Full text
PDF


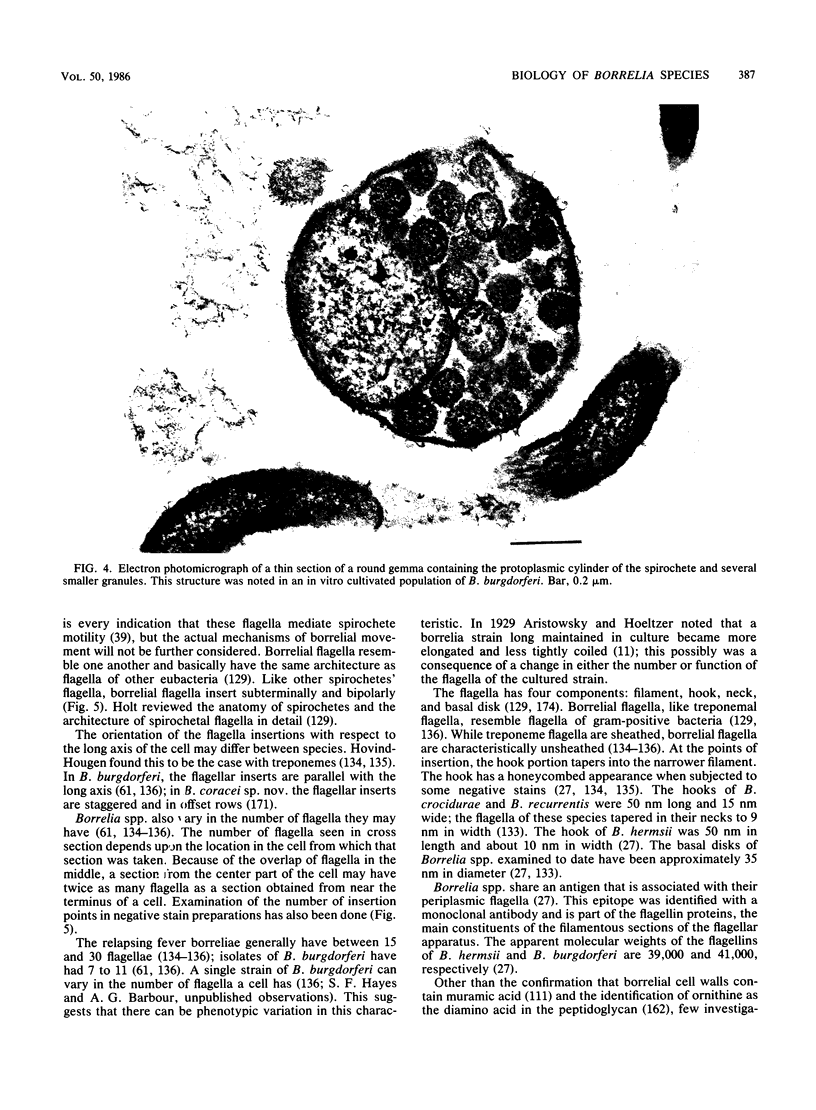


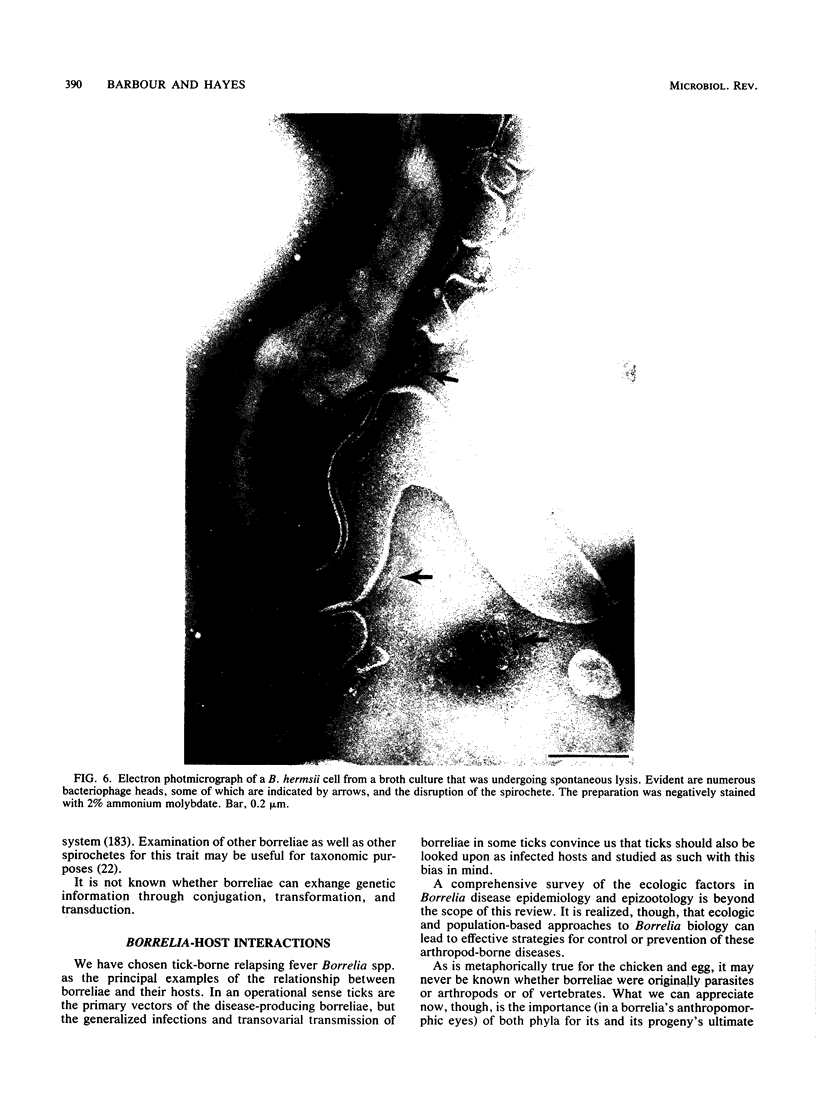



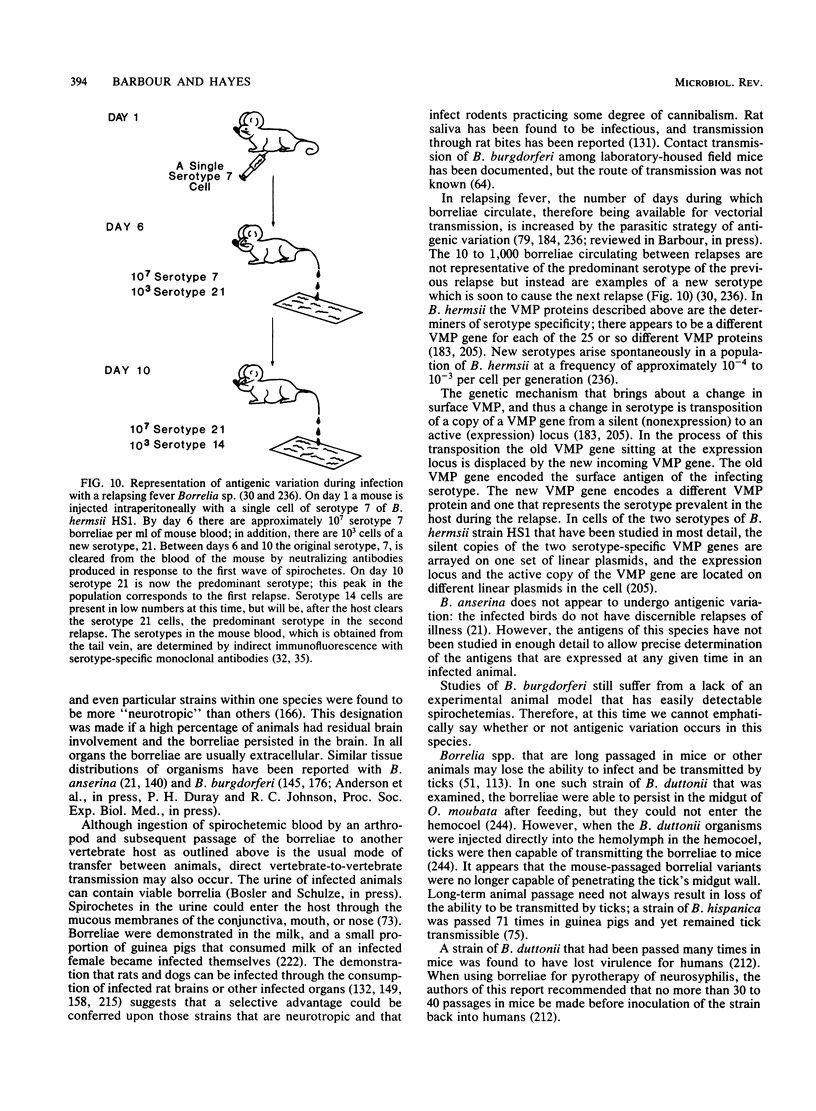






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AESCHLIMANN A. Developpement embryonnaire d'Ornithodorus moubata (Murray) et transmission transovarienne de Borrelia duttoni. Acta Trop. 1958;15(1):15–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abramson I. J., Smibert R. M. Inhibition of growth of treponemes by antimicrobial agents. Br J Vener Dis. 1971 Dec;47(6):407–412. doi: 10.1136/sti.47.6.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aeschlimann A., Geigy R., Hecker H. Observations of the Ultrastructure of Various Borrelia species (blood and tissue forms). Acta Trop. 1968;25(2):176–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Johnson R. C., Magnarelli L. A., Hyde F. W. Involvement of birds in the epidemiology of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):394–396. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.394-396.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):818–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin F. E., Barbieri J. T., Corin R. E., Grigas K. E., Cox C. D. Distribution of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities among Treponema pallidum and other spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):372–379. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.372-379.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., BAHMANYAR M., CHAMSA M. Sur l'usage du cobaye pour la différenciation des spirochètes récurrents; individualité du groupe B. crocidurae. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(6):864–877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M. Ornithodorus tartakovskyi olenev 1931 et Borrelia (Spirochaeta) latychevi sofiev 1941; note préliminaire. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1952;27(1-3):311–328. doi: 10.1051/parasite/1952271311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGDORFER W. Analyse des Infektionsverlaufes bei Ornithodorus moubata (Murray) und der natürlichen Uebertragung von Spirochaeta duttoni. Acta Trop. 1951;8(3):193–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGDORFER W. On the occult infection in relapsing fevers. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(5):664–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandopadhyay A. C., Vegad J. L. Observations on the pathology of experimental avian spirochaetosis. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbeyron T., Kean K., Forterre P. DNA adenine methylation of GATC sequences appeared recently in the Escherichia coli lineage. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.586-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Barrera O., Judd R. C. Structural analysis of the variable major proteins of Borrelia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2127–2140. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Heiland R. A., Schrumpf M. E., Tessier S. L. A Borrelia-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):549–554. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.549-554.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Hayes S. F. Variation in a major surface protein of Lyme disease spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):94–100. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.94-100.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Stoenner H. G. Variable major proteins of Borrellia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1312–1324. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Tessier S. L., Todd W. J. Lyme disease spirochetes and ixodid tick spirochetes share a common surface antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):795–804. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.795-804.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Todd W. J., Stoenner H. G. Action of penicillin on Borrelia hermsii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):823–829. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barstad P. A., Coligan J. E., Raum M. G., Barbour A. G. Variable major proteins of Borrelia hermsii. Epitope mapping and partial sequence analysis of CNBr peptides. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1302–1314. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck G., Habicht G. S., Benach J. L., Coleman J. L. Chemical and biologic characterization of a lipopolysaccharide extracted from the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi). J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):108–117. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S. Experimental transmission of the Lyme disease spirochete to rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):786–787. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.786-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Turner L. Movement of microorganisms in viscous environments. Nature. 1979 Mar 22;278(5702):349–351. doi: 10.1038/278349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Kaplan M. H., Rothenberg I. R., Barbour A. G. Isolation and characterization of the Lyme disease spirochete from the skin of patients with erythema chronicum migrans. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985 Sep;13(3):444–449. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(85)70187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Coleman J. L., Benach J. L., Massey D. A., Hanrahan J. P., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Natural Distribution of the Ixodes dammini spirochete. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):321–322. doi: 10.1126/science.6836274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler E. M., Ormiston B. G., Coleman J. L., Hanrahan J. P., Benach J. L. Prevalence of the Lyme disease spirochete in populations of white-tailed deer and white-footed mice. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):651–659. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryceson A. D., Parry E. H., Perine P. L., Warrell D. A., Vukotich D., Leithead C. S. Louse-borne relapsing fever. Q J Med. 1970 Jan;39(153):129–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Péter O., Aeschlimann A. Erythema chronicum migrans--a tickborne spirochetosis. Acta Trop. 1983 Mar;40(1):79–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. Discovery of the Lyme disease spirochete and its relation to tick vectors. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):515–520. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. The New Zealand white rabbit: an experimental host for infecting ticks with Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):609–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Varma M. G. Trans-stadial and transovarial development of disease agents in arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol. 1967;12:347–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.12.010167.002023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess E. C., Amundson T. E., Davis J. P., Kaslow R. A., Edelman R. Experimental inoculation of Peromyscus spp. with Borrelia burgdorferi: evidence of contact transmission. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Mar;35(2):355–359. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler T., Hazen P., Wallace C. K., Awoke S., Habte-Michael A. Infection with Borrelia recurrentis: pathogenesis of fever and petechiae. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):665–675. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUSINEAU J. G., McKIEL J. A. In vitro sensitivity of Leptospira to varioqs antimicrobial agents. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Oct;7:751–758. doi: 10.1139/m61-089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callow L. L. Observations on tick-transmitted spirochaetes of cattle in Australia and South Africa. Br Vet J. 1967 Nov;123(11):492–497. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)39704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charon N. W., Lawrence C. W., O'Brien S. Movement of antibody-coated latex beads attached to the spirochete Leptospira interrogans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7166–7170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS G. E., BURGDORFER W. On the susceptibility of the guinea pig to the relapsing fever spirochete Borrelia duttonii. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1954;47(4):498–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS G. E. Biology as an aid to the identification of two closely related species of ticks of the genus Ornithodoros. J Parasitol. 1952 Oct;38(5):477–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS G. E., HOOGSTRAAL H. Etude sur la biologie du spirochète Borrelia persica, trouvé chez la tique Ornithodorus tholazani (Argasinae) récoltée dans le governorate du Désert Occidental Egyptien; commentaires sur la distribution et l'écologie de la tique vectrice. Ann Parasitol Hum Comp. 1956 Jan-Mar;31(1-2):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELAMATER E. D., NEWCOMER V. D. Studies on the life cycles of spirochetes; the use of phase contrast microscopy. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1950 Mar;34(2):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLAMATER E. D., HAANES M., WIGGALL R. H., PILLSBURY D. M. Studies on the life cycle of spirochetes. VIII. Summary and comparison of observations on various organisms. J Invest Dermatol. 1951 Apr;16(4):231–256. doi: 10.1038/jid.1951.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diab F. M., Soliman Z. R. An experimental study of Borrelia anserina in four species of Argas ticks. 1. Spirochete localization and densities. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Sep 21;53(2):201–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00380465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge R. W. Culture of Ethiopian strains of Borrelia recurrentis. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jun;25(6):935–939. doi: 10.1128/am.25.6.935-939.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELSENFELD O. BORRELIAE, HUMAN RELAPSING FEVER, AND PARASITE-VECTOR-HOST RELATIONSHIPS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:46–74. doi: 10.1128/br.29.1.46-74.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTON J. D., SMITH P. J. Carbohydrate metabolism in Spirochaeta recurrentis. 1. The metabolism of spirochaetes in vivo and in vitro. Biochem J. 1960 Sep;76:491–499. doi: 10.1042/bj0760491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fumarola D., Munno I., Miragliotta G. "Endotoxicity" of the Lyme disease spirochete. Infection. 1983 Nov-Dec;11(6):345–345. doi: 10.1007/BF01641362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., AESCHLIMANN A. LANGFRISTIGE BEOBACHTUNGEN UEBER TRANSOVARIELLE UBERTRAGUNG VON BORRELIA DUTTONI DURCH ORNITHODORUS MOUBATA. Acta Trop. 1964;21:87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., BURGDORFER W. Unterschiedliches Verhalten verschiedener Stämme von Spirochaeta duttoni in der weissen Maus. Acta Trop. 1951;8(2):151–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., MOOSER H., WEYER F. Untersuchungen an Stämmen von afrikanischem Rückfallfieber aus Tanganyika. Acta Trop. 1956;13(3):193–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., SARASIN G. Isolatstämme von Borrelia duttoni und ihr Immunisierungsverhaiten gegenüber der weissen Maus. Acta Trop. 1958;15(3):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., SARASIN G. [Environment-related factors in habitat and behavior of the pathogen of relapsing fever Borrelia duttonii]. Acta Trop. 1961;18:359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIGY R., WAGNER O., AESCHLIMANN A. Transmission génitale de Borrelia duttoni chez Ornithodorus moubata. Acta Trop. 1954;11(1):81–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINGER C. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF MURAMIC ACID FROM TWO SPIROCHAETES: BORRELIA DUTTONI AND LEPTOSPIRA BIFLEXA. Nature. 1963 Jul 13;199:159–159. doi: 10.1038/199159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber M. S., Khalil G. M., Hoogstraal H., Aboul-Nasr A. E. Borrelia crocidurae localization and transmission in Ornithodoros erraticus and O. savignyi. Parasitology. 1984 Jun;88(Pt 3):403–413. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000054676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber M. S., Khalil G. M., Hoogstraal H. Borrelia crocidurae: venereal transfer in Egyptian Ornithodoros erraticus ticks. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Oct;54(2):182–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway R. E., Levin J., Butler T., Naff G. B., Goldsmith G. H., Saito H., Awoke S., Wallace C. K. Activation of protein mediators of inflammation and evidence for endotoxemia in Borrelia recurrentis infection. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):933–938. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABERKORN A. UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DAS VERHALTEN VON RUECKFALLFIEBERSPIROCHAETEN INSBESONDERE DER BORRELIA-CROCIDURAE-GRUPPE IN DER KLEIDERLAUS. 2. Z Tropenmed Parasitol. 1963 Jul;14:209–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMPP E. G. Morphologic characteristics of the smaller oral treponemes and Borrelia vincenti as revealed by stained smear, darkfield and electron microscopic technics. J Am Dent Assoc. 1950 Jan;40(1):1-11, illust. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1950.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B., CHAMSA M., SEYDIAN B., HARVEY A. E. The behaviour of spirochaetes in lice with special reference to the negative phase. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1957 Sep-Oct;50(5):735–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B. Do spirochaetes have a negative phase in lice? Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1955;48(3):322–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B., SPARROW H., HARVEY A. E. The behavior of Spirochaeta recurrentis Lebert in lice. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1960 Mar-Apr;53:140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORRENBERGER R. Transmission expérimentale de Spirochaeta hispanica au chien par la morsure de rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1955 Jul;149(13-14):1432–1434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORRENBERGER R. Transmission expérimentale de Spirochaeta hispanica de Buen, 1926, par morsure de rat. Arch Inst Pasteur Alger. 1955 Mar;33(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of the major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:91–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampp E. G., Scott D. B., Wyckoff R. W. Morphologic Characteristics of Certain Cultured Strains of Oral Spirochetes and Treponema pallidum as Revealed by the Electron Microscope. J Bacteriol. 1948 Dec;56(6):755–769. doi: 10.1128/jb.56.6.755-769.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy P. H., Jr, Levin J. Lack of endotoxin in Borrelia hispanica and Treponema pallidum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1983 Oct;174(1):47–52. doi: 10.3181/00379727-174-41702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes S. F., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Bacteriophage in the Ixodes dammini spirochete, etiological agent of Lyme disease. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1436–1439. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1436-1439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Sakaguchi K. Analysis of linear plasmids isolated from Streptomyces: association of protein with the ends of the plasmid DNA. Plasmid. 1982 Jan;7(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. C. Anatomy and chemistry of spirochetes. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Mar;42(1):114–160. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.1.114-160.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogstraal H. Argasid and nuttalliellid ticks as parasites and vectors. Adv Parasitol. 1985;24:135–238. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60563-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen K. H. Electron microscopy of Borrelia merionesi and Borrelia recurrentis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Dec;82(6):799–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K. Determination by means of electron microscopy of morphological criteria of value for classification of some spirochetes, in particular treponemes. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1976;(255):1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovind-Hougen K. Ultrastructure of spirochetes isolated from Ixodes ricinus and Ixodes dammini. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):543–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe T. R., Mayer L. W., Barbour A. G. A single recombinant plasmid expressing two major outer surface proteins of the Lyme disease spirochete. Science. 1985 Feb 8;227(4687):645–646. doi: 10.1126/science.3969554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde F. W., Johnson R. C. Genetic relationship of lyme disease spirochetes to Borrelia, Treponema, and Leptospira spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):151–154. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.151-154.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. C., ROGERS P. 5-FLUOROURACIL AS A SELECTIVE AGENT FOR GROWTH OF LEPTOSPIRAE. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:422–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.422-426.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Hyde F. W., Rumpel C. M. Taxonomy of the Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):529–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C. The spirochetes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:89–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. E., Klein G. C., Schmid G. P., Bowen G. S., Feeley J. C., Schulze T. Lyme disease: a selective medium for isolation of the suspected etiological agent, a spirochete. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):81–82. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.81-82.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. E., Klein G. C., Schmid G. P., Feeley J. C. Susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete to seven antimicrobial agents. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):549–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAWATA T. Electron microscopy of fine structure of Borrelia duttonii. Jpn J Microbiol. 1961 Apr;5:203–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1961.tb00201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karimi Y., Hovind-Hougen K., Birch-Andersen A., Asmar M. Borrelia persica and B. baltazardi sp. nov.: experimental pathogenicity for some animals and comparison of the ultrastructure. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1979 Aug-Sep;130B(2):157–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. Cultivation of Borrelia hermsi. Science. 1971 Jul 30;173(3995):443–444. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3995.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Hirai K., Gunge N., Hishinuma F. Hairpin plasmid--a novel linear DNA of perfect hairpin structure. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1881–1886. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaviter E. C., Johnson R. C. Isolation of the outer envelope, chemical components, and ultrastructure of Borrelia hermsi grown in vitro. Acta Trop. 1979 Jun;36(2):123–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornblatt A. N., Steere A. C., Brownstein D. G. Experimental Lyme disease in rabbits: spirochetes found in erythema migrans and blood. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.220-223.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Burgdorfer W., Hayes S. F., Barbour A. G. Isolation of a spirochete from the soft tick, Ornithodoros coriaceus: a possible agent of epizootic bovine abortion. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.3898367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore B. P., Bey R. F., Johnson R. C. Lipid metabolism of Borrelia hermsi. Infect Immun. 1978 Apr;20(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.1.215-220.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren R., Soule M. H. The Effect of Low Temperature on the Spirochetes of Relapsing Fever: II. The Structure and Motility of Spirochaeta novyi. J Bacteriol. 1945 Sep;50(3):313–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.50.3.313-321.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lofgren R., Soule M. H. The Structure of Spirochaeta novyi as Revealed by the Electron Microscope. J Bacteriol. 1945 Dec;50(6):679–690. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loken K. I., Wu C. C., Johnson R. C., Bey R. F. Isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete from mammals in Minnesota. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Jul;179(3):300–302. doi: 10.3181/00379727-179-42100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINI E. Zur älteren Geschichte der Recurrens im europäischen Raum. Ergeb Hyg Bakteriol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1955;29:213–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Burgdorfer W., Chappell W. A. Parasitism by Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae) and antibodies to spirochetes in mammals at Lyme disease foci in Connecticut, USA. J Med Entomol. 1984 Jan 26;21(1):52–57. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/21.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Chappell W. A. Antibodies to spirochetes in white-tailed deer and prevalence of infected ticks from foci of Lyme disease in Connecticut. J Wildl Dis. 1984 Jan;20(1):21–26. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-20.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. T., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Antigenic variation is associated with DNA rearrangements in a relapsing fever Borrelia. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman K., Jr, Johnson R. C. In vivo evidence that an intact lytic complement pathway is not essential for successful removal of circulating Borrelia turicatae from mouse blood. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):465–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.465-469.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman K., Jr, Johnson R. C. T-cell-independent elimination of Borrelia turicatae. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):572–576. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.572-576.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osebold J. W., Spezialetti R., Jennings M. B., Pritchett R. F., Bushnell R. B. Congenital spirochetosis in calves: association with epizootic bovine abortion. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1986 Feb 15;188(4):371–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PILLOT J., DUPOUEY P., RYTER A. LA SIGNIFICATION DES FORMES ATYPIQUES ET LA NOTION DE CYCLE 'EVOLUTIF CHEZ LES SPIROCH'ETES. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:663–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett J., Kelly R. Lipid catabolism of relapsing fever borreliae. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):279–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.279-285.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillot J., Ryter A. Structure des spirochètes. 1. Etude des generes Treponema, Borrelia et Leptospira au microscope electronique. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 Jun;108(6):791–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Simon M. I., Barbour A. G. Transposition of structural genes to an expression sequence on a linear plasmid causes antigenic variation in the bacterium Borrelia hermsii. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):257–263. doi: 10.1038/318257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISS-GUTFREUND R. J. [Culture of Borellia recurrentis (Ethiopan strains) in fertilized hen egg]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1960 Jan;98:131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLLO I. M., WILLIAMSON J., PLACKETT R. L. Acquired resistance to penicillin and to neoarsphenamine in Spirochaeta recurrentis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Mar;7(1):33–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb00686.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE N. R., MORTON H. E. The morphologic variation of treponema. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1952 Jan;36(1):17–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L., Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Shope R. E., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 1979 Jul;58(4):281–294. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARASIN G. [on the organotropism of the spirochaetes B. duttoni to the transmitting tick]. Acta Trop. 1959;16:218–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT J. M., STANIER R. Y. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF BACTERIOPHAGES ACTIVE AGAINST STALKED BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Apr;39:95–107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUHARDT V. T., WILKERSON M. Relapse phenomena in rats infected with single spirochetes (Borrelia recurrentis var. turicatae). J Bacteriol. 1951 Aug;62(2):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.2.215-219.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPARROW H. Rappel d'observations concernant le comportement des spirochètes de la fièvre récurrente dans le pou. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1956 Mar-Apr;49(2):246–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWAIN R. H. Electron microscopic studies of the morphology of pathogenic spirochaetes. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):117–128. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saheb S. A. Spirochetal organisms from pigs. 3. Preliminary observations on bacteriophage particles associated with spirochetes of the genus. Treponema. Rev Can Biol. 1974 Mar;33(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Steigerwalt A. G., Johnson S. E., Barbour A. G., Steere A. C., Robinson I. M., Brenner D. J. DNA characterization of the spirochete that causes Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):155–158. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.155-158.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid G. P., Verardo L., Highsmith A. K., Weisfeld J. S. Failure to detect endotoxin in sera from patients with Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):616–616. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtmann E. T., Bushnell R. B., Loomis E. C., Oliver M. N., Theis J. H. Experimental and epizootiologic evidence associating Ornithodoros coriaceus Koch (Acari: Argasidae) with the exposure of cattle to epizootic bovine abortion in California. J Med Entomol. 1976 Dec 8;13(3):292–299. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/13.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Brener J., Osorno M., Ristic M. Pathobiology of Borrelia theileri in the tropical cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. J Invertebr Pathol. 1978 Sep;32(2):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(78)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. D., Miranpuri G. S., Adams J. H., Ahrens E. H. Borrelia theileri: isolation from ticks (Boophilus microplus) and tick-borne transmission between splenectomized calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Jun;46(6):1396–1398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanek G., Wewalka G., Groh V., Neumann R., Kristoferitsch W. Differences between Lyme disease and European arthropod-borne Borrelia infections. Lancet. 1985 Feb 16;1(8425):401–401. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton T. B., Canale-Parola E. Enumeration and selective isolation of rumen spirochetes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):965–973. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.965-973.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Pachner A. R., Malawista S. E. Neurologic abnormalities of Lyme disease: successful treatment with high-dose intravenous penicillin. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):767–772. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stepan D. E., Johnson R. C. Helical conformation of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), Treponema paraluis-cuniculi, Treponema denticola, Borrelia turicatae, and unidentified oral spirochetes. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):937–940. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.937-940.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G. Biology of Borrelia hermsii in Kelly medium. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):540–543. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.540-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoenner H. G., Dodd T., Larsen C. Antigenic variation of Borrelia hermsii. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1297–1311. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON P. E., DUNN M. C., WINDER C. V. Comparison of the action of chloramphenicol and penicillin G against relapsing fever in mice. J Infect Dis. 1950 Mar-Apr;86(2):110–121. doi: 10.1093/infdis/86.2.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto T., Namikawa I. Electron microscopy of the spherical body of oral spirochetes in vitro. Further studies. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(4):321–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARMA M. G. Comparative studies on the transmission of two strains of Spirochaeta duttoni by Ornithodoros moubata and of S. turicatae by O. turicata. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1956 Mar;50(1):1–17. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1956.11685734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARMA M. G. Infections of Ornithodoros ticks with relapsing fever spirochaetes, and the mechanisms of their transmission. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1956 Mar;50(1):18–31. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1956.11685735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER-JEVSEENKO O. Fortpflanzung bei Ornithodorus moubata und genitale Ubertragung von Borrelia duttoni. Acta Trop. 1958;15(2):118–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTPHAL A. NEUE UNTERSUCHUNGEN ZUR FRAGE DER KOERNCHENSTADIEN VON BORRELIEN IM BLUTE. Arch Hyg Bakteriol. 1963 Aug;147:349–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young E. J., Weingarten N. M., Baughn R. E., Duncan W. C. Studies on the pathogenesis of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction: development of an animal model and evidence against a role for classical endotoxin. J Infect Dis. 1982 Nov;146(5):606–615. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaher M. A., Soliman Z. R., Diab F. M. An experimental study of Borrelia anserina in four species of Argas ticks. 2. Transstadial survival and transovarial transmission. Z Parasitenkd. 1977 Sep 21;53(2):213–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00380466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]