Full text
PDF





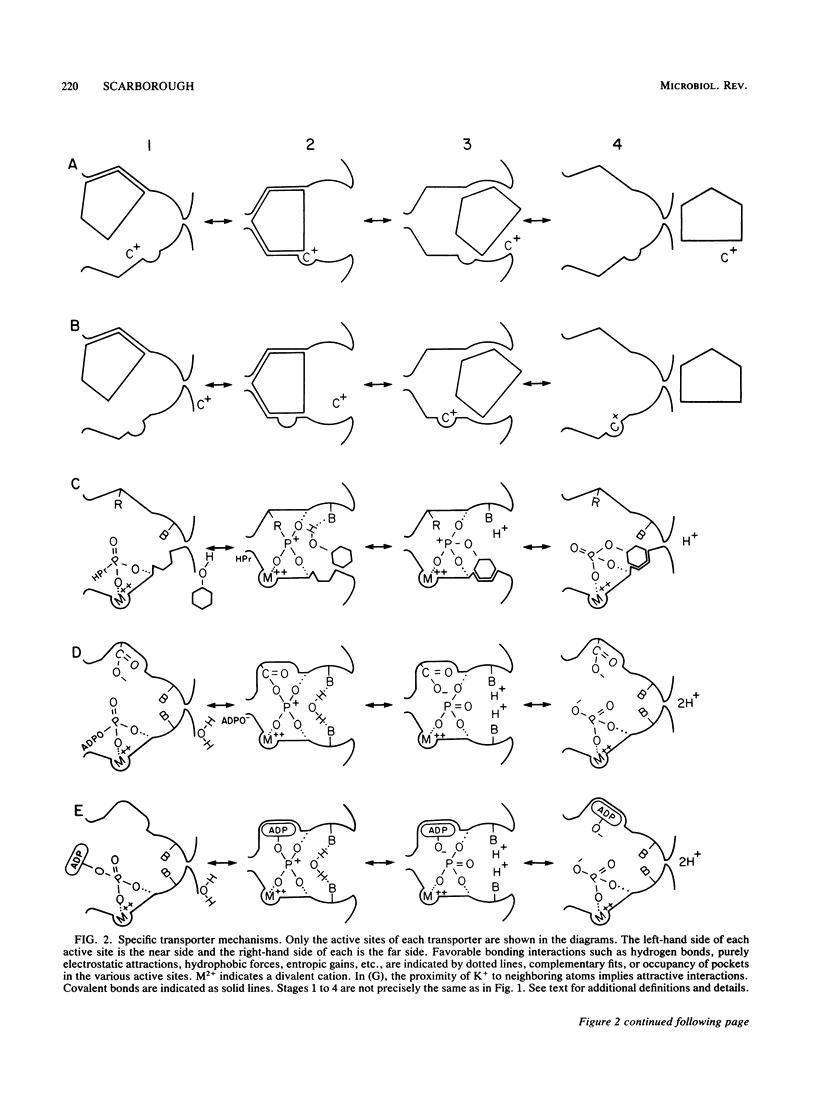
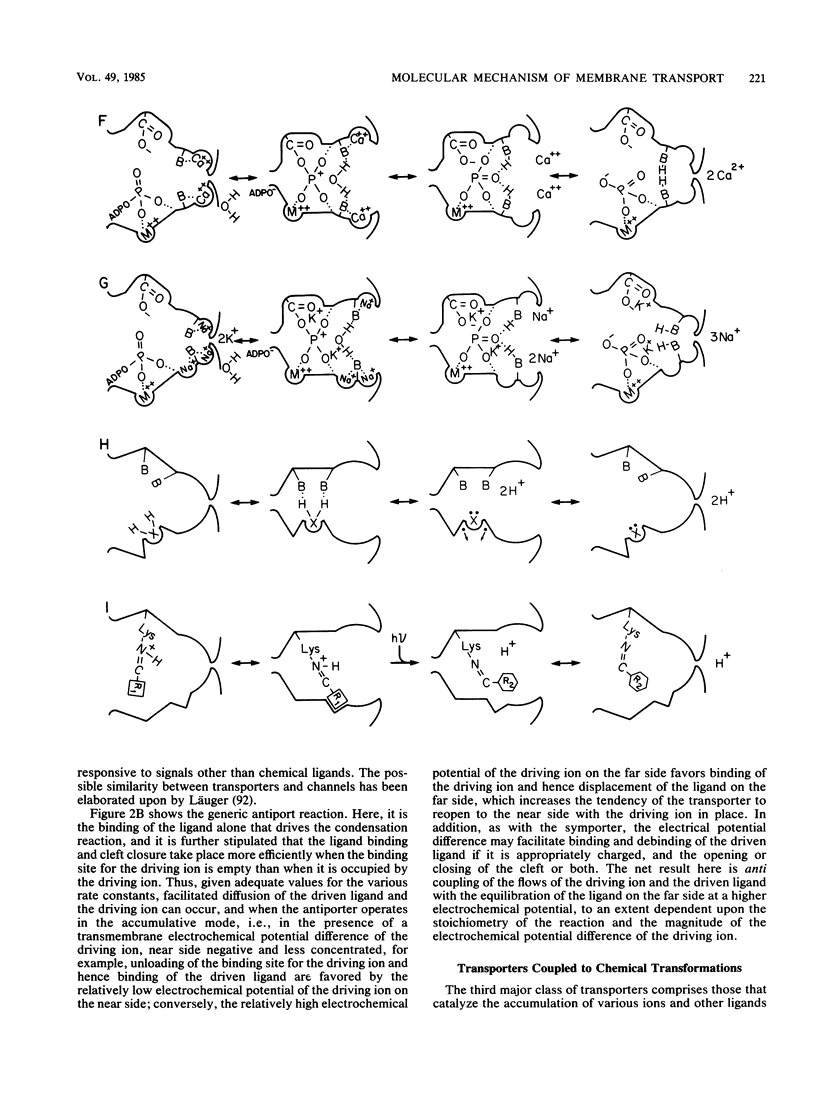










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amzel L. M., Pedersen P. L. Proton atpases: structure and mechanism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:801–824. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. M., Zucker F. H., Steitz T. A. Space-filling models of kinase clefts and conformation changes. Science. 1979 Apr 27;204(4391):375–380. doi: 10.1126/science.220706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamberg E., Dencher N. A., Fahr A., Heyn M. P. Transmembranous incorporation of photoelectrically active bacteriorhodopsin in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7502–7506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beers M. F., Carty S. E., Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. H+-ATPase and catecholamine transport in chromaffin granules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:116–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begley G. S., Hansen D. E., Jacobson G. R., Knowles J. R. Stereochemical course of the reactions catalyzed by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate:glucose phosphotransferase system. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5552–5556. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P. The energetics and kinetics of sodium-calcium exchange in barnacle muscles, squid axons, and mammalian heart: the role of ATP. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1984;38:129–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D., Kohlbrenner W. E., McIntosh D. B., Smith L. T., O'Neal C. C. ATP and ADP modulations of catalysis by F1 and Ca2+, Mg2+-ATPases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:65–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brey R. N., Rosen B. P. Cation/proton antiport systems in Escherichia coli. Properties of the calcium/proton antiporter. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1957–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherus J. R., Møller J. V., Jørgensen P. L. Soluble and active renal Na, K-ATPase with maximum protein molecular mass 170,000 +/- 9,000 daltons; formation of larger units by secondary aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):146–154. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürkler J., Solioz M. The ATP-dependent Ca2+-pumping system of Streptococcus faecium. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:422–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carafoli E., Zurini M., Niggli V., Krebs J. The calcium-transporting ATPase of erythrocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:304–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Devillers-Thiéry A., Chemouilli P. Acetylcholine receptor: an allosteric protein. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1335–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.6382611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri N. Conformational adaptability in enzymes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;37:397–648. doi: 10.1002/9780470122822.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. The size and detergent binding of membrane proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5459–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L. The mechanism and regulation of ATP synthesis by F1-ATPases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:681–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Scarborough G. A. Identification of the phosphorylated intermediate of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase as beta-aspartyl phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10724–10730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. L., Tanford C. Properties of a delipidated, detergent-activated Ca2+--ATPase. Biochemistry. 1978 May 2;17(9):1683–1690. doi: 10.1021/bi00602a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencher N. A., Heyn M. P. Bacteriorhodopsin monomers pump protons. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 15;108(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80552-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorset D. L., Engel A., Häner M., Massalski A., Rosenbusch J. P. Two-dimensional crystal packing of matrix porin. A channel forming protein in Escherichia coli outer membranes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Apr 25;165(4):701–710. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Rees E. D., Singer S. J. An experiment eliminating the rotating carrier mechanism for the active transport of Ca ion in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1532–1536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Ca2+-ATPase membrane crystals in sarcoplasmic reticulum. The effect of trypsin digestion. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10111–10115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux L., Martonosi A. Two-dimensional arrays of proteins in sarcoplasmic reticulum and purified Ca2+-ATPase vesicles treated with vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2599–2603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy A. A. Slip and leak models of gradient-coupled solute transport. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Jun;8(3):271–273. doi: 10.1042/bst0080271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Nordström B., Zeppezauer E., Söderlund G., Ohlsson I., Boiwe T., Söderberg B. O., Tapia O., Brändén C. I., Akeson A. Three-dimensional structure of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2-4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 25;102(1):27–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund H., Samma J. P., Wallén L., Brändén C. I., Akeson A., Jones T. A. Structure of a triclinic ternary complex of horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase at 2.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 15;146(4):561–587. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W., Whitelaw V., Hesse J. A K+ transport ATPase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6666–6668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faller L., Jackson R., Malinowska D., Mukidjam E., Rabon E., Saccomani G., Sachs G., Smolka A. Mechanistic aspects of gastric (H+ + K+)-ATPase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:146–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Sigman D. S. The synthesis of ATP by the membrane-bound ATP synthase complex from medium 32Pi under completely uncoupled conditions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12178–12183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson S. J., Sorgato M. C. Proton electrochemical gradients and energy-transduction processes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:185–217. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. The proton-translocating pumps of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1079–1113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgac M., Cantley L., Wiedenmann B., Altstiel L., Branton D. Clathrin-coated vesicles contain an ATP-dependent proton pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1300–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukada H., Sturtevant J. M., Quiocho F. A. Thermodynamics of the binding of L-arabinose and of D-galactose to the L-arabinose-binding protein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13193–13198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S. D., Capaldi R. A., Henderson R. Structure of cytochrome c oxidase in deoxycholate-drived two-dimensional crystals. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):305–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Kanazawa H. Structure and function of proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase (F0F1): biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):285–312. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.285-312.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabizon R., Schuldiner S. The amine transporter from bovine chromaffin granules. Partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3001–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garavito R. M., Jenkins J., Jansonius J. N., Karlsson R., Rosenbusch J. P. X-ray diffraction analysis of matrix porin, an integral membrane protein from Escherichia coli outer membranes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 25;164(2):313–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland G. L., Quiocho F. A. Structure of the L-arabinose-binding protein from Escherichia coli at 2.4 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1981 Mar 5;146(3):341–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goffeau A., Slayman C. W. The proton-translocating ATPase of the fungal plasma membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 30;639(3-4):197–223. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham C. M. Characterization of ATP binding sites of sheep kidney medulla (Na+ + K+)--ATPase using CrATP. J Inorg Biochem. 1981 Feb;14(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/s0162-0134(00)80013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham C. M., Gupta R. K., Barnett R. E., Mildvan A. S. Thallium-205 nuclear relaxation and kinetic studies of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6738–6744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham C. M., Mildvan A. S. Magnetic resonance and kinetic studies of the mechanism of membrane-bound sodium and potassium ion- activated adenosine triphosphatase. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(3):304–313. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C. Protein interfaces and intersubunit bonding. The case of tomato bushy stunt virus. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):139–153. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84930-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert H., Jørgensen P. L., Skriver E., Maunsbach A. B. Crystallization patterns of membrane-bound (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 12;689(3):571–574. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Wieczorek L., Altendorf K., Reicin A. S., Dorus E., Epstein W. Sequence homology between two membrane transport ATPases, the Kdp-ATPase of Escherichia coli and the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfer U., Groseclose R. The mechanism of Na+-dependent D-glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4453–4462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüdig H., Hengstenberg W. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate dependent phosphotransferase system (PTS): solubilisation and kinetic parameters of the glucose-specific membrane bound enzyme II component of Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 19;114(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80869-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Wodak S. J. Structural domains in proteins and their role in the dynamics of protein function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1983;42(1):21–78. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):969–970. doi: 10.1038/211969a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Oligomeric structure and the anion transport function of human erythrocyte band 3 protein. J Membr Biol. 1984;80(2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01868768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Pfister D., Carty S. E., Scarpa A. Biological amine transport in chromaffin ghosts. Coupling to the transmembrane proton and potential gradients. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10963–10972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Chemiosmotic coupling and its application to the accumulation of biological amines in secretory granules. Soc Gen Physiol Ser. 1984;38:71–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. N., Nickson J. K. Identifying the monosaccharide transport protein in the human erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jun 16;115(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Mechanism of the Na+, K+ pump. Protein structure and conformations of the pure (Na+ +K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 11;694(1):27–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L., Skriver E., Hebert H., Maunsbach A. B. Structure of the Na,K pump: crystallization of pure membrane-bound Na,K-ATPase and identification of functional domains of the alpha-subunit. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:207–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The lac carrier protein in Escherichia coli. J Membr Biol. 1983;76(2):95–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02000610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase system in the transport of sugars by isolated membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3711–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa Y., Sone N., Hirata H., Yoshida M. Structure and function of H+-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1979 Aug;11(3-4):39–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00743196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanner B. I., Fishkes H., Maron R., Sharon I., Schuldiner S. Reserpine as a competitive and reversible inhibitor of the catecholamine transporter of bovine chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus M., McCammon J. A. Dynamics of proteins: elements and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:263–300. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara M., Hinkle P. C. Reconstitution and purification of the D-glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7384–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khananshvili D., Gromet-Elhanan Z. Evidence that the Mg-dependent low-affinity binding site for ATP and Pi demonstrated on the isolated beta subunit of the F0.F1 ATP synthase is a catalytic site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1886–1890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Carter-Su C. Membrane potentials and the energetics of intestinal Na+-dependent transport systems. Am J Physiol. 1978 Sep;235(3):C73–C81. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.235.3.C73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingenberg M. Membrane protein oligomeric structure and transport function. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):449–454. doi: 10.1038/290449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. R. Enzyme-catalyzed phosphoryl transfer reactions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:877–919. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Neet K. E. The catalytic and regulatory properties of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:359–410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov I. A., Skulachev V. P. H+-Adenosine triphosphatase and membrane energy coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 21;463(1):29–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(77)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. Molecular considerations relevant to the mechanism of active transport. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):201–204. doi: 10.1038/292201a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J. The reactions of sodium and potassium ion-activated adenosine triphosphatase with specific antibodies. Implications for the mechanism of active transport. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3652–3660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFevre P. G. A comparison of recent suggestions for the functional organization of red-cell sugar-transport sites based on kinetic observations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:398–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lienhard G. E. Enzymatic catalysis and transition-state theory. Science. 1973 Apr 15;180(4082):149–154. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4082.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe A. G., Lambert A. Chloride-bicarbonate exchange and related transport processes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec;694(4):353–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuger P. Kinetic properties of ion carriers and channels. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 30;57(3):163–78(-RETURN-). doi: 10.1007/BF01869585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. A general theory of membrane transport from studies of bacteria. Nature. 1957 Jul 20;180(4577):134–136. doi: 10.1038/180134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P., MOYLE J. Group-translocation: a consequence of enzyme-catalysed group-transfer. Nature. 1958 Aug 9;182(4632):372–373. doi: 10.1038/182372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Energy coupling to ATP synthesis by the proton-translocating ATPase. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao B., McCammon J. A. Structural study of hinge bending in L-arabinose-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4964–4970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao B., McCammon J. A. Theoretical study of hinge bending in L-arabinose-binding protein. Internal energy and free energy changes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12543–12547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao B., Pear M. R., McCammon J. A., Quiocho F. A. Hinge-bending in L-arabinose-binding protein. The "Venus's-flytrap" model. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1131–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Monomeric solubilized sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca pump protein: demonstration of Ca binding and dissociation coupled to ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6623–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer I., Dahms A. S., Riezler W., Klingenberg M. Interaction of fluorescent adenine nucleotide derivatives with the ADP/ATP carrier in mitochondria. 1. Comparison of various 3'-O-ester adenine nucleotide derivatives. Biochemistry. 1984 May 22;23(11):2436–2442. doi: 10.1021/bi00306a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCammon J. A., Karplus M. Internal motions of antibody molecules. Nature. 1977 Aug 25;268(5622):765–766. doi: 10.1038/268765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEnery M. W., Buhle E. L., Jr, Aebi U., Pedersen P. L. Proton ATPase of rat liver mitochondria. Preparation and visualization of a functional complex using the novel zwitterionic detergent 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4642–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalak M., Famulski K., Carafoli E. The Ca2+-pumping ATPase in skeletal muscle sarcolemma. Calmodulin dependence, regulation by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation, and purification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15540–15547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H. Characterization and crystal packing of three-dimensional bacteriorhodopsin crystals. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1267–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Oesterhelt D., Henderson R. Orthorhombic two-dimensional crystal form of purple membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):338–342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H., Oesterhelt D. Three-dimensional crystals of membrane proteins: bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1283–1285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel H. Three-dimensional crystals of a membrane protein complex. The photosynthetic reaction centre from Rhodopseudomonas viridis. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):567–572. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., 3rd, Olson J. S., Pflugrath J. W., Quiocho F. A. Rates of ligand binding to periplasmic proteins involved in bacterial transport and chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13665–13672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misset O., Blaauw M., Postma P. W., Robillard G. T. Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase system. Mechanism of the transmembrane sugar translocation and phosphorylation. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6163–6170. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. A chemiosmotic molecular mechanism for proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1974 Jul 15;43(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80997-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Hypothesis: cation-translocating adenosine triphosphatase models: how direct is the participation of adenosine triphosphate and its hydrolysis products in cation translocation? FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 15;33(3):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80209-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Koppenol W. H. Chemiosmotic ATPase mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:584–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P., Moyle J. Alternative hypotheses of proton ejection in cytochrome oxidase vesicles. Transmembrane proton pumping or redox-linked deprotonation of phospholipid-cytochrome c complex(es). FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Proton translocation mechanisms and energy transduction by adenosine triphosphatases: an answer to criticisms. FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80465-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. The Ninth Sir Hans Krebs Lecture. Compartmentation and communication in living systems. Ligand conduction: a general catalytic principle in chemical, osmotic and chemiosmotic reaction systems. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar 15;95(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus J. M. The receptor protein of phage lambda: purification, characterization and preliminary electrical studies in planar lipid bilayers. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Jan;133A(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Gilliland G. L., Quiocho F. A. L-Arabinose-binding protein-sugar complex at 2.4 A resolution. Stereochemistry and evidence for a structural change. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13213–13217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer M. E., Lewis B. A., Quiocho F. A. The radius of gyration of L-arabinose-binding protein decreases upon binding of ligand. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13218–13222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Active transport of basic amino acids driven by a proton motive force in vacuolar membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2079–2082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Modyanov N. N. Structural basis of proton-translocating protein function. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:445–463. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.002305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Suzuki H., Tanaka M. Crystallization of part of the mitochondrial electron transfer chain: cytochrome c oxidase--cytochrome c complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):928–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Tanaka M., Shimomura Y. Crystallization of cytochrome bc1 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):921–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Tanaka M., Shimomura Y. Crystallization of the middle part of the mitochondrial electron transfer chain: cytochrome bc1-cytochrome c complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5084–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa T., Tanaka M., Wakabayashi T. Crystallization of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7175–7179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret J., Gay P. Kinetic study of a phosphoryl exchange reaction between fructose and fructose 1-phosphate catalyzed by the membrane-bound enzyme II of the phosphoenolpyruvate-fructose 1-phosphotransferase system of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Dec;102(1):237–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb06285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Sutko J. L. Sodium-calcium ion exchange in cardiac membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):590–594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reider E., Wagner E. F., Schweiger M. Control of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase-mediated sugar transport in Escherichia coli by energization of the cell membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5529–5533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S., Wiegand G., Huber R. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of two different forms of citrate synthase at 2.7 and 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):111–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard G. T. The enzymology of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sugar transport systems. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Jul 7;46(1):3–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00215577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross A. H., McConnell H. M. Reconstitution of the erythrocyte anion channel. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 10;253(13):4777–4782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein A., Cabantchik Z. I., Knauf P. Mechanism of anion transport in red blood cells: role of membrane proteins. Fed Proc. 1976 Jan;35(1):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein A., Knauf P. A., Grinstein S., Shami Y. A model for the action of the anion exchange protein of the red blood cell. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1979;30:483–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase systems: structural, functional, and evolutionary interrelationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Dec;41(4):856–871. doi: 10.1128/br.41.4.856-871.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarborough G. A. Chemiosmotic models for the mechanisms of the cation-motive ATPases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;402:99–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb25735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. The red cell calcium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:303–312. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Rosenbusch J. P. Matrix protein in planar membranes: clusters of channels in a native environment and their functional reassembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2302–2306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobert B., Lanyi J. K. Halorhodopsin is a light-driven chloride pump. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10306–10313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Fishkes H., Kanner B. I. Role of a transmembrane pH gradient in epinephrine transport by chromaffin granule membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3713–3716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz G. E., Schirmer R. H., Sachsenheimer W., Pai E. F. The structure of the flavoenzyme glutathione reductase. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):120–124. doi: 10.1038/273120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza G., Kessler M., Hosang M., Weber J., Schmidt U. Biochemistry of the Na+, D-glucose cotransporter of the small-intestinal brush-border membrane. The state of the art in 1984. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 3;779(3):343–379. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(84)90016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Wise J. G. The proton-ATPase of bacteria and mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(2):105–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01870434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Plasma membrane ATPase of fungi and plants as a novel type of proton pump. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;23:87–126. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152823-2.50007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver E., Maunsbach A. B., Jørgensen P. L. Formation of two-dimensional crystals in pure membrane-bound Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 31;131(2):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80371-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Hinkle P. C. Proton transport by cytochrome c oxidase from the thermophilic bacterium PS3 reconstituted in liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12600–12604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and related pigments of halobacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:587–616. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckenius W., Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A. Bacteriorhodopsin and the purple membrane of halobacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 14;505(3-4):215–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. K., Xie X. S., Racker E. An ATP-driven proton pump in clathrin-coated vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4059–4062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Dame J. B., Scarborough G. A. The Neurospora plasma membrane Ca2+ pump. Fed Proc. 1980 May 15;39(7):2437–2441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Scarborough G. A. Active transport of calcium in Neurospora plasma membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3102–3106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Yamamoto T., Tonomura Y. Molecular mechanism of active calcium transport by sarcoplasmic reticulum. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jan;58(1):1–79. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Mechanism of free energy coupling in active transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:379–409. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Simple model for the chemical potential change of a transported ion in active transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2882–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Twenty questions concerning the reaction cycle of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(2):123–151. doi: 10.3109/10409238409113603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., O'Shea P. S., Petrone G., Azzi A. Proton translocation by a native and subunit III-depleted cytochrome c oxidase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. Use of fluorescein-phosphatidylethanolamine as an intravesicular pH indicator. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3626–3631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver G. A. Inhibition of parallel flux and augmentation of counter flux shown by transport models not involving a mobile carrier. J Theor Biol. 1966 Feb;10(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser L., Robinson N. C., Tanford C. The two-domain structure of cytochrome b5 in deoxycholate solution. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1194–1199. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warncke J., Slayman C. L. Metabolic modulation of stoichiometry in a proton pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 8;591(2):224–233. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb M. R., Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S., Trentham D. R. The stereochemical course of phosphoric residue transfer catalyzed by beef heart mitochondrial ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11637–11639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C. Kinetic properties of the reconstituted glucose transporter from human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8907–8914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Krab K. Proton-pumping cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 17;549(2):177–122. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(79)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M., Krab K., Saraste M. Proton-translocating cytochrome complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:623–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikström M. Pumping of protons from the mitochondrial matrix by cytochrome oxidase. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):558–560. doi: 10.1038/308558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B. Cellular transport mechanisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:933–965. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Enzyme catalysis: conflicting requirements of substrate access and transition state affinity. Mol Cell Biochem. 1974 May 30;3(3):207–211. doi: 10.1007/BF01686645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Transition state analogues for enzyme catalysis. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):704–705. doi: 10.1038/223704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman J. The turning wheel: a study in steady states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3983–3987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


