Full text
PDF





































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER S. LEISHMANIA. Adv Parasitol. 1964;2:35–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60586-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLEN J. M., BRIEGER E. M., REES R. J. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF THE HOST-CELL PARASITE RELATION IN MURINE LEPROSY. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:301–306. doi: 10.1002/path.1700890131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANACKER R. L., FUKUSHI K., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF COXIELLA BURNETII IN THE CHICK YOLK SAC. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1130-1138.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Davis B. K. Structural properties and features of parasitic Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):948–965. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.948-965.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Huff C. G., Spinz H. Comparative feeding mechanisms of avian and primate malarial parasites. Mil Med. 1966 Sep;131(9 Suppl):969–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Johnson J., Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):72–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth S., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Differential neutralization of spontaneous and centrifuge-assisted chlamydial infectivity. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):61–67. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akporiaye E. T., Rowatt J. D., Aragon A. A., Baca O. G. Lysosomal response of a murine macrophage-like cell line persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1155–1162. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1155-1162.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcantara A., Brener Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: role of macrophage membrane components in the phagocytosis of bloodstream forms. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Aug;50(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. J. Effect of infection with the meningopneumonitis agent on deoxyribonucleic acid and protein synthesis by its L-cell host. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):653–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.653-657.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. J. Separation of protein synthesis in meningopneumonitisgent from that in L cells by differential susceptibility to cycloheximide. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.327-332.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. Effect of the antiphagocytic agent cytochalasin B on macrophage invasion by Leishmania mexicana promastigotes and Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes. J Protozool. 1975 May;22(2):237–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. Leishmania mexicana: inhibition and stimulation of phagosome-lysosome fusion in infected macrophages. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Oct;52(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J., Vickerman K. Fusion of host cell secondary lysosomes with the parasitophorous vacuoles of Leishmania mexicana-infected macrophages. J Protozool. 1975 Nov;22(4):502–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1975.tb05219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan I., Pearce J. H. Amino acid requirements of strains of Chlamydia trachomatis and C. psittaci growing in McCoy cells: relationship with clinical syndrome and host origin. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):2001–2007. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan I., Pearce J. H. Differential amino acid utilization by Chlamydia psittaci (strain guinea pig inclusion conjunctivitis) and its regulatory effect on chlamydial growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jul;129(7):1991–2000. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-7-1991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan I., Pearce J. H. Modulation by centrifugation of cell susceptibility to chlamydial infection. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Mar;111(1):87–92. doi: 10.1099/00221287-111-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. R., Hopps H. E., Barile M. F., Bernheim B. C. Comparison of the ultrastructure of several rickettsiae, ornithosis virus, and Mycoplasma in tissue culture. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1387–1404. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1387-1404.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Phagosome-lysosome interactions in cultured macrophages infected with virulent tubercle bacilli. Reversal of the usual nonfusion pattern and observations on bacterial survival. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson W. H., Winkler H. H. Transport of AMP by Rickettsia prowazekii. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):32–38. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.32-38.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BADER J. P., MORGAN H. R. Latent viral infection of cells in tissue culture. VI. Role of amino acids, glutamine, and glucose in psittacosis virus propagation in L cells. J Exp Med. 1958 Nov 1;108(5):617–630. doi: 10.1084/jem.108.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., ALLEN E. G. Reversible inactivation of the toxicity and hemolytic activity of typhus rickettsiae by starvation. J Bacteriol. 1957 Nov;74(5):637–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.5.637-645.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R. Phosphorylation accompanying the oxidation of glutamate by the Madrid E strain of typhus rickettsiae. J Biol Chem. 1956 May;220(1):353–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., SCHNEIDER L. The incorporation of glycine-1-C14 by typhus rickettsiae. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1727–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOVARNICK M. R., SCHNEIDER L., WALTER H. The incorporation of labeled methionine by typhus rickettsiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jun;33(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOZEMAN F. M., HOPPS H. E., DANAUSKAS J. X., JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. I. A tissue culture system for quantitative estimations of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1956 Jun;76(6):475–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Akporiaye E. T., Aragon A. S., Martinez I. L., Robles M. V., Warner N. L. Fate of phase I and phase II Coxiella burnetii in several macrophage-like tumor cell lines. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):258–266. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.258-266.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Q fever and Coxiella burnetii: a model for host-parasite interactions. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):127–149. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.127-149.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baca O. G., Scott T. O., Akporiaye E. T., DeBlassie R., Crissman H. A. Cell cycle distribution patterns and generation times of L929 fibroblast cells persistently infected with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):366–369. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.366-369.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H., Butcher G. A., Dennis E. D., Mitchell G. H. Structure and invasive behaviour of Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites in vitro. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):483–491. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000047247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H. The interactions of intracellular Protista and their host cells, with special reference to heterotrophic organisms. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Apr 11;204(1155):141–163. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Amano K., Hackstadt T., Perry L., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydia trachomatis has penicillin-binding proteins but not detectable muramic acid. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):420–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.420-428.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale L., Kim K. S. Mycobacterium. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):217–372. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.217-372.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavoil P., Ohlin A., Schachter J. Role of disulfide bonding in outer membrane structure and permeability in Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):479–485. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.479-485.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaman L., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. VI. Differential opsonizing and neutralizing action of human typhus rickettsia-specific cytophilic antibodies in cultures of human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1071–1076. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1071-1076.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker Y., Asher Y. Synthesis of trachoma agent proteins in emetine-treated cells. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):966–970. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.966-970.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Dwyer D. M., Wyler D. J. Multiplication of Leishmania in human macrophages in vitro. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):375–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.375-379.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein D. I., Hubbard T., Wenman W. M., Johnson B. L., Jr, Holmes K. K., Liebhaber H., Schachter J., Barnes R., Lovett M. A. Mediastinal and supraclavicular lymphadenitis and pneumonitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis serovars L1 and L2. N Engl J Med. 1984 Dec 13;311(24):1543–1546. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198412133112405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird R. G., Smith M. D. Cryptosporidiosis in man: parasite life cycle and fine structural pathology. J Pathol. 1980 Nov;132(3):217–233. doi: 10.1002/path.1711320304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S. K., Liebhaber H. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis, cell cycle progression, and division of Chlamydia-infected HeLa 229 cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):953–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.953-957.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S. K., Paul R. G. Purification of Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum elementary bodies and their interaction with HeLa cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Jun;128(6):1371–1379. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-6-1371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose S. K., Smith G. B., Paul R. G. Influence of lectins, hexoses, and neuraminidase on the association of purified elementary bodies of Chlamydia trachomatis UW-31 with HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1060–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1060-1067.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovarnick M. R. INCORPORATION OF ACETATE-1-C INTO LIPID BY TYPHUS RICKETTSIAE. J Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80(4):508–512. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.4.508-512.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovarnick M. R., Schneider L. ROLE OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE IN THE HEMOLYSIS OF SHEEP ERYTHROCYTES BY TYPHUS RICKETTSIAE. J Bacteriol. 1960 Sep;80(3):344–354. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.3.344-354.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brener Z. Biology of Trypanosoma cruzi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:347–382. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G. J., Coan C. C. Interaction of red cell ATP levels and malaria, and the treatment of malaria with hyperoxia. Mil Med. 1969 Sep;134(10):1056–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownridge E., Wyrick P. B. Interaction of Chlamydia psittaci reticulate bodies with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):697–700. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.697-700.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Growth of Pasteurella pseudotuberculosis in simulated intracellular and extracellular environments. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):403–417. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The Vwa+ virulence factor of yersiniae: the molecular basis of the attendant nutritional requirement for Ca++. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S748–S758. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnham J. C., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Ultrastructure and cell division of a facultatively parasitic strain of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):997–1004. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.997-1004.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Kordová N., Paretsky D. Electron microscopic studies of the rickettsia Coxiella burneti: entry, lysosomal response, and fate of rickettsial DNA in L-cells. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Feb;17(2):143–150. doi: 10.1139/m71-025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton P. R., Stueckemann J., Welsh R. M., Paretsky D. Some ultrastructural effects of persistent infections by the rickettsia Coxiella burnetii in mouse L cells and green monkey kidney (Vero) cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):556–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.556-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher G. A., Mitchell G. H., Cohen S. Letter: Mechanism of host specificity in malarial infection. Nature. 1973 Jul 6;244(5410):40–41. doi: 10.1038/244040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Krueger D. A. Lymphokine-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia replication in mouse fibroblasts is neutralized by anti-gamma interferon immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1152-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Moulder J. W. Parasite-specified phagocytosis of Chlamydia psittaci and Chlamydia trachomatis by L and HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):598–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.598-606.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I. Requirements for ingestion of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):645–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.645-651.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büngener W., Nielsen G. Nukleinsäurenstoffwechsel bei experimenteller Malarie. 1. Untersuchungen über den Einbau von Thymidin, Uridin und Adenosin in Malariaparasiten (Plasmodium berghei und Plasmodium vinckei) Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1967 Dec;18(4):456–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H. The use of phosphorus 32 in studies on Plasmodium gallinaceum. II. Studies on conditions affecting parasite growth in intact cells and in lysates. J Exp Med. 1952 Nov;96(5):451–463. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.5.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BOZEMAN F. M., CAMPBELL J. M., HUMPHRIES J. W., SAWYER T. K. Study on growth of Rickettsia. V. Penetration of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into mammalian cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1959 Mar 1;109(3):271–292. doi: 10.1084/jem.109.3.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLON J. I. The role of folic acid in the metabolism of members of the psittacosis group of microorganisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Mar 5;98:234–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1962.tb30548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROCKER T. T., PELC S. R., NIELSEN B. I., EASTWOOD J. M., BANKS J. POPULATION DYNAMICS AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN HELA CELLS INFECTED WITH AN ORNITHOSIS AGENT. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:105–122. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Perry L. J. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity with antibodies to the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):745–754. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.745-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrol M. E., Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Phagolysosome formation, cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and the fate of Salmonella typhimurium within mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):421–429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceballos M. M., Hatch T. P. Use of HeLa cell guanine nucleotides by Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):98–102. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.98-102.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intracellular symbiosis in leishmaniasis. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1983;14:267–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Leishmania donovani. Hamster macrophage interactions in vitro: cell entry, intracellular survival, and multiplication of amastigotes. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):515–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Dwyer D. M. Multiplication of a human parasite (Leishmania donovani) in phagolysosomes of hamster macrophages in vitro. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):678–680. doi: 10.1126/science.948742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P., Fong D. Cell biology of host-parasite membrane interactions in leishmaniasis. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;99:113–137. doi: 10.1002/9780470720806.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. P. Leishmanicidal mechanisms of human polymorphonuclear phagocytes. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Mar;30(2):322–333. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian R. G., Paretsky D. Synthesis of ribonucleotides and their participation in ribonucleic acid synthesis by Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):841–846. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.841-846.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coolbaugh J. C., Progar J. J., Weiss E. Enzymatic activities of cell-free extracts of Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):298–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.298-305.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs G. H. Proteinases of Leishmania mexicana and other flagellate protozoa. Parasitology. 1982 Feb;84(1):149–155. doi: 10.1017/s003118200005174x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Allison A. C. Effects of cytochalasin B on endocytosis and exocytosis. Front Biol. 1978;46:143–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. A., Alderson T., Thomas A. W., Mitchell G. H., Lennox E. S., Cohen S. Rat monoclonal antibodies which inhibit the in vitro multiplication of Plasmodium knowlesi. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Aug;49(2):297–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis M. W., Storz J. Infectivity of Chlamydia psittaci of bovine and ovine origins for cultured cells. Am J Vet Res. 1982 Nov;43(11):1897–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhople A. M., Hanks J. H. In vitro growth of Mycobacterium lepraemurium, an obligate intracellular microbe. Science. 1977 Jul 22;197(4301):379–381. doi: 10.1126/science.327548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhople A. M., Hanks J. H. Role of sulfhydryls in in vitro growth of Mycobacterium lepraemurium. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):352–357. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.352-357.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich D. L., Duran C. P., Conti S. F. Acquisition of Escherichia coli outer membrane proteins by Bdellovibrio sp. strain 109D. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):329–334. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.329-334.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue J. P., Thompson H. A. Protein synthesis in cell-free extracts of Coxiella burnetti. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Dec;121(2):293–302. doi: 10.1099/00221287-121-2-293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughri A. M., Storz J., Altera K. P. Mode of entry and release of chlamydiae in infections of intestinal epithelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1972 Dec;126(6):652–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.6.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Miller L. H., Whitehouse W. C., Shiroishi T. Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria merozoites. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):748–750. doi: 10.1126/science.803712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANDSON A. L., Jr, MACKEY W. H. Nutrition of Shigella: growth of Shigella flexneri in a simple chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):253–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.253-257.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Wyrick P. B., Davis C. H., Rumpp J. W. Chlamydia psittaci elementary body envelopes: ingestion and inhibition of phagolysosome fusion. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):741–751. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.741-751.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg L. G., Wyrick P. B. Inhibition of phagolysosome fusion is localized to Chlamydia psittaci-laden vacuoles. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):889–896. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.889-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eksztejn M., Varon M. Elongation and cell division in Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Aug 26;114(2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00410781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-On J., Bradley D. J., Freeman J. C. Leishmania donovani: action of excreted factor on hydrolytic enzyme activity of macrophages from mice with genetically different resistance to infection. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Apr;49(2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsbach P., Weiss J. A reevaluation of the roles of the O2-dependent and O2-independent microbicidal systems of phagocytes. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5(5):843–853. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.5.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Shipley P. L. Plasmid-mediated factors associated with virulence of bacteria to animals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:465–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelking H. M., Seidler R. J. The involvement of extracellular enzymes in the metabolism of Bdellovibrio. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Feb 13;95(4):293–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02451770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N., Miller L. H., Kaushel D. C., Udeinya I. J., Rener J., Howard R. J., Asofsky R., Aikawa M., Hess R. L. Monoclonal antibodies against a specific surface determinant on malarial (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites block erythrocyte invasion. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Newton H. E., Levy L. Early response of mouse foot pads to Mycobacterium laprae. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):76–85. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.76-85.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing E. P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Shirai A., Osterman J. V. Experimental infection of mouse peritoneal mesothelium with scrub typhus rickettsiae: an ultrastructural study. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1068–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1068-1075.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., GRANT P. T. The sulphur requirements of the erythrocytic from of Plasmodium knowlesi. Biochem J. 1956 Jun;63(2):274–282. doi: 10.1042/bj0630274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairfield A. S., Meshnick S. R., Eaton J. W. Malaria parasites adopt host cell superoxide dismutase. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):764–766. doi: 10.1126/science.6348944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferone R. Folate metabolism in malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):291–298. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields B. S., Shotts E. B., Jr, Feeley J. C., Gorman G. W., Martin W. T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Mar;47(3):467–471. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.3.467-471.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. The proton-translocating pumps of oxidative phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1079–1113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Invasive enteric pathogens. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S702–S707. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Dubey J. P., Miller N. L. Toxoplasma gondii in cats: fecal stages identified as coccidian oocysts. Science. 1970 Feb 6;167(3919):893–896. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3919.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Pursuing toxoplasma. J Infect Dis. 1970 Dec;122(6):553–559. doi: 10.1093/infdis/122.6.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Allweiss B., O'Brien P. C., Halstead S. A., Macsai M. S. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: in vitro studies. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):241–249. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.241-249.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., O'Brien P. C., Macsai M. S. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: in vivo studies. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.234-240.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Ramseur J. M. Mechanisms of persistent infections by cytopathic viruses in tissue culture. Brief review. Arch Virol. 1979;60(2):83–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01348025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. 3. Influence of human immune serum and complement on the fate of Rickettsia mooseri within the human macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):631–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.631-640.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambrill M. R., Wisseman C. L., Jr Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. I. Multiplication of typhus rickettsiae in human macrophage cell cultures in the nonimmune system: influence of virulence of rickettsial strains and of chloramphenicol. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):519–527. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.519-527.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett A. J., Harrison M. J., Manire G. P. A search for the bacterial mucopeptide component, muramic acid, in Chlamydia. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jan;80(1):315–318. doi: 10.1099/00221287-80-1-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilead Z., Becker Y. Effect of emetine on ribonucleic acid biosynthesis in HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):143–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. D., Stewart R. B. Effect of metabolic inhibitors on the production of Chlamydia psittaci by infected L cells. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Nov;16(11):1079–1085. doi: 10.1139/m70-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. H., Hart P. D., Young M. R. Ammonia inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):79–80. doi: 10.1038/286079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., Brokl O., Schaefer W. B. Lipids of putative relevance to virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: correlation of virulence with elaboration of sulfatides and strongly acidic lipids. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.142-149.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory W. W., Byrne G. I., Gardner M., Moulder J. W. Cytochalasin B does not inhibit ingestion of Chlamydia psittaci by mouse fibroblasts (L cells) and mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):463–466. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.463-466.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Leider J. E., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. I. Requirements for circumferential attachment of particle-bound ligands to specific receptors on the macrophage plasma membrane. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1263–1282. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst C. A., Kumar N., Carter R., Kaushal D. C. A surface protein expressed during the transformation of zygotes of Plasmodium gallinaceum is a target of transmission-blocking antibodies. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):775–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.775-777.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Sherman I. W. Isolation and characterization of the plasma membrane of human erythrocytes infected with the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1087–1091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutter B., Becker Y. Synthesis and maturation of ribosomal RNA during the developmental cycle of trachoma agent, a prokaryotic obligate parasite of eukaryocytes. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):239–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90476-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGASHI N. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE MODE OF REPRODUCTION OF TRACHOMA VIRUS AND PSITTACOSIS VIRUS IN CELL CULTURES. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:24–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90021-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., JACKSON E. B., DANAUSKAS J. X., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of rickettsiae. III. Influence of extracellular environment on the growth of Rickettsia tsutsugamusni in tissue culture cells. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):161–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. Biochemical stratagem for obligate parasitism of eukaryotic cells by Coxiella burnetii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. Stability of the adenosine 5'-triphosphate pool in Coxiella burnetii: influence of pH and substrate. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):419–425. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.419-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackstadt T., Williams J. C. pH dependence of the Coxiella burnetii glutamate transport system. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):598–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.598-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of Henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the bacterium. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):879–886. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.879-886.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the host cell. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.887-894.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J., Schad P. A., Austin S., Formal S. B. Characterization of virulence plasmids and plasmid-associated outer membrane proteins in Shigella flexneri, Shigella sonnei, and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):340–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.340-350.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks J. H. Host-dependent microbes. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):114–135. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.114-135.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson B. A. Effect of immune serum on infectivity of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):341–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.341-349.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. T., Coombs G. H. Leishmania mexicana: energy metabolism of amastigotes and promastigotes. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):397–409. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A., Brown C. A., Draper P. Ultrastructural study of the behavior of macrophages toward parasitic mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.803-807.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Interference with normal phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages, using ingested yeast cells and suramin. Nature. 1975 Jul 3;256(5512):47–49. doi: 10.1038/256047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R., Jordan M. M., Perkins W. J., Geisow M. J. Chemical inhibitors of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages also inhibit saltatory lysosomal movements. A combined microscopic and computer study. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):477–492. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Manipulations of the phagosome-lysosome fusion response in cultured macrophages. Enhancement of fusion by chloroquine and other amines. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90516-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. The effect of inhibitors and enhancers of phagosome--lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages on the phagosome membranes of ingested yeasts. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Feb;118(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90160-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Al-Hossainy E., Silverman J. A. Adenine nucleotide and lysine transport in Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):662–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.662-670.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Structural and polypeptide differences between envelopes of infective and reproductive life cycle forms of Chlamydia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.13-20.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Competition between Chlamydia psittaci and L cells for host isoleucine pools: a limiting factor in chlamydial multiplication. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):211–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.211-220.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Utilization of L-cell nucleoside triphosphates by Chlamydia psittaci for ribonucleic acid synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):393–400. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.393-400.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P. Utilization of exogenous thymidine by Chlamydia psittaci growing in the thymidine kinase-containing and thymidine kinase-deficient L cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):706–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.706-712.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch T. P., Vance D. W., Jr, Al-Hossainy E. Attachment of Chlamydia psittaci to formaldehyde-fixed and unfixed L cells. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Aug;125(2):273–283. doi: 10.1099/00221287-125-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes J. D., Diggs C. L., Hines F. A., Desjardins R. E. Culture of human malaria parasites Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):767–769. doi: 10.1038/263767a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus on heat-treated Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1156–1162. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1156-1162.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Miozzari G. F., Rittenberg S. C. Ribonucleic acid destruction and synthesis during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.481-491.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hespell R. B., Rosson R. A., Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Respiration of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strain 109J and its energy substrates for intraperiplasmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1280–1288. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1280-1288.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman T. C., McNeil P. L., Muscatine L. Phagosome-lysosome fusion inhibited by algal symbionts of Hydra viridis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):56–63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden E. P., Winkler H. H., Wood D. O., Leinbach E. D. Intracellular growth of Legionella pneumophila within Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.18-24.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Nardin E. H., Tharavanij S., Schwartz A. L., Nussenzweig R. S. Inhibition of entry of Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax sporozoites into cultured cells; an in vitro assay of protective antibodies. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):909–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Zavala F., Nussenzweig R. S., Nussenzweig V. Antibodies to the protective antigen of Plasmodium berghei sporozoites prevent entry into cultured cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1929–1930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., Jr Lipids and the malarial parasite. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):237–248. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homewood C. A. Carbohydrate metabolism of malarial parasites. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):229–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoschak K. D., Moulder J. W. Division of single host cells after infection with chlamydiae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):281–286. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.281-286.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz A. T., Kessel M., Shilo M. Growth cycle of predacious Bdellovibrios in a host-free extract system and some properties of the host extract. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):270–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.270-282.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of microorganisms. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;4(1):104–123. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Intracellular multiplication of Legionnaires' disease bacteria (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes is reversibly inhibited by erythromycin and rifampin. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):15–26. doi: 10.1172/JCI110744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Symbiotic interactions between Legionella pneumophila and human leukocytes. Int Rev Cytol Suppl. 1983;14:307–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis in cell culture. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.698-703.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells R. E. Electron microscope observations on the development and schizogony of the erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Sep;64(3):305–307. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Starr M. P. Possible enzymatic base of bacteriolysis by bdellovibrios. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Feb 5;89(2):147–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00425030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison W. M., Dunachie J. F., Work K., Siim J. C. The life cycle of the coccidian parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, in the domestic cat. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(3):380–399. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(71)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob F. Evolution and tinkering. Science. 1977 Jun 10;196(4295):1161–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.860134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs R. F., Locksley R. M., Wilson C. B., Haas J. E., Klebanoff S. J. Interaction of primate alveolar macrophages and Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1515–1523. doi: 10.1172/JCI111357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F., Jr, Paretsky D. Physiology of rickettsiae. VI. Host-independent synthesis of polyribonucleotides by Coxiella burnetii. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1063–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1063-1068.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushal D. C., Carter R., Rener J., Grotendorst C. A., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Monoclonal antibodies against surface determinants on gametes of Plasmodium gallinaceum block transmission of malaria parasites to mosquitoes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2557–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg K. R., Horoschak K. D., Moulder J. W. Toxicity of low and moderate multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1977 Nov;18(2):531–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.2.531-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Cayley P. J., Silverman R. H., Knight M. The antiviral action of interferon. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Sep 24;299(1094):59–67. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Shilo M. Relationship of Bdellovibrio elongation and fission to host cell size. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):477–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.477-480.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. A unique histidine-rich polypeptide from the malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4650–4655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A., Abati A., Trager W. Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium coatneyi: immunogenicity of "knob-like protrusions" on infected erythrocyte membranes. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Jun;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Does a histidine-rich protein from Plasmodium lophurae have a function in merozoite penetration? J Protozool. 1976 May;23(2):272–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Homology between a histidine-rich protein from Plasmodium lophurae and a protein associated with the knob-like protrusions on membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1534–1538. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. Immunological cross-reactivity of the histidine-rich protein of Plasmodium lophurae and the knob protein of Plasmodium falciparum. J Parasitol. 1983 Apr;69(2):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopmans-Gargantiel A. I., Wisseman C. L., Jr Differential requirements for enriched atmospheric carbon dioxide content for intracellular growth in cell culture among selected members of the genus Rickettsia. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1277–1280. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1277-1280.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenen J. G., Rittenberg S. C. Incorporation of long-chain fatty acids of the substrate organism by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus during intraperiplasmic growth. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1145–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1145-1157.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C. Cultures of Chlamydia trachomatis in mouse peritoneal macrophages: factors affecting organism growth. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):439–445. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.439-445.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C. Immediate cytotoxicity of Chlamydia trachomatis for mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.613-618.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Königk E. Salvage syntheses and their relationship to nucleic acid metabolism. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):249–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITWIN J. The growth cycle of the psittacosis group of micro-organisms. J Infect Dis. 1959 Sep-Oct;105:129–160. doi: 10.1093/infdis/105.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladd T. I., Ventullo R. M., Wallis P. M., Costerton J. W. Heterotrophic activity and biodegradation of labile and refractory compounds by groundwater and stream microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):321–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.321-329.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladda R., Aikawa M., Sprinz H. Penetration of erythrocytes by merozoites of mammalian and avian malarial parasites. J Parasitol. 1969 Jun;55(3):633–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G. Electron microscope cytochemistry of host-parasite membrane interactions in malaria. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):171–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G. Feeding mechanisms in extracellular Babesia microti and Plasmodium lophurae. J Protozool. 1976 May;23(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langreth S. G., Trager W. Fine structure of the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae developing extracellularly in vitro. J Protozool. 1973 Nov;20(5):606–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1973.tb03584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn A. M., Blyth W. A., Taverne J. Interactions of TRIC agents with macrophages and BHK-21 cells observed by electron microscopy. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Sep;71(3):515–528. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K. Factors affecting the rate as which a trachoma strain of Chlamydia trachomatis establishes persistent infections in mouse fibroblasts (McCoy cells). Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):954–957. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.954-957.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K. Interaction between a trachoma strain of Chlamydia trachomatis and mouse fibroblasts (McCoy cells) in the absence of centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.584-591.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Moulder J. W. Persistent infection of mouse fibroblasts (McCoy cells) with a trachoma strain of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):822–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.822-829.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J., Moulder J. W. Attachment of cell walls of Chlamydia psittaci to mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1059–1065. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1059-1065.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J. Wheat germ agglutinin blockage of chlamydial attachment sites: antagonism by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):946–953. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.946-953.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. H. Infection of tissue culture cells of low phagocytic ability by Leishmania mexicana mexicana. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1974 Sep;68(3):327–336. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1974.11686955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. H., Peters W. The resistance of intracellular Leishmania parasites to digestion by lysosomal enzymes. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1977 Sep;71(3):295–312. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1977.11687192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. S. Inhibition of thymidine kinase activity and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in L cells infected with the meningopneumonitis agent. J Bacteriol. 1968 Dec;96(6):2054–2065. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.6.2054-2065.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie D. B., Aber V. R., Jackett P. S. Phagosome-lysosome fusion and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in macrophages infected with Mycobacterium microti, Mycobacterium bovis BCG or Mycobacterium lepraemurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):431–441. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Miller L. H. Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Ultrastructure of parasitized erythrocytes in cardiac vessels. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1971 Sep;20(5):655–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lushbaugh W. B., McGhee R. B., Singh S. D. Fine structure of Plasmodium gallinaceum in embryonic and neonate chicks. J Protozool. 1976 Feb;23(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb05255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. R. Latent viral infection of cells in tissue culture. I. Studies on latent infection of chick embryo tissues with psittacosis virus. J Exp Med. 1956 Jan 1;103(1):37–47. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Jenkin H. M., Yu H. M., Townsend D. Lipid composition of Chlamydia psittaci grown in monkey kidney cells in defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.62-70.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marecki N., Becker F., Baca O. G., Paretsky D. Changes in liver and L-cell plasma membranes during infection with Coxiella burnetii. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):272–280. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.272-280.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Rittenberg S. C. Kinetics of deoxyribonucleic acid destruction and synthesis during growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strain 109D on pseudomonas putida and escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):664–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.664-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazier D., Landau I., Druilhe P., Miltgen F., Guguen-Guillouzo C., Baccam D., Baxter J., Chigot J. P., Gentilini M. Cultivation of the liver forms of Plasmodium vivax in human hepatocytes. 1984 Jan 26-Feb 1Nature. 307(5949):367–369. doi: 10.1038/307367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe R. E., Remington J. S., Araujo F. G. Mechanisms of invasion and replication of the intracellular stage in Trypanosoma cruzi. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):372–376. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.372-376.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaul T. F., Williams J. C. Developmental cycle of Coxiella burnetii: structure and morphogenesis of vegetative and sporogenic differentiations. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):1063–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.1063-1076.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan T. F., Dame J. B., Miller L. H., Barnwell J. Evolutionary relatedness of Plasmodium species as determined by the structure of DNA. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.6382604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Stephens D. S., Hoffman L. H., Schlech W. F., 3rd, Horn R. G. Mechanisms of mucosal invasion by pathogenic Neisseria. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S708–S714. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., Bannister L. H., Trigg P. I., Butcher G. A. A freeze-fracture study on the parasite-erythrocyte interrelationship in Plasmodium knowlesi infections. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):199–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrell B. R., Weiss E., Dasch G. A. Morphological and cell association characteristics of Rochalimaea quintana: comparison of the Vole and Fuller strains. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.633-640.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milder R., Kloetzel J. The development of Trypanosoma cruzi in macrophages in vitro. Interaction with lysosomes and host cell fate. Parasitology. 1980 Feb;80(1):139–145. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000000597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Dvorak J. A. Malaria (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites: immunity and the surface coat. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1237–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Johnson J. G., Shiroishi T. Interaction between cytochalasin B-treated malarial parasites and erythrocytes. Attachment and junction formation. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):172–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., David P. H., Hudson D. E., Hadley T. J., Richards R. L., Aikawa M. Monoclonal antibodies to a 140,000-m.w. protein on Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites inhibit their invasion of rhesus erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):438–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., McAuliffe F. M., Mason S. J. Erythrocyte receptors for malaria merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):204–208. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mor N. Intracellular location of Mycobacterium leprae in macrophages of normal and immune-deficient mice and effect of rifampin. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):802–811. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.802-811.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Glucose Metabolism of L Cells Before and After Infection with Chlamydia psittaci. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1189–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1189-1196.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Hatch T. P., Byrne G. I., Kellogg K. R. Immediate toxicity of high multiplicities of Chlamydia psittaci for mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):277–289. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.277-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. Inhibition of onset of overt multiplication of Chlamydia psittaci in persistently infected mouse fibroblasts (L cells). Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):898–907. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.898-907.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
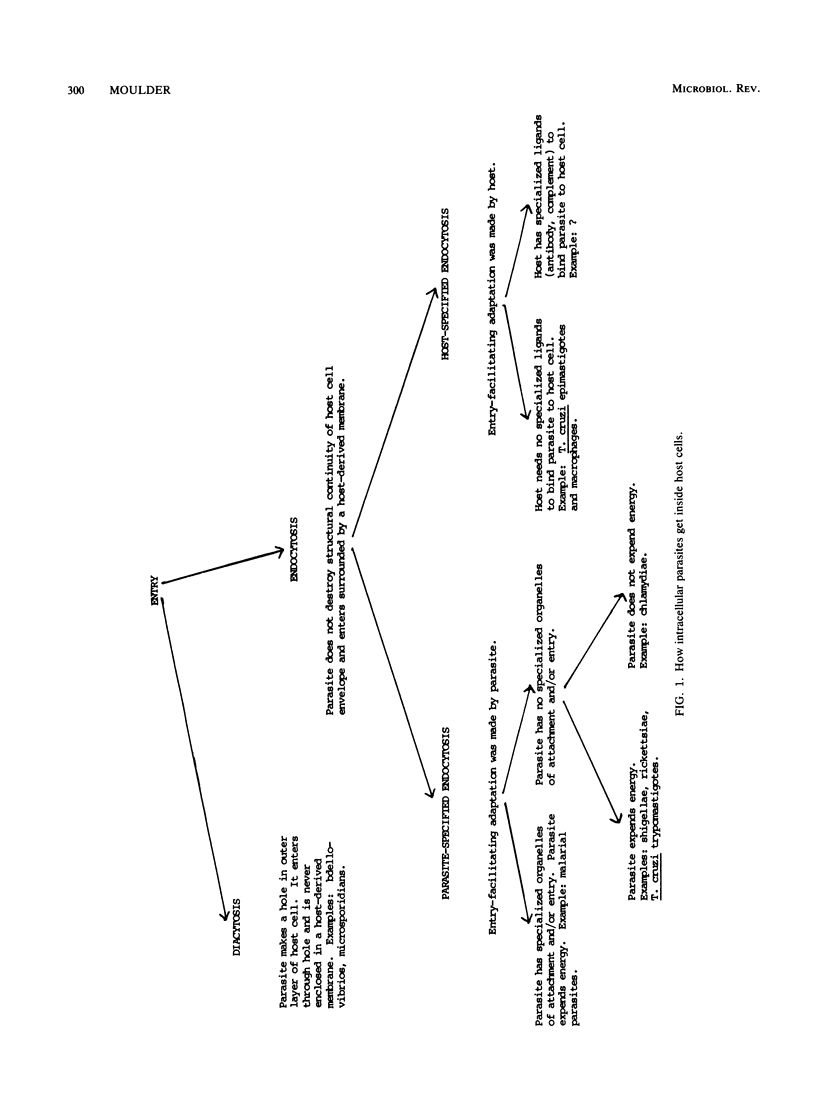
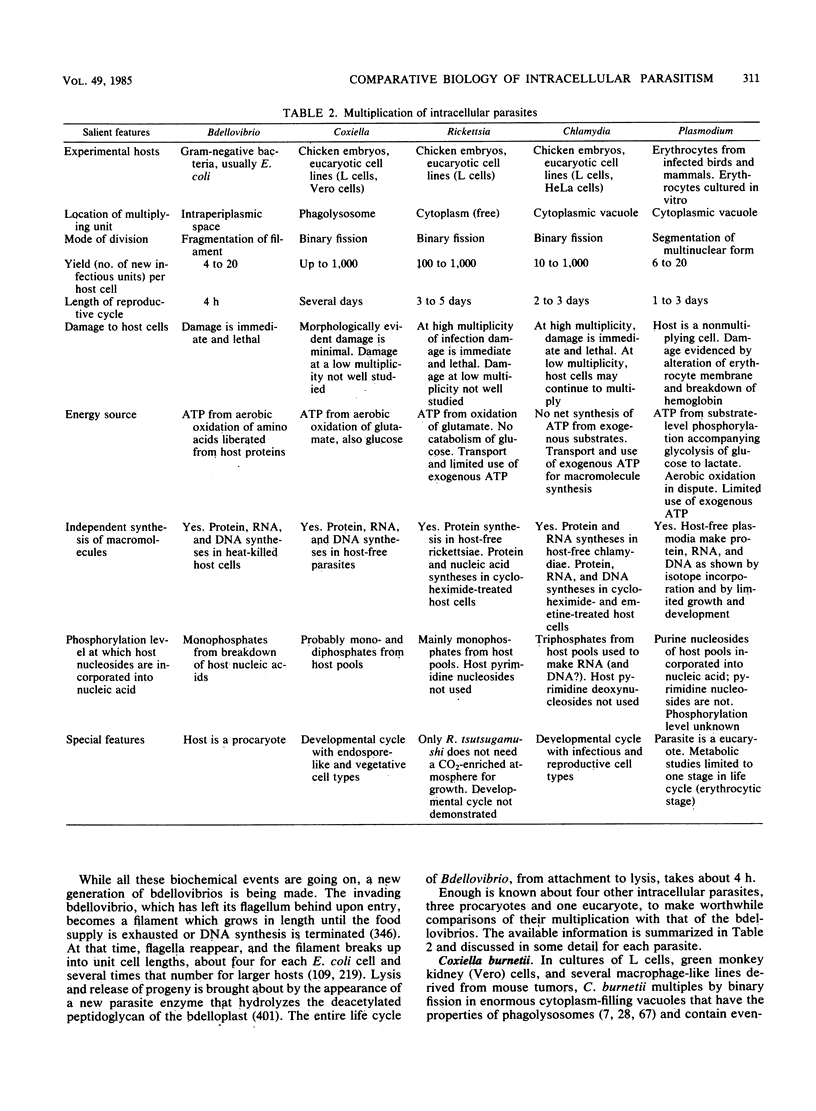
- Moulder J. W. Intracellular parasitism: life in an extreme environment. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):300–306. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Levy N. J., Schulman L. P. Persistent infection of mouse fibroblasts (L cells) with Chlamydia psittaci: evidence for a cryptic chlamydial form. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):874–883. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.874-883.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Levy N. J., Zeichner S. L., Lee C. K. Attachment defect in mouse fibroblasts (L cells) persistently infected with Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):285–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.285-291.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. The cell as an extreme environment. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Apr 11;204(1155):199–210. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W. The relation of basic biology to pathogenic potential in the genus Chlamydia. Infection. 1982;10 (Suppl 1):S10–S18. doi: 10.1007/BF01640709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulder J. W., Zeichner S. L., Levy N. J. Association between resistance to superinfection and patterns of surface protein labeling in mouse fibroblasts (L cells) persistently infected with Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):834–839. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.834-839.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscatine L., Pool R. R. Regulation of numbers of intracellular algae. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Apr 11;204(1155):131–139. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M. Multiplication of Mycobacterium lepraemurium in cell-free medium containing -ketoglutaric acid and cytochrome c. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(1):193–195. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M. Quantitative multiplication of Mycobacterium lepraemurium in a cell-free liquid medium (NC-5). J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):385–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navin T. R., Juranek D. D. Cryptosporidiosis: clinical, epidemiologic, and parasitologic review. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6(3):313–327. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.3.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame K. D., Homewood C. A. Alterations in the permeability of mouse erythrocytes infected with the malaria parasite, Plasmodium berghei. Int J Parasitol. 1975 Oct;5(5):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(75)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newbold C. I., Boyle D. B., Smith C. C., Brown K. N. Identification of a schizont- and species-specific surface glycoprotein on erythrocytes infected with rodent malarias. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1982 Jan;5(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(82)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newhall W. J., Jones R. B. Disulfide-linked oligomers of the major outer membrane protein of chlamydiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):998–1001. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.998-1001.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: mechanism of entry and intracellular fate in mammalian cells. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1402–1420. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. L. Inhibition of vacuolar membrane fusion by intracellular symbiotic algae in Hydra viridis (Florida strain). J Exp Zool. 1982 Nov 1;223(3):211–218. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402230303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., PEACOCK M. G. METABOLIC ACTIVITY IN COXIELLA BURNETII. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1205–1210. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1205-1210.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMSBEE R. A., WEISS E. TRACHOMA AGENT: GLUCOSE UTILIZATION BY PURIFIED SUSPENSIONS. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1077–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSSOWSKI L., BECKER Y., BERNKOPF H. AMINO ACID REQUIREMENTS OF TRACHOMA STRAINS AND OTHER AGENTS OF THE PLT GROUP IN CELL CULTURE. Isr J Med Sci. 1965 Mar;1:186–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockenhouse C. F., Schulman S., Shear H. L. Induction of crisis forms in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum by gamma-interferon-activated, monocyte-derived macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1601–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okoye V. C., Bennett V. Plasmodium falciparum malaria: band 3 as a possible receptor during invasion of human erythrocytes. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):169–171. doi: 10.1126/science.3880920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouaissi M. A., Afchain D., Capron A., Grimaud J. A. Fibronectin receptors on Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes and their biological function. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):380–382. doi: 10.1038/308380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. G., Whisenand J., McIntosh A. T. Effects of cytochalasin B on actin and myosin association with particle binding sites in mouse macrophages: implications with regard to the mechanism of action of the cytochalasins. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones in cultured cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:239–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Wainscoat J. S., Weatherall D. J. Erythrocytes deficiency in glycophorin resist invasion by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):64–66. doi: 10.1038/297064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce J. Depressive disorder in childhood. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1977 Jan;18(1):79–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1977.tb00419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M., Bretscher M. S. Membrane recycling by coated vesicles. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:85–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeling R., Maclean I. W., Brunham R. C. In vitro neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis with monoclonal antibody to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):484–488. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.484-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. E. Surface proteins of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites binding to the erythrocyte receptor, glycophorin. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):788–798. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. Inhibitory effects of erythrocyte membrane proteins on the in vitro invasion of the human malarial parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) into its host cell. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):563–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotto J., Keister D. B., Gelderman A. H. Incorporation of precursors into Toxoplasma DNA. J Protozool. 1971 Aug;18(3):470–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Guyre P. M. Inhibition of growth of Toxoplasma gondii in cultured fibroblasts by human recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):211–216. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.211-216.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R. Interferon gamma blocks the growth of Toxoplasma gondii in human fibroblasts by inducing the host cells to degrade tryptophan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):908–912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn E. R., Pfefferkorn L. C. Specific labeling of intracellular Toxoplasma gondii with uracil. J Protozool. 1977 Aug;24(3):449–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb04774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Winkler H. H. Regulatory properties of citrate synthase from Rickettsia prowazekii. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):718–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.718-725.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlenz J., Bemrick W. J., Moon H. W., Cheville N. F. Bovine cryptosporidiosis: a transmission and scanning electron microscopic study of some stages in the life cycle and of the host-parasite relationship. Vet Pathol. 1978 May;15(3):417–427. doi: 10.1177/030098587801500318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polet H., Conrad M. E. Malaria: extracellular amino acid requirements for in vitro growth of erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium knowlesi. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jan;127(1):251–253. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pupkis M. F., Coombs G. H. Purification and characterization of proteolytic enzymes of Leishmania mexicana mexicana amastigotes and promastigotes. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2375–2383. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G. Perturbation of the normal mechanisms of intraleukocytic killing of bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):189–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Phagocytosis: the engulfment stage. Semin Hematol. 1968 Apr;5(2):134–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Identification of cholesterol in the receptor site for rickettsiae on sheep erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):120–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.120-126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramm L. E., Winkler H. H. Rickettsial hemolysis: adsorption of rickettsiae to erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1973 Jan;7(1):93–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.1.93-99.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Feder R., Pavlovec A., Blobel G. Primary structure and genomic organization of the histidine-rich protein of the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):616–620. doi: 10.1038/312616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Anderson L. E., Jenkin H. M. Use of cycloheximide to study independent lipid metabolism of Chlamydia trachomatis cultivated in mouse L cells grown in serum-free medium. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):668–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.668-673.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes F. H. Gradualism, punctuated equilibrium and the Origin of Species. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):269–272. doi: 10.1038/305269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Ito S. Effect of antibody on entry of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into polymorphonuclear leukocyte cytoplasm. Infect Immun. 1983 Feb;39(2):928–938. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.2.928-938.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Ito S. Entry of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):343–350. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.343-350.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikihisa Y., Ito S. Localization of electron-dense tracers during entry of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi into polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1980 Oct;30(1):231–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.1.231-243.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristic M., Kreier J. P. Hemotropic bacteria. N Engl J Med. 1979 Oct 25;301(17):937–939. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197910253011708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Hespell R. B. Energy efficiency of intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1158–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1158-1165.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Hespell R. B. Energy efficiency of intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1158–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1158-1165.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Shilo M. Early host damage in the infection cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):149–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.149-160.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosson R. A., Rittenberg S. C. Regulated breakdown of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):620–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.620-633.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothermel C. D., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Gamma-interferon is the factor in lymphokine that activates human macrophages to inhibit intracellular Chlamydia psittaci replication. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2542–2544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Rittenberg S. C. Attachment of diaminopimelic acid to bdelloplast peptidoglycan during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):597–602. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.597-602.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruby E. G., Rittenberg S. C. Differentiation after premature release of intraperiplasmically growing Bdellovibrio bacteriovorous. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):32–40. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.32-40.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., BOZEMAN F. M., SMADEL J. E. Study on the growth of Rickettsiae. II. Morphologic observations of living Rickettsiae in tissue culture cells. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):160–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLP H., STARR M. P. BDELLOVIBRIO BACTERIOVORUS GEN. ET SP. N., A PREDATORY, ECTOPARASITIC, AND BACTERIOLYTIC MICROORGANISM. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:217–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02046064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Perkins P. V. Identification of an infective stage of Leishmania promastigotes. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.6701528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Becker Y. Deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase activity in purified trachoma elementary bodies: effect of sodium chloride on ribonucleic acid transcription. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):593–598. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.593-598.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachter J., Caldwell H. D. Chlamydiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:285–309. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Amino acid metabolism and protein synthesis in malarial parasites. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):265–276. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W. Biochemistry of Plasmodium (malarial parasites). Microbiol Rev. 1979 Dec;43(4):453–495. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.4.453-495.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Jones L. A. Plasmodium lophurae: membrane proteins of erythrocyte-free plasmodia and malaria-infected red cells. J Protozool. 1979 Aug;26(3):489–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04659.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Jones L. A. Protein synthesis by a cell-free preparation from the bird malaria, Plasmodium lophurae. J Protozool. 1976 May;23(2):277–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Jones L. A. The Plasmodium lophurae (avian malaria) ribosome. J Protozool. 1977 May;24(2):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb00989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Tanigoshi L. Glucose transport in the malarial (Plasmodium lophurae) infected erythrocyte. J Protozool. 1974 Oct;21(4):603–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03711.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Tanigoshi L. Purification of Plasmodium lophurae cathepsin D and its effects on erythrocyte membrane proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jul;8(3):207–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Bond S. B. Infection of human vascular endothelial cells by Rickettsia rickettsii. J Infect Dis. 1984 Feb;149(2):201–206. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J. Rickettsia rickettsii-induced cellular injury of human vascular endothelium in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):545–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.545-553.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr In vitro studies of rickettsia-host cell interactions: ultrastructural changes induced by Rickettsia rickettsii infection of chicken embryo fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):714–727. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.714-727.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman D. J., Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. In vitro studies of Rickettsia-host cell interactions: ultrastructural study of Rickettsia prowazekii-infected chicken embryo fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):778–790. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.778-790.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein S. C., Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:669–722. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. K., Winkler H. H. Characterization of a lysine-specific active transport system in Rickettsia prowazeki. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1349–1355. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1349-1355.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears P., Storz J. Biotyping of Chlamydia psittaci based on inclusion morphology and response to diethylaminoethyl-dextran and cycloheximide. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):224–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.224-232.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P. A generalized scheme for classifying organismic associations. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):1–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Baigent N. L. Parasitic interaction of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus with other bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2006–2017. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2006-2017.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes G. V. Proteinase produced by Chlamydia psittaci in L cells. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):616–620. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.616-620.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolp H. Interactions between Bdellovibrio and its host cell. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Apr 11;204(1155):211–217. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Harmon P. A. Yersinia pestis grows within phagolysosomes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):655–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.655-659.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Attachment and internalization of a Chlamydia trachomatis lymphogranuloma venereum strain by McCoy cells: kinetics of infectivity and effect of lectins and carbohydrates. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):930–935. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.930-935.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Effect of methylamine and monodansylcadaverine on the susceptibility of McCoy cells to Chlamydia trachomatis infection. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):534–541. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.534-541.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund G., Kihlström E. Physicochemical surface properties of elementary bodies from different serotypes of chlamydia trachomatis and their interaction with mouse fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):893–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.893-899.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAGER W. Studies on the extracellular cultivation of an intracellular parasite (avian malaria). I. Development of the organisms in erythrocyte extracts, and the favoring effect of adenosinetriphosphate. J Exp Med. 1950 Oct 1;92(4):349–366. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Manire G. P. Preparation and chemical composition of the cell membranes of developmental reticulate forms of meningopneumonitis organisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1184-1188.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesh M. J., Miller R. D. Amino acid requirements for Legionella pneumophila growth. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):865–869. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.865-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theakston R. D., Fletcher K. A., Maegraith B. G. The use of electron microscope autoradiography for examining the uptake and degradation of haemoglobin by Plasmodium berghei. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1970 Mar;64(1):63–71. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1970.11686664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: N-deacetylation of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan amino sugars. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1008-1014.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: attachment of long-chain fatty acids to escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1015-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: solubilization of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.998-1007.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd W. J., Storz J. Ultrastructural cytochemical evidence for the activation of lysosomes in the cytocidal effect of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):638–646. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.638-646.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W. Cofactors and vitamins in the metabolism of malarial parasites. Factors other than folates. Bull World Health Organ. 1977;55(2-3):285–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W. Cultivation of malaria parasites. Br Med Bull. 1982 May;38(2):129–131. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W. Malaria parasites (Plasmodium lophurae) developing extracellularly in vitro: incorporation of labeled precursors. J Protozool. 1971 Aug;18(3):392–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I., Friis R. R., Moulder J. W. Effect of chloramphenicol, rifampicin, and nalidixic acid on Chlamydia psittaci growing in L cells. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):155–163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribby I. I., Moulder J. W. Availability of bases and nucleosides as precursors of nucleic acids in L cells and in the agent of meningopneumonitis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2362–2367. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2362-2367.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Thompson H. A., Winkler H. H. Interferon-gamma inhibits growth of Coxiella burnetii in mouse fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):781–783. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.781-783.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Differentiation between virulent and avirulent strains of Rickettsia prowazekii by macrophage-like cell lines. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):783–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.783-791.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Effect of mouse lymphokines and cloned mouse interferon-gamma on the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii with mouse macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):303–308. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.303-308.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzipori S. Cryptosporidiosis in animals and humans. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):84–96. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.84-96.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeinya I. J., Schmidt J. A., Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Green I. Falciparum malaria-infected erythrocytes specifically bind to cultured human endothelial cells. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.7017935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINSON J. W., FULLER H. S. Studies on trench fever. I. Propagation of Rickettsia-like microorganisms from a patient's blood. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1961;24(Suppl):152–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance D. W., Jr, Hatch T. P. Surface properties of Chlamydia psittaci. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):175–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.175-180.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderberg J. P., Gupta S. K., Schulman S., Oppenheim J. D., Furthmayr H. Role of the carbohydrate domains of glycophorins as erythrocyte receptors for invasion by Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):201–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.201-210.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Drucker I., Shilo M. Early effects of Bdellovibrio infection on the syntheses of protein and RNA of host bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 22;37(3):518–525. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90946-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhave J. P., Meis J. F. The biology of tissue forms and other asexual stages in mammalian plasmodia. Experientia. 1984 Dec 15;40(12):1317–1329. doi: 10.1007/BF01951885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetterling J. M., Takeuchi A., Madden P. A. Ultrastructure of Cryptosporidium wrairi from the guinea pig. J Protozool. 1971 May;18(2):248–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1971.tb03316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Jahiel R. I. Action of interferon and its inducers aginst nonviral infectious agents. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):69–77. doi: 10.1001/archinte.126.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS E., DRESSLER H. R. Centrifugation and Rickettsiae and viruses onto cells and its effect on infection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:691–695. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFELD P. R. Studies on the nucleic acids of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium berghei; Vincke & Lips. Aust J Biol Sci. 1953 May;6(2):234–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Firth W. T., Ballard J. G., Hegarty B. C. Role of phospholipase-associated penetration mechanism in cell injury by Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):840–842. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.840-842.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Mattern W. D. Rickettsial vasculitis. Am Heart J. 1980 Dec;100(6 Pt 1):896–906. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(80)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. H., Tidwell R. R., Rector T. M., Geratz J. D. Effect of synthetic protease inhibitors of the amidine type on cell injury by Rickettsia rickettsii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):582–585. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S. Rickettsial interactions with human endothelial cells in vitro: adherence and entry. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.205-210.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker T. S., Winkler H. H. Penetration of cultured mouse fibroblasts (L cells) by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):200–208. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.200-208.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. J., Sherman I. W. Isolation, characterization and synthesis of DNA from a malaria parasite. J Protozool. 1968 Aug;15(3):503–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. E., Murray A. Control mechanisms governing the infectivity of Chlamydia trachomatis for HeLa cells: mechanisms of endocytosis. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Jul;130(7):1765–1780. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-7-1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner E., Byrd W. The microsporidian spore invasion tube. II. Role of calcium in the activation of invasion tube discharge. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):970–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner E., Trager W. Adenosine triphosphate in the extracellular survival of an intracellular parasite (Nosema michaelis, Microsporidia). J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):586–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner E. Ultrastructural study of microsporidian invasion into cells. Z Parasitenkd. 1972;40(3):227–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00329623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Adenosine Triphosphate and Other Requirements for the Utilization of Glucose by Agents of the Psittacosis-Trachoma Group. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.243-253.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Dasch G. A., Woodman D. R., Williams J. C. Vole agent identified as a strain of the trench fever rickettsia, Rochalimaea quintana. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1013-1020.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Green A. E., Grays R., Newman L. M. Metabolism of Richettsia tsutsugamushi and Rickettsia rickettsi in irradiated host cells. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):4–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.4-7.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. Growth and physiology of rickettsiae. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):259–283. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.259-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Newman L. W., Grays R., Green A. E. Metabolism of Rickettsia typhi and Rickettsia akari in irradiated L cells. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):50–57. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.50-57.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. The biology of rickettsiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:345–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C. Adenine nucleotide degradation by the obligate intracellular bacterium Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):74–81. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.74-81.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Peterson J. C. Enzymatic activities leading to pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis from cell-free extracts of Rickettsia typhi. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):439–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.439-448.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Weiss E. Energy metabolism of Rickettsia typhi: pools of adenine nucleotides and energy charge in the presence and absence of glutamate. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.884-892.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Bygrave F. L., Lehninger A. L. Characterization of the atractyloside-sensitive adenine nucleotide transport system in rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 10;243(1):20–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Inhibitory and restorative effects of adenine nucleotides on rickettsial adsorption and hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.119-126.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Activated complex of L-cells and Rickettsia prowazekii with N-ethylmaleimide-insensitive phospholipase A. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):577–581. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.577-581.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A activity in the hemolysis of sheep and human erythrocytes by Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):316–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.316-321.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Miller E. T. Phospholipase A and the interaction of Rickettsia prowazekii and mouse fibroblasts (L-929 cells). Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):109–113. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.109-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Ramm L. E. Adsorption of typhus rickettsiae to ghosts of sheep erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1244–1251. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1244-1251.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsial permeability. An ADP-ATP transport system. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):389–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Edlinger E. A., Waddell A. D., Jones M. R. Infection cycle of Rickettsia rickettsii in chicken embryo and L-929 cells in culture. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1052–1064. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1052-1064.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D. In vitro studies on rickettsia-host cell interactions: intracellular growth cycle of virulent and attenuated Rickettsia prowazeki in chicken embryo cells in slide chamber cultures. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1391–1404. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1391-1401.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. D., Walsh W. T. Mechanisms of immunity in typhus infections. IV. Failure of chicken embryo cells in culture to restrict growth of antibody-sensitized Rickettsia prowazeki. Infect Immun. 1974 Mar;9(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.3.571-575.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. C., Ewing E. P., Jr, Callaway C. S., Peacock W. L., Jr Intracellular multiplication of Legionella pneumophila in cultured human embryonic lung fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1014-1018.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A. Growth of Chlamydia psittaci in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1054-1060.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A., Ivins B. E. Interaction of Chlamydia psittaci with mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1061–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1061-1067.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichner S. L. Isolation and characterization of macrophage phagosomes containing infectious and heat-inactivated Chlamydia psittaci: two phagosomes with different intracellular behaviors. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):956–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.956-966.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Thompson H. A. Protein synthesis by intact Coxiella burnetii cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):186–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.186-191.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


