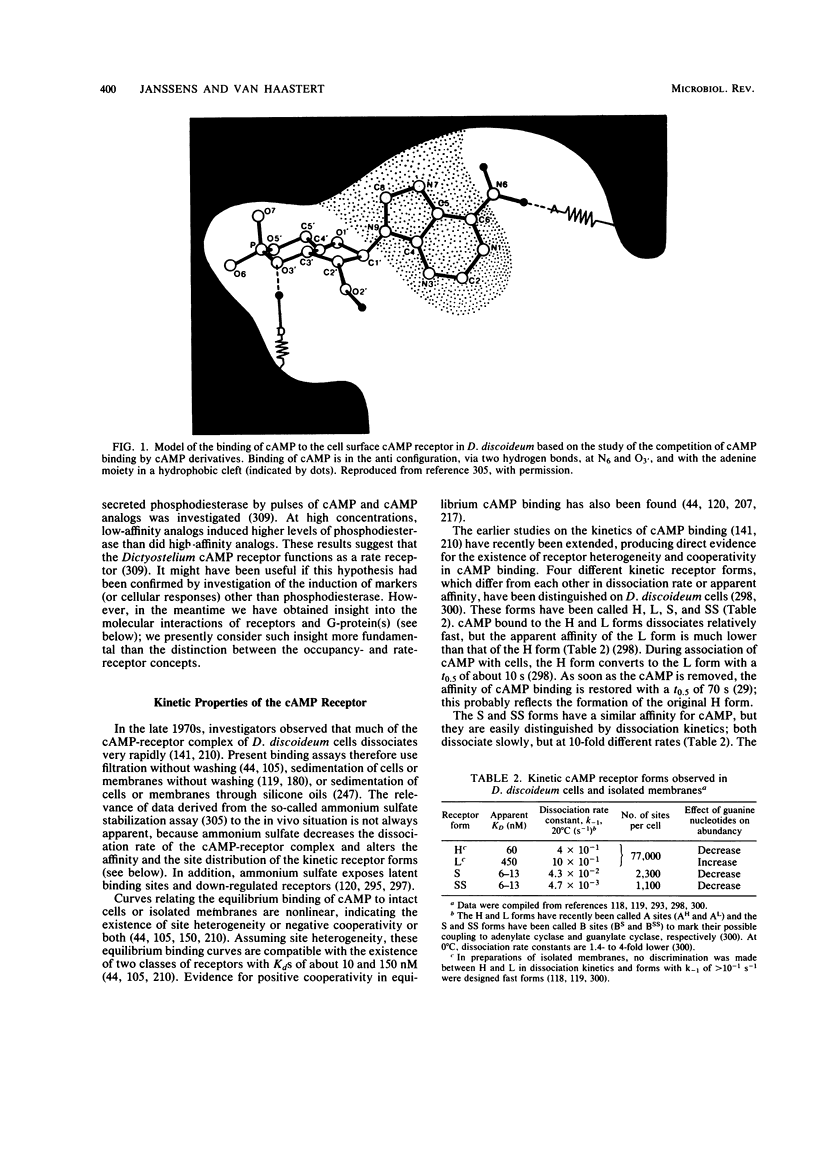
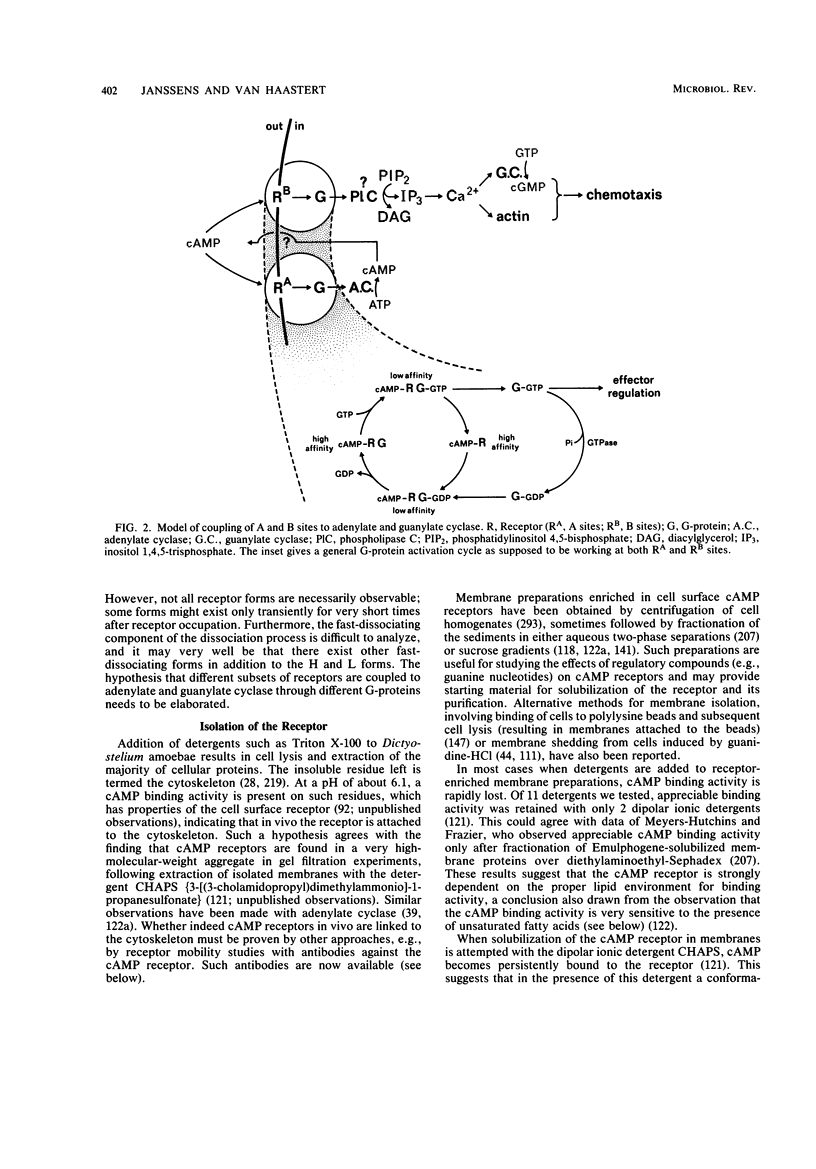
Full text
PDF




















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achar S. B., Weisman R. A. Adenylate cyclase activity during growth and encystment of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 7;629(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aeckerle S., Wurster B., Malchow D. Oscillations and cyclic AMP-induced changes of the K+ concentration in Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):39–43. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcantara F., Monk M. Signal propagation during aggregation in the slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Dec;85(2):321–334. doi: 10.1099/00221287-85-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen H. A., Flodgaard H., Klenow H., Leick V. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates chemotaxis and nucleic acid synthesis in the protozoan Tetrahymena. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 10;782(4):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bigay J., Deterre P., Bockaert J., Homburger V. Tissue expression and phylogenetic appearance of the beta and gamma subunits of GTP binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Sep 9;189(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80830-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay S. L., Henderson E. J. Altered cyclic-AMP receptor activity and morphogenesis in a chemosensory mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1986;33(2):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barclay S. L., Henderson E. J. Thermosensitive development and tip regulation in a mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckner S. K., Hattori S., Shih T. Y. The ras oncogene product p21 is not a regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):71–72. doi: 10.1038/317071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Mayor F., Jr, Somers R. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Light-dependent phosphorylation of rhodopsin by beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):869–872. doi: 10.1038/321869a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Pike L. J., Cerione R. A., Staniszewski C., Yoshimasa T., Codina J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation of the mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Regulation of the rate of receptor phosphorylation and dephosphorylation by agonist occupancy and effects on coupling of the receptor to the stimulatory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7094–7101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Spudich J. A., Devreotes P. N. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in myosin phosphorylation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein R. L., Van Driel R. Control of folate deamine activity of Dictyostelium discoideum by cyclic AMP. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):249–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Cell signalling through phospholipid metabolism. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:137–153. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L., Codina J., Mattera R., Cerione R. A., Hildebrandt J. D., Sunyer T., Rojas F. J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Iyengar R. Regulation of hormone receptors and adenylyl cyclases by guanine nucleotide binding N proteins. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1985;41:41–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571141-8.50006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland W., Marner F. J., Jaenicke L., Müller D. G., Fölster E. Comparative receptor study in gamete chemotaxis of the seaweeds Ectocarpus siliculosus and Cutleria multifida. An approach to interspecific communication of algal gametes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jul 15;134(1):97–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Casperson G. F., Van Dop C., Abood M. E., Beiderman B. B., Steinberg F., Walker N. Mutations of adenylate cyclase in yeast, mouse, and man. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. GTP-binding proteins. One molecular machine can transduce diverse signals. 1986 Jun 26-Jul 2Nature. 321(6073):814–816. doi: 10.1038/321814a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Transducing proteins. Yeast RAS and Tweedledee's logic. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):16–17. doi: 10.1038/317016b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutelet F., Petitjean A., Hilger F. Yeast cdc35 mutants are defective in adenylate cyclase and are allelic with cyr1 mutants while CAS1, a new gene, is involved in the regulation of adenylate cyclase. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2635–2641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzaro S. Cell surface carbohydrates and cell recognition in Dictyostelium. Cell Differ. 1985 Aug;17(2):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(85)90473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Padh H. Forskolin does not activate cyclic AMP synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum in vivo or in vitro. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1983;9(4-5):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M., Thoms S. D. Caffeine blocks activation of cyclic AMP synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1984 Jan;101(1):136–146. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Samiy N., Fasano O., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F., Northup J., Wigler M. Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Levinson W., Spudich J. A. Cytoskeletal elements of chick embryo fibroblasts revealed by detergent extraction. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(2):119–130. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bumann J., Wurster B., Malchow D. Attractant-induced changes and oscillations of the extracellular Ca++ concentration in suspensions of differentiating Dictyostelium cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):173–178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. N., Carlile M. J. Binding of isovaleraldehyde, an attractant, to zoospores of the fungus Phytophthora palmivora in relation to zoospore chemotaxis. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:273–281. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantore M. L., Galvagno M. A., Passeron S. Variations in the levels of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and in the activities of adenylate cyclase and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase during aerobic morphogenesis of Mucor rouxii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Feb;199(2):312–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantore M. L., Passeron S. Kinetic properties, solubilization, and molecular characterization of Mucor rouxii adenylate cyclase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Nov;219(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90127-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Bourne H. R. Isolation of the gene encoding adenylate cyclase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5060–5063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Brasier A. R., Bourne H. R. A guanine nucleotide-sensitive adenylate cyclase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7911–7914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. Y. Cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterase produced by the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1968 Jul 5;161(3836):57–59. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3836.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Bradham L. S., Lynch T. J., Lin Y. M., Tallant E. A. Protein activator of cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of bovine or rat brain also activates its adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiarugi V., Porciatti F., Pasquali F., Bruni P. Transformation of BALB/3T3 cells with EJ/T24/H-ras oncogene inhibits adenylate cyclase response to beta-adrenergic agonist while increases muscarinic receptor dependent hydrolysis of inositol lipids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 15;132(3):900–907. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91892-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chlapowski F. J., Butcher R. W. Activation of adenylate cyclase in Acanthamoeba palestinensis. Life Sci. 1986 Mar 3;38(9):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti-Tronconi B. M., Raftery M. A. The nicotinic cholinergic receptor: correlation of molecular structure with functional properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:491–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coukell M. B., Chan F. K. The precocious appearance and activation of an adenylate cyclase in a rapid developing mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80017-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps M. M., Rutherford C. L. A stage-specific inhibitor of adenylate cyclase in Dictostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jun;133(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler L. S., Rossomando E. F. Localization of adenylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum. II. Cytochemical studies on whole cells and isolated plasma membrane vesicles. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90611-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Silveira J. F., Zingales B., Colli W. Characterization of an adenylyl cyclase activity in particulate preparations from epimastigote forms of Trypanosoma cruzi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 12;481(2):722–733. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90306-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M., Barra J., Brachet P. The role of phosphodiesterase in aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Sci. 1978 Jun;31:233–243. doi: 10.1242/jcs.31.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit R. J., Bulgakov R. Guanine nucleotides modulate the ligand binding properties of cell surface folate receptors in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 7;179(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80530-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit R. J., Bulgakov R., Rinke de Wit T. F., Konijn T. M. Developmental regulation of the pathways of folate-receptor-mediated stimulation of cAMP and cGMP synthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1986;32(3):192–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00573.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit R. J., Snaar-Jagalska B. E. Folate and cAMP modulate GTP binding to isolated membranes of Dictyostelium discoideum. Functional coupling between cell surface receptors and G-proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Wit R. J., van der Velden R. J., Konijn T. M. Characterization of the folic acid C9-N10-cleaving enzyme of Dictyostelium minutum V3. J Bacteriol. 1983 May;154(2):859–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.2.859-863.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M., Koller R., Dhar R. ras-Related gene sequences identified and isolated from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):707–709. doi: 10.1038/306707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Derstine P. L., Steck T. L. Cyclic 3',5' AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum. I. A technique to monitor responses to controlled stimuli. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):291–299. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Sherring J. A. Kinetics and concentration dependence of reversible cAMP-induced modification of the surface cAMP receptor in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6378–6384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Steck T. L. Cyclic 3',5' AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum. II. Requirements for the initiation and termination of the response. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):300–309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N. The effect of folic acid on cAMP-elicited cAMP production in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1983 Jan;95(1):154–162. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., MacKay S. A., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3',5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum III. The relationship of cAMP synthesis and secretion during the cAMP signaling response. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):537–544. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Steck T. L., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3',5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum IV. Recovery of the cAMP signaling response after adaptation to cAMP. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):545–553. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Steck T. L., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3',5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum V. Adaptation of the cAMP signaling response during cAMP stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):554–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenschlos C. D., Paladini A. A., Molina y Vedia L., Torres H. N., Flawiá M. M. Evidence for the existence of an Ns-type regulatory protein in Trypanosoma cruzi membranes. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 1;237(3):913–917. doi: 10.1042/bj2370913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenschlos C., Flawiá M. M., Torruella M., Torres H. N. Interaction of Trypanosoma cruzi adenylate cyclase with liver regulatory factors. Biochem J. 1986 May 15;236(1):185–191. doi: 10.1042/bj2360185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., McClue S. J., Newell P. C. Inhibition of aggregation in Dictyostelium by EGTA-induced depletion of calcium. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1984 Jan;21(1):21–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1984.tb00179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. Calcium transport in the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. Cyclic AMP stimulates accumulation of inositol trisphosphate in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci. 1987 Mar;87(Pt 2):221–229. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. GTP analogues stimulate inositol trisphosphate formation transiently in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci. 1987 May;87(Pt 4):513–518. doi: 10.1242/jcs.87.4.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate induces calcium release from a non- mitochondrial pool in amoebae of Dictyostelium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Aug 1;887(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90163-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and calcium stimulate actin polymerization in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jun;82:41–51. doi: 10.1242/jcs.82.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Europe-Finner G. N., Newell P. C. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate induces cyclic GMP formation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 15;130(3):1115–1122. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91731-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham C. J. Cytochemical localization of adenylate cyclase and 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 1;91(1):36–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90138-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. R., Smith E., Williams K. L. An extracellular chemical signal controlling phototactic behavior by D. discoideum slugs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):799–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90444-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flawiá M. M., Kornblihtt A. R., Reig J. A., Torruella M., Torres H. N. Reconstitution of a hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase with membrane extracts from Neurospora and avian erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8255–8259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke J., Kessin R. A defined minimal medium for axenic strains of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futrelle R. P., Traut J., McKee W. G. Cell behavior in Dictyostelium discoideum: preaggregation response to localized cyclic AMP pulses. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):807–821. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galvin N. J., Stockhausen D., Meyers-Hutchins B. L., Frazier W. A. Association of the cyclic AMP chemotaxis receptor with the detergent-insoluble cytoskeleton of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):584–595. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Van Obberghen E. Protein kinase activity of the insulin receptor. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 1;235(1):1–11. doi: 10.1042/bj2350001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G. Chemotaxis in Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:535–552. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Hess B. Cyclic-AMP-controlled oscillations in suspended Dictyostelium cells: their relation to morphogenetic cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2118–2122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Hülser D., Malchow D., Wick U. Cell communication by periodic cyclic-AMP pulses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 6;272(915):181–192. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Malchow D. Cyclic AMP receptors and the control of cell aggregation in Dictyostelium. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1976;7:49–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Wick U. Intracellular oscillations and release of cyclic AMP from Dictyostelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):364–370. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Codina J., Simons C., Birnbaumer L., Spiegel A. Antisera against a guanine nucleotide binding protein from retina cross-react with the beta subunit of the adenylyl cyclase-associated guanine nucleotide binding proteins, Ns and Ni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):727–731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., McCune R. W. Guanosine 3',5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:1–45. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152815-7.50005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. A., Newell P. C. Evidence for the existence of two types of cAMP binding sites in aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1975 Oct;6(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. E., Thompson G. A., Jr Further studies of dopamine metabolism and function in Tetrahymena. J Protozool. 1985 Feb;32(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1985.tb03008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagmann J. Adenylate cyclase of Dictyostelium discoideum: solubilization and Mn2+-dependency. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1985 May;9(5):491–494. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(85)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haribabu B., Dottin R. P. Pharmacological characterization of cyclic AMP receptors mediating gene regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2402–2408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. J. The cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Binding characteristics of aggregation-competent cells and variation of binding levels during the life cycle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4730–4736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E. J., Ugol H. B., Das O. P. Guanidine hydrochloride-induced shedding of a Dictyostelium discoideum plasma membrane fraction enriched in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 25;690(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90238-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintermann R., Parish R. W. The intracellular location of adenylyl cyclase in the cellular slime molds Dictyostelium discoideum and Polysphondylium pallidum. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 15;123(2):429–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoessli D. C., Rungger-Brändle E. Isolation of plasma membrane domains from murine T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin L. E. Receptors and phosphoinositide-generated second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:205–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchins B. L., Frazier W. A. Purification and characterization of a membrane-associated cAMP-binding protein from developing Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4379–4388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens P. M., van Essen H. W., Guijt J. J., de Waal A., van Driel R. Cell fractionation, detergent sensitivity and solubilization of Dictyostelium adenylate cyclase and guanylate cyclase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1987 Jul;76(1):55–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00219398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssens P. M., van der Geer P. L., Arents J. C., van Driel R. Guanine nucleotides modulate the function of chemotactic cyclic AMP receptors in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 Jul;67(2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02370170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes P. K., McDonough J. P., Mahler H. R. Properties and possible functions of the adenylate cyclase in plasma membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1481–1491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to Saccharomyces cerevisiae a cells: dissociation constant and number of binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):318–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jett M., Seed T. M., Jamieson G. A. Isolation and characterization of plasma membranes and intact nuclei from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2134–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josefsson J. O., Johansson P. Naloxone-reversible effect of opioids on pinocytosis in Amoeba proteus. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):78–80. doi: 10.1038/282078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliani M. H., Klein C. Calcium ion effects on cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate bindings to the plasma membrane of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Apr 27;497(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliani M. H., Klein C. Photoaffinity labeling of the cell surface adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum and its modification in down-regulated cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Miyajima A., Arai K., Matsumoto K. Possible involvement of RAS-encoded proteins in glucose-induced inositolphospholipid turnover in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8172–8176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakiuchi S., Sobue K., Yamazaki R., Nagao S., Umeki S., Nozawa Y., Yazawa M., Yagi K. Ca2+-dependent modulator proteins from Tetrahymena pyriformis, sea anemone, and scallop and guanylate cyclase activation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S. Folic acid increases the cAMP binding activity of Dictyostelium discoideum cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):27–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81303-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S. Induction of cAMP receptors by disaggregation of the multicellular complexes of Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Mar;126(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90480-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Phosphorylation of rhodopsin by protein kinase C in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4749–4757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessin R. H., Orlow S. J., Shapiro R. I., Franke J. Binding of inhibitor alters kinetic and physical properties of extracellular cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5450–5454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachatrian L., Howlett A., Klein C. Guanine nucleotide inhibition of adenylate cyclase in a membrane fraction from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(2):179–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Frazier W. A. Properties of the oscillatory cAMP binding component of Dictyostelium discoideum cells and isolated plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7168–7176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Bhalla D. K., Dragsten P., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J. Model for capping derived from inhibition of surface receptor capping by free fatty acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):437–441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Kleinfeld A. M., Hoover R. L., Karnovsky M. J. Lipid domains in membranes. Evidence derived from structural perturbations induced by free fatty acids and lifetime heterogeneity analysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1286–1295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. A slowly dissociating form of the cell surface cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12573–12578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. Adenylate cyclase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae and its changes during differentiation. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80419-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. Binding of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate to plasma membranes of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10050–10053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Brachet P., Darmon M. Periodic changes in adenylate cyclase and cAMP receptors in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):145–147. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80140-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Darmon M. Effects of cyclic AMP pulses on adenylate cyclase and the phosphodiesterase inhibitor of D. discoideum. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):76–78. doi: 10.1038/268076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C. Induction of phosphodiesterase by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7134–7138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Juliani M. H. cAMP,-induced changes in cAMP-binding sites on D; discoideum amebae. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Lubs-Haukeness J., Simons S. cAMP induces a rapid and reversible modification of the chemotactic receptor in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):715–720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Sadeghi H., Simons S. Immunological analyses of the chemotactic receptor of Dictyosteleum discoideum. Identification of cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15192–15196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Knox B., Borleis J., Devreotes P. Purification of the surface cAMP receptor in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):352–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Theibert A., Fontana D., Devreotes P. N. Identification and cyclic AMP-induced modification of the cyclic AMP receptor in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1757–1764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P., Vaughan R., Borleis J., Devreotes P. The surface cyclic AMP receptor in Dictyostelium. Levels of ligand-induced phosphorylation, solubilization, identification of primary transcript, and developmental regulation of expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klumpp S., Kleefeld G., Schultz J. E. Calcium/calmodulin-regulated guanylate cyclase of the excitable ciliary membrane from Paramecium. Dissociation of calmodulin by La3+: calmodulin specificity and properties of the reconstituted guanylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12455–12459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox B. E., Devreotes P. N., Goldbeter A., Segel L. A. A molecular mechanism for sensory adaptation based on ligand-induced receptor modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2345–2349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP as a first messenger. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1972;1:17–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M., Van De Meene J. G., Bonner J. T., Barkley D. S. The acrasin activity of adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1152–1154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr Biochemistry of sensing and adaptation in a simple bacterial system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:765–782. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Ui M. Dual pathways of receptor-mediated cyclic GMP generation in NG108-15 cells as differentiated by susceptibility to islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 May 1;238(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Roberts C., Jr, Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Receptors for intercellular messenger molecules in microbes: similarities to vertebrate receptors and possible implications for diseases in man. Experientia. 1986 Jul 15;42(7):782–788. doi: 10.1007/BF01941525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Cotecchia S., Lomasney J. W., DeBernardis J. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Phorbol esters promote alpha 1-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation and receptor uncoupling from inositol phospholipid metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5651–5655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leichtling B. H., Coffman D. S., Yaeger E. S., Rickenberg H. V., al-Jumaliy W., Haley B. E. Occurrence of the adenylate cyclase "G protein" in membranes of Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Oct 30;102(4):1187–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levandowsky M., Hauser D. C. Chemosensory responses of swimming algae and protozoa. Int Rev Cytol. 1978;53:145–210. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. Regulation of phosphoinositide breakdown by guanine nucleotides. Life Sci. 1986 Jul 21;39(3):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90529-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Klein C., Brachet P. The effect of divalent cations on aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1978;12(2):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb00993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loumaye E., Thorner J., Catt K. J. Yeast mating pheromone activates mammalian gonadotrophs: evolutionary conservation of a reproductive hormone? Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1323–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6293058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs-Haukeness J., Klein C. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent phosphorylation in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12204–12208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Gerisch G. Vesicle formation in Dictyostelium discoideum cells during oscillations of cAMP synthesis and release. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Nov;110(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Böhme R., Gras U. On the role of calcium in chemotaxis and oscillations of dictyostelium cells. Biophys Struct Mech. 1982;9(2):131–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00539112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Böhme R., Rahmsdorf H. J. Regulation of phosphorylation of myosin heavy chain during the chemotactic response of Dictyostelium cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Gerisch G. Cyclic AMP binding to living cells of Dictyostelium discoideum in presence of excess cyclic GMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Nov 1;55(1):200–204. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80079-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Nanjundiah V., Gerisch G. PH oscillations in cell suspensions of Dictyostelium discoideum: their relation to cyclic-amp signals. J Cell Sci. 1978 Apr;30:319–330. doi: 10.1242/jcs.30.1.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Nanjundiah V., Wurster B., Eckstein F., Gerisch G. Cyclic AMP-induced pH changes in Dictyostelium discoideum and their control by calcium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Feb 1;538(3):473–480. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90408-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Nägele B., Schwarz H., Gerisch G. Membrane-bound cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in chemotactically responding cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jun 23;28(1):136–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marin F. T., Rothman F. G. Regulation of development in Dictyostelium discoideum. IV. Effects of ions on the rate of differentiation and cellular response to cyclic AMP. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):823–827. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin B. R., Voorheis H. P., Kennedy E. L. Adenylate cyclase in bloodstream forms of Trypanosoma (Trypanozoon) brucei sp. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):207–212. doi: 10.1042/bj1750207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Baltes W., Dieter P., Marmé D., Gerisch G. Myosin heavy chain kinase inactivated by Ca2+/calmodulin from aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):535–542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. W., Rasmussen H., Dibella F. 3'5' AMP and Ca 2+ in slime mold aggregation. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):156–160. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90631-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M. Activation of Dictyostelium discoideum guanylate cyclase by ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Jastorff B., Morr M., Konijn T. M. A model for cyclic AMP-chemoreceptor interaction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 1;544(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Konijn T. M. Chemotaxis and binding of cyclic AMP in cellular slime molds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 7;385(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Konijn T. M. The chemotactic of cyclic AMP and AMP derivatives with substitutions in the phosphate moiety in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Krens F. A., van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. 3':5'-cyclic AMP-dependent 3':5'-cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2348–2351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Malchow D. Guanylate cyclase activation in response to chemotactic stimulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 1;90(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80311-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Marín-Cao D. Protein and phospholipid methylation during chemotaxis in Dictyostelium discoideum and its relationship to calcium movements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6106–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Rhijnsburger E. H., Dobbe F. C., Konijn T. M. Cyclic AMP and folic acid mediated cyclic GMP accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):331–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80814-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Woelders H., van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. Cyclic GMP binding activity in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jun 15;90(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Konijn T. M. Chemotaxis in Dictyostelium discoideum: effect of concanavalin A on chemoattractant mediated cyclic gmp accumulation anlight scattering decrease. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Mar;2(2):163–170. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. A new model for chemotactic signal transduction in Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):1076–1083. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80243-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. Changes in actin associated with the cytoskeleton following chemotactic stimulation of dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. Chemoattractant-mediated changes in cytoskeletal actin of cellular slime moulds. J Cell Sci. 1984 Jun;68:139–151. doi: 10.1242/jcs.68.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkle R. K., Rutherford C. L. Localization of adenylate cyclase during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullens I. A., Newell P. C. cAMP binding to cell surface receptors of Dictyostelium. Differentiation. 1978 May 26;10(3):171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1978.tb00960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murad F., Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Braughler J. M. Properties and regulation of guanylate cyclase and some proposed functions for cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;11:175–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Kudo S., Nozawa Y. Inhibitory effects of calmodulin antagonists on plasma membrane cyclases in Tetrahymena: calmodulin-dependent guanylate cyclase and calmodulin-independent adenylate cyclase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 1;32(17):2501–2504. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandini-Kishore S. G., Frazier W. A. [3H]Methotrexate as a ligand for the folate receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Kaibuchi K. Phospholipid turnover in hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1984;40:301–345. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571140-1.50012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The detertent-resistant cytoskeleton of tissue culture cells includes the nucleus and the microfilament bundles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte A. P., Plomp M. J., Arents J. C., Janssens P. M., van Driel R. Production and turnover of cAMP signals by prestalk and prespore cells in Dictyostelium discoideum cell aggregates. Differentiation. 1986;32(3):185–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama M., Blumberg D. D. Interaction of cAMP with the cell-surface receptor induces cell-type-specific mRNA accumulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padh H., Brenner M. Studies of the guanylate cyclase of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 15;229(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padh H., Brenner M. The role of enzyme sequestration in the regulation of the adenylate cyclase of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3613–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahlic M., Rutherford C. L. Adenylate cyclase activity and cyclic AMP levels during the development of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9703–9707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Adenosine 3',5'-phosphate in fungi. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):462–480. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.462-480.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Determination of the active portion of the folic acid molecule in cellular slime mold chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.185-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Folic acid as second chemotactic substance in the cellular slime moulds. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jun 7;237(75):181–182. doi: 10.1038/newbio237181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Wurster B. Inactivation of the chemoattractant folic acid by cellular slime molds and identification of the reaction product. J Bacteriol. 1978 Dec;136(3):955–959. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.3.955-959.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannbacker R. G., Bravard L. J. Phosphodiesterase in Dictyostelium discoideum and the chemotactic response to cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science. 1972 Mar 3;175(4025):1014–1015. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4025.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish R. W. Plasma membrane proteins in Dictyostelium. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;50(1):75–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00225281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Amiel T., Hinze E., Auersperg N., Neave N., Sobolewski A., Weeks G. Regulation of a ras-related protein during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):33–39. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash K., Seligy V. L. Oncogene related sequences in fungi: linkage of some to actin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):293–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91874-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Cyclic AMP-induced phosphorylation in Dictyostelium of a polypeptide comigrating with myosin heavy chains. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):322–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reig J. A., Kornblihtt A. R., Flawiá M. M., Torres H. N. Soluble adenylate cyclase activity in Neurospora crassa. Biochem J. 1982 Oct 1;207(1):43–49. doi: 10.1042/bj2070043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart M. F., Sebastián J., Mato J. M. Adenylate cyclase activity in permeabilized cells from Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1981 Nov;5(11):1045–1054. doi: 10.1016/s0309-1651(81)80032-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Nellen W., Theibert A., Devreotes P., Firtel R. A. Phenotypic changes induced by a mutated ras gene during the development of Dictyostelium transformants. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):340–343. doi: 10.1038/323340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Nellen W., Firtel R. A. Regulated expression of ras gene constructs in Dictyostelium transformants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7005–7009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhamsdorf H. J. A defined, synthetic growth medium for Dictyostelium discoideum, strain Ax-2. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 Apr;358(4):527–529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel V., Malchow D., Gerisch G., Nägele B. Cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase interaction with its inhibitor of the slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):279–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90660-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. D., Grutsch J. F. Aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90087-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roof D. J., Applebury M. L., Sternweis P. C. Relationships within the family of GTP-binding proteins isolated from bovine central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16242–16249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W., Gerisch G. Receptor-mediated adenylate cyclase activation in Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 1;68(2):170–172. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80429-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Adenylyl cyclase and the control of cell differentiation in Dictyostelium dicoideum. Cell Differ. 1977 Oct;6(3-4):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(77)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W., Nanjundiah V., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Amplification of cyclic-AMP signals in aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos W., Scheidegger C., Gerish G. Adenylate cyclase activity oscillations as signals for cell aggregation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):259–261. doi: 10.1038/266259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. B., Pall M. L. Characterization of an ATP-Mg2+-dependent guanine nucleotide-stimulated adenylate cyclase from Neurospora crassa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. B., Pall M. L. Reconstitution of adenylate cyclase in Neurospora from two components of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Feb 15;221(1):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross F. M., Newell P. C. Genetics of aggregation pattern mutations in the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Dec;115(2):289–300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross F. M., Newell P. C. Streamers: chemotactic mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum with altered cyclic GMP metabolism. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):339–350. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M. Effect of extracellular Ca2+ on the morphogenesis of Dictyostelium discoideum. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., Wang M. Interactions between adenosine and oscillatory cAMP signaling regulate size and pattern in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90545-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., Wang M. The possible involvement of oscillatory cAMP signaling in multicellular morphogenesis of the cellular slime molds. Dev Biol. 1984 Oct;105(2):470–478. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap P., van Driel R. V. Induction of post-aggregative differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum by cAMP. Evidence of involvement of the cell surface cAMP receptor. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Aug;159(2):388–398. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Selinger Z. Message transmission: receptor controlled adenylate cyclase system. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1350–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.6147897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. E., Klumpp S. Calcium/calmodulin-regulated guanylate cyclases in the ciliary membranes from Paramecium and tetrahymena. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:275–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel L. A., Goldbeter A., Devreotes P. N., Knox B. E. A mechanism for exact sensory adaptation based on receptor modification. J Theor Biol. 1986 May 21;120(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80171-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe P. T., Watts D. J. The role of the cell cycle in differentiation of the cellular slime mould Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biochem. 1985 May;67(1):3–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00220979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimomura O., Suthers H. L., Bonner J. T. Chemical identity of the acrasin of the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium violaceum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7376–7379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinitzky M., Souroujon M. Passive modulation of blood-group antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4438–4440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Molecular mechanisms of receptor desensitization using the beta-adrenergic receptor-coupled adenylate cyclase system as a model. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):124–129. doi: 10.1038/317124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small N. V., Europe-Firmer G. N., Newell P. C. Calcium induces cyclic GMP formation in Dictyostelium. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jul 14;203(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser R. H., Sibley D. R., Lefkowitz R. J. A novel catecholamine-activated adenosine cyclic 3',5'-phosphate independent pathway for beta-adrenergic receptor phosphorylation in wild-type and mutant S49 lymphoma cells: mechanism of homologous desensitization of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1371–1377. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman R., Sussman M. Cultivation of Dictyostelium discoideum in axenic medium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Oct 11;29(1):53–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90539-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A., Devreotes P. N. Adenosine and its derivatives inhibit the cAMP signaling response in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1984 Nov;106(1):166–173. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3', 5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum: adaptation is independent of activation of adenylate cyclase. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):173–177. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A., Devreotes P. N. Surface receptor-mediated activation of adenylate cyclase in Dictyostelium. Regulation by guanine nucleotides in wild-type cells and aggregation deficient mutants. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15121–15125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A., Klein P., Devreotes P. N. Specific photoaffinity labeling of the cAMP surface receptor in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12318–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theibert A., Palmisano M., Jastorff B., Devreotes P. The specificity of the cAMP receptor mediating activation of adenylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1986 Apr;114(2):529–533. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomchik K. J., Devreotes P. N. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate waves in Dictyostelium discoideum: a demonstration by isotope dilution--fluorography. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.6259734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Town C., Stanford E. An oligosaccharide-containing factor that induces cell differentiation in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Mitsuzawa H., Matsumoto K., Tanaka K., Oshima T., Ishikawa T. Reconstitution of the GTP-dependent adenylate cyclase from products of the yeast CYR1 and RAS2 genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel R. Binding of the chemoattractant folic acid by Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):391–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05250.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Alteration of receptor/G-protein interaction by putative endogenous protein kinase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3239–3243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Binding of cAMP and adenosine derivatives to Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Relationships of binding, chemotactic, and antagonistic activities. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9643–9648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J. Demonstration of receptor heterogeneity and affinity modulation by nonequilibrium binding experiments. The cell surface cAMP receptor of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13321–13328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J., Grijpma Y., Konijn T. M. Identification of a pterin as the acrasin of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium lacteum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6270–6274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J., Van Lookeren Campagne M. M. Ca2+- or phorbol ester- dependent effect of ATP on a subpopulation of cAMP cell-surface receptors in membranes from D. discoideum. A role for protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91662-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Dijkgraaf P. A., Konijn T. M., Abbad E. G., Petridis G., Jastorff B. Substrate specificity of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from beef heart and from Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Apr 5;131(3):659–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Down-regulation of cell surface cyclic AMP receptors and desensitization of cyclic AMP-stimulated adenylate cyclase by cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Kinetics and concentration dependence. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7700–7704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Guanine nucleotides modulate cell surface cAMP-binding sites in membranes from Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):597–604. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91596-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Jastorff B., Pinas J. E., Konijn T. M. Analogs of cyclic AMP as chemoattractants and inhibitors of Dictyostelium chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):99–105. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.99-105.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Kesbeke F., Reymond C. D., Firtel R. A., Luderus E., Van Driel R. Aberrant transmembrane signal transduction in Dictyostelium cells expressing a mutated ras gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4905–4909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Kien E. Binding of cAMP derivatives to Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Activation mechanism of the cell surface cAMP receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9636–9642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Relationship between adaptation of the folic acid and the cAMP mediated cGMP response in Dictyostelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):130–136. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90979-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. Sensory adaptation of Dictyostelium discoideum cells to chemotactic signals. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1559–1565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Snaar-Jagalska B. E., Janssens P. M. The regulation of adenylate cyclase by guanine nucleotides in Dictyostelium discoideum membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jan 15;162(2):251–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10592.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J. The modulation of cell surface cAMP receptors from Dictyostelium discoideum by ammonium sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 May 30;845(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van Der Meer R. C., Konijn T. M. Evidence that the rate of association of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate to its chemotactic receptor induces phosphodiesterase activity in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jul;147(1):170–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.1.170-175.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van Walsum H., Pasveer F. J. Nonequilibrium kinetics of a cyclic GMP-binding protein in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):271–278. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haastert P. J., Van der Heijden P. R. Excitation, adaptation, and deadaptation of the cAMP-mediated cGMP response in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):347–353. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorheis H. P., Martin B. R. 'Swell dialysis' demonstrates that adenylate cyclase in Trypanosoma brucei is regulated by calcium ions. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Dec;113(1):223–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorheis H. P., Martin B. R. Characteristics of the calcium-mediated mechanism activating adenylate cyclase in Trypanosoma brucei. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun 1;116(3):471–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Frazier W. A. Photoaffinity labeling of cyclic-AMP- and AMP-binding proteins differentiating Dictyostelium discoideum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4250–4254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R. D., Slutzky G. M., Greenblatt C. L. Effect of leishmanial excreted factor on the activities of adenylate cyclase from hamster liver and Leishmania tropica. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1982 Sep;33(3):137–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A., Brenner M. Guanylate cyclase from Dictyostelium discoideum. Life Sci. 1977 Oct 1;21(7):997–1008. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks G. The manipulation of the fatty acid composition of Dictyostelium discoideum and its effect on cell differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 21;450(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weijer C. J., Durston A. J. Influence of cyclic AMP and hydrolysis products on cell type regulation in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Apr;86:19–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick U., Malchow D., Gerisch G. Cyclic-AMP stimulated calcium influx into aggregating cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Jan;2(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Wilson J., Hames B. D. Spore coat protein synthesis during development of Dictyostelium discoideum requires a low-molecular-weight inducer and continued multicellularity. Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;107(1):38–46. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Bek F., Butz U. Folic acid and pterin deaminases in Dictyostelium discoideum: kinetic properties and regulation by folic acid, pterin, and adenosine 3',5'-phosphate. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):183–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.183-192.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Bozzaro S., Gerisch G. Cyclic GMP regulation and responses of Polysphondylium violaceum to chemoattractants. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Jan;2(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90085-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Butz U. A study on sensing and adaptation in Dictyostelium discoideum: guanosine 3',5'-phosphate accumulation and light-scattering responses. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1566–1570. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Butz U. Reversible binding of the chemoattractant folic acid to cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):613–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Schubiger K., Brachet P. Cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP changes in response to folic acid pulses during cell development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Differ. 1979 Jun;8(3):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(79)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Schubiger K. Oscillations and cell development in Dictyostelium discoideum stimulated by folic acid pulses. J Cell Sci. 1977;27:105–114. doi: 10.1242/jcs.27.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Schubiger K., Wick U., Gerisch G. Cyclic GMP in Dictyostelium discoideum, Oscillations and pulses in response to folic acid and cyclic AMP signals. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 15;76(2):141–144. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80139-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager R. E., Heideman W., Rosenberg G. B., Storm D. R. Purification of the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase from bovine cerebral cortex. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3776–3783. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh R. P., Chan F. K., Coukell M. B. Independent regulation of the extracellular cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase-inhibitor system and membrane differentiation by exogenous cyclic AMP in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1978 Oct;66(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Castro S. L., Oliveira M. M. Radioligand binding characterization of beta-adrenergic receptors in the protozoa Trypanosoma cruzi. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1987;87(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0742-8413(87)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Gunzburg J., Véron M., Brachet P. Non-michaelian kinetics of adenylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1980 Jun;4(6):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(80)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. Identification of the acrasin of Dictyostelium minutum as a derivative of folic acid. Cell Differ. 1983 Apr;12(4):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(83)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., De Wit R. J., Konijn T. M. Antagonists of chemoattractants reveal separate receptors for cAMP, folic acid and pterin in Dictyostelium. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Aug;140(2):453–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., Konijn T. M. Signal transduction in the cellular slime molds. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1982 Apr;26(1-2):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(82)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J. cAMP activates adenylate and guanylate cyclase of Dictyostelium discoideum cells by binding to different classes of cell-surface receptors. A study with extracellular Ca2+. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Sep 30;846(3):324–333. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., de Wit R. J., Janssens P. M., Kesbeke F., DeGoede J. G-protein-mediated interconversions of cell-surface cAMP receptors and their involvement in excitation and desensitization of guanylate cyclase in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6904–6911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haastert P. J., van Lookeren Campagne M. M., Ross F. M. Altered cGMP-phosphodiesterase activity in chemotactic mutants of Dictyostelium discoideum. FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 18;147(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ophem P., van Driel R. Induction by folate and folate analogs of extracellular and membrane-bound phosphodiesterase from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):143–146. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.143-146.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Waarde A. Rapid, transient methylation of four proteins in aggregative amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum as a response to stimulation with cyclic AMP. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 29;149(2):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81114-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


