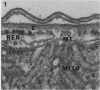
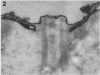
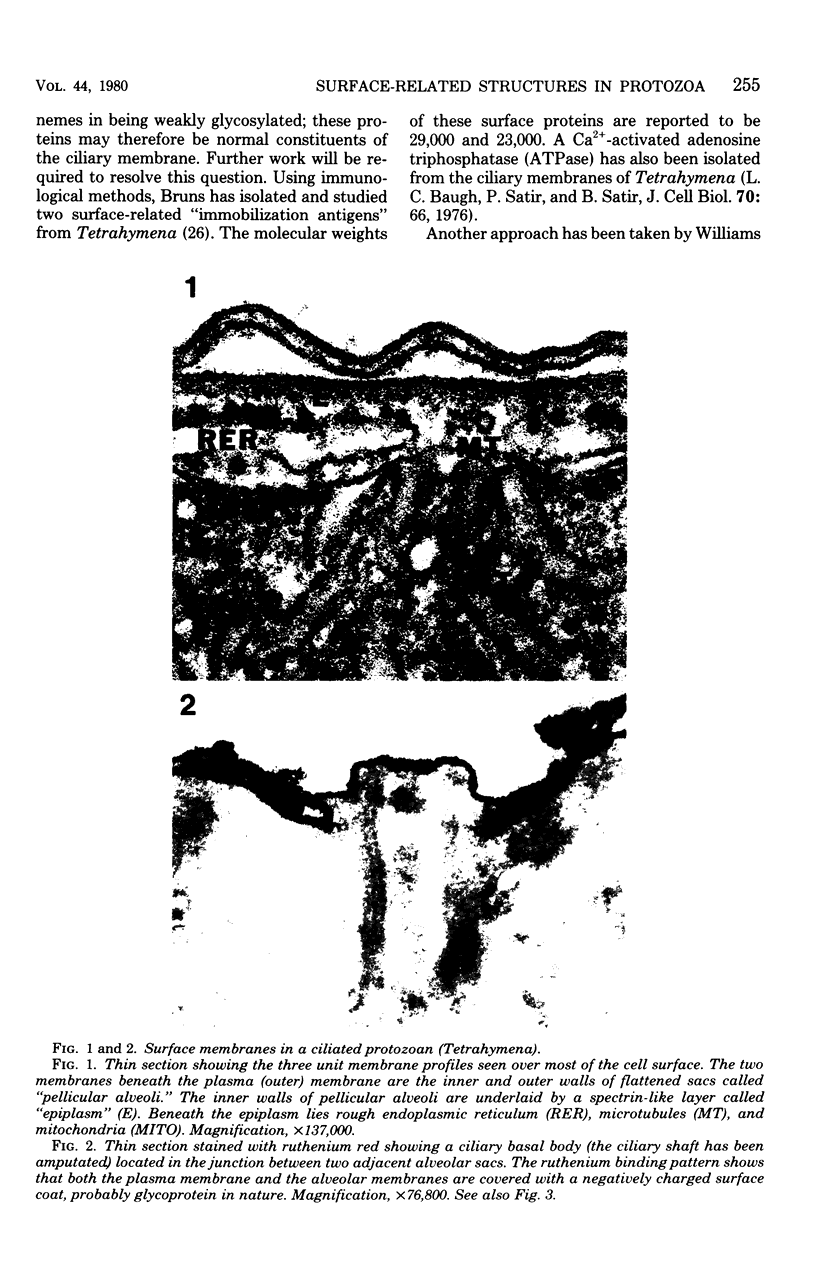
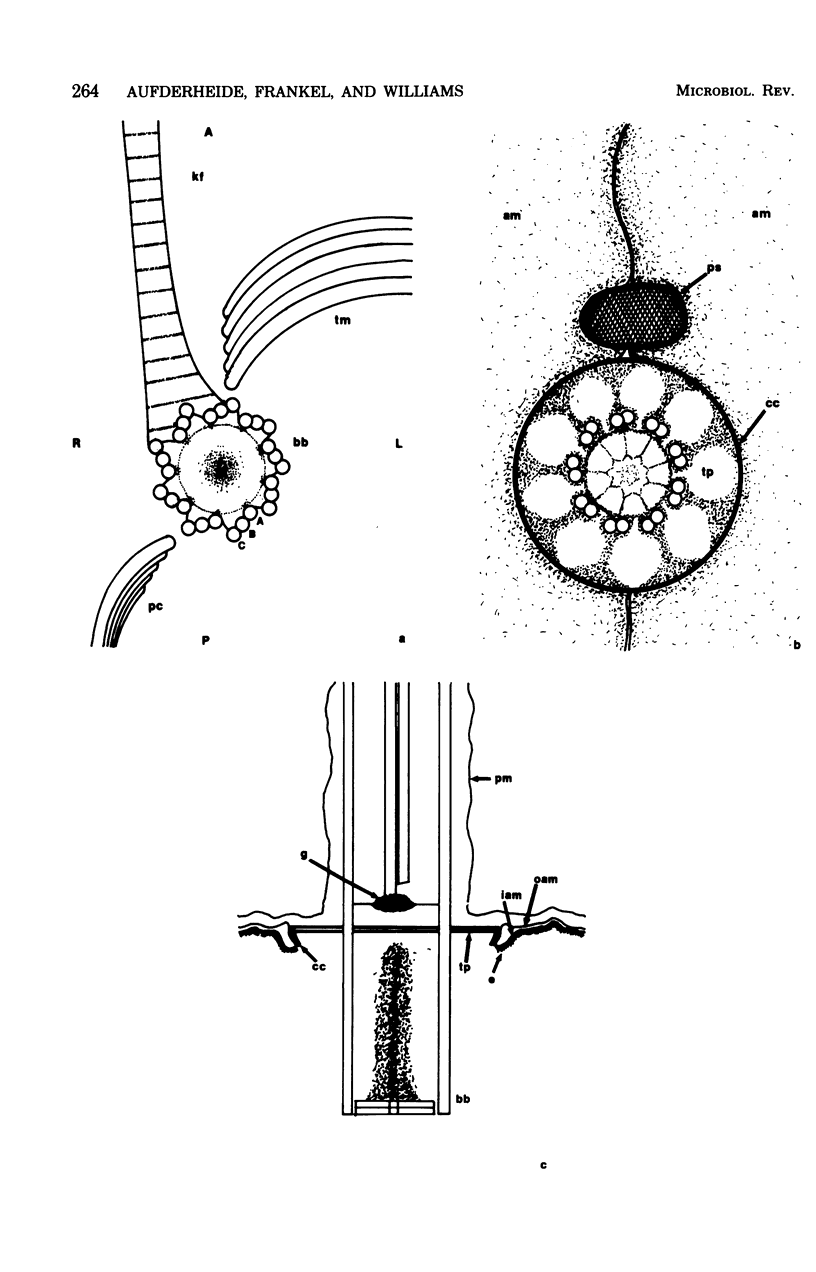
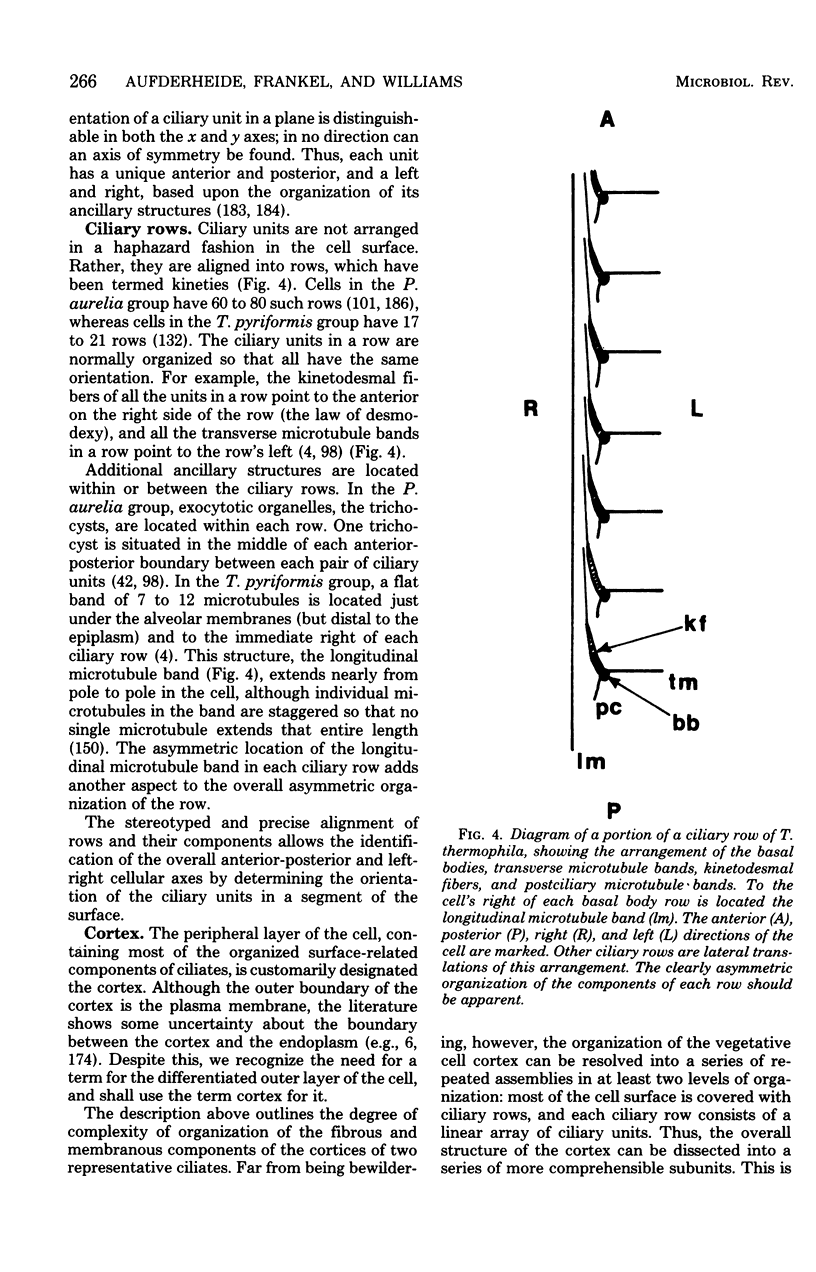
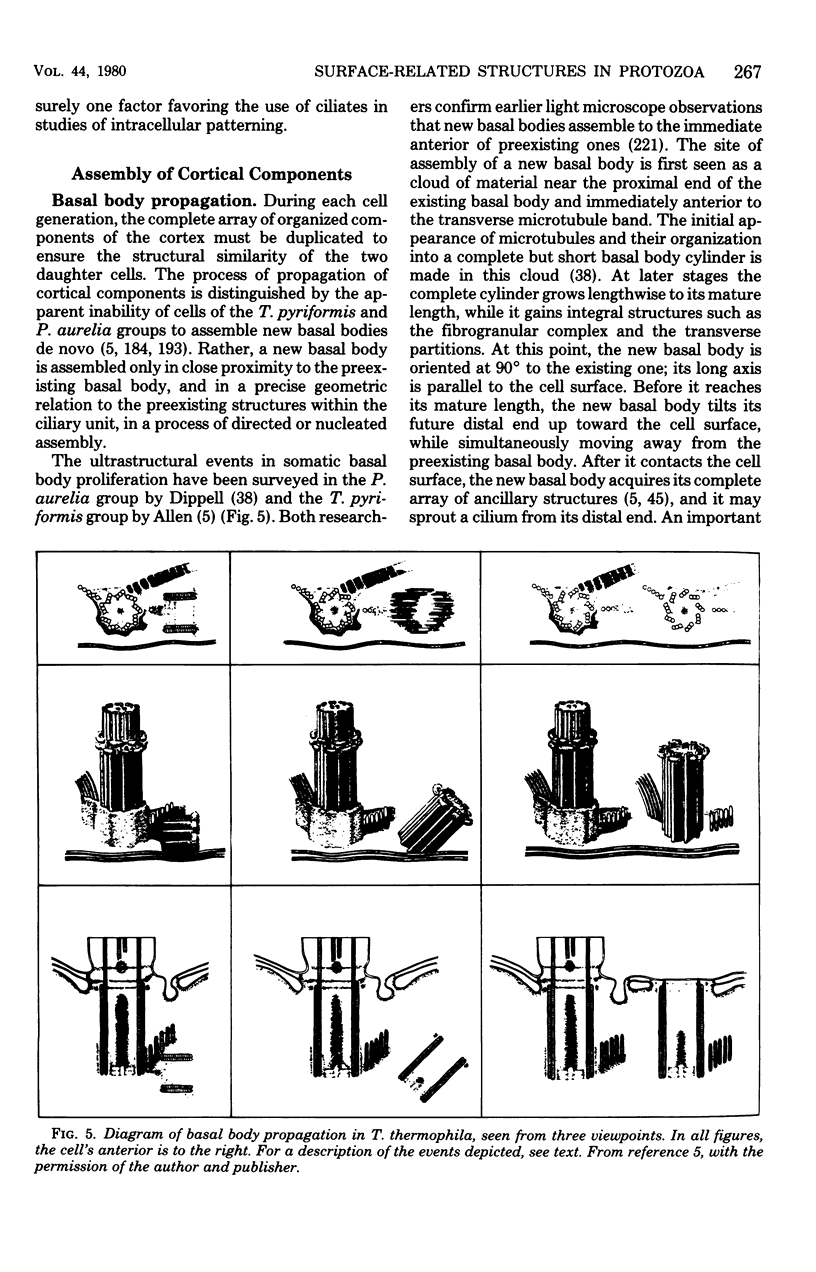
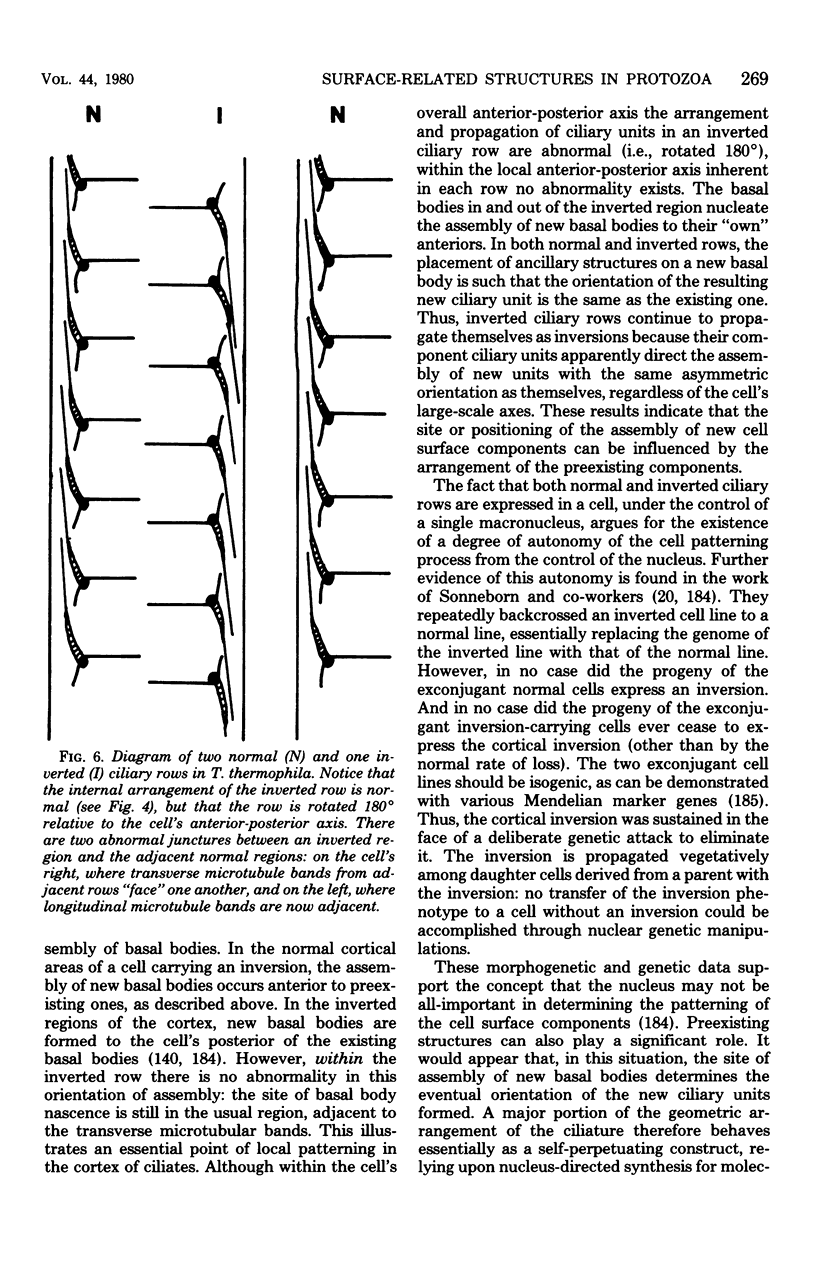
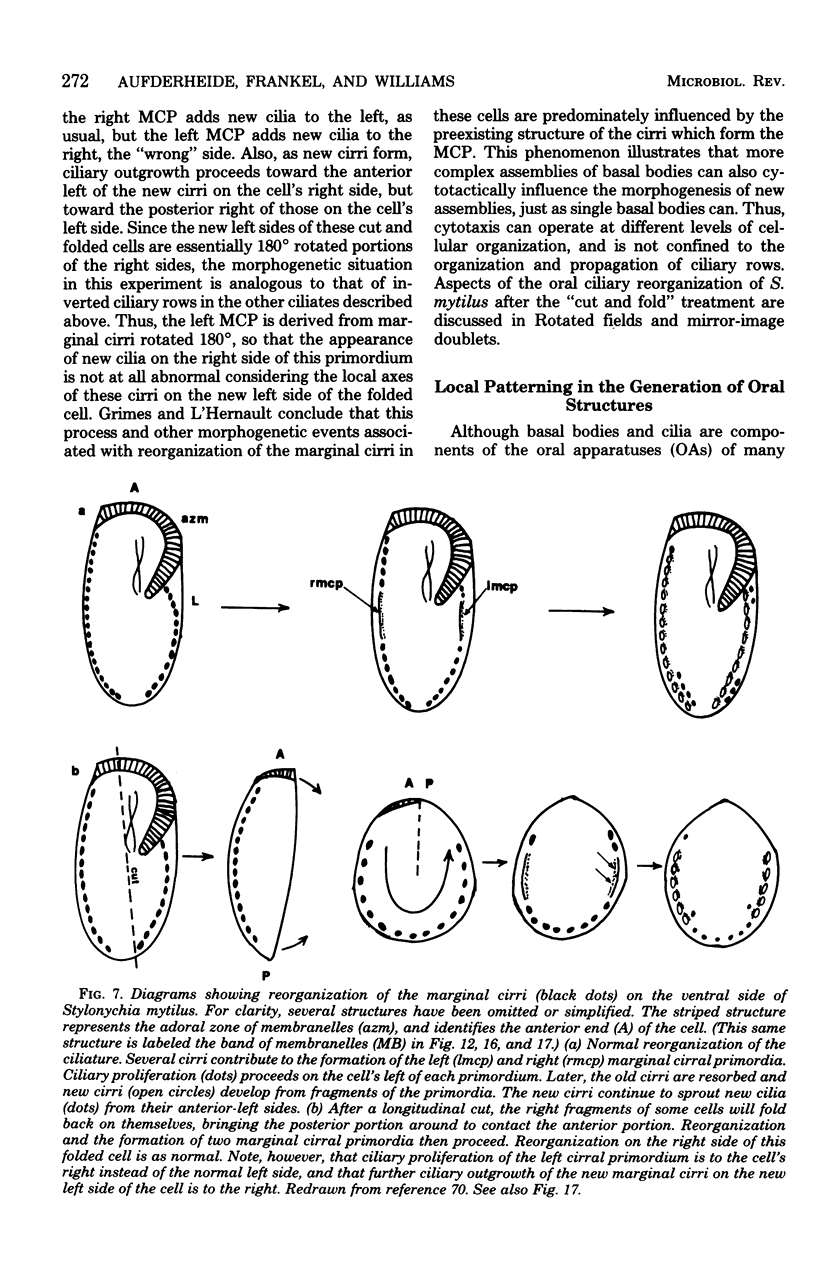
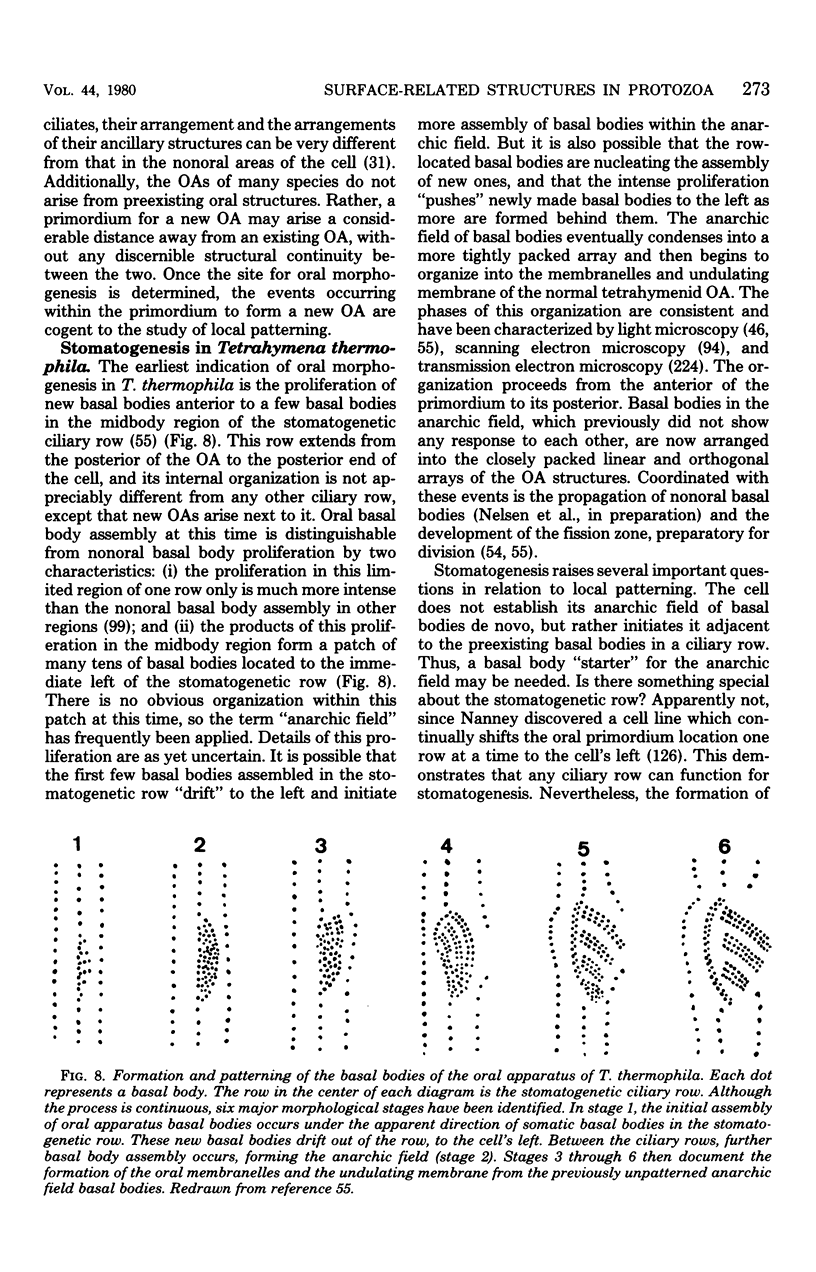
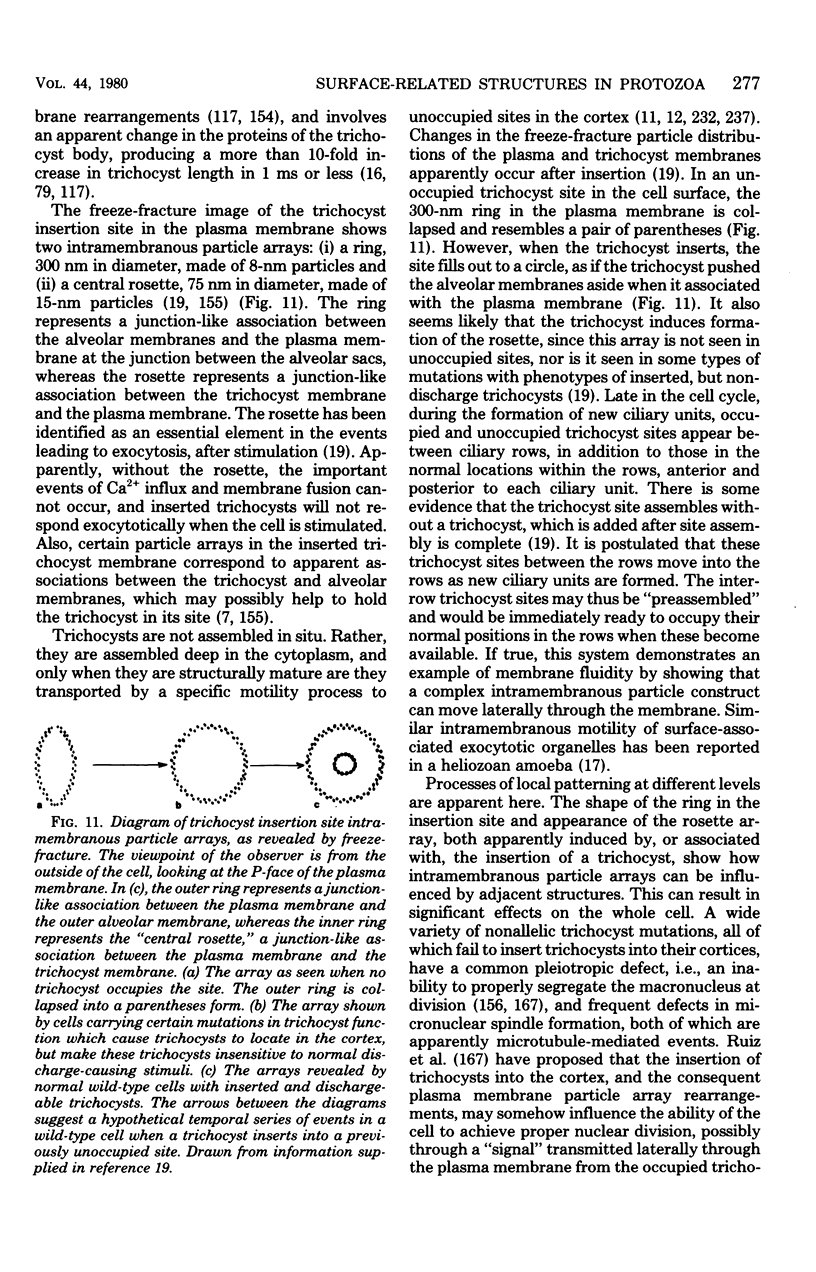
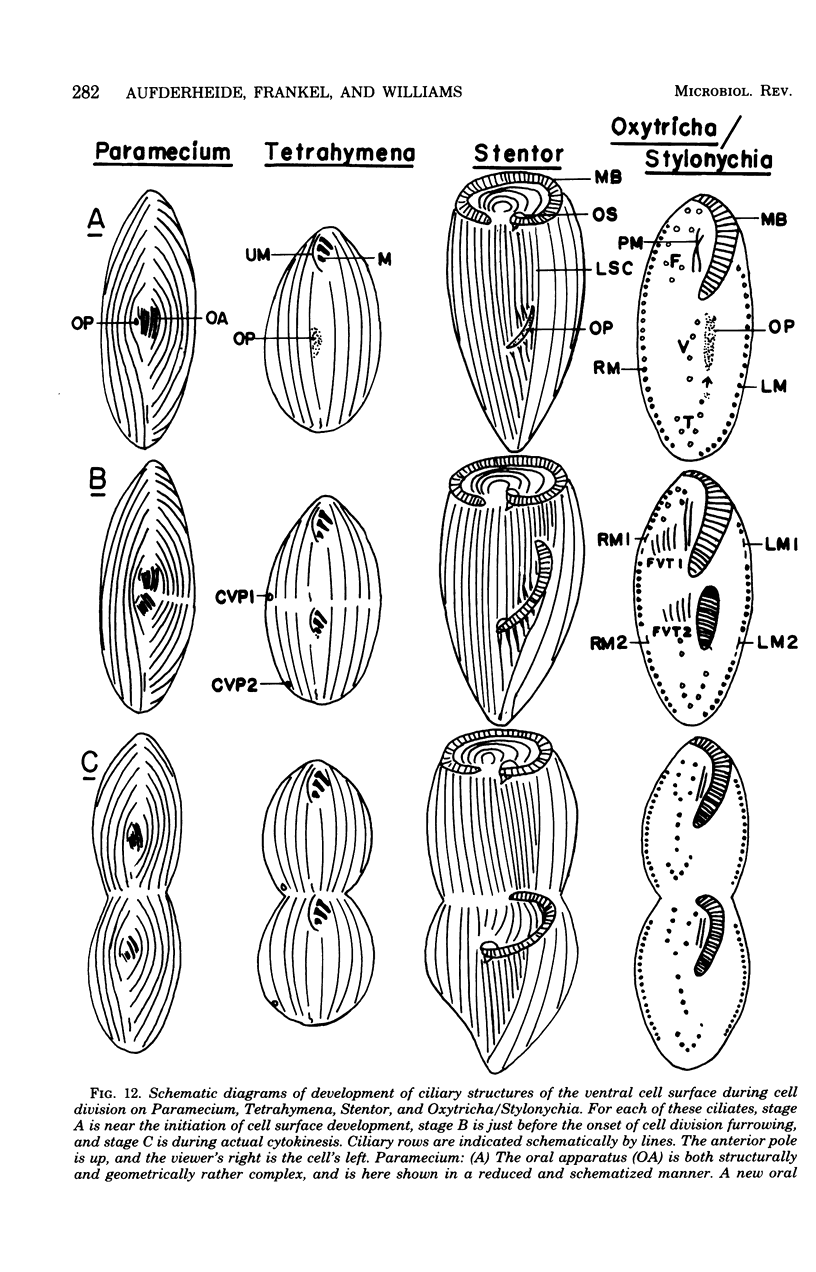
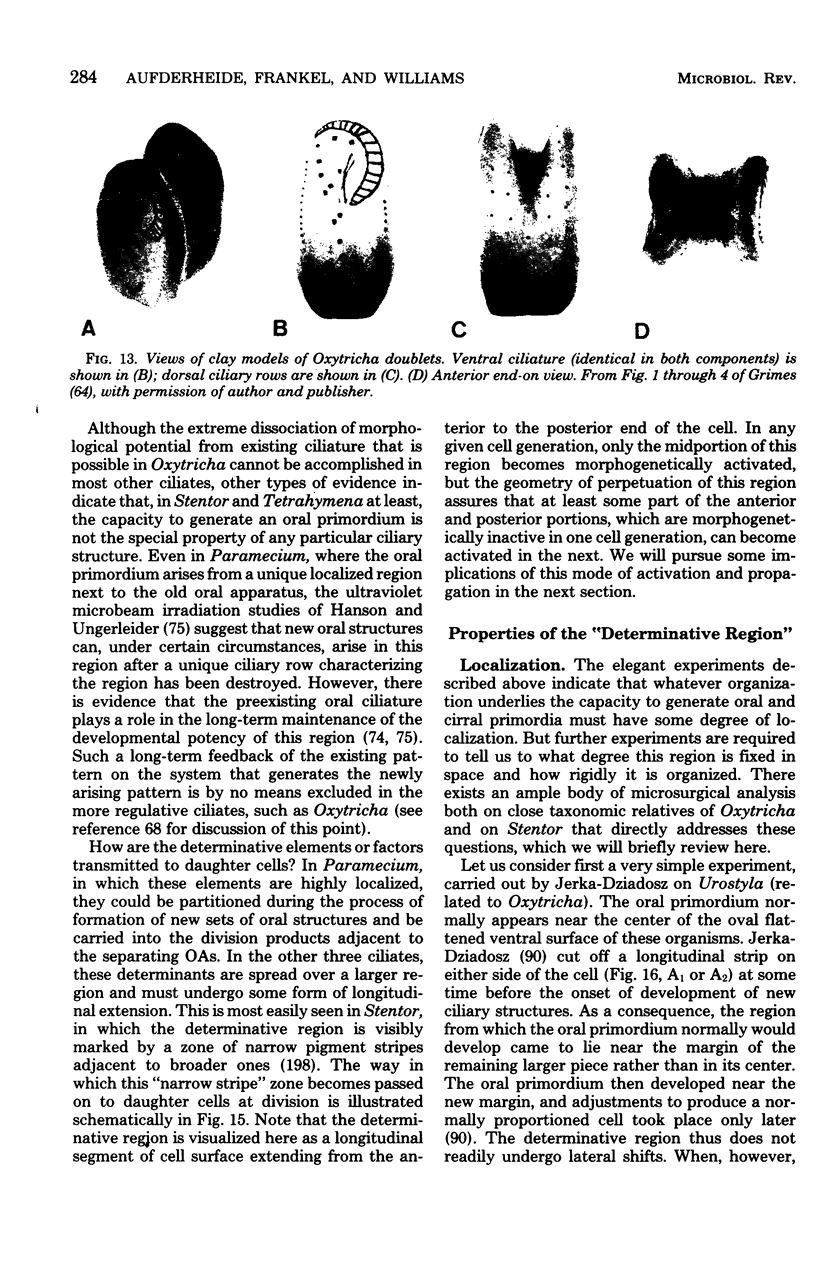
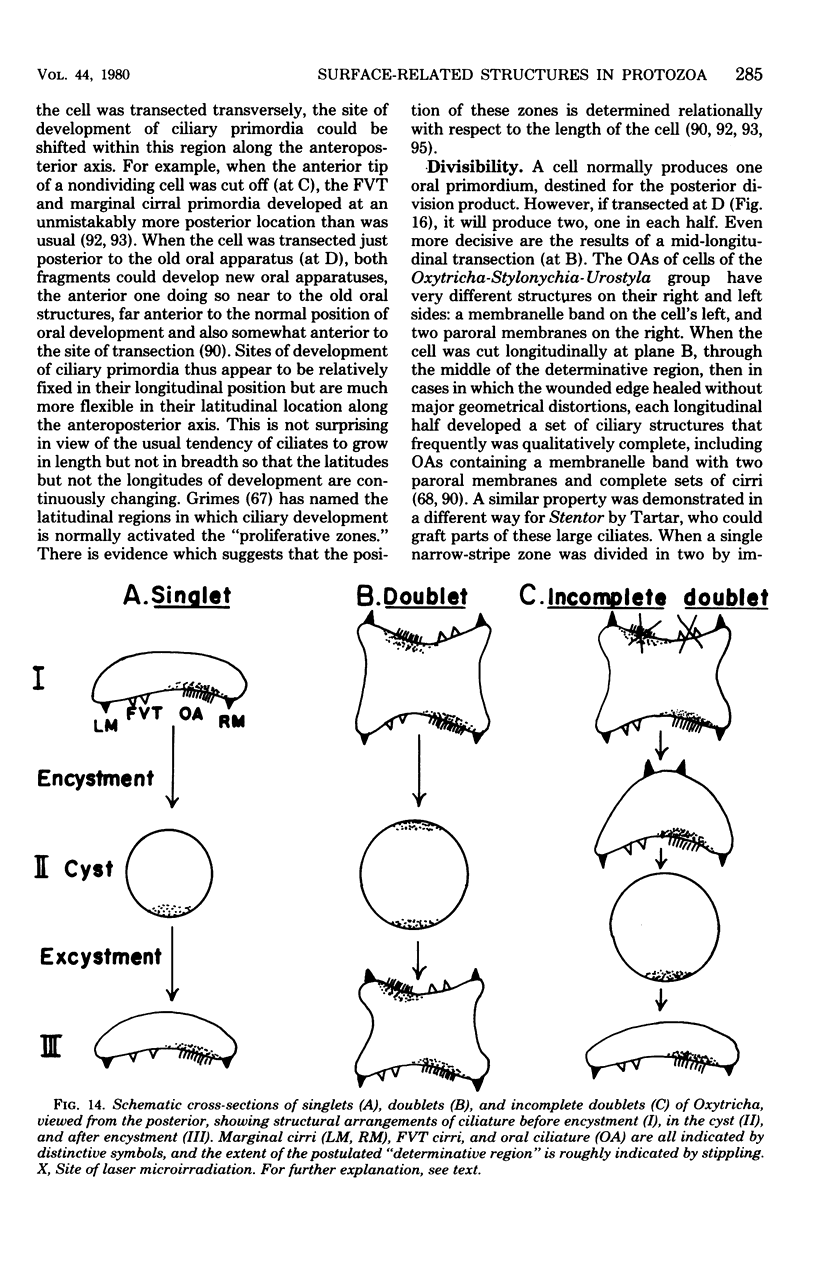
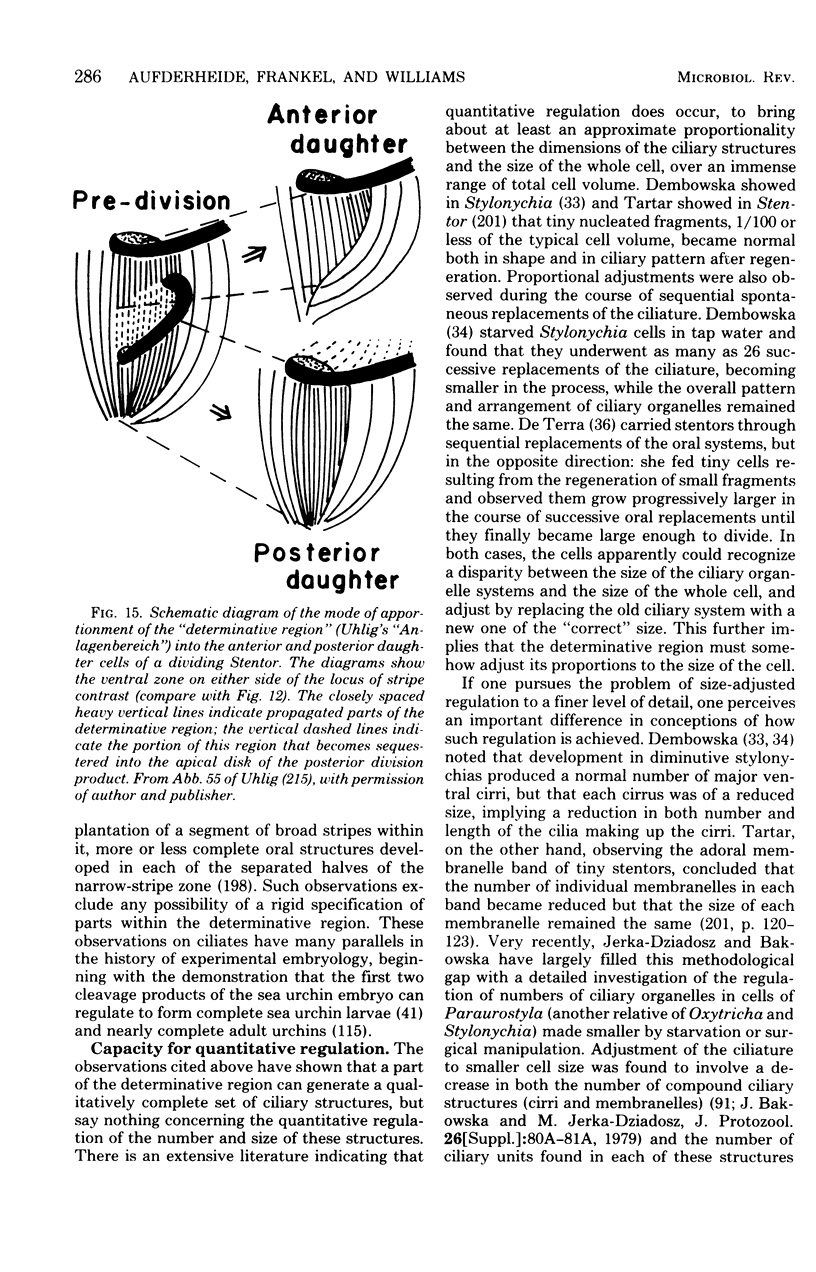
Full text
PDF


































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adoutte A., Ramanathan R., Lewis R. M., Dute R. R., Ling K. Y., Kung C., Nelson D. L. Biochemical studies of the excitable membrane of Paramecium tetraurelia. III. Proteins of cilia and ciliary membranes. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):717–738. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht-Buehler G. Daughter 3T3 cells. Are they mirror images of each other? J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):595–603. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht-Buehler G. The tracks of moving cells. Sci Am. 1978 Apr;238(4):68–76. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0478-68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D. Fine structure of membranous and microfibrillar systems in the cortex of Paramecium caudatum. J Cell Biol. 1971 Apr;49(1):1–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D. Fine structure, reconstruction and possible functions of components of the cortex of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1967 Nov;14(4):553–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D., Hausmann K. Membrane behavior of exocytic vesicles. I. The ultrastructure of Paramecium trichocysts in freeze-fracture preparations. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Feb;54(2):224–234. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80152-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. D. The morphogenesis of basal bodies and accessory structures of the cortex of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):716–733. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R. G. The biogenesis of cell structures and the expression of assembly information. J Theor Biol. 1977 Aug 7;67(3):535–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(77)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews D., Nelson D. L. Biochemical studies of the excitable membrane of Paramecium tetraurelia. II. Phospholipids of ciliary and other membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 19;550(2):174–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufderheide K. J. Genetic aspects of intracellular motility: cortical localization and insertion of trichocysts in Paramecium tetraurelia. J Cell Sci. 1978 Jun;31:259–273. doi: 10.1242/jcs.31.1.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufderheide K. J. Mitochondrial associations with specific microtubular components of the cortex of Tetrahymena thermophila. II. Response of the mitochondrial pattern to changes in the microtubule pattern. J Cell Sci. 1980 Apr;42:247–260. doi: 10.1242/jcs.42.1.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aufderheide K. J. Motility events of trichocyst insertion in Paramecium tetraurelia. J Protozool. 1978 Aug;25(3 Pt 2):362–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03904.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEISSON J., SONNEBORN T. M. CYTOPLASMIC INHERITANCE OF THE ORGANIZATION OF THE CELL CORTEX IN PARAMECIUM AURELIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:275–282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister L. H. The structure of trichocysts in Paramecium caudatum. J Cell Sci. 1972 Nov;11(3):899–929. doi: 10.1242/jcs.11.3.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardele C. F. Organization and control of microtubule pattern in centrohelidan heliozoa. J Protozool. 1977 Feb;24(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb05274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardele C. F. Particle movement in heliozoan axopods associated with lateral displacement of highly ordered membrane domains. Z Naturforsch C. 1976 Mar-Apr;31(3-4):190–194. doi: 10.1515/znc-1976-3-418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisson J., Lefort-Tran M., Pouphile M., Rossignol M., Satir B. Genetic analysis of membrane differentiation in Paramecium. Freeze-fracture study of the trichocyst cycle in wild-type and mutant strains. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):126–143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibring T., Baxandall J., Denslow S., Walker B. Heterogeneity of the alpha subunit of tubulin and the variability of tubulin within a single organism. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):301–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck G. B., Rogalski A., Valaitis A. Surface organization and composition of Euglena. II. Flagellar mastigonemes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jun;77(3):805–826. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouck G. B. The structure, origin, isolation, and composition of the tubular mastigonemes of the Ochromas flagellum. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):362–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Rogers K. A. Hydrostatic pressure-induced internalization of flagellar axonemes, disassembly, and reutilization during flagellar regeneration in Polytomella. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):313–324. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns P. J., Sanford Y. M. Mass isolation and fertility testing of temperature-sensitive mutants in Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3355–3358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne B., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in chlamydomonas. II. Re-utilization of flagellar proteins. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):777–781. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Terra N. Differential growth in the cortical fibrillar system as the trigger for oral differentiation and cell division in Stentor. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jul;56(1):142–153. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90407-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. III. structures attached to the tips of flagellar microtubules and their relationship to the directionality of flagellar microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1977 Sep;74(3):747–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippell R. V. Effects of nuclease and protease digestion on the ultrastructure of Paramecium basal bodies. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):622–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippell R. V. The development of basal bodies in paramecium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):461–468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran D. J. The life cycle of Eimeria dispersa Tyzzer, 1929 in turkeys. J Protozool. 1978 Aug;25(3 Pt 2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EHRET C. F., POWERS E. L. The cell surface of Paramecium. Int Rev Cytol. 1959;8:97–133. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62729-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT A. M., BAK I. J. THE CONTRACTILE VACUOLE AND RELATED STRUCTURES IN TETRAHYMENA PYRIFORMIS. J Protozool. 1964 May;11:250–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1964.tb01752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. A genically determined abnormality in the number and arrangement of basal bodies in a ciliate. Dev Biol. 1973 Feb;30(2):336–365. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J., Jenkins L. M. A mutant of Tetrahymena thermophila with a partial mirror-image duplication of cell surface pattern. II. Nature of genic control. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1979 Jan;49:203–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J., Nelsen E. M., Jenkins L. M. Mutations affecting cell division in Tetrahymena pyriformis, syngen 1. II. Phenotypes of single and double homozygotes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):255–275. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. Positional information in unicellular organisms. J Theor Biol. 1974 Oct;47(2):439–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90209-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. The stability of cortical phenotypes in continuously growing cultures of Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1972 Nov;19(4):648–654. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1972.tb03550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel J. The synchronization of oral development without cell division in Tetrahymena pyriformis GL-C. J Exp Zool. 1970 Jan;173(1):79–99. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401730106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch A., Levkovitz H., Loyter A. Inhibition of conjugation in Tetrahymena pyriformis by concanavalin A. Binding of concanavalin A to material secreted during starvation and to washed cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch A., Loyter A. Inhibition of conjugation in Tetrahymena pyriformis by ConA. Localization of ConA-binding sites. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Dec;110(2):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin R. H. The oral apparatus of Tetrahymena pyriformis, mating type 1, variety 1. I. Solubilization and electrophoretic separation of oral apparatus proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 30;85(1):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould R. R. The basal bodies of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Formation from probasal bodies, isolation, and partial characterization. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):65–74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes G. W. Differentiation during encystment and excystment in Oxytricha fallax. J Protozool. 1973 Feb;20(1):92–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1973.tb06009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes G. W., L'Hernault S. W. Cytogeometrical determination of ciliary pattern formation in the hypotrich ciliate Stylonychia mytilus. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):372–395. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes G. W. Laser microbeam induction of incomplete doublets of Oxytricha fallax. Genet Res. 1976 Apr;27(2):213–226. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes G. W. Morphological discontinuity of kinetosomes during the life cycle of Oxytricha fallax. J Cell Biol. 1973 Apr;57(1):229–232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman S. D., Gorovsky M. A. Cilia regeneration in starved tetrahymena: an inducible system for studying gene expression and organelle biogenesis. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):307–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90156-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON E. D. Morphogenesis and regeneration of oral structures in Paramecium aurelia: an analysis of intracellular development. J Exp Zool. 1962 Jun;150:45–67. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401500107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammersmith R. L. The redevelopment of heteropolar doublets and monster cells of Oxytricha fallax after cystment. J Cell Sci. 1976 Dec;22(3):563–573. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.3.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Kung C. Studies of the cell surface of Paramecium. Ciliary membrane proteins and immobilization antigens. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;152(3):523–528. doi: 10.1042/bj1520523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson E. D., Ungerleider R. M. The formation of the feeding organelle in Paramecium aurelia. J Exp Zool. 1973 Aug;185(2):175–188. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401850206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman H., Puma J. P., Gruney T., Jr Evidence for the association of RNA with the ciliary basal bodies of Tetrahymena. J Cell Sci. 1974 Nov;16(2):241–259. doi: 10.1242/jcs.16.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann K., Frankel J. Genic control of cortical pattern in Euplotes. J Exp Zool. 1968 May;168(1):11–37. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401680103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidemann S. R., Kirschner M. W. Aster formation in eggs of Xenopus laevis. Induction by isolated basal bodies. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):105–117. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann C., Bouck G. B. Immunological and structural evidence for patterned intussusceptive surface growth in a unicellular organism. A postulated role for submembranous proteins and microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):693–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Piperno G., Luck D. J. Paralyzed flagella mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Defective for axonemal doublet microtubule arms. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3091–3099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Pitelka D. R. The contractile process in the ciliate, Stentor coeruleus. I. The role of microtubules and filaments. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):704–728. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Rifkin M. R., Luck D. J. Temperature-sensitive mutations affecting flagellar assembly and function in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):67–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagel L. A. Cortical ultrastructure of Paramecium aurelia. Studies on isolated pellicles. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):779–801. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerka-Dziadosz M. An analysis of the formation of ciliary primordia in the hypotrichous ciliate Urostyla weissei. II. Results from ultraviolet microbeam irradiation. J Exp Zool. 1972 Jan;179(1):81–95. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401790107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerka-Dziadosz M., Frankel J. A mutant of Tetrahymena thermophila with a partial mirror-image duplication of cell surface pattern. I. Analysis of the phenotype. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1979 Jan;49:167–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerka-Dziadosz M., Frankel J. An analysis of the formation of ciliary primordia in the hypotrich ciliate Urostyla weissei. J Protozool. 1969 Nov;16(4):612–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson U. G., Porter K. R. Fine structure of cell division in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Basal bodies and microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1968 Aug;38(2):403–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. R. Oral morphogenesis during asexual reproduction in Paramecium tetraurelia. Genet Res. 1976 Apr;27(2):187–204. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczanowski A. Gradients of proliferation of ciliary basal bodies and the determination of the position of the oral primordium in Tetrahymena. J Exp Zool. 1978 Jun;204(3):417–430. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402040313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan D., Oren R., Aaronson S., Behrens U. Fine structure of the cell surface and Golgi apparatus of Ochromonas. J Protozool. 1978 Feb;25(1):30–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1978.tb03860.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy K. E., Thompson G. A., Jr Phosphonolipids: localization in surface membranes of Tetrahymena. Science. 1970 May 22;168(3934):989–991. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3934.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Mykolajewycz N. Bacteriophage T4 tail assembly: proteins of the sheath, core and baseplate. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):339–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura A., Hiwatashi K. Mating-reactive membrane vesicles from cilia of Paramecium caudatum. J Cell Biol. 1976 Jun;69(3):736–740. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Fulton C. Programmed synthesis of tubulin for the flagella that develop during cell differentiation in Naegleria gruberi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2877–2881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P. A., Nordstrom S. A., Moulder J. E., Rosenbaum J. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. IV. Effects of flagellar detachment, regeneration, and resorption on the induction of flagellar protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):8–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck D., Piperno G., Ramanis Z., Huang B. Flagellar mutants of Chlamydomonas: studies of radial spoke-defective strains by dikaryon and revertant analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3456–3460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. The structure and properties of the cell surface coat. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;45:291–382. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60081-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa S. Dissociation constant of Tetrahymena tubulin-colchicine complex. J Biochem. 1978 Sep;84(3):641–646. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa S., Sakai H. Characterization and in vitro polymerization of Tetrahymena tubulin. J Biochem. 1978 Apr;83(4):1065–1075. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Furthmayr H., Tomita M. The red cell membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:667–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus N. H. Developmental aberrations associated with twinning in laboratory-reared sea urchins. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):274–277. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. J., MacDonald R. C. Phospholipid exchange between bilayer membrane vesicles. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):321–327. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matt H., Bilinski M., Plattner H. Adenosinetriphosphate, calcium and temperature requirements for the final steps of exocytosis in Paramecium cells. J Cell Sci. 1978 Aug;32:67–86. doi: 10.1242/jcs.32.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. R., Miller G. J. Organization of the cell membrane in Euglena. Protoplasma. 1978;95(1-2):11–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01279691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake A., Maffei M., Nobili R. Propagation of meiosis and other nuclear changes in multicellular complexes of Blepharisma. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Sep;108(2):245–251. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80031-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naitoh Y., Eckert R. Ionic mechanisms controlling behavioral responses of paramecium to mechanical stimulation. Science. 1969 May 23;164(3882):963–965. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3882.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L., Chow M., Wozencraft B. Considerations of symmetry in the cortical integration of tetrahymena doublets. J Exp Zool. 1975 Jul;193(1):1–14. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401930102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Cortical integration in Tetrahymena: an exercise in cytogeometry. J Exp Zool. 1966 Apr;161(3):307–317. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401610302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Corticotype transmission in Tetrahymena. Genetics. 1966 Oct;54(4):955–968. doi: 10.1093/genetics/54.4.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Cytogeometric integration in the ciliate cortex. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1972 Aug 25;193:14–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1972.tb27820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L., McCoy J. W. Characterization of the species of the Tetrahymena pyriformis complex. Trans Am Microsc Soc. 1976 Oct;95(4):664–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Molecules and morphologies: the perpetuation of pattern in the ciliated protozoa. J Protozool. 1977 Feb;24(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb05277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Patterns of basal body addition in ciliary rows in Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jun;65(3):503–512. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.3.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanney D. L. Patterns of cortical stability in Tetrahymena. J Protozool. 1968 Feb;15(1):109–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1968.tb02094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelsen E. M. Regulation of tubulin during ciliary regeneration in non-growing Tetrahymena. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Aug;94(1):152–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90542-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. F. Analysis of contractile vacuole pore morphogenesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis by 180 degree rotation of ciliary meridians. J Cell Sci. 1977 Jun;25:233–246. doi: 10.1242/jcs.25.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. F. Directionality of microtubule assembly: an in vivo study with the ciliate Tetrahymena. J Cell Sci. 1978 Oct;33:227–234. doi: 10.1242/jcs.33.1.227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. F., Frankel J. 180 degrees rotation of ciliary rows and its morphogenetic implications in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1115–1119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. F. Unidirectional regeneration is an intrinsic property of longitudinal microtubules in Tetrahymena--an in vivo study. J Cell Sci. 1979 Apr;36:109–119. doi: 10.1242/jcs.36.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. F., Williams R. J. An ultrastructural investigation of 180 degrees-rotated ciliary meridians in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Protozool. 1977 May;24(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb00975.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa Y., Thompson G. A., Jr Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis. II. Isolation and lipid analysis of cell fractions. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):712–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa Y., Thompson G. A., Jr Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis. V. Lipid incorporation into various cellular membranes of stationary phase cells, starving cells, and cells treated with metabolic inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 1;282(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson P. J., Tucker J. B. Control of shape and pattern during the assembly of a large microtubule bundle. Evidence for a microtubule-nucleating-template. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 May 16;180(2):241–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00231956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Huang B., Luck D. J. Two-dimensional analysis of flagellar proteins from wild-type and paralyzed mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1600–1604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Luck D. J. An actin-like protein is a component of axonemes from Chlamydomonas flagella. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2187–2190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Luck D. J. Axonemal adenosine triphosphatases from flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Purification of two dyneins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3084–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plapp F. V., Burchill B. R. Ciliary proteins and cytodifferentiation in Stentor coeruleus. J Protozool. 1972 Nov;19(4):633–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1972.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner H. Intramembraneous changes on cationophore-triggered exocytosis in Paramecium. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):722–724. doi: 10.1038/252722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner H., Miller F., Bachmann L. Membrane specializations in the form of regular membrane-to-membrane attachment sites in Paramecium. A correlated freeze-etching and ultrathin-sectioning analysis. J Cell Sci. 1973 Nov;13(3):687–719. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.3.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. Mutations affecting the trichocysts in Paramecium aurelia. I. Morphology and description of the mutants. J Protozool. 1974 May;21(2):352–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1974.tb03669.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannestad J. The regeneration of cilia in partially deciliated Tetrahymena. J Cell Biol. 1974 Dec;63(3):1009–1017. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.3.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rannestad J., Williams N. E. The synthesis of microtubule and other proteins of the oral apparatus in Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1971 Sep;50(3):709–720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. E., Kaneshiro E. S. Characterizations of phospholipids from Paramecium tetraurelia cells and cilia. J Protozool. 1979 May;26(2):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb02790.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. E. Biosynthesis of membrane and a membrane glycoprotein in Tetrahymen a pyriformis. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1976;55(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(76)90173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Carlson K. Cilia regeneration in Tetrahymena and its inhibition by colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):415–425. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Moulder J. E., Ringo D. L. Flagellar elongation and shortening in Chlamydomonas. The use of cycloheximide and colchicine to study the synthesis and assembly of flagellar proteins. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):600–619. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth L. E., Pihlaja D. J. Gradionation: hypothesis for positioning and patterning. J Protozool. 1977 Feb;24(1):2–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb05273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth L. E., Pihlaja D. J., Shigenaka Y. Microtubules in the heliozoan axopodium. I. The gradion hypothesis of allosterism in structural proteins. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Jan;30(1):7–37. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz F., Adoutte A., Rossignol M., Beisson J. Genetic analysis of morphogenetic processes in Paramecium. I. A mutation affecting trichocyst formation and nuclear division. Genet Res. 1976 Apr;27(2):109–122. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300016323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONNEBORN T. M. THE DETERMINANTS AND EVOLUTION OF LIFE. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:915–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satir B., Sale W. S., Satir P. Membrane renewal after dibucaine deciliation of Tetrahymena. Freeze-fracture technique, cilia, membrane structure. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:83–91. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satir B. Ultrastructural aspects of membrane fusion. J Supramol Struct. 1974;2(5-6):529–537. doi: 10.1002/jss.400020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster F. L., Prazak B., Ehret C. F. Induction of trichocyst discharge in Paramecium bursaria. J Protozool. 1967 Aug;14(3):483–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shay J. W., Peters T. T., Fuseler J. W. Cytoplasmic transfer of microtubule organizing centers in mouse tissue culture cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota S., Sato C., Enomoto M. Temperature-sensitive Chlamydomonas mutants manifesting flagellar regression at a restrictive temperature. J Protozool. 1979 May;26(2):232–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb02767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Sonneborn J., Plaut W. Evidence for the presence of DNA in the pellicle of Paramecium. J Cell Sci. 1967 Jun;2(2):225–234. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.2.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. D., Ecker R. E. Uterine suppression of biochemical and morphogenetic events in Rana pipiens. Dev Biol. 1970 Aug;22(4):622–637. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soll D. R., Sonneborn D. R. Zoospore germination in Blastocladiella emersonii: cell differentiation without protein synthesis? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon F. Detailed neurite morphologies of sister neurolbastoma cells are related. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonneborn T. M. Gene action in development. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Dec 1;176(1044):347–366. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1970.0054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Differential protein synthesis and utilization during cilia formation in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):311–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E., Edds K. T. Microtubules: structure, chemistry, and function. Physiol Rev. 1976 Oct;56(4):709–777. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1976.56.4.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Primary structural differences among tubulin subunits from flagella, cilia, and the cytoplasm. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2882–2891. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah P. V., Thompson G. A., Jr Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena pyriformis. The biosynthesis of proteins and their assembly into membranes of growing cells. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1302–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARTAR V. Reconstitution of minced Stentor coeruleus. J Exp Zool. 1960 Jul;144:187–207. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401440208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm S. L., Sonneborn T. M., Dippell R. V. The role of cortical orientation in the control of the direction of ciliary beat in Paramecium. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jan;64(1):98–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson G. A., Jr, Nozawa Y. Tetrahymena: a system for studying dynamic membrane alterations within the eukaryotic cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 31;472(1):55–92. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G. How microtubule patterns are generated. The relative importance of nucleation and bridging of microtubules in the formation of the axoneme of Raphidiophrys. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):837–854. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyohara A., Shigenaka Y., Mohri H. Microtubules in protozoan cells. III. Ultrastructural changes during disintegration and reformation of heliozoan microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1978 Aug;32:87–98. doi: 10.1242/jcs.32.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Development and deployment of cilia, basal bodies, and other microtubular organelles in the cortex of the ciliate Nassula. J Cell Sci. 1971 Nov;9(3):539–567. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.3.539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B., Dunn M., Pattisson J. B. Control of microtubule pattern during the development of a large organelle in the ciliate Nassula. Dev Biol. 1975 Dec;47(2):439–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90297-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Endocytosis and streaming of highly gelated cytoplasm alongside rows of arm-bearing microtubules in the ciliate Nassula. J Cell Sci. 1978 Feb;29:213–232. doi: 10.1242/jcs.29.1.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Initiation and differentiation of microtubule patterns in the ciliate Nassula. J Cell Sci. 1970 Nov;7(3):793–821. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.3.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Morphogenesis of a large microtubular organelle and its association with basal bodies in the ciliate Nassula. J Cell Sci. 1970 Mar;6(2):385–429. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.2.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Shape and pattern specification during microtubule bundle assembly. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):22–26. doi: 10.1038/266022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker J. B. Spatial discrimination in the cytoplasm during microtubule morphogenesis. Nature. 1971 Aug 6;232(5310):387–389. doi: 10.1038/232387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Williams N. E. Cytoskeletal proteins of the cell surface in Tetrahymena. II. Turnover of major proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 15;123(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90474-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Williams N. E., Frankel J., Vaudaux C. Inter-strain variability of structural proteins in Tetrahymena. J Protozool. 1977 Aug;24(3):453–458. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb04775.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. Isolation and identification of specific cortical proteins in Tetrahymena pyriformis strain GL. J Protozool. 1976 Aug;23(3):458–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1976.tb03813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. P., Collis P. S. Induction of microtubule protein synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardi during flagellar regeneration. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):15–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. P., Collis P., Gealt M. A. Control of induction of tubulin synthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Nature. 1977 Aug 18;268(5621):667–668. doi: 10.1038/268667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E. Biochemical approaches to problems of cellular patterning. J Protozool. 1977 Feb;24(1):14–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1977.tb05275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Frankel J. Regulation of microtubules in Tetrahymena. I. Electron microscopy of oral replacement. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):441–457. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Luft J. H. Use of a nitrogen mustard derivative in fixation for electron microscopy and observations on the ultrastructure of Tetrahymena. J Ultrastruct Res. 1968 Nov;25(3):271–292. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(68)80074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Nelsen E. M. Regulation of microtubules in Tetrahymena. II. Relation between turnover of microtubule proteins and microtubule dissociation and assembly during oral replacement. J Cell Biol. 1973 Feb;56(2):458–465. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E. Regulation of microtubules in Tetrahymena. Int Rev Cytol. 1975;41:59–86. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60966-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Subbaiah P. V., Thompson G. A., Jr Studies of membrane formation in Tetrahymena. The identification of membrane proteins and turnover rates in nongrowing cells. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):296–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams N. E., Vaudaux P. E., Skriver L. Cytoskeletal proteins of the cell surface in Tetrahymena I. Identification and localization of major proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 15;123(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90473-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W. Transfer of phospholipids between membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 16;344(2):95–117. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Carlson K., Berliner J., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas flagella. I. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of microtubules, matrix, membranes, and mastigonemes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):507–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B. The site of in vivo assembly of flagellar microtubules. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:178–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert L. Positional information and the spatial pattern of cellular differentiation. J Theor Biol. 1969 Oct;25(1):1–47. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(69)80016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyroba E. Studies on the surface coat of Paramecium aurelia. II. Relationship to the immobilization antigen. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Jul 11;181(2):245–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00219984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUSA A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDY ON REGENERATION OF TRICHOCYSTS IN PARAMECIUM CAUDATUM. J Protozool. 1963 Aug;10:253–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1963.tb01673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]