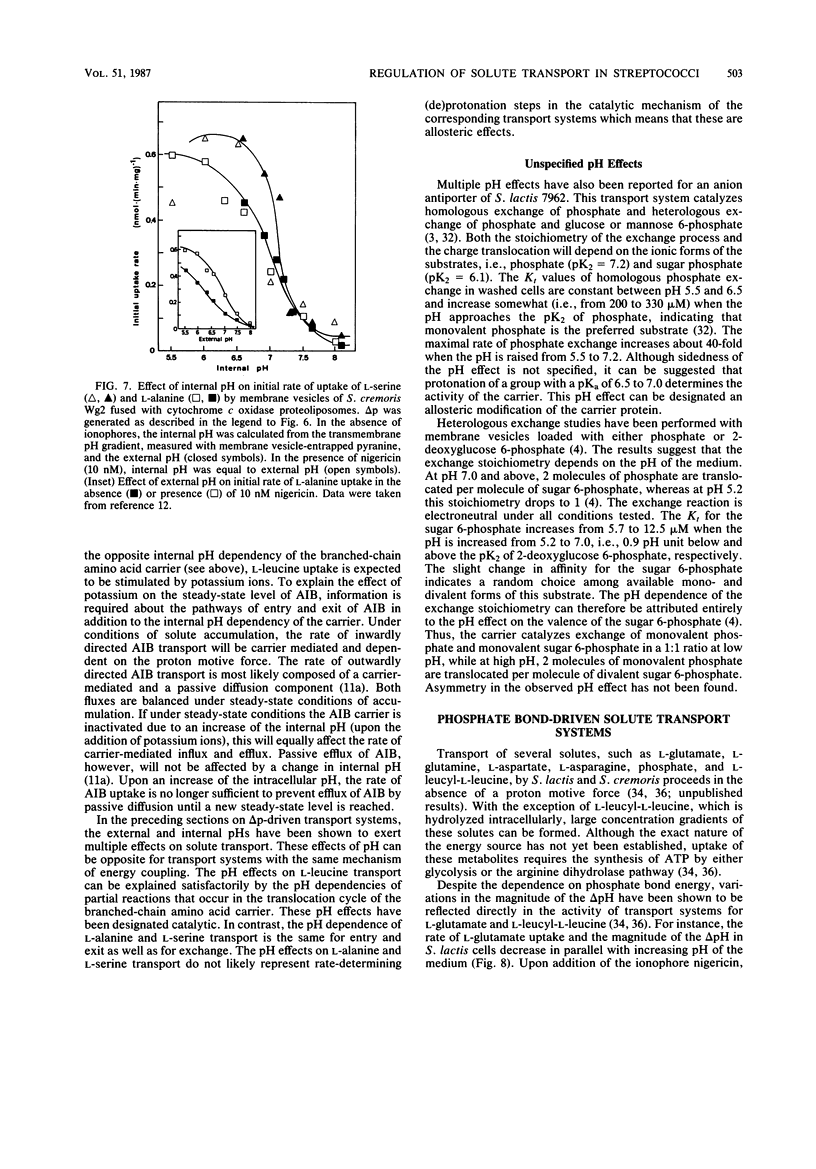
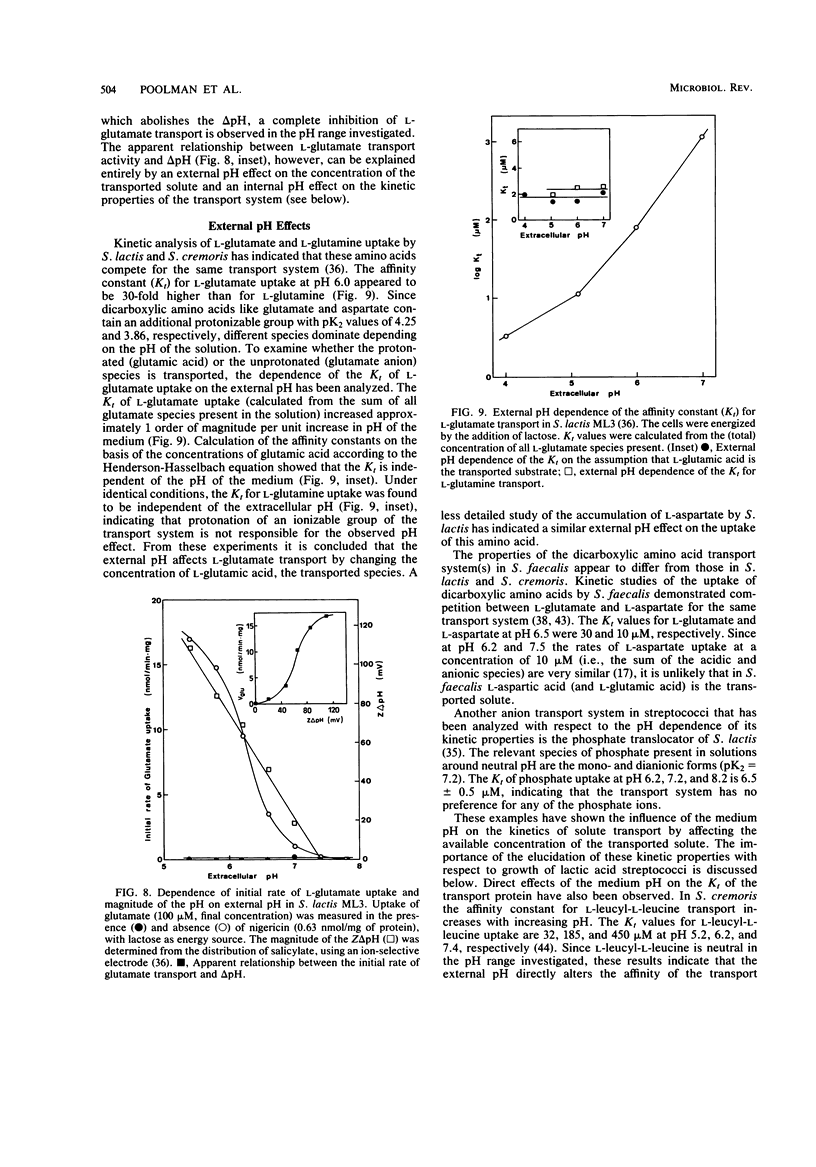
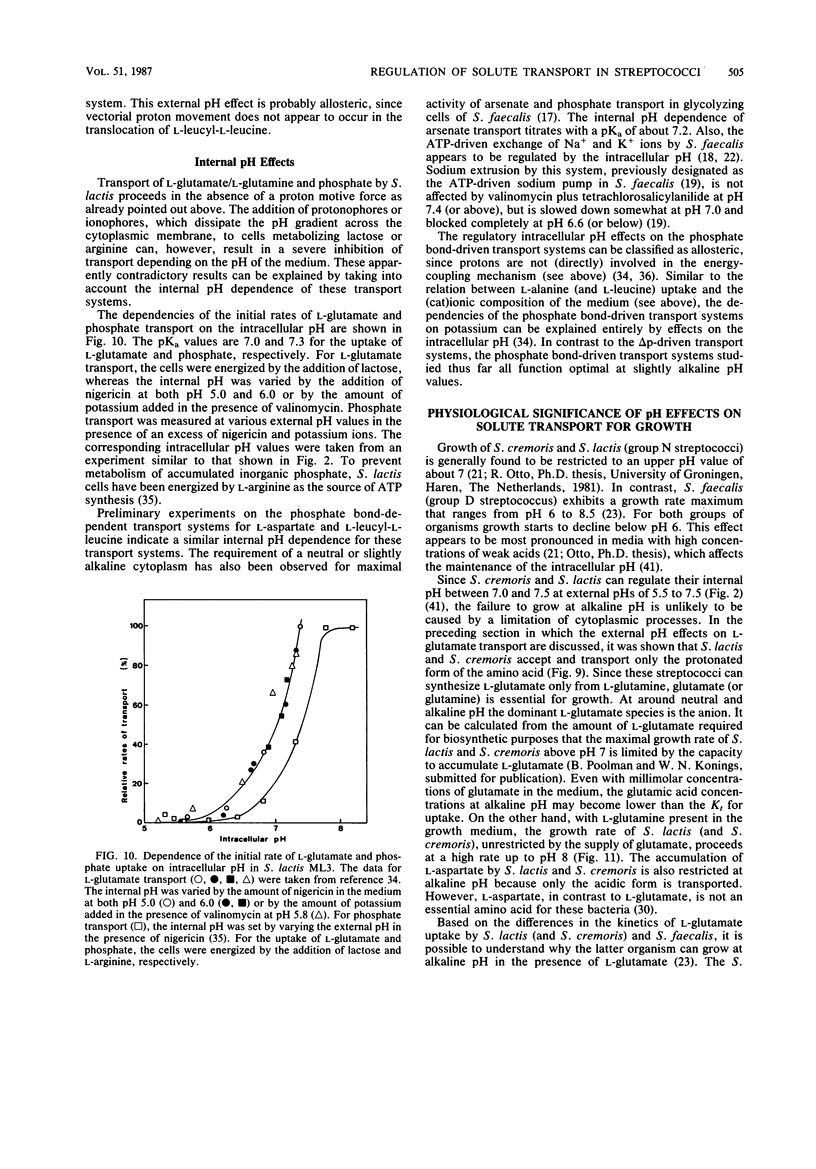
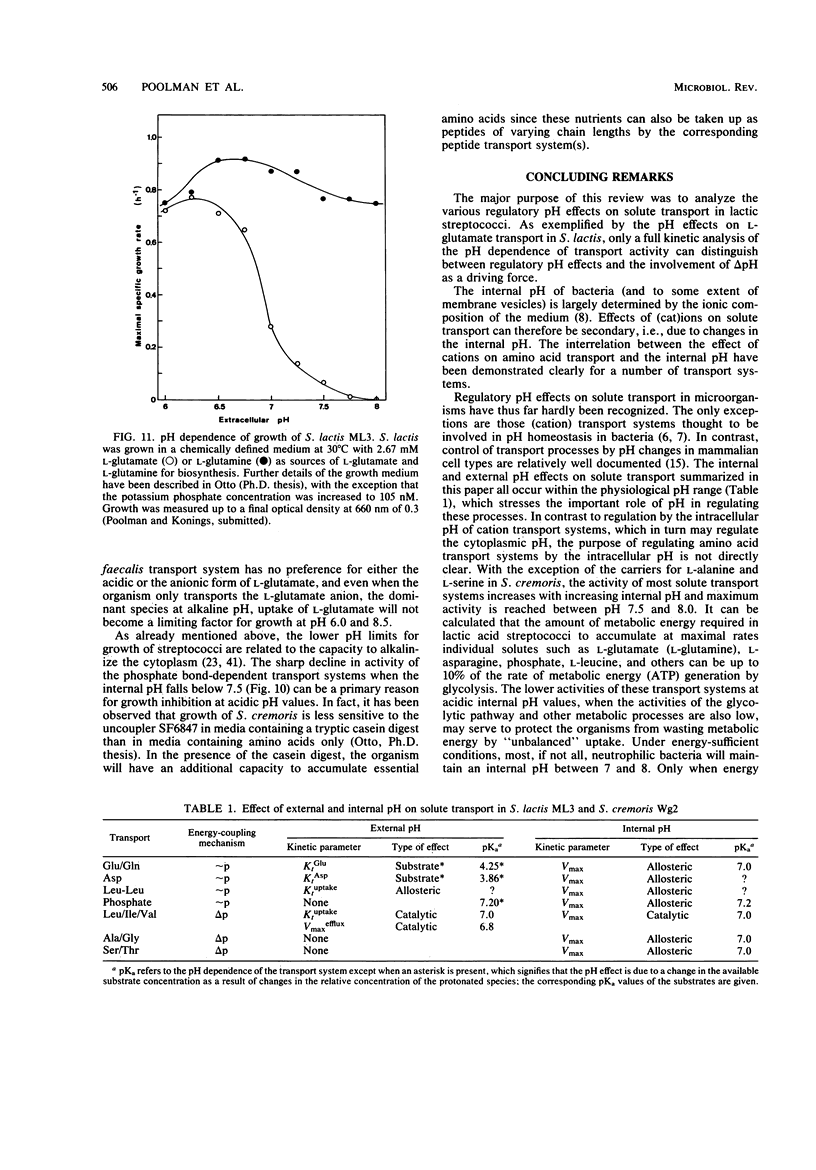
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. Quantitative measurements of the proton-motive force and its relation to steady state lactose accumulation in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):573–581. doi: 10.1042/bj2000573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed S., Booth I. R. The effects of partial and selective reduction in the components of the proton-motive force on lactose uptake in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):583–589. doi: 10.1042/bj2000583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar S. V., Maloney P. C. Characterization of phosphate:hexose 6-phosphate antiport in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12576–12585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambudkar S. V., Sonna L. A., Maloney P. C. Variable stoichiometry of phosphate-linked anion exchange in Streptococcus lactis: implications for the mechanism of sugar phosphate transport by bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):280–284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. The effects of weak acids on potassium uptake by Escherichia coli K-12 inhibition by low cytoplasmic pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 5;730(2):379–386. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90355-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Mechanism of energy coupling to entry and exit of neutral and branched chain amino acids in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12438–12443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Kodde J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Neutral amino acid transport by membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris is subject to regulation by internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2748-2754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Poolman B., Kiewiet R., Konings W. Arginine transport in Streptococcus lactis is catalyzed by a cationic exchanger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6093–6097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Transport of branched-chain amino acids in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5193–5200. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5193-5200.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Vrij W., Konings W. N. Functional incorporation of beef-heart cytochrome c oxidase into membranes of Streptococcus cremoris. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):617–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., de Vrij W., Konings W. N. Incorporation of beef heart cytochrome c oxidase as a proton-motive force-generating mechanism in bacterial membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elferink M. G., Friedberg I., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. The role of the proton-motive force and electron flow in light-driven solute transport in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 1;129(3):583–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Solioz M. The vanadate-sensitive ATPase of Streptococcus faecalis pumps potassium in a reconstituted system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4302–4308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Goetz J. D., Cohen S., Rothstein A., Gelfand E. W. Regulation of Na+/H+ exchange in lymphocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;456:207–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb14866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Spitz E. Accumulation of arsenate, phosphate, and aspartate by Sreptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):266–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.266-277.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Harold F. M. ATP-driven sodium pump in Streptococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2798–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heefner D. L., Harold F. M. ATP-linked sodium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. I. The sodium circulation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11396–11402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Friedberg I., Lolkema J. S., Michels P. A., Konings W. N. Energy coupling of facilitated transport of inorganic ions in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1183-1191.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugenholtz J., Splint R., Konings W. N., Veldkamp H. Selection of Protease-Positive and Protease-Negative Variants of Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Feb;53(2):309–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.2.309-314.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakinuma Y., Harold F. M. ATP-driven exchange of Na+ and K+ ions by Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2086–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H. A proton-translocating ATPase regulates pH of the bacterial cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):72–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Murakami N., Unemoto T. Regulation of the cytoplasmic pH in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13246–13252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Suzuki T., Kinoshita N., Unemoto T. Amplification of the Streptococcus faecalis proton-translocating ATPase by a decrease in cytoplasmic pH. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1157–1160. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1157-1160.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Suzuki T., Unemoto T. Streptococcal cytoplasmic pH is regulated by changes in amount and activity of a proton-translocating ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):627–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Van Brunt J., Harold F. M. ATP-linked calcium transport in cells and membrane vesicles of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2085–2092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll R. G., Booth I. R. The relationship between intracellular pH, the pH gradient and potassium transport in Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):709–716. doi: 10.1042/bj2160709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C., Ambudkar S. V., Thomas J., Schiller L. Phosphate/hexose 6-phosphate antiport in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):238–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.238-245.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney P. C. Relationship between phosphorylation potential and electrochemical H+ gradient during glycolysis in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Mar;153(3):1461–1470. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.3.1461-1470.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of arginine-ornithine exchange and the arginine deiminase pathway in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5597–5604. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5597-5604.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of the glutamate-glutamine transport system by intracellular pH in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2272–2276. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2272-2276.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Nijssen R. M., Konings W. N. Dependence of Streptococcus lactis phosphate transport on internal phosphate concentration and internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5373–5378. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5373-5378.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Konings W. N. Kinetic properties of a phosphate-bond-driven glutamate-glutamine transport system in Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2755–2761. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2755-2761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. The electrochemical gradient of protons and its relationship to active transport in Escherichia coli membrane vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid K. G., Utech N. M., Holden J. T. Multiple transport components for dicarboxylic amino acids in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5261–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. E., Kaczorowski G. J., Garcia M. L., Kaback H. R. Active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli: the electrochemical proton gradient alters the distribution of the lac carrier between two different kinetic states. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5692–5702. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Keach D. Energy-dependent arsenate efflux: the mechanism of plasmid-mediated resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Characteristics and energy requirements of an alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport system in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):719–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.719-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utech N. M., Reid K. G., Holden J. T. Properties of a dicarboxylic amino acid transport-deficient mutant of Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Oct 25;245(20):5273–5280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Brink B., Otto R., Hansen U. P., Konings W. N. Energy recycling by lactate efflux in growing and nongrowing cells of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):383–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.383-390.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Boven A., Konings W. N. A Phosphate-Bond-Driven Dipeptide Transport System in Streptococcus cremoris Is Regulated by the Internal pH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2897–2902. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2897-2902.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



