., Acuña G., Arigoni F., Hennecke H. One member of a gro-ESL-like chaperonin multigene family in Bradyrhizobium japonicum is co-regulated with symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2901–2912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. Essential and non-essential domains in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein: identification of indispensable cysteine residues potentially involved in redox reactivity and/or metal binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2207–2224. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. M., Fritsche S., Herzog B., Hennecke H. Critical spacing between two essential cysteine residues in the interdomain linker of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81083-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Rhizobium--plant signal exchange. Nature. 1992 Jun 25;357(6380):655–660. doi: 10.1038/357655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster-Hartnett D., Kranz R. G. Analysis of the promoters and upstream sequences of nifA1 and nifA2 in Rhodobacter capsulatus; activation requires ntrC but not rpoN. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(8):1049–1060. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franssen H. J., Vijn I., Yang W. C., Bisseling T. Developmental aspects of the Rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):89–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00015608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann M., Hennecke H. Rhizobium japonicum nitrogenase Fe protein gene (nifH). J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1005–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1005-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E., Bancroft S., Rhee S. G., Kustu S. The product of a newly identified gene, gInF, is required for synthesis of glutamine synthetase in Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1662–1666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. A haemoprotein with kinase activity encoded by the oxygen sensor of Rhizobium meliloti. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):170–172. doi: 10.1038/350170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles-Gonzalez M. A., Gonzalez G. Regulation of the kinase activity of heme protein FixL from the two-component system FixL/FixJ of Rhizobium meliloti. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16293–16297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. I., Axtell K. M., Bindoff L. A., Beard S. E., Gill R. E., Frerman F. E. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding human electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):277–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govezensky D., Bochkareva E. S., Zamir A., Girshovich A. S. Chaperonins as potential gene regulatory factors. In vitro interaction and solubilization of NifA, the nif transcriptional activator, with GroEL. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14003–14006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govezensky D., Greener T., Segal G., Zamir A. Involvement of GroEL in nif gene regulation and nitrogenase assembly. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6339–6346. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6339-6346.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Guest J. R. Activation of FNR-dependent transcription by iron: an in vitro switch for FNR. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Oct 15;113(2):219–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06517.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Guest J. R. Regulation of transcription at the ndh promoter of Escherichia coli by FNR and novel factors. Mol Microbiol. 1994 May;12(3):433–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Sharrocks A. D., Green B., Geisow M., Guest J. R. Properties of FNR proteins substituted at each of the five cysteine residues. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):61–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Trageser M., Six S., Unden G., Guest J. R. Characterization of the FNR protein of Escherichia coli, an iron-binding transcriptional regulator. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 May 22;244(1310):137–144. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönger P., Manian S. S., Reiländer H., O'Connell M., Priefer U. B., Pühler A. Organization and partial sequence of a DNA region of the Rhizobium leguminosarum symbiotic plasmid pRL6JI containing the genes fixABC, nifA, nifB and a novel open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):31–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler M. Fine-tuning of nif and fix gene expression by upstream activator sequences in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):149–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01804.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler M., Zürcher T., Hennecke H. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum fixBCX operon: identification of fixX and of a 5' mRNA region affecting the level of the fixBCX transcript. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gussin G. N., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Regulation of nitrogen fixation genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:567–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Grob P., Hennecke H. Proposed regulatory pathway encoded by the nodV and nodW genes, determinants of host specificity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2680–2684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M. Regulation and function of rhizobial nodulation genes. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jan;10(1-2):39–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartl F. U., Hlodan R., Langer T. Molecular chaperones in protein folding: the art of avoiding sticky situations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):20–25. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R. Developmentally regulated gene rearrangements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:113–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins F. K., Johnston A. W. Transcription of a Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli gene needed for melanin synthesis is activated by nifA of Rhizobium and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1988 May;2(3):331–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Chamberlin M. J. Structure and function of bacterial sigma factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:839–872. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Hartl F. U. Molecular chaperone functions of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:349–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H. Nitrogen fixation genes involved in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum-soybean symbiosis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H. Regulation of bacterial gene expression by metal-protein complexes. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1621–1628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00538.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Ferrari E. Localization of Bacillus subtilis sacU(Hy) mutations to two linked genes with similarities to the conserved procaryotic family of two-component signalling systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5102–5109. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5102-5109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertig C., Li R. Y., Louarn A. M., Garnerone A. M., David M., Batut J., Kahn D., Boistard P. Rhizobium meliloti regulatory gene fixJ activates transcription of R. meliloti nifA and fixK genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1736–1738. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1736-1738.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo E., Demple B. An iron-sulfur center essential for transcriptional activation by the redox-sensing SoxR protein. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):138–146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06243.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Smith C. A. Effects of Rhizobium meliloti nif and fix mutants on alfalfa root nodule development. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1137-1146.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman J., Wong P. K., Sei K., Keener J., Kustu S. Products of nitrogen regulatory genes ntrA and ntrC of enteric bacteria activate glnA transcription in vitro: evidence that the ntrA product is a sigma factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7525–7529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeycutt R. J., McClelland M., Sobral B. W. Physical map of the genome of Rhizobium meliloti 1021. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6945–6952. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6945-6952.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoover T. R., Santero E., Porter S., Kustu S. The integration host factor stimulates interaction of RNA polymerase with NIFA, the transcriptional activator for nitrogen fixation operons. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90284-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium meliloti NifA is sufficient to activate transcription from the R. meliloti nifH promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3354–3365. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3354-3365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Moon A. L., Ausubel F. M. Aerobic inactivation of Rhizobium meliloti NifA in Escherichia coli is mediated by lon and two newly identified genes, snoB and snoC. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):382–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.382-390.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Stigter J., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium leguminosarum DctD functions independently to activate transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1428–1431. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1428-1431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. P., Magasanik B. Transcription of glnA by purified Escherichia coli components: core RNA polymerase and the products of glnF, glnG, and glnL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8453–8457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iismaa S. E., Ealing P. M., Scott K. F., Watson J. M. Molecular linkage of the nif/fix and nod gene regions in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1753–1764. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iismaa S. E., Watson J. M. The nifA gene product from Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii lacks the N-terminal domain found in other NifA proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):943–955. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory gene xylR of the TOL plasmid from Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1988 Jun 30;66(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iuchi S., Lin E. C. Adaptation of Escherichia coli to redox environments by gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Brigle K. E., Bennett L. T., Setterquist R. A., Wilson M. S., Cash V. L., Beynon J., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Physical and genetic map of the major nif gene cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1017–1027. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1017-1027.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Cash V. L., Weiss M. C., Laird N. F., Newton W. E., Dean D. R. Biochemical and genetic analysis of the nifUSVWZM cluster from Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):49–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00261156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang J., Gu B. H., Albright L. M., Nixon B. T. Conservation between coding and regulatory elements of Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium leguminosarum dct genes. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5244–5253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5244-5253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. G., Prusti R. K., Roitsch T., Ankenbauer R. G., Nester E. W. Phosphorylation of the VirG protein of Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the autophosphorylated VirA protein: essential role in biological activity of VirG. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4945–4950. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4945-4950.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S., Ishimoto K., Lory S. Nucleotide sequence of the rpoN gene and characterization of two downstream open reading frames in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1316–1322. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1316-1322.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger R. D., Premakumar R., Bishop P. E. Tn5-induced mutants of Azotobacter vinelandii affected in nitrogen fixation under Mo-deficient and Mo-sufficient conditions. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):673–682. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.673-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R., Haselkorn R. The DNA sequence of the Rhodobacter capsulatus ntrA, ntrB and ntrC gene analogues required for nitrogen fixation. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):507–516. doi: 10.1007/BF00427050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., David M., Domergue O., Daveran M. L., Ghai J., Hirsch P. R., Batut J. Rhizobium meliloti fixGHI sequence predicts involvement of a specific cation pump in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):929–939. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.929-939.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn D., Ditta G. Modular structure of FixJ: homology of the transcriptional activator domain with the -35 binding domain of sigma factors. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):987–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Desnoues N., Elmerich C. The expression of nifA in Azorhizobium caulinodans requires a gene product homologous to Escherichia coli HF-I, an RNA-binding protein involved in the replication of phage Q beta RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4663–4667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Elmerich C. Involvement of fixLJ in the regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azorhizobium caulinodans. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):665–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Mandon K., Arigoni F., Desnoues N., Elmerich C. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azorhizobium caulinodans: identification of a fixK-like gene, a positive regulator of nifA. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1983–1991. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski P. A., Norel F., Desnoues N., Kush A., Salzano G., Elmerich C. Characterization of the fixABC region of Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 and identification of a new nitrogen fixation gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):496–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00330486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. Overlapping transcription of the nifA regulatory gene in Rhizobium meliloti. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90319-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Gabel C., Maier R. J. Expression of hydrogenase in Hupc strains of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1993;160(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00258144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Yu C., Maier R. J. Common cis-acting region responsible for transcriptional regulation of Bradyrhizobium japonicum hydrogenase by nickel, oxygen, and hydrogen. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):3993–3999. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.3993-3999.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. M., Ahn K. J., Beppu T., Uozumi T. Nucleotide sequence of the nifLA operon of Klebsiella oxytoca NG13 and characterization of the gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):253–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00430436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klier A., Msadek T., Rapoport G. Positive regulation in the gram-positive bacterium: Bacillus subtilis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:429–459. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipp W., Reiländer H., Schlüter A., Krey R., Pühler A. The Rhizobium meliloti fdxN gene encoding a ferredoxin-like protein is necessary for nitrogen fixation and is cotranscribed with nifA and nifB. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):293–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00334368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondorosi A., Kondorosi E., John M., Schmidt J., Schell J. The role of nodulation genes in bacterium-plant communication. Genet Eng (N Y) 1991;13:115–136. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3760-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz R. G., Foster-Hartnett D. Transcriptional regulatory cascade of nitrogen-fixation genes in anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria: oxygen- and nitrogen-responsive factors. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Nov;4(11):1793–1800. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranz R. G., Haselkorn R. Anaerobic regulation of nitrogen-fixation genes in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6805–6809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krey R., Pühler A., Klipp W. A defined amino acid exchange close to the putative nucleotide binding site is responsible for an oxygen-tolerant variant of the Rhizobium meliloti NifA protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):433–441. doi: 10.1007/BF00538703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Fritsche S., Knobel H., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H., Fischer H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has two differentially regulated, functional homologs of the sigma 54 gene (rpoN). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1125–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1125-1138.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Debarbouille M., Msadek T., Young M., Mauel C., Karamata D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Deduced polypeptides encoded by the Bacillus subtilis sacU locus share homology with two-component sensor-regulator systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5093–5101. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5093-5101.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Santero E., Keener J., Popham D., Weiss D. Expression of sigma 54 (ntrA)-dependent genes is probably united by a common mechanism. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Sep;53(3):367–376. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.3.367-376.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Alvarez J. F., Harayama S. Regulation of the rpoN, ORF102 and ORF154 genes in Pseudomonas putida. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Jan 15;115(2-3):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kündig C., Hennecke H., Göttfert M. Correlated physical and genetic map of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110 genome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):613–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.613-622.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudenbach D. E., Grossman A. R. Characterization and mutagenesis of sulfur-regulated genes in a cyanobacterium: evidence for function in sulfate transport. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2739–2750. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2739-2750.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazazzera B. A., Bates D. M., Kiley P. J. The activity of the Escherichia coli transcription factor FNR is regulated by a change in oligomeric state. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1993–2005. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledebur H., Gu B., Sojda J., 3rd, Nixon B. T. Rhizobium meliloti and Rhizobium leguminosarum dctD gene products bind to tandem sites in an activation sequence located upstream of sigma 54-dependent dctA promoters. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3888–3897. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3888-3897.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Berger D. K., Kustu S. Activity of purified NIFA, a transcriptional activator of nitrogen fixation genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2266–2270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Ishihama A., Kustu S. The C terminus of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase is not essential for transcriptional activation of sigma 54 holoenzyme. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2479–2482. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2479-2482.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. S., Narberhaus F., Kustu S. In vitro activity of NifL, a signal transduction protein for biological nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7683–7688. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7683-7688.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharides of Rhizobium: synthesis, regulation and symbiotic function. Trends Genet. 1994 Feb;10(2):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90151-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J. M., Nunes-Düby S., Lesser C. F., Youderian P., Susskind M. M., Landy A. The phi 80 and P22 attachment sites. Primary structure and interaction with Escherichia coli integration host factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4468–4477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Y. Y., Kaminski P. A., Elmerich C. Identification of a nifA-like regulatory gene of Azospirillum brasilense Sp7 expressed under conditions of nitrogen fixation and in the presence of air and ammonia. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2735–2744. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Y. Y., de Zamaroczy M., Arsène F., Paquelin A., Elmerich C. Regulation of nitrogen fixation in Azospirillum brasilense Sp7: involvement of nifA, glnA and glnB gene products. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 15;100(1-3):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb14028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisser S., Margalit H. Compilation of E. coli mRNA promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1507–1516. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois A. F., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The oxygen sensor FixL of Rhizobium meliloti is a membrane protein containing four possible transmembrane segments. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(4):1103–1109. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.1103-1109.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois A. F., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Autophosphorylation and phosphatase activities of the oxygen-sensing protein FixL of Rhizobium meliloti are coordinately regulated by oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4370–4375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Roberts G. P. Regulation of nitrogenase activity by reversible ADP ribosylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1989;30:23–56. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152830-0.50004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes J. I., Kim J. E., Lian C. J., Soltes G. A. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae hlyX gene homology with the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4587–4592. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4587-4592.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B. Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:135–168. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.001031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandon K., Kaminski P. A., Elmerich C. Functional analysis of the fixNOQP region of Azorhizobium caulinodans. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2560-2568.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandon K., Kaminski P. A., Mougel C., Desnoues N., Dreyfus B., Elmerich C. Role of the fixGHI region of Azorhizobium caulinodans in free-living and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Dec 1;114(2):185–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Verstraete I., Débarbouillé M., Klier A., Rapoport G. Mutagenesis of the Bacillus subtilis "-12, -24" promoter of the levanase operon and evidence for the existence of an upstream activating sequence. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jul 5;226(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Chapman K. A., Chelm B. K. Role of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum ntrC gene product in differential regulation of the glutamine synthetase II gene (glnII). J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5452–5459. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5452-5459.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masepohl B., Klipp W., Pühler A. Genetic characterization and sequence analysis of the duplicated nifA/nifB gene region of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):27–37. doi: 10.1007/BF00322441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masepohl B., Kutsche M., Riedel K. U., Schmehl M., Klipp W., Pühler A. Functional analysis of the cysteine motifs in the ferredoxin-like protein FdxN of Rhizobium meliloti involved in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00587558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maupin J. A., Shanmugam K. T. Genetic regulation of formate hydrogenlyase of Escherichia coli: role of the fhlA gene product as a transcriptional activator for a new regulatory gene, fhlB. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4798–4806. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4798-4806.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung C. R., Somerville J. E., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Structure of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene hemA encoding 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase. Gene. 1987;54(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer W. G., Tabita F. R. Isolation and characterization of the nifUSVW-rpoN gene cluster from Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(12):3855–3866. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.12.3855-3866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melville S. B., Gunsalus R. P. Mutations in fnr that alter anaerobic regulation of electron transport-associated genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18733–18736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercado-Blanco J., García F., Fernández-López M., Olivares J. Melanin production by Rhizobium meliloti GR4 is linked to nonsymbiotic plasmid pRmeGR4b: cloning, sequencing, and expression of the tyrosinase gene mepA. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5403–5410. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5403-5410.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Coppard J. R. Mutations in genes downstream of the rpoN gene (encoding sigma 54) of Klebsiella pneumoniae affect expression from sigma 54-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1765–1775. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00162.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J. In a class of its own--the RNA polymerase sigma factor sigma 54 (sigma N). Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):903–909. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M. J., Stewart W. D. Studies on the regulation and function of the Klebsiella pneumoniae ntrA gene. Gene. 1985;35(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Chambers S. The helix-turn-helix motif of sigma 54 is involved in recognition of the -13 promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7221–7226. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7221-7226.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick M., Gibbins J., Toukdarian A. The nucleotide sequence of the sigma factor gene ntrA (rpoN) of Azotobacter vinelandii: analysis of conserved sequences in NtrA proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):323–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00325701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels J., D'hooghe I., Verreth C., Pelemans H., Vanderleyden J. Characterization of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli nifA gene, a positive regulator of nif gene expression. Arch Microbiol. 1994;161(5):404–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00288950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michiels J., Vanderleyden J. Cloning and sequence of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli fixA gene. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Sep 13;1144(2):232–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90179-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monson E. K., Weinstein M., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. The FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti can be separated into a heme-binding oxygen-sensing domain and a functional C-terminal kinase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. In vivo studies on the interaction of RNA polymerase-sigma 54 with the Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhizobium meliloti nifH promoters. The role of NifA in the formation of an open promoter complex. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 5;210(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Buck M. NifA-dependent in vivo protection demonstrates that the upstream activator sequence of nif promoters is a protein binding site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9401–9405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Cannon W., Buck M. The DNA-binding domain of the transcriptional activator protein NifA resides in its carboxy terminus, recognises the upstream activator sequences of nif promoters and can be separated from the positive control function of NifA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11469–11488. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Fischer H. M., Hennecke H. Influence of oxygen on DNA binding, positive control, and stability of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum NifA regulatory protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3478–3487. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3478-3487.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Segovia L. The sigma 54 bacterial enhancer-binding protein family: mechanism of action and phylogenetic relationship of their functional domains. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(19):6067–6074. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.19.6067-6074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. J., Heycke N., Banfalvi Z., Tate M. E., de Bruijn F., Kondorosi A., Tempé J., Schell J. Genes for the catabolism and synthesis of an opine-like compound in Rhizobium meliloti are closely linked and on the Sym plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. J., Heycke N., Trenz S. P., Ratet P., de Bruijn F. J., Schell J. Synthesis of an opine-like compound, a rhizopine, in alfalfa nodules is symbiotically regulated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9133–9137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. J., Trenz S. P., Grzemski W., De Bruijn F. J., Schell J. The Rhizobium meliloti rhizopine mos locus is a mosaic structure facilitating its symbiotic regulation. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5193–5204. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5193-5204.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nees D. W., Stein P. A., Ludwig R. A. The Azorhizobium caulinodans nifA gene: identification of upstream-activating sequences including a new element, the 'anaerobox'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9839–9853. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N. Regulation of the cell division cycle and differentiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:689–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa A. J., Ninfa E. G., Lupas A. N., Stock A., Magasanik B., Stock J. Crosstalk between bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction proteins and regulators of transcription of the Ntr regulon: evidence that nitrogen assimilation and chemotaxis are controlled by a common phosphotransfer mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5492–5496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Two-component regulatory systems responsive to environmental stimuli share strongly conserved domains with the nitrogen assimilation regulatory genes ntrB and ntrC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7850–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noonan B., Motherway M., O'Gara F. Ammonia regulation of the Rhizobium meliloti nitrogenase structural and regulatory genes under free-living conditions: involvement of the fixL gene product? Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Sep;234(3):423–428. doi: 10.1007/BF00538701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. K., Klose K. E., Stedman K. M., Kustu S. Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4267–4273. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4267-4273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noti J. D., Folkerts O., Turken A. N., Szalay A. A. Organization and characterization of genes essential for symbiotic nitrogen fixation from Bradyrhizobium japonicum I110. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.774-783.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osuna R., Bender R. A. Klebsiella aerogenes catabolite gene activator protein and the gene encoding it (crp). J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6626–6631. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6626-6631.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Kofoid E. C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. Signal transduction schemes of bacteria. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):857–871. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90267-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriarca E. J., Riccio A., Taté R., Colonna-Romano S., Iaccarino M., Defez R. The ntrBC genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are part of a complex operon subject to negative regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):569–577. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W., Merrick M. The roles of the nifW, nifZ and nifM genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in nitrogenase biosynthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):675–682. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowski K., Klosse U., de Bruijn F. J. Characterization of a novel Azorhizobium caulinodans ORS571 two-component regulatory system, NtrY/NtrX, involved in nitrogen fixation and metabolism. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Dec;231(1):124–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00293830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Jones M. K., Hunter C. N. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of regA, a putative response regulator gene of Rhodobacter sphaeroides. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994 Mar 1;116(3):269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1994.tb06714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popham D. L., Szeto D., Keener J., Kustu S. Function of a bacterial activator protein that binds to transcriptional enhancers. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):629–635. doi: 10.1126/science.2563595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig O., Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. Genes for a microaerobically induced oxidase complex in Bradyrhizobium japonicum are essential for a nitrogen-fixing endosymbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preker P., Hübner P., Schmehl M., Klipp W., Bickle T. A. Mapping and characterization of the promoter elements of the regulatory nif genes rpoN, nifA1 and nifA2 in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Apr;6(8):1035–1047. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., De La Vega H., Flores M., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A., Pardo M. A., Azpiroz R., De Lourdes Girard M., Calva E., Palacios R. Nitrogenase reductase: A functional multigene family in Rhizobium phaseoli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1170–1174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratet P., Pawlowski K., Schell J., de Bruijn F. J. The Azorhizobium caulinodans nitrogen-fixation regulatory gene, nifA, is controlled by the cellular nitrogen and oxygen status. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jun;3(6):825–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Reizer A., Saier M. H., Jr, Jacobson G. R. A proposed link between nitrogen and carbon metabolism involving protein phosphorylation in bacteria. Protein Sci. 1992 Jun;1(6):722–726. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renalier M. H., Batut J., Ghai J., Terzaghi B., Gherardi M., David M., Garnerone A. M., Vasse J., Truchet G., Huguet T. A new symbiotic cluster on the pSym megaplasmid of Rhizobium meliloti 2011 carries a functional fix gene repeat and a nod locus. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2231–2238. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2231-2238.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuber T. L., Reed J., Glazebrook J., Glucksmann M. A., Ahmann D., Marra A., Walker G. C. Rhizobium meliloti exopolysaccharides: genetic analyses and symbiotic importance. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):636–641. doi: 10.1042/bst0190636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuber T. L., Walker G. C. Biosynthesis of succinoglycan, a symbiotically important exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium meliloti. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):269–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90418-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyrat J. M., David M., Batut J., Boistard P. FixL of Rhizobium meliloti enhances the transcriptional activity of a mutant FixJD54N protein by phosphorylation of an alternate residue. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):1969–1976. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.1969-1976.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyrat J. M., David M., Blonski C., Boistard P., Batut J. Oxygen-regulated in vitro transcription of Rhizobium meliloti nifA and fixK genes. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6867–6872. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6867-6872.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P., Debellé F., Lerouge P., Vasse J., Truchet G., Promé J. C., Dénarié J. The lipo-oligosaccharidic symbiotic signals of Rhizobium meliloti. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 May;20(2):288–291. doi: 10.1042/bst0200288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelvink P. W., Hontelez J. G., van Kammen A., van den Bos R. C. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory nifA gene of Rhizobium leguminosarum PRE: transcriptional control sites and expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1441–1447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Astwood P. M., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Deduced products of C4-dicarboxylate transport regulatory genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are homologous to nitrogen regulatory gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7921–7934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Albright L. M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti ntrA (rpoN) gene is required for diverse metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2424–2431. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2424-2431.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Nixon B. T., Ausubel F. M. Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):579–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C., Boistard P., Dénarié J., Casse-Delbart F. Genes controlling early and late functions in symbiosis are located on a megaplasmid in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):326–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00272926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossbach S., Hennecke H. Identification of glyA as a symbiotically essential gene in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossbach S., Loferer H., Acuña G., Appleby C. A., Hennecke H. Cloning, sequencing and mutational analysis of the cytochrome c552 gene (cycB) from Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain 110. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90345-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossbach S, Schell J, de Bruijn F J. The ntrC gene of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 controls glutamine synthetase (GSII) activity, growth on nitrate and chromosomal but not Ti-encoded arginine catabolism pathways. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Oct;209(3):419–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00331144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusanganwa E., Gupta R. S. Cloning and characterization of multiple groEL chaperonin-encoding genes in Rhizobium meliloti. Gene. 1993 Apr 15;126(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90591-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruvkun G. B., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. Directed transposon Tn5 mutagenesis and complementation analysis of Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic nitrogen fixation genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):551–559. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90171-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffarini D. A., Nealson K. H. Sequence and genetic characterization of etrA, an fnr analog that regulates anaerobic respiration in Shewanella putrefaciens MR-1. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(24):7938–7944. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.24.7938-7944.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint C. P., Wexler M., Murphy P. J., Tempé J., Tate M. E., Murphy P. J. Characterization of genes for synthesis and catabolism of a new rhizopine induced in nodules by Rhizobium meliloti Rm220-3: extension of the rhizopine concept. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5205–5215. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5205-5215.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation site of NtrC, a protein phosphatase whose covalent intermediate activates transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5117–5122. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5117-5122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. A., Gillece-Castro B. L., Stock A. M., Burlingame A. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of the site of phosphorylation of the chemotaxis response regulator protein, CheY. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21770–21778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan J., Olivares J. Implication of nifA in regulation of genes located on a Rhizobium meliloti cryptic plasmid that affect nodulation efficiency. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4154–4161. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4154-4161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan J., Olivares J. NifA-NtrA regulatory system activates transcription of nfe, a gene locus involved in nodulation competitiveness of Rhizobium meliloti. Arch Microbiol. 1991;155(6):543–548. doi: 10.1007/BF00245347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T. R., North A. K., Berger D. K., Porter S. C., Kustu S. Role of integration host factor in stimulating transcription from the sigma 54-dependent nifH promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):602–620. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein NIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawers R. G. Identification and molecular characterization of a transcriptional regulator from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 exhibiting structural and functional similarity to the FNR protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1469–1481. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaman H. R., Okker R. J., Lugtenberg B. J. Regulation of nodulation gene expression by NodD in rhizobia. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5177–5182. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5177-5182.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlensog V., Böck A. Identification and sequence analysis of the gene encoding the transcriptional activator of the formate hydrogenlyase system of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Aug;4(8):1319–1327. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter A., Patschkowski T., Unden G., Priefer U. B. The Rhizobium leguminosarum FnrN protein is functionally similar to Escherichia coli Fnr and promotes heterologous oxygen-dependent activation of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3395–3404. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder C. J., Dobrogosz W. J. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of the wild-type and mutant cyclic AMP receptor protein genes from Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):616–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.616-622.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüddekopf K., Hennecke S., Liese U., Kutsche M., Klipp W. Characterization of anf genes specific for the alternative nitrogenase and identification of nif genes required for both nitrogenases in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(4):673–684. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sganga M. W., Bauer C. E. Regulatory factors controlling photosynthetic reaction center and light-harvesting gene expression in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90037-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrocks A. D., Green J., Guest J. R. FNR activates and represses transcription in vitro. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Sep 23;245(1314):219–226. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrocks A. D., Green J., Guest J. R. In vivo and in vitro mutants of FNR the anaerobic transcriptional regulator of E. coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81248-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the fnr gene and primary structure of the Enr protein of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):6119–6130. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.6119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Rice D. W., Guest J. R. Homology between CAP and Fnr, a regulator of anaerobic respiration in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 15;166(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Swart S., Lugtenberg B. J., Kijne J. W. Molecular mechanisms of attachment of Rhizobium bacteria to plant roots. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):2897–2903. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G., McClelland M. Electrophoretic separation of the three Rhizobium meliloti replicons. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5173–5180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5173-5180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soto M. J., Zorzano A., Mercado-Blanco J., Lepek V., Olivares J., Toro N. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation competitiveness genes nfe. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):570–576. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza E. M., Funayama S., Rigo L. U., Yates M. G., Pedrosa F. O. Sequence and structural organization of a nif A-like gene and part of a nifB-like gene of Herbaspirillum seropedicae strain Z78. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jul;137(7):1511–1522. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-7-1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. FNR and its role in oxygen-regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Aug;6(4):399–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Inactivation of the FNR protein of Escherichia coli by targeted mutagenesis in the N-terminal region. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):701–707. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Guest J. R. Regulation and over-expression of the fnr gene of Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Dec;133(12):3279–3288. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-12-3279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro S., Roberts R. E., Guest J. R. FNR-dependent repression of the ndh gene of Escherichia coli and metal ion requirement for FNR-regulated gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):601–608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart V., Parales J., Jr Identification and expression of genes narL and narX of the nar (nitrate reductase) locus in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1589–1597. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1589-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigter J., Schneider M., de Bruijn F. J. Azorhizobium caulinodans nitrogen fixation (nif/fix) gene regulation: mutagenesis of the nifA -24/-12 promoter element, characterization of a ntrA(rpoN) gene, and derivation of a model. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1993 Mar-Apr;6(2):238–252. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-6-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Stock A. M., Mottonen J. M. Signal transduction in bacteria. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):395–400. doi: 10.1038/344395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker K., Reijnders W. N., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Initial cloning and sequencing of hydHG, an operon homologous to ntrBC and regulating the labile hydrogenase activity in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4448–4456. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4448-4456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Ames B. N. Transcriptional regulator of oxidative stress-inducible genes: direct activation by oxidation. Science. 1990 Apr 13;248(4952):189–194. doi: 10.1126/science.2183352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storz G., Tartaglia L. A., Farr S. B., Ames B. N. Bacterial defenses against oxidative stress. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90278-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout V., Gottesman S. RcsB and RcsC: a two-component regulator of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):659–669. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.659-669.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Porter S., Kustu S., Echols H. DNA-looping and enhancer activity: association between DNA-bound NtrC activator and RNA polymerase at the bacterial glnA promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaresan V., Jones J. D., Ow D. W., Ausubel F. M. Klebsiella pneumoniae nifA product activates the Rhizobium meliloti nitrogenase promoter. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):728–732. doi: 10.1038/301728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Nixon B. T., Ronson C. W., Ausubel F. M. Identification and characterization of the Rhizobium meliloti ntrC gene: R. meliloti has separate regulatory pathways for activation of nitrogen fixation genes in free-living and symbiotic cells. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1423–1432. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1423-1432.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szeto W. W., Zimmerman J. L., Sundaresan V., Ausubel F. M. A Rhizobium meliloti symbiotic regulatory gene. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1035–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Hattori T., Nakanishi T., Nohno T., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Taniguchi S. Repression of in vitro transcription of the Escherichia coli fnr and nar X genes by FNR protein. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. Dual control of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum symbiotic nitrogen fixation regulatory operon fixR nifA: analysis of cis- and trans-acting elements. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4162–4169. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4162-4169.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Fischer H. M., Anthamatten D., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. The symbiotic nitrogen fixation regulatory operon (fixRnifA) of Bradyrhizobium japonicum is expressed aerobically and is subject to a novel, nifA-independent type of activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8479–8499. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Hennecke H. The -24/-12 promoter comes of age. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;5(4):341–357. doi: 10.1016/0168-6445(89)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toukdarian A., Kennedy C. Regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Azotobacter vinelandii: isolation of ntr and glnA genes and construction of ntr mutants. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):399–407. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint B., Bosc C., Richaud P., Colbeau A., Vignais P. M. A mutation in a Rhodobacter capsulatus gene encoding an integration host factor-like protein impairs in vivo hydrogenase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10749–10753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint B., Delic-Attree I., De Sury D'Aspremont R., David L., Vinçon M., Vignais P. M. Purification of the integration host factor homolog of Rhodobacter capsulatus: cloning and sequencing of the hip gene, which encodes the beta subunit. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(20):6499–6504. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.20.6499-6504.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trageser M., Spiro S., Duchêne A., Kojro E., Fahrenholz F., Guest J. R., Unden G. Isolation of intact FNR protein (Mr 30,000) of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jan;4(1):21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuli R., Merrick M. J. Over-production and characterization of the nifA gene product of Klebsiella pneumoniae--the transcriptional activator of nif gene expression. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Feb;134(2):425–432. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-2-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Kondorosi A. Nucleotide sequence of the R.meliloti nitrogenase reductase (nifH) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5711–5723. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardi M. K., Lister D. L., Day D. A. Isolation and characterization of a ntrC mutant of Bradyrhizobium (Parasponia) sp. ANU289. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 May;138(5):1019–1025. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-5-1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Trageser M., Duchêne A. Effect of positive redox potentials (greater than +400 mV) on the expression of anaerobic respiratory enzymes in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Feb;4(2):315–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unden G., Trageser M. Oxygen regulated gene expression in Escherichia coli: control of anaerobic respiration by the FNR protein. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 Feb;59(2):65–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00445650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Soom C., Verreth C., Sampaio M. J., Vanderleyden J. Identification of a potential transcriptional regulator of hydrogenase activity in free-living Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 May;239(1-2):235–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00281623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance C. P. Rhizobium infection and nodulation: a beneficial plant disease? Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:399–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasse J., de Billy F., Camut S., Truchet G. Correlation between ultrastructural differentiation of bacteroids and nitrogen fixation in alfalfa nodules. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4295–4306. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4295-4306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virts E. L., Stanfield S. W., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Common regulatory elements control symbiotic and microaerobic induction of nifA in Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3062–3065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens F., Foglia A., Morel J. B., Fourment J., Batut J., Boistard P. Molecular genetic analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti fixK promoter: identification of sequences involved in positive and negative regulation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(11):1447–1456. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallington E. J., Lund P. A. Rhizobium leguminosarum contains multiple chaperonin (cpn60) genes. Microbiology. 1994 Jan;140(Pt 1):113–122. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Stacey G. Ammonia regulation of nod genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Sep;223(2):329–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00265071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. P., Birkenhead K., Boesten B., Manian S., O'Gara F. Genetic analysis and regulation of the Rhizobium meliloti genes controlling C4-dicarboxylic acid transport. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90473-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J. Analysis of the C4-dicarboxylate transport genes of Rhizobium meliloti: nucleotide sequence and deduced products of dctA, dctB, and dctD. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 May-Jun;3(3):174–181. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Chan Y. K., Wheatcroft R., Yang A. F., Han S. H. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for C4-dicarboxylate transport and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are located on a megaplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):927–934. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.927-934.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Reiländer H., Pühler A. Mapping and expression of a regulatory nitrogen fixation gene (fixD) of Rhizobium meliloti. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2751–2756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03999.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. Structure of a complex of catabolite gene activator protein and cyclic AMP refined at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei T. F., Ramasubramanian T. S., Pu F., Golden J. W. Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 bifA gene encoding a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein cloned by in vivo transcriptional interference selection. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):4025–4035. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.4025-4035.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidenhaupt M., Fischer H. M., Acuña G., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H. Use of a promoter-probe vector system in the cloning of a new NifA-dependent promoter (ndp) from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Gene. 1993 Jul 15;129(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90693-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Guillen N., Dubnau D. A. Sequence and transcription mapping of Bacillus subtilis competence genes comB and comA, one of which is related to a family of bacterial regulatory determinants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5362–5375. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5362-5375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Penchev R., Dubnau E., Smith I., Dubnau D. A Bacillus subtilis regulatory gene product for genetic competence and sporulation resembles sensor protein members of the bacterial two-component signal-transduction systems. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):860–872. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Lois A. F., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Mutants of the two-component regulatory protein FixJ of Rhizobium meliloti that have increased activity at the nifA promoter. Gene. 1993 Dec 8;134(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90088-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M., Lois A. F., Monson E. K., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R. Isolation of phosphorylation-deficient mutants of the Rhizobium meliloti two-component regulatory protein, FixJ. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Aug;6(15):2041–2049. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss D. S., Batut J., Klose K. E., Keener J., Kustu S. The phosphorylated form of the enhancer-binding protein NTRC has an ATPase activity that is essential for activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):155–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90579-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston L. A., Kadner R. J. Role of uhp genes in expression of the Escherichia coli sugar-phosphate transport system. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3375–3383. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3375-3383.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehall S., Austin S., Dixon R. The function of the upstream region of the sigma 54-dependent Klebsiella pneumoniae nifL promoter is sensitive to DNA supercoiling. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):1107–1117. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wootton J. C., Drummond M. H. The Q-linker: a class of interdomain sequences found in bacterial multidomain regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1989 May;2(7):535–543. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Mori H., Nagai H., Nagata T., Ishihama A., Fujita N., Isono K., Mizobuchi K., Nakata A. Systematic sequencing of the Escherichia coli genome: analysis of the 0-2.4 min region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3305–3308. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Nagai H., Mori H. Regulation of the heat-shock response in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:321–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng L., White R. H., Cash V. L., Jack R. F., Dean D. R. Cysteine desulfurase activity indicates a role for NIFS in metallocluster biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2754–2758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Szeto W. W., Ausubel F. M. Molecular characterization of Tn5-induced symbiotic (Fix-) mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1025–1034. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1025-1034.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Reimmann C., Galimand M., Haas D. Anaerobic growth and cyanide synthesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa depend on anr, a regulatory gene homologous with fnr of Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jun;5(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Rossbach S., Schneider M., Ratet P., Messmer S., Szeto W. W., Ausubel F. M., Schell J. Rhizobium meliloti 1021 has three differentially regulated loci involved in glutamine biosynthesis, none of which is essential for symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1673–1682. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1673-1682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Crecy-Lagard V., Glaser P., Lejeune P., Sismeiro O., Barber C. E., Daniels M. J., Danchin A. A Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris protein similar to catabolite activation factor is involved in regulation of phytopathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5877–5883. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5877-5883.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Philip P., Batut J., Boistard P. Rhizobium meliloti Fix L is an oxygen sensor and regulates R. meliloti nifA and fixK genes differently in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4255–4262. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4255-4262.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Philip P., Soupène E., Batut J., Boistard P. Modular structure of the FixL protein of Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Oct;235(1):49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00286180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Slooten J. C., Cervantes E., Broughton W. J., Wong C. H., Stanley J. Sequence and analysis of the rpoN sigma factor gene of rhizobium sp. strain NGR234, a primary coregulator of symbiosis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5563–5574. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5563-5574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]