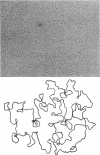
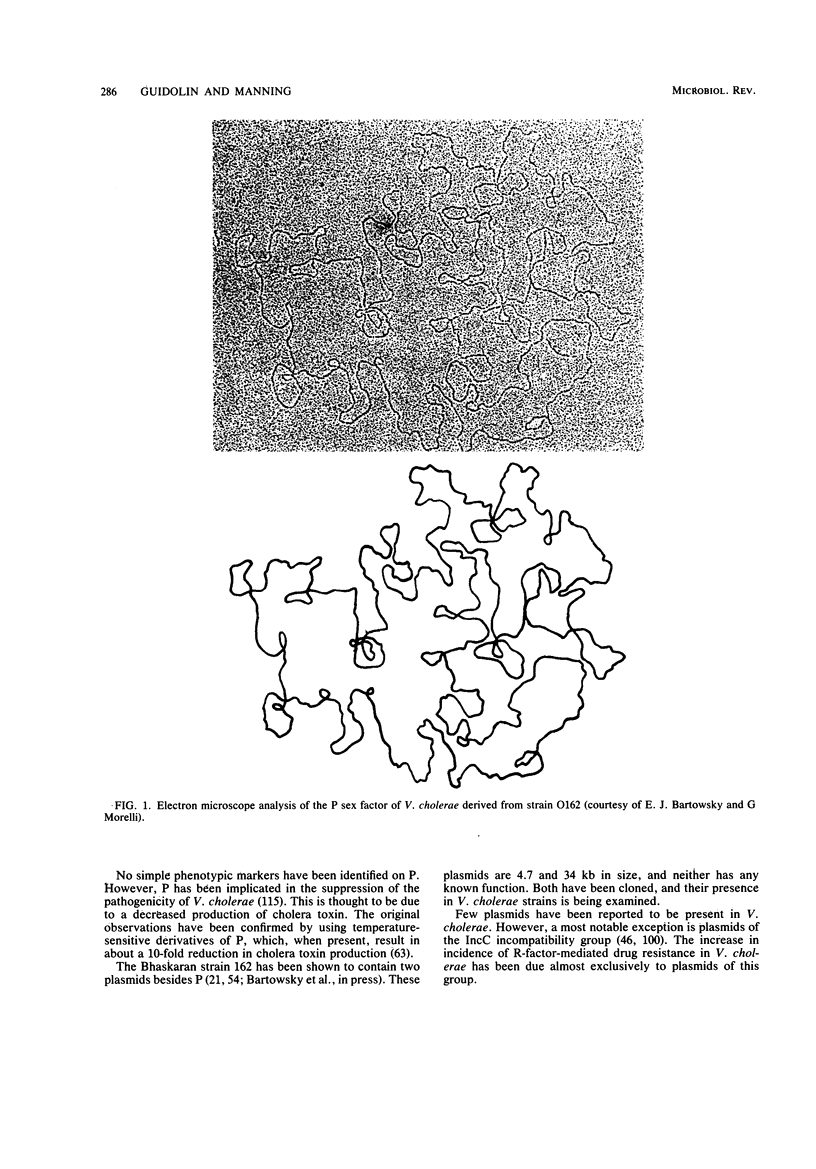
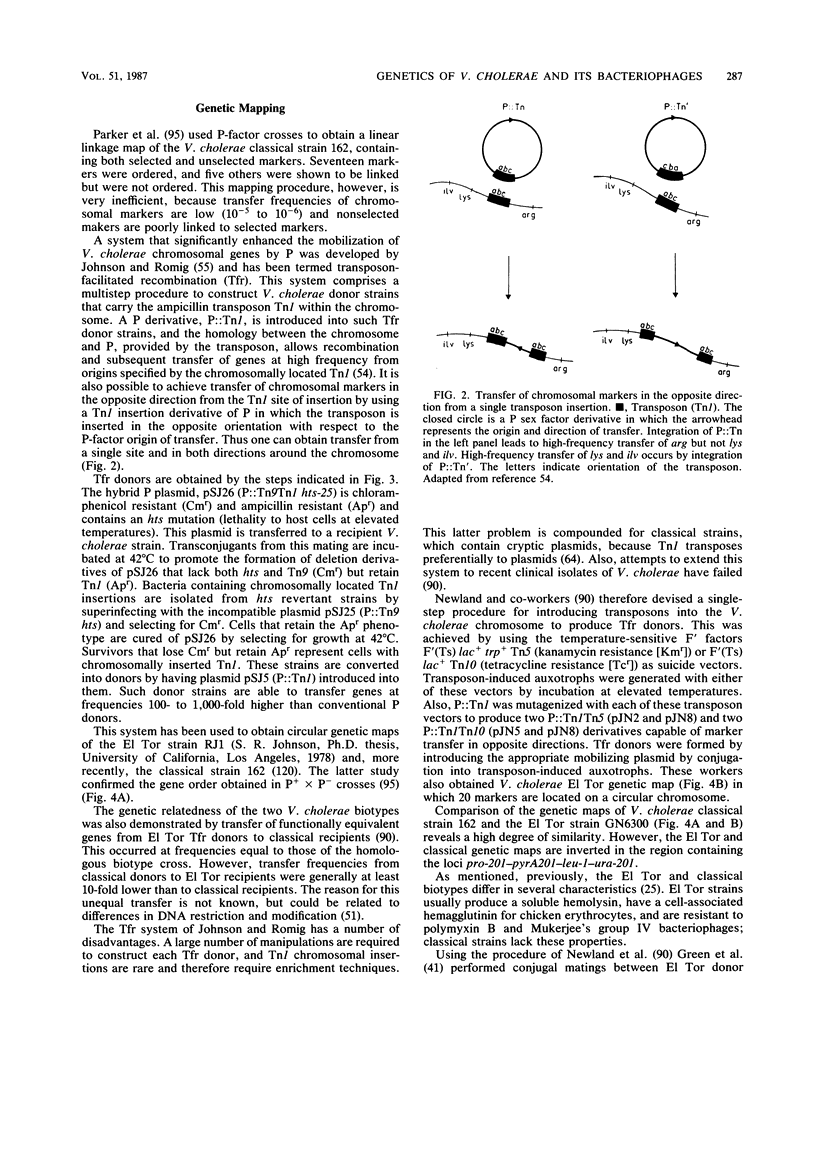
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. J., Wilson J. M., Oxender D. L. Defective transport and other phenotypes of a periplasmic "leaky" mutant of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.351-358.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong I. L., Redmond J. W. The fatty acids present in the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae 569B (Inaba). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 29;348(2):302–305. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(74)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attridge S. R., Rowley D. The specificity of Vibrio cholerae adherence and the significance of the slime agglutinin as a second mediator of in vitro attachment. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):873–881. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHASKARAN K. Genetic recombination in Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):71–75. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHASKARAN K. Observations of the nature of genetic recombination in Vibrio cholerae. Indian J Med Res. 1959 May;47(3):253–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BHASKARAN K. Recombination of characters between mutant stocks of Vibrio cholerae, strain 162. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:47–54. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus H. DNA packaging initiation of Salmonella bacteriophage P22: determination of cut sites within the DNA sequence coding for gene 3. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.458-465.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baine W. B., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Genetic mapping of mutations in independently isolated nontoxinogenic mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.194-200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balganesh M., Das J. Transfection of Vibrio cholerae by bacteriophage phi 149 DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 12;90(3):726–733. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91888-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Rolfe B., Onodera K. Pleiotropic properties and genetic organization of the tolA,B locus of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):74–83. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.74-83.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth B. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Finkelstein R. A. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/protease nicks cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):558–560. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.558-560.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brade H. Occurrence of 2-keto-deoxyoctonic acid 5-phosphate in lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio cholerae Ogawa and Inaba. J Bacteriol. 1985 Feb;161(2):795–798. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.2.795-798.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broady K. W., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O. The chemical structure of the lipid A component of lipopolysaccharides from Vibrio cholerae. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(3):463–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukhari A. I. Bacteriophage mu as a transposition element. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:389–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.002133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S. N., Das J., Barua D. Electron microscopy of cholera phages. Indian J Med Res. 1965 Oct;53(10):934–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury R., Das J. Infection by choleraphage phi 138: bacteriophage DNA and replicative intermediates. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):960–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.960-967.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman K., Dougan G., Arbuthnott J. P. Cloning, and expression in Escherichia coli K-12, of the chromosomal hemolysin (phospholipase C) determinant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):909–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.909-915.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MOOR C. E. A NON-HAEMOLYTIC EL TOR VIBRIO AS THE CAUSE OF AN OUTBREAK OF PARACHOLERA IN WEST NEW GUINEA. THE EL TOR PROBLEM AND PANDEMIC PARACHOLERA IN THE WEST PACIFIC. Trop Geogr Med. 1963 Jun;15:97–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., Parker C. D., Wohlhieter J. A., Baron L. S. Isolation and characterization of the fertility factor P of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):763–771. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.763-771.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans R. J., Jackson E. N. Restriction endonuclease Hin dIII cleavage site map of bacteriophage P22. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):359–372. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90491-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEELEY J. C. CLASSIFICATION OF VIBRIO CHOLERAE (VIBRIO COMMA), INCLUDING EL TOR VIBRIOS, BY INFRASUBSPECIFIC CHARACTERISTICS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:665–670. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.665-670.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Boesman-Finkelstein M., Holt P. Vibrio cholerae hemagglutinin/lectin/protease hydrolyzes fibronectin and ovomucin: F.M. Burnet revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1092–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Hanne L. F. Purification and characterization of the soluble hemagglutinin (cholera lectin)( produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1199–1208. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1199-1208.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. I. Isolation of mutants with altered toxinogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):117–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focareta T., Manning P. A. Extracellular proteins of Vibrio cholerae: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and characterization of the deoxyribonuclease (DNase) together with its periplasmic localization in Escherichia coli K-12. Gene. 1987;53(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzon V. L., Manning P. A. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the gene for a hemagglutinin from Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):279–284. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.279-284.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gangarosa E. J., Sanati A., Saghari H., Feeley J. C. Multiple serotypes of vibrio cholerae isolated from a case of cholera. Evidence suggesting in-vivo mutation. Lancet. 1967 Mar 25;1(7491):646–648. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. C., Romig W. R. Complete and Defective Bacteriophages of Classical Vibrio cholerae: Relationship to the Kappa Type Bacteriophage. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1231–1238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1231-1238.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Mekalanos J. J. Cloning of the Vibrio cholerae recA gene and construction of a Vibrio cholerae recA mutant. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):715–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.715-722.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Mekalanos J. J. Effect of a recA mutation on cholera toxin gene amplification and deletion events. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):723–731. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.723-731.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. L., Murphy J. R. Cloning and characterization of the hemolysin determinants from Vibrio cholerae RV79(Hly+), RV79(Hly-), and 569B. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):35–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.35-41.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S. L., Murphy J. R. Molecular cloning of the hemolysin determinant from Vibrio cholerae El Tor. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):239–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.239-244.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S., Murphy J. R. Molecular epidemiological studies of United States Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae strains: integration site of mutator vibriophage VcA-3. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.224-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green B. A., Newland J. W., Holmes R. K. Mapping of chromosomal genes that determine the El Tor biotype in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):924–929. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.924-929.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidolin A., Manning P. A. Bacteriophage CP-T1 of Vibrio cholerae. Identification of the cell surface receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 15;153(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09271.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidolin A., Morelli G., Kamke M., Manning P. A. Vibrio cholerae bacteriophage CP-T1: characterization of bacteriophage DNA and restriction analysis. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):163–169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.163-169.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Rosén A., Holme T. Monoclonal antibodies against Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):449–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.449-454.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Finkelstein R. A. Characterization and distribution of the hemagglutinins produced by Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):209–214. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.209-214.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Vialard J. L., Pearson N. J., O'Grady F. R plasmids from Asian strains of Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):585–588. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisatsune K., Kondo S. Lipopolysaccharides of R mutants isolated from Vibria cholerae. Biochem J. 1980 Jan 1;185(1):77–81. doi: 10.1042/bj1850077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Vasil M. L., Finkelstein R. A. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. III. Characterization of nontoxinogenic mutants in vitro and in experimental animals. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):551–560. doi: 10.1172/JCI107962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Purification and characterization of a hemolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae biotype El Tor: another toxic substance produced by cholera vibrios. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1020-1027.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Finkelstein R. A. Selection and characteristics of a Vibrio cholerae mutant lacking the A (ADP-ribosylating) portion of the cholera enterotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):2052–2056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbesi F., Manning P. A. Biotype-specific restriction and modification of DNA in Vibrio cholerae. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):552–554. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.552-554.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jann B., Jann K., Beyaert G. O. 2-Amino-2,6-dideoxy-d-glucose (D-quinovosamine): a constituent of the lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio cholerae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):531–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03015.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Romig W. R. Transposon-facilitated recombination in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 16;170(1):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00268584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Romig W. R. Vibrio cholerae conjugative plasmid pSJ15 contains transposable prophage dVcA1. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):632–638. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.632-638.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Romig W. R. Vibrio cholerae hybrid sex factor that contains ampicillin transposon Tn1. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):531–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.531-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabir S. Composition and immunochemical properties of outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):382–389. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.382-389.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehoe M., Duncan J., Foster T., Fairweather N., Dougan G. Cloning, expression, and mapping of the Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin determinant in Escherichia coli K-12. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1105–1111. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1105-1111.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. T., Parker C. D. Identification and preliminary characterization of Vibrio cholerae outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1018–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1018-1024.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Gustafsson B., Holme T. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1982 Mar 1;100:341–349. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Holme T., Holmgren J. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Jan;68(1):C14–C16. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan A. A., Srivastava R., Sinha V. B., Srivastava B. S. Regulation of toxin biosynthesis by plasmids in Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Oct;131(10):2653–2657. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Cohen S. N. Selected translocation of plasmid genes: frequency and regional specificity of translocation of the Tn3 element. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.888-899.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kufer B., Backhaus H., Schmieger H. The packaging initiation site of phage P22. Analysis of packaging events by transduction. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):510–515. doi: 10.1007/BF00332636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Young C. R., Lanata C., Sears S., Honda T., Finkelstein R. Texas Star-SR: attenuated "Vibrio cholerae" oral vaccine candidate. Dev Biol Stand. 1983;53:59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Peters R., Bernheimer H., Berendsen W. Influence of cultural conditions and mutations on the composition of the outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Sep 23;147(3):251–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00582876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONSUR K. A., RIZVI S. S., HUQ M. I., BENENSON A. S. EFFECT OF MUKERJEE'S GROUP IV PHAGE ON EL TOR VIBRIOS. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:211–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Bartowsky E. J., Leavesly D. I., Hackett J. A., Heuzenroeder M. W. Molecular cloning using immune sera of a 22-kDal minor outer membrane protein of Vibrio cholerae. Gene. 1985;34(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90299-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Brown M. H., Heuzenroeder M. W. Cloning of the structural gene (hly) for the haemolysin of Vibrio cholerae El Tor strain 017. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning P. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Yeadon J., Leavesley D. I., Reeves P. R., Rowley D. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli K-12 of the O antigens of the Inaba and Ogawa serotypes of the Vibrio cholerae O1 lipopolysaccharides and their potential for vaccine development. Infect Immun. 1986 Aug;53(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.2.272-277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Affinity filters, a new approach to the isolation of tox mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Purification of cholera toxin and its subunits: new methods of preparation and the use of hypertoxinogenic mutants. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.552-558.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Moseley S. L., Murphy J. R., Falkow S. Isolation of enterotoxin structural gene deletion mutations in Vibrio cholerae induced by two mutagenic vibriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Sublett R. D., Romig W. R. Genetic mapping of toxin regulatory mutations in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):859–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.859-865.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercurio A., Manning P. A. Cellular localization and export of the soluble haemolysin of Vibrio cholerae El Tor. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;200(3):472–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00425733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Mekalanos J. J. Synthesis of cholera toxin is positively regulated at the transcriptional level by toxR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3471–3475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Nucleotide sequence homology between the heat-labile enterotoxin gene of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):444–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.444-446.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWMAN F. S., EISENSTARK A. PHAGE-HOST RELATIONSHIPS IN VIBRIO CHOLERAE. J Infect Dis. 1964 Jun;114:217–225. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.3.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill R. J., Ivins B. E., Holmes R. K. Synthesis and secretion of the plasmid-coded heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli in Vibrio cholerae. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):289–291. doi: 10.1126/science.6857285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. Protection of infant mice against cholera by antibodies to three antigens of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):41–47. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neoh S. H., Rowley D. The antigens of Vibrio cholerae involved in the vibriocidal action of antibody and complement. J Infect Dis. 1970 May;121(5):505–513. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.5.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Green B. A., Foulds J., Holmes R. K. Cloning of extracellular DNase and construction of a DNase-negative strain of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):691–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.691-696.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newland J. W., Green B. A., Holmes R. K. Transposon-mediated mutagenesis and recombination in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1984 Aug;45(2):428–432. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.2.428-432.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Ogg B. J., Shrestha M. B., Poudayl L. Antigenic changes in Vibrio cholerae biotype eltor serotype Ogawa after bacteriophage infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):974–978. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.974-978.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Shrestha M. B., Poudayl L. Phage-induced changes in Vibrio cholerae: serotype and biotype conversions. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.231-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogg J. E., Timme T. L., Alemohammad M. M. General Transduction in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):737–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.737-741.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C., Gauthier D., Tate A., Richardson K., Romig W. R. Expanded linkage map of Vibrio cholerae. Genetics. 1979 Feb;91(2):191–214. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C., Romig W. R. Self-transfer and genetic recombination mediated by P, the sex factor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):707–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.707-714.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Mekalanos J. J. Molecular cloning of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlner J., Meyer T. F., Jalajakumari M. B., Manning P. A. Nucleotide sequence of ompV, the gene for a major Vibrio cholerae outer membrane protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):494–500. doi: 10.1007/BF00338088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlner J., Meyer T. F., Manning P. A. Serological properties and processing in Escherichia coli K12 of OmpV fusion proteins of Vibrio cholerae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Dec;205(3):501–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00338089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. M., Datta A., Datta G. C. R-factors in Calcutta strains of Vibrio cholerae and members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(6):971–973. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROY C., MUKERJEE S. Variability in the haemolytic property of El Tor vibrios. Ann Biochem Exp Med. 1962 Nov;22:295–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Sengupta A., Das J. Phosphate repression of phage protein synthesis during infection by choleraphage phi 149. Virology. 1984 Jul 15;136(1):110–124. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W. 4-Amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-mannose (D-perosamine): a component of the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae 569B (Inaba). FEBS Lett. 1975 Feb 1;50(2):147–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80476-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W., Korsch M. J., Jackson G. D. Immunochemical studies to the O-antigens of vibrio cholerae. Partial characterization of an acid-labile antigenic determinant. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1973 Apr;51(2):229–235. doi: 10.1038/icb.1973.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W. The 4-amino sugars present in the lipopolysaccharides of vibro cholerae and related vibrios. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 6;542(3):378–384. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W. The structure of the O-antigenic side chain of the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae 569B (Inaba). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 1;584(2):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Miller C. E. Progressive changes of Vibrio serotypes in germ-free mice infected with Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.688-695.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K. Somatic antigen variation in Vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1971 Apr;24(2):93–100. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.24.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders D. W., Bramucci M. G. Genetic mapping of the tox-1000 locus of Vibrio cholerae El Tor strain RJ1. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):829–831. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.829-831.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. IV. Differences in outer membrane proteins due to strain and cultural differences. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):454–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.454-464.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. R., Parker C. D. Isolation and characterization of protease-deficient mutants of vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Aug;138(2):143–151. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.2.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R. A classification of cholera vibrios into biotypes and their value for epidemiological purposes. Indian J Med Res. 1969 May;57(5):856–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta A., Ray P., Das J. Characterization and physical map of choleraphage phi 149 DNA. Virology. 1985 Jan 30;140(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha V. B., Srivastava B. S. Suppression of pathogenicity by P and V plasmids in Vibrio cholerae. J Gen Microbiol. 1978 Feb;104(2):251–255. doi: 10.1099/00221287-104-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporecke I., Castro D., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic mapping of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.253-261.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava R., Srivastava B. S. Isolation of a non-adhesive mutant of Vibrio cholerae and chromosomal localization of the gene controlling mannose-sensitive adherence. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):275–278. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G., Leavesley D. I., Lagnado C. A., Heuzenroeder M. W., Manning P. A. Purification of the 25-kDa Vibrio cholerae major outer-membrane protein and the molecular cloning of its gene: ompV. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):385–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08850.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sublett R. D., Romig W. R. Transposon-facilitated recombination in classical biotypes of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1132-1138.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Strömberg G. J., Holmgren J. Purification of Vibrio cholerae soluble hemagglutinin and development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for antigen and antibody quantitations. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.237-243.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEYA K., SHIMODORI S. "PROPHAGE-TYPING" OF EL TOR VIBRIOS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Apr;85:957–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.4.957-958.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L. BACTERIOPHAGE-INDUCED MUTATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1043–1051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya K., Shimodori S. New method for the detection of a lethal factor in vibrios. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):339–340. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.339-340.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dongen W. M., De Graaf F. K. Molecular cloning of a gene coding for a Vibrio cholerae haemagglutinin. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Aug;132(8):2225–2234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-8-2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K., Finkelstein R. A. Conjugal transfer of a chromosomal gene determining production of enterotoxin in vibrio cholerae. Science. 1975 Mar 7;187(4179):849–850. doi: 10.1126/science.1114331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S., Levine M. Replication in situ and DNA encapsulation following induction of an excision-defective lysogen of Salmonella bacteriophage P22. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):389–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston L., Drexler H., Richardson S. H. Characterization of vibriophage VA-1. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:155–158. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Al-Omani M., Honda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae hemolysin: purification, partial characterization, and immunological relatedness to El Tor hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.192-196.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ichinose Y., Nakasone N., Tanabe M., Nagahama M., Sakurai J., Iwanaga M. Identity of hemolysins produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and V. cholerae O1, biotype El Tor. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):927–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.927-931.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Mechow S., Vaidya A. B., Bramucci M. G. Mapping of a gene that regulates hemolysin production in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):799–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.799-802.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]