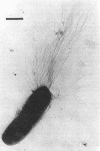
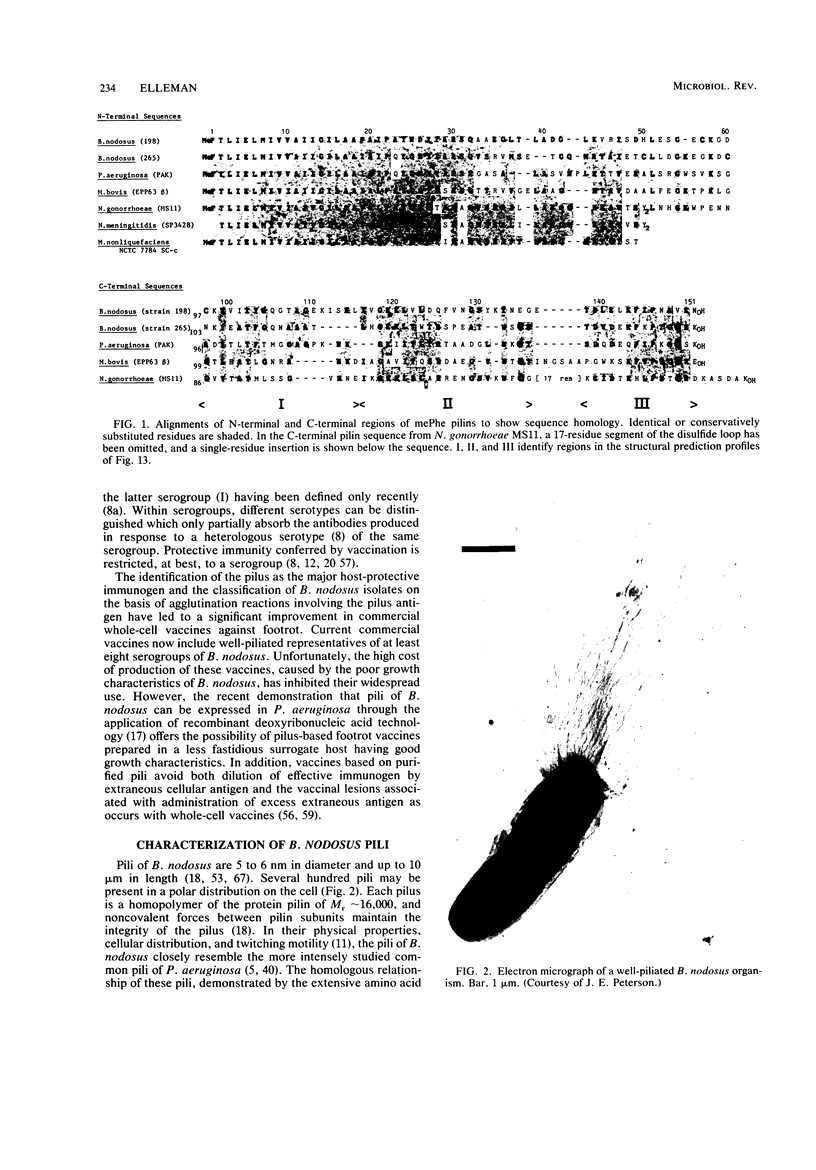
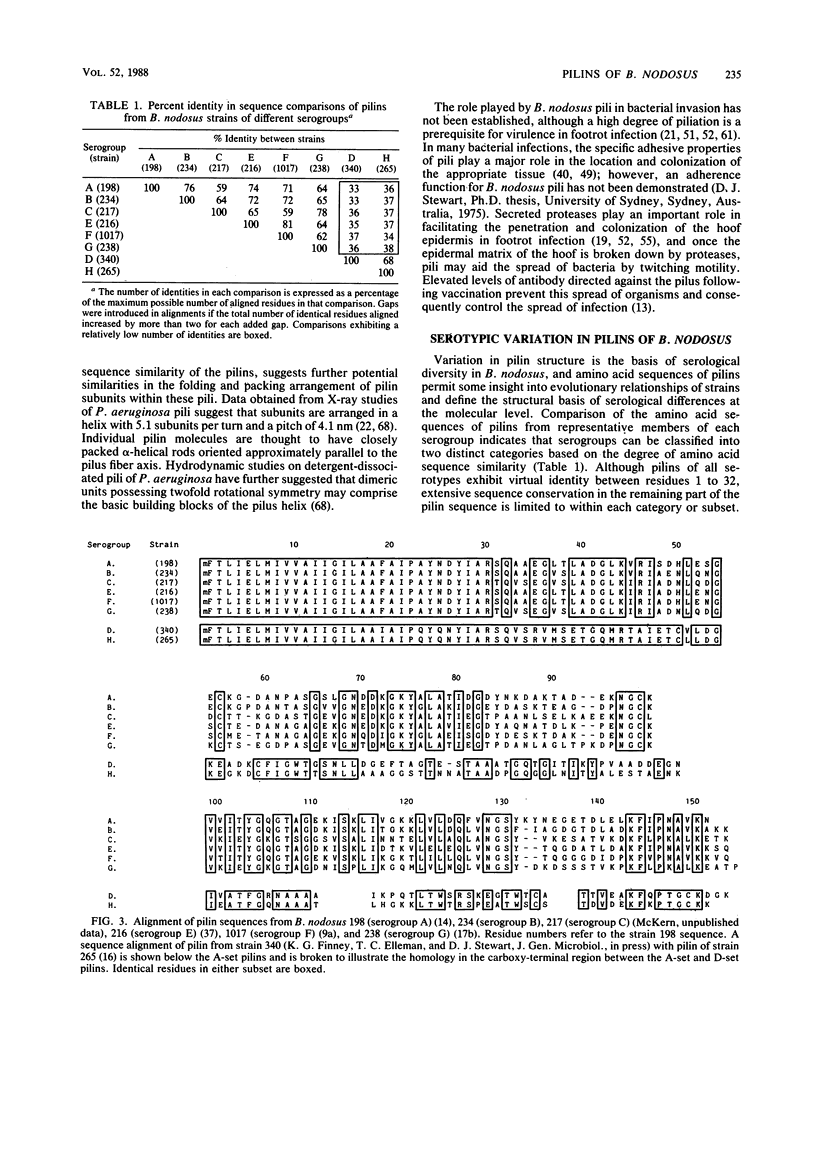
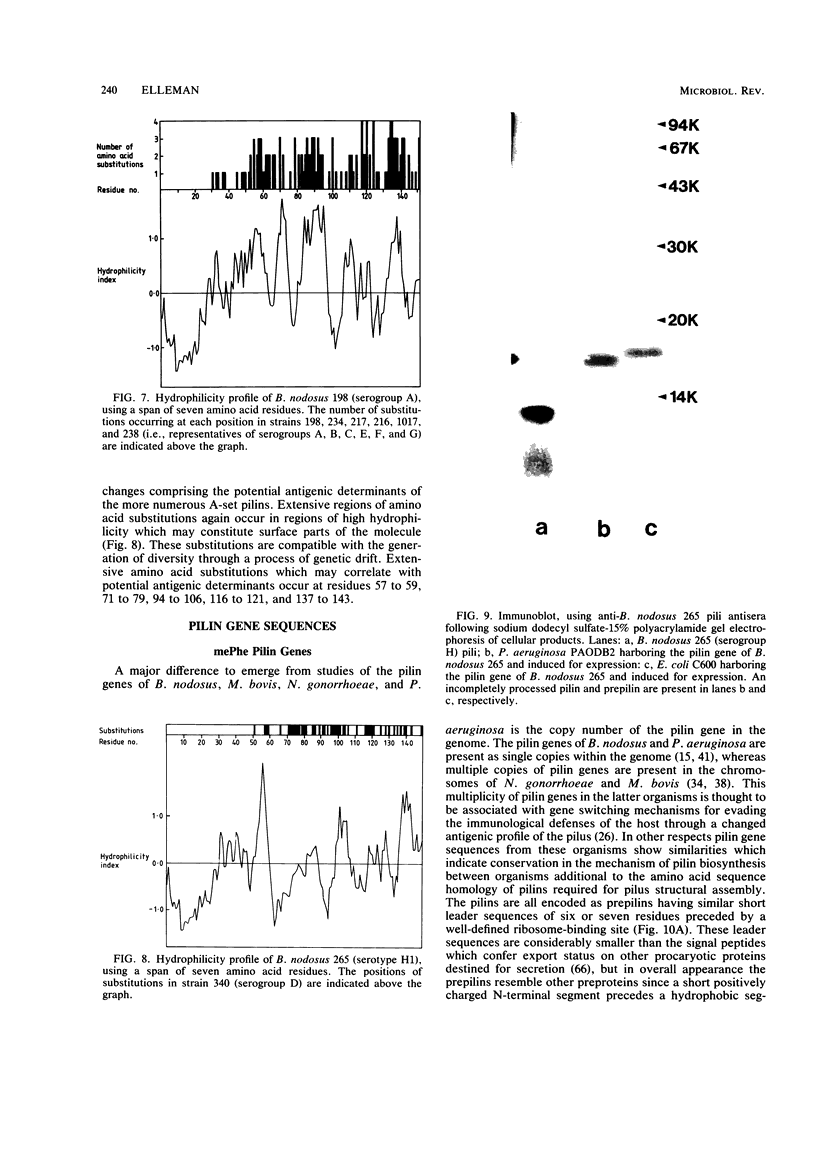
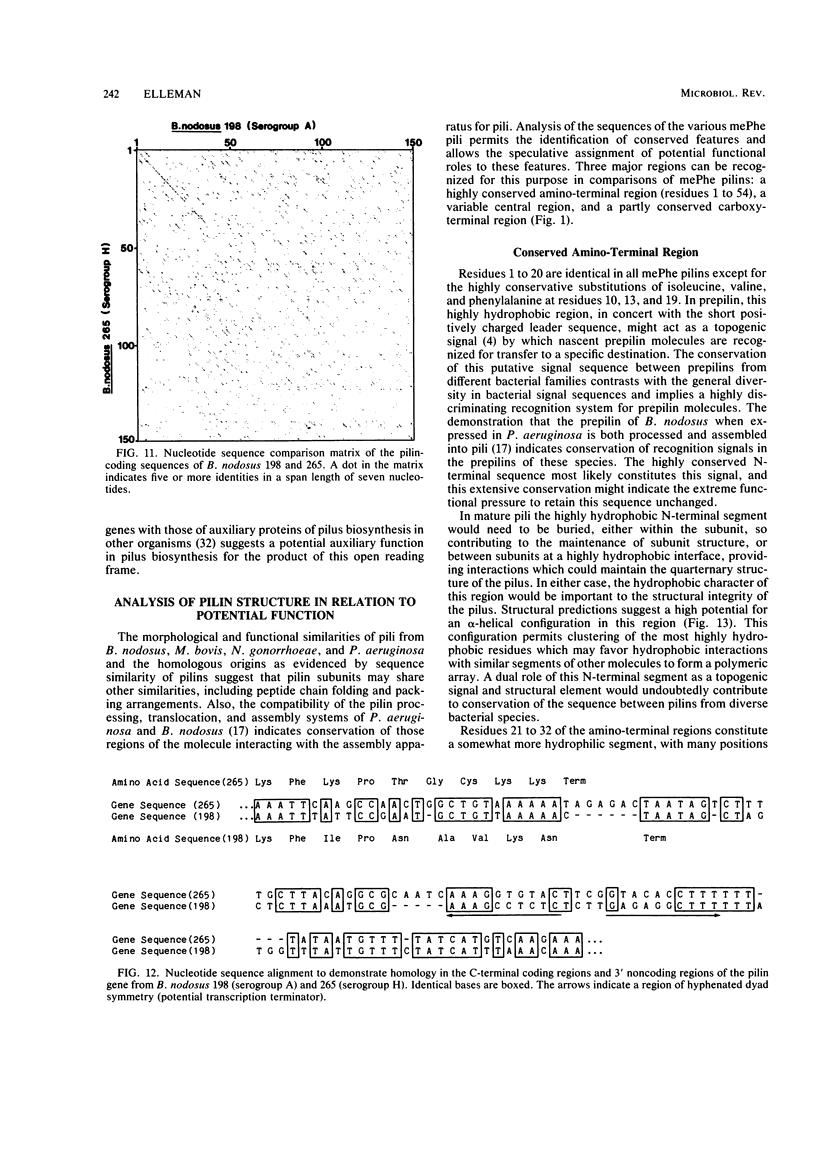
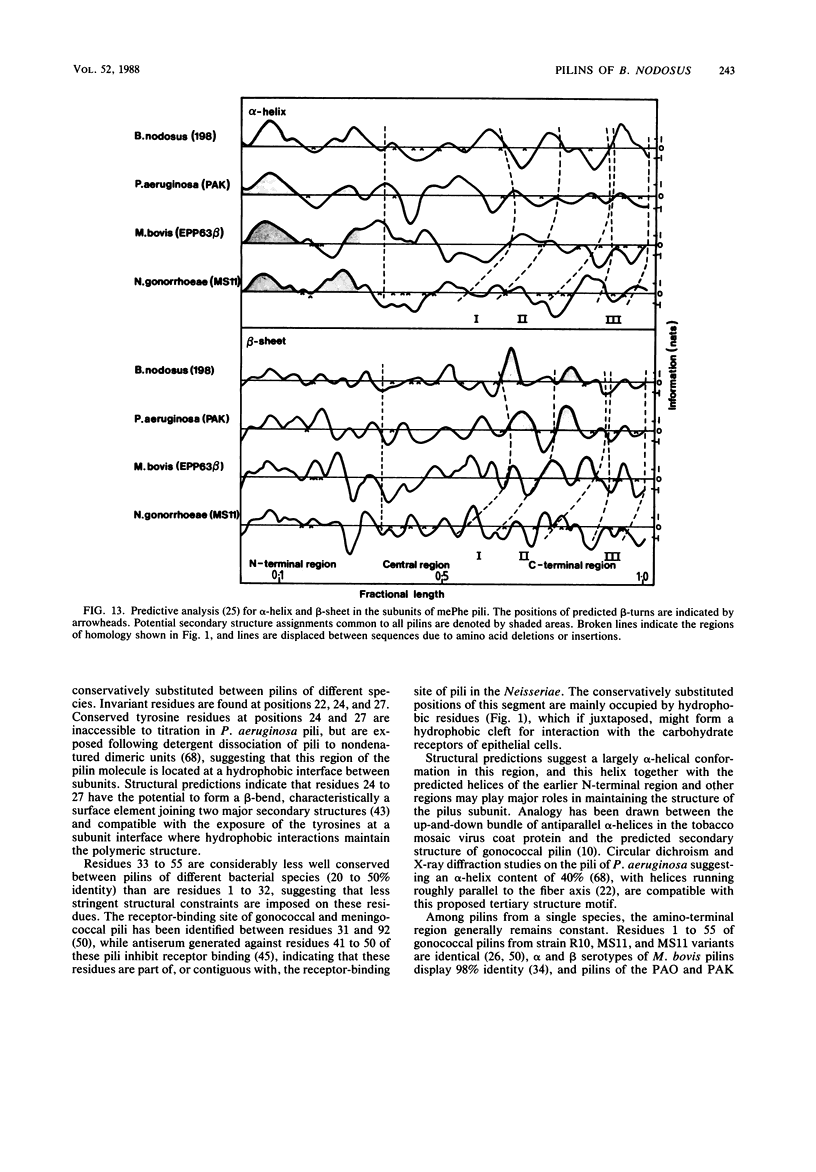
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. J., Kristo C. L., Egerton J. R., Mattick J. S. Variation in the structural subunit and basal protein antigens of Bacteroides nodosus fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1986 May;166(2):453–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.2.453-460.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):146–154. doi: 10.1139/m80-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton C. C., Jr The structure, function, synthesis and genetic control of bacterial pili and a molecular model for DNA and RNA transport in gram negative bacteria. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun;27(8):1003–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1965.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claxton P. D., Ribeiro L. A., Egerton J. R. Classification of Bacteroides nodosus by agglutination tests. Aust Vet J. 1983 Nov;60(11):331–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb02834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple B., Mattick J. S. An analysis of the organization and evolution of type 4 fimbrial (MePhe) subunit proteins. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(3):261–269. doi: 10.1007/BF02100020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depiazzi L. J., Richards R. B. Motility in relation to virulence of Bacteroides nodosus. Vet Microbiol. 1985 Jan;10(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(85)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R., Roberts D. S. Vaccination against ovine foot-rot. J Comp Pathol. 1971 Apr;81(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(71)90091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egerton J. R. Significance of Fusiformis nodosus serotypes in resistance of vaccinated sheep to experimental foot-rot. Aust Vet J. 1974 Feb;50(2):59–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1974.tb05252.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Hoyne P. A., McKern N. M., Stewart D. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the two-subunit pilin of Bacteroides nodosus 265. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):243–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.243-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Hoyne P. A. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding pilin of Bacteroides nodosus, the causal organism of ovine footrot. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1184–1187. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1184-1187.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Hoyne P. A., Stewart D. J., McKern N. M., Peterson J. E. Expression of pili from Bacteroides nodosus in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):574–580. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.574-580.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., von Ahlefeldt D. A. Nucleotide sequence of the pilin gene from Bacteroides nodosus strain 238 (serogroup G). Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7189–7189. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D. Proteinase isoenzyme patterns of Bacteroides nodosus: distinction between ovine virulent isolates, ovine benign isolates and bovine isolates. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Apr;128(4):809–812. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D. Purification of pili from Bacteroides nodosus and an examination of their chemical, physical and serological properties. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Dec;115(2):309–316. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D., Skerman T. M. Protection of sheep against experimental footrot by vaccination with pili purified from Bacteroides nodosus. N Z Vet J. 1982 Oct;30(10):156–158. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1982.34921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Every D., Skerman T. M. Surface structure of Bacteroides nodosus in relation to virulence and immunoprotection in sheep. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Jan;129(1):225–234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkhard W., Marvin D. A., Watts T. H., Paranchych W. Structure of polar pili from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains K and O. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froholm L. O., Sletten K. Purification and N-terminal sequence of a fimbrial protein from Moraxella nonliquefaciens. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):29–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost L. S., Carpenter M., Paranchych W. N-methylphenylalanine at the N-terminus of pilin isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa K. Nature. 1978 Jan 5;271(5640):87–89. doi: 10.1038/271087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagblom P., Segal E., Billyard E., So M. Intragenic recombination leads to pilus antigenic variation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):156–158. doi: 10.1038/315156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. The occurrence of twitching motility among gram-negative bacteria. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Jun;83(3):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00089.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J. Twitching motility. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1983;37:81–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.37.100183.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermodson M. A., Chen K. C., Buchanan T. M. Neisseria pili proteins: amino-terminal amino acid sequences and identification of an unusual amino acid. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):442–445. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Parker M. L., Lory S. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional initiation site of two Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15703–15708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemm P. Fimbrial adhesions of Escherichia coli. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):321–340. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehr C., Jayappa H. G., Goodnow R. A. Serologic and protective characterization of Moraxella bovis pili. Cornell Vet. 1985 Oct;75(4):484–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Schoolnik G., Koomey J. M., Hardy J., Rothbard J., Falkow S. Cloning and sequencing of a Moraxella bovis pilin gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):132–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.132-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney D., Tramont E. C., Boslego J. W., Ciak J., Sadoff J., Brinton C. C. Genital antibody response to a parenteral gonococcal pilus vaccine. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1006–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1006-1012.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Inglis A. S., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Amino acid sequence of pilin from Bacteroides nodosus (strain 198), the causative organism of ovine footrot. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKern N. M., O'Donnell I. J., Stewart D. J., Clark B. L. Primary structure of pilin protein from Bacteroides nodosus strain 216: comparison with the corresponding protein from strain 198. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jan;131(1):1–6. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Billyard E., Haas R., Storzbach S., So M. Pilus genes of Neisseria gonorrheae: chromosomal organization and DNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olafson R. W., McCarthy P. J., Bhatti A. R., Dooley J. S., Heckels J. E., Trust T. J. Structural and antigenic analysis of meningococcal piliation. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):336–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.336-342.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasloske B. L., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W. Cloning and sequencing of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin gene. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80821-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Export of protein in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Dec;48(4):290–298. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.4.290-298.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Fernandez R., Schoolnik G. K. Strain-specific and common epitopes of gonococcal pili. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):208–221. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothbard J. B., Fernandez R., Wang L., Teng N. N., Schoolnik G. K. Antibodies to peptides corresponding to a conserved sequence of gonococcal pilins block bacterial adhesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):915–919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Finlay B. B., Pasloske B. L., Paranchych W., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B. Comparative studies of the amino acid and nucleotide sequences of pilin derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK and PAO. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):571–577. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.571-577.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B., Paranchych W. Amino acid sequence of pilin isolated from pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jan 24;151(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastry P. A., Pearlstone J. R., Smillie L. B., Paranchych W. Studies on the primary structure and antigenic determinants of pilin isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa K. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;63(4):284–291. doi: 10.1139/o85-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Fernandez R., Tai J. Y., Rothbard J., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal pili. Primary structure and receptor binding domain. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1351–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. A., Thorley C. M., Walker P. D. An electron microscope study of Bacteroides nodusus: ultrastructure of organisms from primary isolates and different colony types. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;40(3):311–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerman T. M., Erasmuson S. K., Every D. Differentiation of Bacteroides nodosus biotypes and colony variants in relation to their virulence and immunoprotective properties in sheep. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):788–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.788-795.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. An electron microscopic study of Fusiformis nodosus. Res Vet Sci. 1973 Jan;14(1):132–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Clark B. L., Emery D. L., Peterson J. E., Fahey K. J. A Bacteroides nodosus immunogen, distinct from the pilus, which induces cross-protective immunity in sheep vaccinated against footrot. Aust Vet J. 1983 Mar;60(3):83–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1983.tb05877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Clark B. L., Peterson J. E., Emery D. L., Smith E. F., Griffiths D. A., O'Donnell I. J. The protection given by pilus and whole cell vaccines of Bacteroides nodosus strain 198 against ovine foot-rot induced by strains of different serogroups. Aust Vet J. 1985 May;62(5):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1985.tb07277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Clark B. L., Peterson J. E., Griffiths D. A., Smith E. F. Importance of pilus-associated antigen in Bacteroides nodosus vaccines. Res Vet Sci. 1982 Mar;32(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Clark B. L., Peterson J. E., Griffiths D. A., Smith E. F., O'Donnell I. J. Effect of pilus dose and type of Freund's adjuvant on the antibody and protective responses of vaccinated sheep to Bacteroides nodosus. Res Vet Sci. 1983 Sep;35(2):130–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J., Elleman T. C. A Bacteroides nodosus pili vaccine produced by recombinant DNA for the prevention and treatment of foot-rot in sheep. Aust Vet J. 1987 Mar;64(3):79–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1987.tb09620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The role of elastase in the differentiation of Bacteroides nodosus infections in sheep and cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1979 Jul;27(1):99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart D. J. The role of various antigenic fractions of Bacteroides nodosus in eliciting protection against foot-rot in vaccinated sheep. Res Vet Sci. 1978 Jan;24(1):14–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley C. M. A simplified method for the isolation of Bacteroides nodusus from ovine foot-rot and studies on its colony morphology and serology. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;40(3):301–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb04178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley C. M., Egerton J. R. Comparison of alum-absorbed or non-alum-absorbed oil emulsion vaccines containing either pilate or non-pilate Bacteroides nodosus cells in inducing and maintaining resistance of sheep to experimental foot rot. Res Vet Sci. 1981 Jan;30(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Inhibition of adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human genital secretions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. D., Short J., Thomson R. O., Roberts D. S. The fine structure of Fusiformis nodosus with special reference to the location of antigens associated with immunogenicity. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Aug;77(2):351–361. doi: 10.1099/00221287-77-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Kay C. M., Paranchych W. Spectral properties of three quaternary arrangements of Pseudomonas pilin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jul 19;22(15):3640–3646. doi: 10.1021/bi00284a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Gratzer W. B. Limitations of the detergent-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method for molecular weight determination of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1971 Apr 22;57(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(71)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Signal sequences. The limits of variation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 5;184(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]