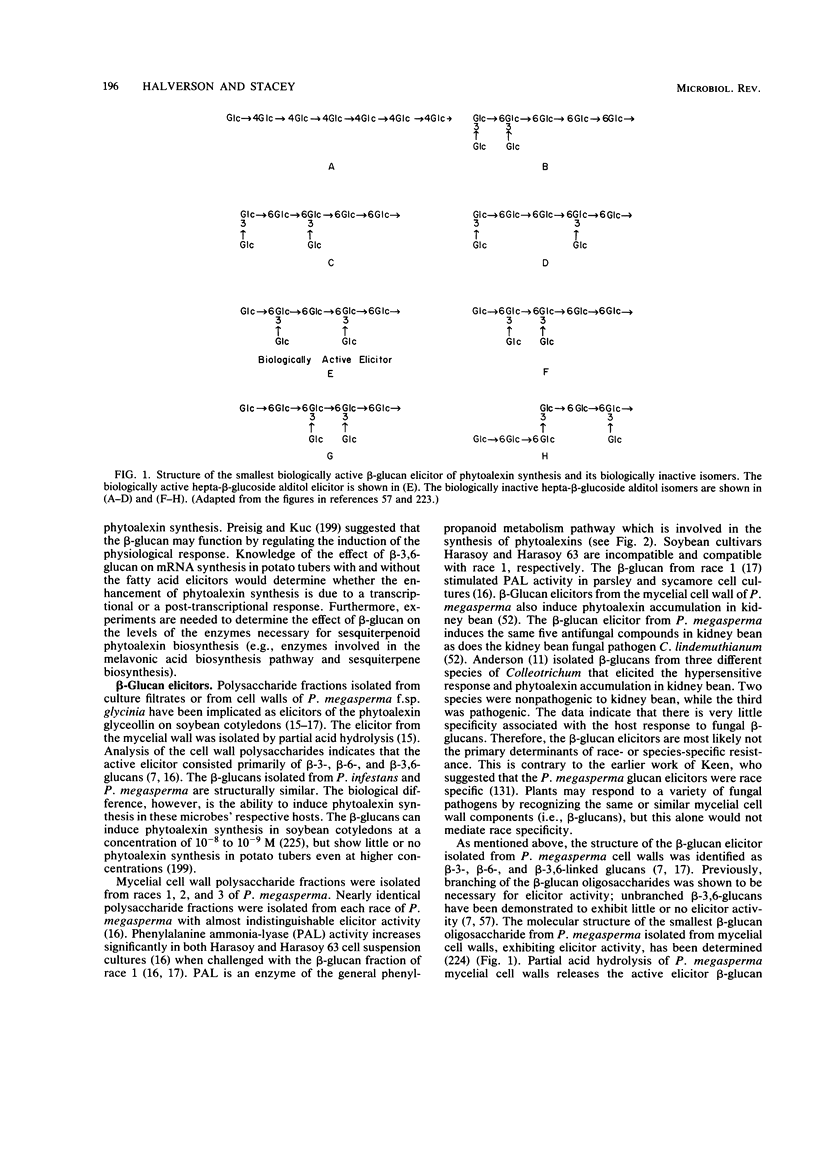
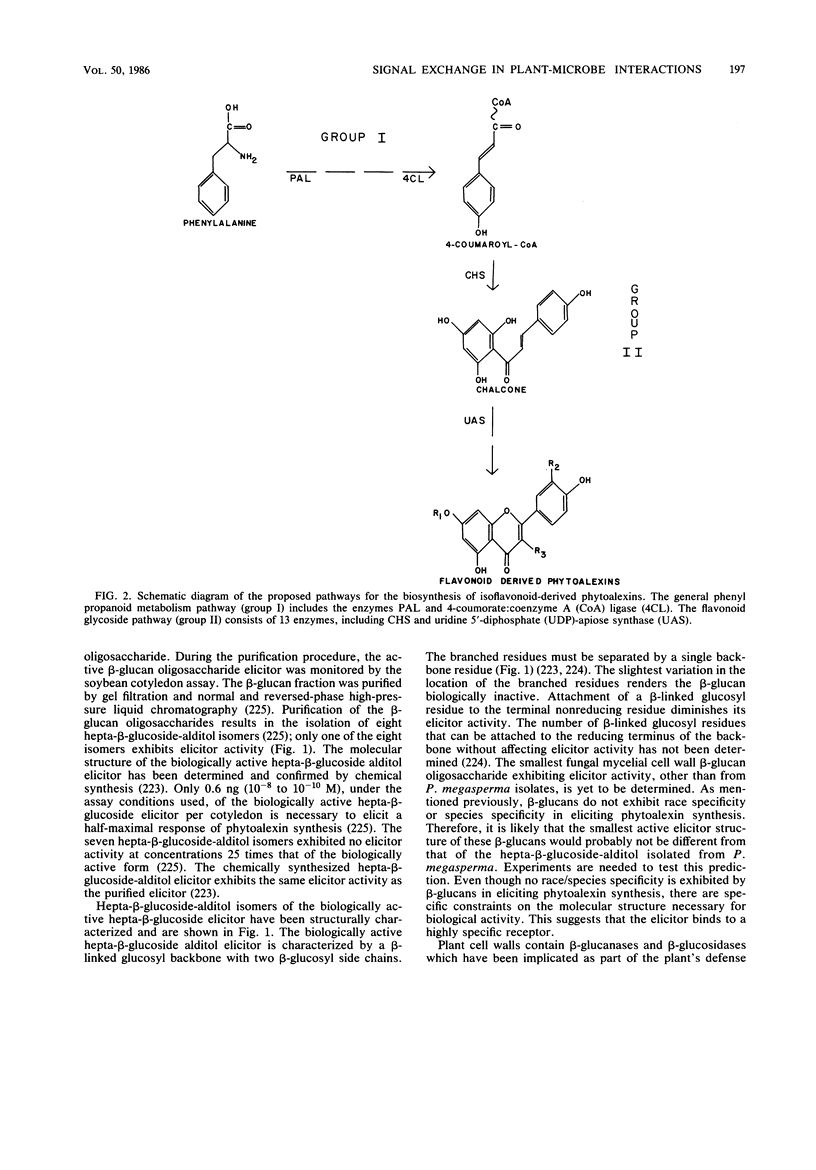
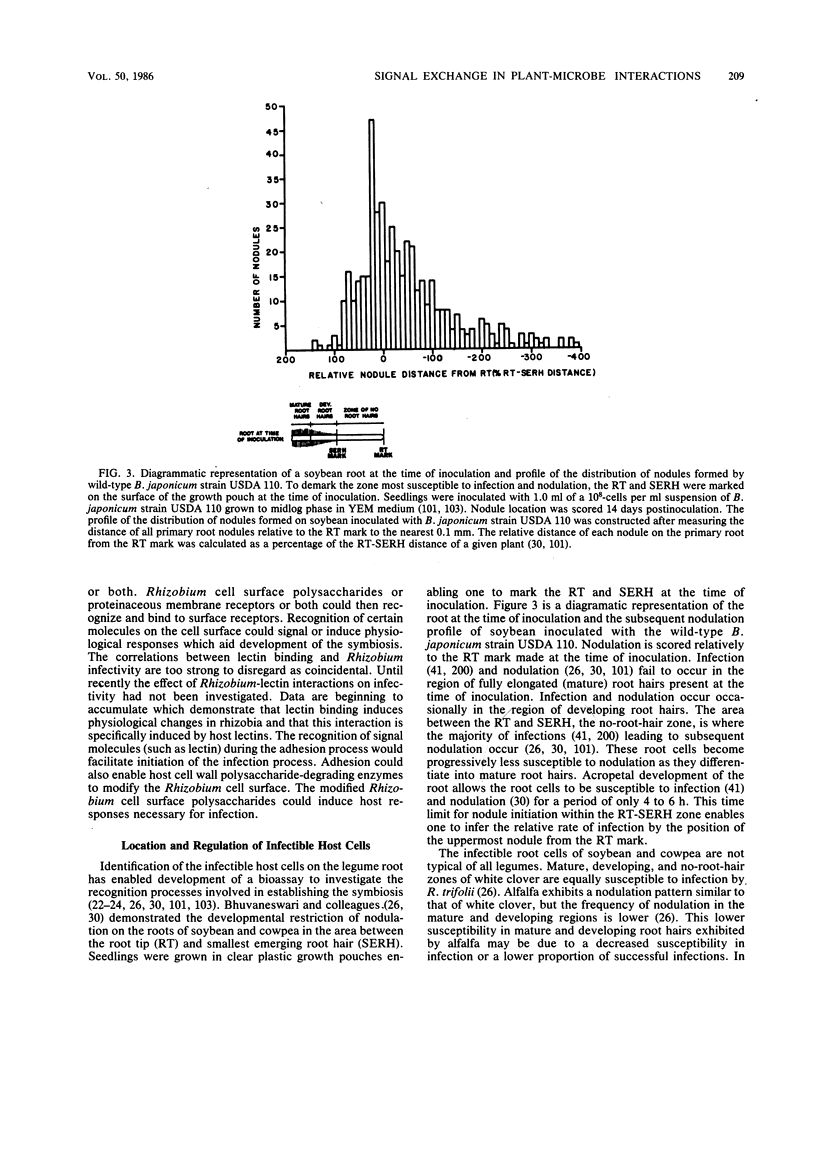
Full text
PDF





























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe M., Sherwood J. E., Hollingsworth R. I., Dazzo F. B. Stimulation of clover root hair infection by lectin-binding oligosaccharides from the capsular and extracellular polysaccharides of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):517–520. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.517-520.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi D. E., Klee H., Amasino R. M., Nester E. W., Gordon M. P. T-DNA of Agrobacterium tumefaciens encodes an enzyme of cytokinin biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5994–5998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyoshi D. E., Morris R. O., Hinz R., Mischke B. S., Kosuge T., Garfinkel D. J., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Cytokinin/auxin balance in crown gall tumors is regulated by specific loci in the T-DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):407–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albersheim P., Valent B. S. Host-pathogen interactions in plants. Plants, when exposed to oligosaccharides of fungal origin, defend themselves by accumulating antibiotics. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):627–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amasino R. M., Miller C. O. Hormonal control of tobacco crown gall tumor morphology. Plant Physiol. 1982 Feb;69(2):389–392. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amasino R. M., Powell A. L., Gordon M. P. Changes in T-DNA methylation and expression are associated with phenotypic variation and plant regeneration in a crown gall tumor line. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(3):437–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00329940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. J. Differences in the biochemical compositions and elicitor activity of extracellular components produced by three races of a fungal plant pathogen, Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Dec;26(12):1473–1479. doi: 10.1139/m80-244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Valent B., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: X. Fractionation and Biological Activity of an Elicitor Isolated from the Mycelial Walls of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):760–765. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Valent B., Ebel J., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XI. Composition and Structure of Wall-released Elicitor Fractions. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):766–774. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee D., Basu M., Choudhury I., Chatterjee G. C. Cell surface carbohydrates of Agrobacterium tumefaciens involved in adherence during crown gall tumor initiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jun 16;100(3):1384–1388. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91977-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. N., Dixon R. A., Bailey J. A., Rowell P. M., Lamb C. J. Differential induction of chalcone synthase mRNA activity at the onset of phytoalexin accumulation in compatible and incompatible plant-pathogen interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3384–3388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann H., Preddie E., Verma D. P. Nodulin-35: a subunit of specific uricase (uricase II) induced and localized in the uninfected cells of soybean nodules. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2333–2339. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01743.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagwat A. A., Thomas J. Legume-Rhizobium interactions: cowpea root exudate elicits faster nodulation response by Rhizobium species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):800–805. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.800-805.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bauer W. D. Role of Lectins in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: III. Influence of Rhizosphere/Rhizoplane Culture Conditions on the Soybean Lectin-binding Properties of Rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):71–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bhagwat A. A., Bauer W. D. Transient susceptibility of root cells in four common legumes to nodulation by rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1981 Nov;68(5):1144–1149. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.5.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Mills K. K., Crist D. K., Evans W. R., Bauer W. D. Effects of culture age on symbiotic infectivity of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):443–451. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.443-451.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Pueppke S. G., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant-microorganism interactions: I. Binding of soybean lectin to rhizobia. Plant Physiol. 1977 Oct;60(4):486–491. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.4.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswari T. V., Turgeon B. G., Bauer W. D. Early Events in the Infection of Soybean (Glycine max L. Merr) by Rhizobium japonicum: I. LOCALIZATION OF INFECTIBLE ROOT CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Dec;66(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.6.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. D., Makus D. J., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor-inducing factor activity in tomato leaves resides in oligosaccharides enzymically released from cell walls. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisseling T., Been C., Klugkist J., Kammen A., Nadler K. Nodule-specific host proteins in effective and ineffective root nodules of Pisum sativum. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):961–966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Immunofluorescent polar tips of Rhizobium japonicum: possible site of attachment or lectin binding. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1188–1194. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1188-1194.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Lectins: a possible basis for specificity in the Rhizobium--legume root nodule symbiosis. Science. 1974 Jul 19;185(4147):269–271. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4147.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock R. M., Kuc J. A., Laine R. A. Eicosapentaenoic and Arachidonic Acids from Phytophthora infestans Elicit Fungitoxic Sesquiterpenes in the Potato. Science. 1981 Apr 3;212(4490):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.212.4490.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostock R. M., Laine R. A., Kuć J. A. Factors affecting the elicitation of sesquiterpenoid phytoalexin accumulation by eicosapentaenoic and arachidonic acids in potato. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1417–1424. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce R. J., West C. A. Elicitation of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean : THE ROLE OF PECTIC FRAGMENTS OF THE PLANT CELL WALL IN ELICITATION BY A FUNGAL ENDOPOLYGALACTURONASE. Plant Physiol. 1982 May;69(5):1181–1188. doi: 10.1104/pp.69.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvert H. E., Lalonde M., Bhuvaneswari T. V., Bauer W. D. Role of lectins in plant--microorganism interactions. IV. Ultrastructural localization of soybean lectin binding sites of Rhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jul;24(7):785–793. doi: 10.1139/m78-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. B., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Genetic analysis of integration mediated by single T-DNA borders. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):655–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.655-664.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Hanley B., Rolfe B. G., Djordejevic M. A. A Structural Comparison of the Acidic Extracellular Polysaccharides from Rhizobium trifolii Mutants Affected in Root Hair Infection. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jan;80(1):134–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. J., McNeil D. L., Gresshoff P. M. A Supernodulation and Nitrate-Tolerant Symbiotic (nts) Soybean Mutant. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):34–40. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll B. J., McNeil D. L., Gresshoff P. M. Isolation and properties of soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] mutants that nodulate in the presence of high nitrate concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4162–4166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilton M. D., Drummond M. H., Merio D. J., Sciaky D., Montoya A. L., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Stable incorporation of plasmid DNA into higher plant cells: the molecular basis of crown gall tumorigenesis. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):263–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua K. Y., Pankhurst C. E., Macdonald P. E., Hopcroft D. H., Jarvis B. D., Scott D. B. Isolation and characterization of transposon Tn5-induced symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium loti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):335–343. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.335-343.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XVII. HYDROLYSIS OF BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE FUNGAL GLUCANS BY ENZYMES ISOLATED FROM SOYBEAN CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):221–228. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XVI. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF A beta-GLUCOSYL HYDROLASE/TRANSFERASE PRESENT IN THE WALLS OF SOYBEAN CELLS. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jul;68(1):207–220. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline K., Wade M., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XV. Fungal Glucans Which Elicit Phytoalexin Accumulation in Soybean Also Elicit the Accumulation of Phytoalexins in Other Plants. Plant Physiol. 1978 Dec;62(6):918–921. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer C. L., Bell J. N., Ryder T. B., Bailey J. A., Schuch W., Bolwell G. P., Robbins M. P., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Co-ordinated synthesis of phytoalexin biosynthetic enzymes in biologically-stressed cells of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):285–289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis K. R., Lyon G. D., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXV. Endopolygalacturonic Acid Lyase from Erwinia carotovora Elicits Phytoalexin Accumulation by Releasing Plant Cell Wall Fragments. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):52–60. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Brill W. J. Receptor site on clover and alfalfa roots for Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.132-136.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Brill W. J. Regulation by fixed nitrogen of host-symbiont recognition in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):18–21. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Hubbell D. H. Cross-reactive antigens and lectin as determinants of symbiotic specificity in the Rhizobium-clover association. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1017–1033. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1017-1033.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Napoli C. A., Hubbell D. H. Adsorption of bacteria to roots as related to host specificity in the Rhizobium-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.166-171.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Truchet G. L., Sherwood J. E., Hrabak E. M., Abe M., Pankratz S. H. Specific phases of root hair attachment in the Rhizobium trifolii-clover symbiosis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1140–1150. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1140-1150.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Truchet G. L., Sherwood J. E., Hrabak E. M., Gardiol A. E. Alteration of the Trifoliin A-Binding Capsule of Rhizobium trifolii 0403 by Enzymes Released from Clover Roots. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):478–490. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.478-490.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Yanke W. E., Brill W. J. Trifolin: a Rhizobium recognition protein from white clover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 20;539(3):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Halperin W., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants affected in attachment to plant cells. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1265–1275. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1265-1275.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Staneloni R. J., Rubin R. A., Nester E. W. Identification and genetic analysis of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens chromosomal virulence region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Mar;161(3):850–860. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.3.850-860.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C., Halperin W., Gordon M., Nester E. Specific attachment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to bamboo cells in suspension cultures. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):764–766. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.764-766.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvick J. P., Sequeira L. Interaction of Pseudomonas solanacearum with Suspension-Cultured Tobacco Cells and Tobacco Leaf Cell Walls In Vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):199–205. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.199-205.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebel J., Schmidt W. E., Loyal R. Phytoalexin synthesis in soybean cells: elicitor induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNAs and correlation with phytoalexin accumulation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Jul;232(1):240–248. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervin S. E., Hubbell D. H. Root Hair Deformations Associated with Fractionated Extracts from Rhizobium trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.61-68.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: I. A Structural Investigation of Cell Wall Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoproteins Which Accumulate in Fungus-infected Plants. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):314–319. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquerré-Tugayé M. T., Lafitte C., Mazau D., Toppan A., Touzé A. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions: II. Evidence for the Accumulation of Hydroxyproline-rich Glycoproteins in the Cell Wall of Diseased Plants as a Defense Mechanism. Plant Physiol. 1979 Aug;64(2):320–326. doi: 10.1104/pp.64.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Hirsch A. M., Leigh J. A., Johansen E., Kuldau G. A., Deegan S., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. Symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that uncouple plant from bacterial differentiation. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gade W., Jack M. A., Dahl J. B., Schmidt E. L., Wold F. The isolation and characterization of a root lectin from soybean (Glycine max (L), cultivar Chippewa). J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12905–12910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. E., Schröder J., Matern U., Hammer D., Hahlbrock K. mRNA-dependent regulation of UDP-apiose synthase activity in irradiated plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10752–10757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Simpson R. B., Ream L. W., White F. F., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of crown gall: fine structure map of the T-DNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Stack S., Krell K., House J. A Comparison of Soybean Agglutinin in Cultivars Resistant and Susceptible to Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae (Race 1). Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):560–566. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glogowski W., Galsky A. G. Agrobacterium tumefaciens Site Attachment as a Necessary Prerequisite for Crown Gall Tumor Formation on Potato Discs. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jun;61(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.6.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. B., Hoschek G., Vodkin L. O. An insertion sequence blocks the expression of a soybean lectin gene. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90428-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahlbrock K., Lamb C. J., Purwin C., Ebel J., Fautz E., Schäfer E. Rapid Response of Suspension-cultured Parsley Cells to the Elicitor from Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae: INDUCTION OF THE ENZYMES OF GENERAL PHENYLPROPANOID METABOLISM. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):768–773. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson L. J., Stacey G. Effect of lectin on nodulation by wild-type Bradyrhizobium japonicum and a nodulation-defective mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):753–760. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.753-760.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson L. J., Stacey G. Host recognition in the Rhizobium-soybean symbiosis : evidence for the involvement of lectin in nodulation. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):621–625. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halverson L. J., Stacey G. Host recognition in the Rhizobium-soybean symbiosis: detection of a protein factor in soybean root exudate which is involved in the nodulation process. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jan;74(1):84–89. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick C. A., Sequeira L. Lipopolysaccharide-Defective Mutants of the Wilt Pathogen Pseudomonas solanacearum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):94–101. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.94-101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn A. G., Clarke L. E., Pearson L., White J. The role of cytosine methylation in the control of nopaline synthase gene expression in a plant tumor. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):315–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi S., Abe M. Promotion of infection thread formation by substances from Rhizobium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):297–301. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.297-301.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi S., Abe M. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Rhizobium trifolii Infection Sites on Root Hairs of White Clover. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1094–1099. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1094-1099.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille J., van Kan J., Schilperoort R. trans-Acting virulence functions of the octopine Ti plasmid from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):754–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.754-756.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Drake D., Jacobs T. W., Long S. R. Nodules are induced on alfalfa roots by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Rhizobium trifolii containing small segments of the Rhizobium meliloti nodulation region. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):223–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.223-230.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. M., Wilson K. J., Jones J. D., Bang M., Walker V. V., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes allow Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Escherichia coli to form pseudonodules on alfalfa. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1133–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1133-1143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth R. I., Abe M., Sherwood J. E., Dazzo F. B. Bacteriophage-induced acidic heteropolysaccharide lyases that convert the acidic heteropolysaccharides of Rhizobium trifolii into oligosaccharide units. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):510–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.510-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrabak E. M., Urbano M. R., Dazzo F. B. Growth-phase-dependent immunodeterminants of Rhizobium trifolii lipopolysaccharide which bind trifoliin A, a white clover lectin. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):697–711. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.697-711.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen E., Finan T. M., Gefter M. L., Signer E. R. Monoclonal antibodies to Rhizobium meliloti and surface mutants insensitive to them. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):454–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.454-457.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. C., Perry K. L., Kado C. I. Indoleacetic acid complementation and its relation to host range specifying genes on the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(3):425–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00330044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T. Specific elicitors of plant phytoalexin production: detenninants of race specificity in pathogens? Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):74–75. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4171.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Yoshikawa M. beta-1,3-Endoglucanase from Soybean Releases Elicitor-Active Carbohydrates from Fungus Cell Walls. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):460–465. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee H. J., White F. F., Iyer V. N., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Mutational analysis of the virulence region of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):878–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.878-883.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee H., Montoya A., Horodyski F., Lichtenstein C., Garfinkel D., Fuller S., Flores C., Peschon J., Nester E., Gordon M. Nucleotide sequence of the tms genes of the pTiA6NC octopine Ti plasmid: two gene products involved in plant tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1728–1732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosslak R. M., Bohlool B. B. Suppression of nodule development of one side of a split-root system of soybeans caused by prior inoculation of the other side. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):125–130. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn D. N., Chappell J., Boudet A., Hahlbrock K. Induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and 4-coumarate:CoA ligase mRNAs in cultured plant cells by UV light or fungal elicitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1102–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGGREN H., FAHRAEUS G. Effect of Rhizobium polysaccharide on the formation of polygalacturonase in lucerne and clover. Nature. 1959 Nov 14;184(Suppl 20):1578–1580. doi: 10.1038/1841578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LJUNGGREN H., FAHRAEUS G. The role of polygalacturonase in root-hair invasion by nodule bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Nov;26:521–528. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-3-521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang-Unnasch N., Ausubel F. M. Nodule-specific polypeptides from effective alfalfa root nodules and from ineffective nodules lacking nitrogenase. Plant Physiol. 1985 Apr;77(4):833–839. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law I. J., Strijdom B. W. Role of Lectins in the Specific Recognition of Rhizobium by Lotononis bainesii. Plant Physiol. 1984 Apr;74(4):779–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.4.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton M. A., Dixon R. A., Hahlbrock K., Lamb C. Rapid induction of the synthesis of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and of chalcone synthase in elicitor-treated plant cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 1;129(3):593–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach J. E., Cantrell M. A., Sequeira L. Hydroxyproline-rich bacterial agglutinin from potato : extraction, purification, and characterization. Plant Physiol. 1982 Nov;70(5):1353–1358. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.5.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Polygalacturonase from Rhizopus stolonifer, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):633–639. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. C., West C. A. Properties of Rhizopus stolonifer Polygalacturonase, an Elicitor of Casbene Synthetase Activity in Castor Bean (Ricinus communis L.) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1981 Apr;67(4):640–645. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.4.640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Identification of "nodule-specific" host proteins (nodoulins) involved in the development of rhizobium-legume symbiosis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein C., Klee H., Montoya A., Garfinkel D., Fuller S., Flores C., Nester E., Gordon M. Nucleotide sequence and transcript mapping of the tmr gene of the pTiA6NC octopine Ti-plasmid: a bacterial gene involved in plant tumorigenesis. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(4):354–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillich T. T., Elkan G. H. Evidence countering the role of polygalacturonase in invasion of root hairs of leguminous plants by Rhizobium spp. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Jun;14(6):617–625. doi: 10.1139/m68-104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott B. B., Lippincott J. A. Bacterial attachment to a specific wound site as an essential stage in tumor initiation by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):620–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.620-628.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Heberlein G. T. The quantitative determination of the infectivity of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Am J Bot. 1965 Sep;52(8):856–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott J. A., Lippincott B. B. Cell walls of crown-gall tumors and embryonic plant tissues lack agrobacterium adherence sites. Science. 1978 Mar 10;199(4333):1075–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4333.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. C., Close T. J., Kado C. I. Genetic complementation of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid mutants in the virulence region. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF00327406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon G. D., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXI. Extraction of a Heat-Labile Elicitor of Phytoalexin Accumulation from Frozen Soybean Stems. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):406–409. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclean D. J., Sargent J. A., Tommerup I. C., Ingram D. S. Hypersensitivity as the primary event in resistance to fungal parasites. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):186–187. doi: 10.1038/249186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. C., Norris H. J. Glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix. Obstet Gynecol. 1982 Aug;60(2):219–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. J., Brill W. J. Ineffective and non-nodulating mutant strains of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):763–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.763-769.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G., Holmes K. V., Gurlitz R. H. Elaboration of cellulose fibrils by Agrobacterium tumefaciens during attachment to carrot cells. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.583-595.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G. Role of bacterial cellulose fibrils in Agrobacterium tumefaciens infection. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):906–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.906-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthysse A. G., Wyman P. M., Holmes K. V. Plasmid-dependent attachment of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to plant tissue culture cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):516–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.516-522.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Hadwiger L. A., Boller T. Ethylene: Symptom, Not Signal for the Induction of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase in Pea Pods by Pathogens and Elicitors. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):607–611. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil D. L., Larue T. A. Effect of nitrogen source on ureides in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1984 Feb;74(2):227–232. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.2.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Fry S. C., Albersheim P. Structure and function of the primary cell walls of plants. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:625–663. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Galun E., Sharon N., Lotan R. Inhibition of fungal growth by wheat germ agglutinin. Nature. 1975 Jul 31;256(5516):414–416. doi: 10.1038/256414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mort A. J., Bauer W. D. Composition of the Capsular and Extracellular Polysaccharides of Rhizobium japonicum: CHANGES WITH CULTURE AGE AND CORRELATIONS WITH BINDING OF SOYBEAN SEED LECTIN TO THE BACTERIA . Plant Physiol. 1980 Jul;66(1):158–163. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.1.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Sanchez A., Fernandez L., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A. Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.148-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Stacey G., Tandon S. R., Silver L. E., Brill W. J. Rhizobium japonicum mutants defective in symbiotic nitrogen fixation. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):485–494. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.485-494.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nothnagel E. A., McNeil M., Albersheim P., Dell A. Host-Pathogen Interactions : XXII. A Galacturonic Acid Oligosaccharide from Plant Cell Walls Elicits Phytoalexins. Plant Physiol. 1983 Apr;71(4):916–926. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.4.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama K., Pelcher L. E., Schaefer A. In Vitro Binding of Agrobacterium tumefaciens to Plant Cells from Suspension Culture. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):382–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okker R. J., Spaink H., Hille J., van Brussel T. A., Lugtenberg B., Schilperoort R. A. Plant-inducible virulence promoter of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):564–566. doi: 10.1038/312564a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooms G., Hooykaas P. J., Moolenaar G., Schilperoort R. A. Grown gall plant tumors of abnormal morphology, induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying mutated octopine Ti plasmids; analysis of T-DNA functions. Gene. 1981 Jun-Jul;14(1-2):33–50. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90146-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paau A. S., Leps W. T., Brill W. J. Agglutinin from Alfalfa Necessary for Binding and Nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Science. 1981 Sep 25;213(4515):1513–1515. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4515.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B. M., Cribbs D. H., Stelzig D. A. Agglutination of plant protoplasts by fungal cell wall glucans. Science. 1978 Jul 28;201(4353):364–365. doi: 10.1126/science.201.4353.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce M., Bauer W. D. A rapid regulatory response governing nodulation in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):286–290. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preisig C. L., Kuć J. A. Arachidonic acid-related elicitors of the hypersensitive response in potato and enhancement of their activities by glucans from Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) deBary. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jan;236(1):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90638-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueppke S. G. Adsorption of slow- and fast-growing rhizobia to soybean and cowpea roots. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):924–928. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pueppke S. G., Benny U. K. Adsorption of tumorigenic Agrobacterium tumefaciens cells to susceptible potato tuber tissues. Can J Microbiol. 1984 Aug;30(8):1030–1037. doi: 10.1139/m84-160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pull S. P., Pueppke S. G., Hymowitz T., Orf J. H. Soybean lines lacking the 120,000-dalton seed lectin. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1277–1279. doi: 10.1126/science.200.4347.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvanesarajah V., Schell F. M., Stacey G., Douglas C. J., Nester E. W. Role for 2-linked-beta-D-glucan in the virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):102–106. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.102-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragg H., Kuhn D. N., Hahlbrock K. Coordinated regulation of 4-coumarate:CoA ligase and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase mRNAs in cultured plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10061–10065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapid switching of plant gene expression induced by fungal elicitor. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1240–1243. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4691.1240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ream L. W., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Multiple mutations in the T region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1660–1664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roby D., Toppan A., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell surfaces in plant-microorganism interactions : v. Elicitors of fungal and of plant origin trigger the synthesis of ethylene and of cell wall hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein in plants. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):700–704. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder T. B., Cramer C. L., Bell J. N., Robbins M. P., Dixon R. A., Lamb C. J. Elicitor rapidly induces chalcone synthase mRNA in Phaseolus vulgaris cells at the onset of the phytoalexin defense response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5724–5728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder G., Waffenschmidt S., Weiler E. W., Schröder J. The T-region of Ti plasmids codes for an enzyme synthesizing indole-3-acetic acid. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):387–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07927.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Kreuzaler F., Schäfer E., Hahlbrock K. Concomitant induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and flavanone synthase mRNAs in irradiated plant cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 10;254(1):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers R., LaRue T. A. Legume agglutinins that bind to Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):784–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.784-789.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shantharam S., Wong P. P. Recognition of leguminous hosts by a promiscuous Rhizobium strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Mar;43(3):677–685. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.3.677-685.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. K., Albersheim P., Ossowski P., Pilotti A., Garegg P., Lindberg B. Comparison of the structures and elicitor activities of a synthetic and a mycelial-wall-derived hexa(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-glucitol. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11341–11345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. K., McNeil M., Albersheim P. The primary structures of one elicitor-active and seven elicitor-inactive hexa(beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-glucitols isolated from the mycelial walls of Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11321–11336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. K., Valent B., Albersheim P. Purification and partial characterization of a beta-glucan fragment that elicits phytoalexin accumulation in soybean. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11312–11320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood J. E., Vasse J. M., Dazzo F. B., Truchet G. L. Development and trifoliin A-binding ability of the capsule of Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):145–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.145-152.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey G., Paau A. S., Brill W. J. Host recognition in the Rhizobium-soybean symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 1980 Oct;66(4):609–614. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey G., Pocratsky L. A., Puvanesarajah V. Bacteriophage that can distinguish between wild-type Rhizobium japonicum and a non-nodulating mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):68–72. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.68-72.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W., Zambryski P. C. A plant cell factor induces Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):379–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. C., Pueppke S. G., Friedman H. P. Lectins and the soybean-Rhizobium symbiosis. I. Immunological investigations of soybean lines, the seeds of which have been reported to lack the 120 000 dalton soybean lectin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):292–304. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow L. S., Reeves S., Thomashow M. F. Crown gall oncogenesis: evidence that a T-DNA gene from the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid pTiA6 encodes an enzyme that catalyzes synthesis of indoleacetic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Nutter R., Postle K., Chilton M. D., Blattner F. R., Powell A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Recombination between higher plant DNA and the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6448–6452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toppan A., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions : IV. Fungal Glycopeptides Which Elicit the Synthesis of Ethylene in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1984 Aug;75(4):1133–1138. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toppan A., Roby D., Esquerré-Tugayé M. T. Cell Surfaces in Plant-Microorganism Interactions : III. In Vivo Effect of Ethylene on Hydroxyproline-Rich Glycoprotein Accumulation in the Cell Wall of Diseased Plants. Plant Physiol. 1982 Jul;70(1):82–86. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truchet G., Rosenberg C., Vasse J., Julliot J. S., Camut S., Denarie J. Transfer of Rhizobium meliloti pSym genes into Agrobacterium tumefaciens: host-specific nodulation by atypical infection. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.134-142.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Dreyfus B. L., Schmidt E. L. Initial stages in the morphogenesis of nitrogen-fixing stem nodules of Sesbania rostrata. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):888–897. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.888-897.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Schmidt E. L. Polarity in the exponential-phase Rhizobium japonicum cell. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1274–1284. doi: 10.1139/m77-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbosch K. A., Noel K. D., Kaneko Y., Newcomb E. H. Nodule initiation elicited by noninfective mutants of Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):950–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.950-959.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin L. O., Rhodes P. R., Goldberg R. B. cA lectin gene insertion has the structural features of a transposable element. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90560-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss E. W., Jr, Fryer J. L., Banowetz G. M. Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of a lectin from chinook salmon ova. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Hadwiger L., Ryan C. A. Chitosans and pectic polysaccharides both induce the accumulation of the antifungal phytoalexin pisatin in pea pods and antinutrient proteinase inhibitors in tomato leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 14;110(1):194–199. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91279-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M., Jin D., West C. A., Hadwiger L., Ryan C. A. Comparison of proteinase inhibitor-inducing activities and phytoalexin elicitor activities of a pure fungal endopolygalacturonase, pectic fragments, and chitosans. Plant Physiol. 1984 Nov;76(3):833–836. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whatley M. H., Bodwin J. S., Lippincott B. B., Lippincott J. A. Role of Agrobacterium cell envelope lipopolysaccharide in infection site attachment. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1080-1083.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. F., Ghidossi G., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Tumor induction by Agrobacterium rhizogenes involves the transfer of plasmid DNA to the plant genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3193–3197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmitzer L., Schmalenbach W., Schell J. Transcription of T-DNA in octopine and nopaline crown gall tumours is inhibited by low concentrations of alpha-amanitin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4801–4812. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert J. S., Albersheim P. Host-symbiont interactions. I. The lectins of legumes interact with the o-antigen-containing lipopolysaccharides of their symbiont Rhizobia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90653-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. H., Pankhurst C. E., Kondorosi A., Broughton W. J. Morphology of root nodules and nodule-like structures formed by Rhizobium and Agrobacterium strains containing a Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):787–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. P. Interactions between Rhizobia and Lectins of Lentil, Pea, Broad Bean, and Jackbean. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jun;65(6):1049–1052. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.6.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York W. S., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Inhibition of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid-stimulated elongation of pea stem segments by a xyloglucan oligosaccharide. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jun;75(2):295–297. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York W. S., McNeil M., Darvill A. G., Albersheim P. Beta-2-linked glucans secreted by fast-growing species of Rhizobium. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):243–248. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.243-248.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Keen N. T., Wang M. C. A receptor on soybean membranes for a fungal elicitor of phytoalexin accumulation. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):497–506. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Matama M., Masago H. Release of a Soluble Phytoalexin Elicitor from Mycelial Walls of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae by Soybean Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1981 May;67(5):1032–1035. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.5.1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa M., Yamauchi K., Masago H. De Novo Messenger RNA and Protein Synthesis Are Required for Phytoalexin-mediated Disease Resistance in Soybean Hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1978 Mar;61(3):314–317. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Szeto W. W., Ausubel F. M. Molecular characterization of Tn5-induced symbiotic (Fix-) mutants of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1025–1034. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1025-1034.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer U., Ebel J., Grisebach H. Induction of phytoalexin synthesis in soybean. Elicitor-induced increase in enzyme activities of flavonoid biosynthesis and incorporation of mevalonate into glyceollin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jun;188(2):450–455. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(78)80029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rensburg H. J., Strijdom B. W. Root Surface Association in Relation to Nodulation of Medicago sativa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):93–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.93-97.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


