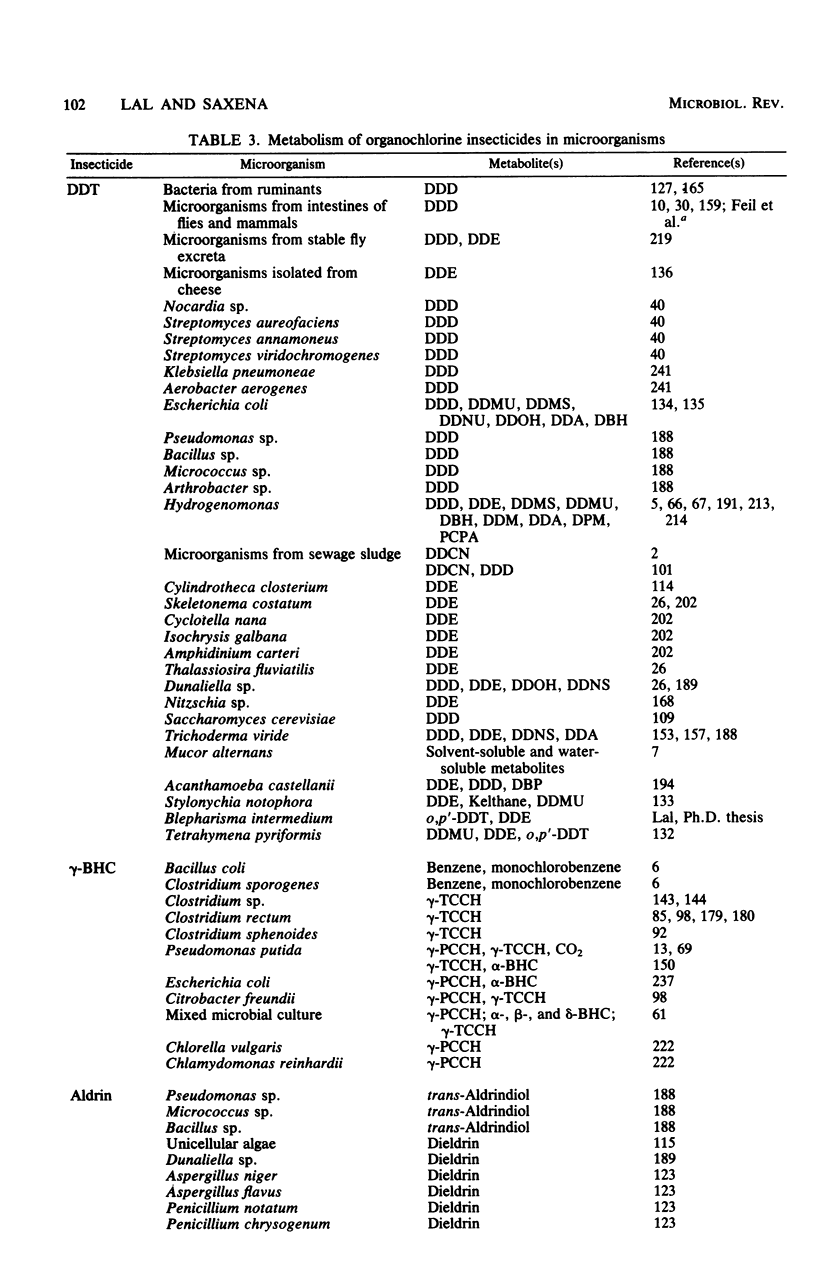
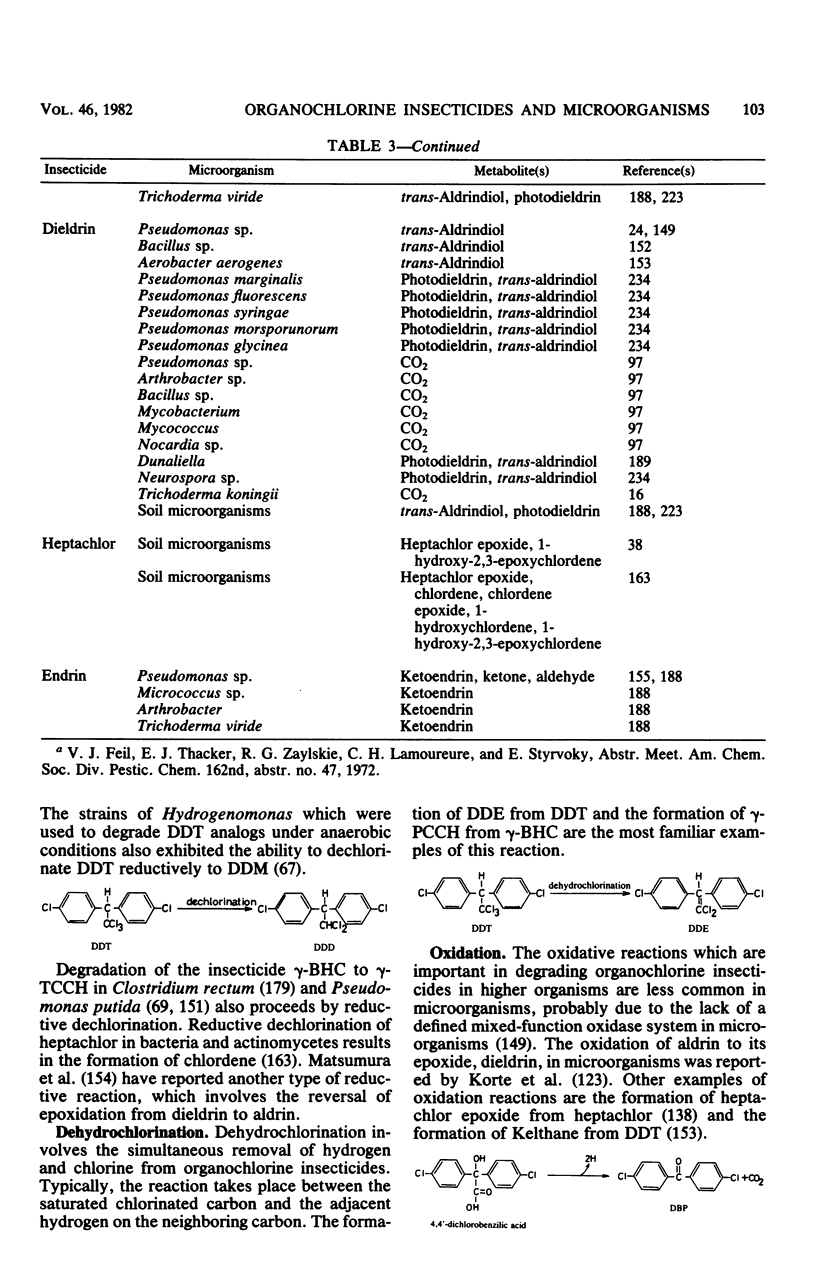
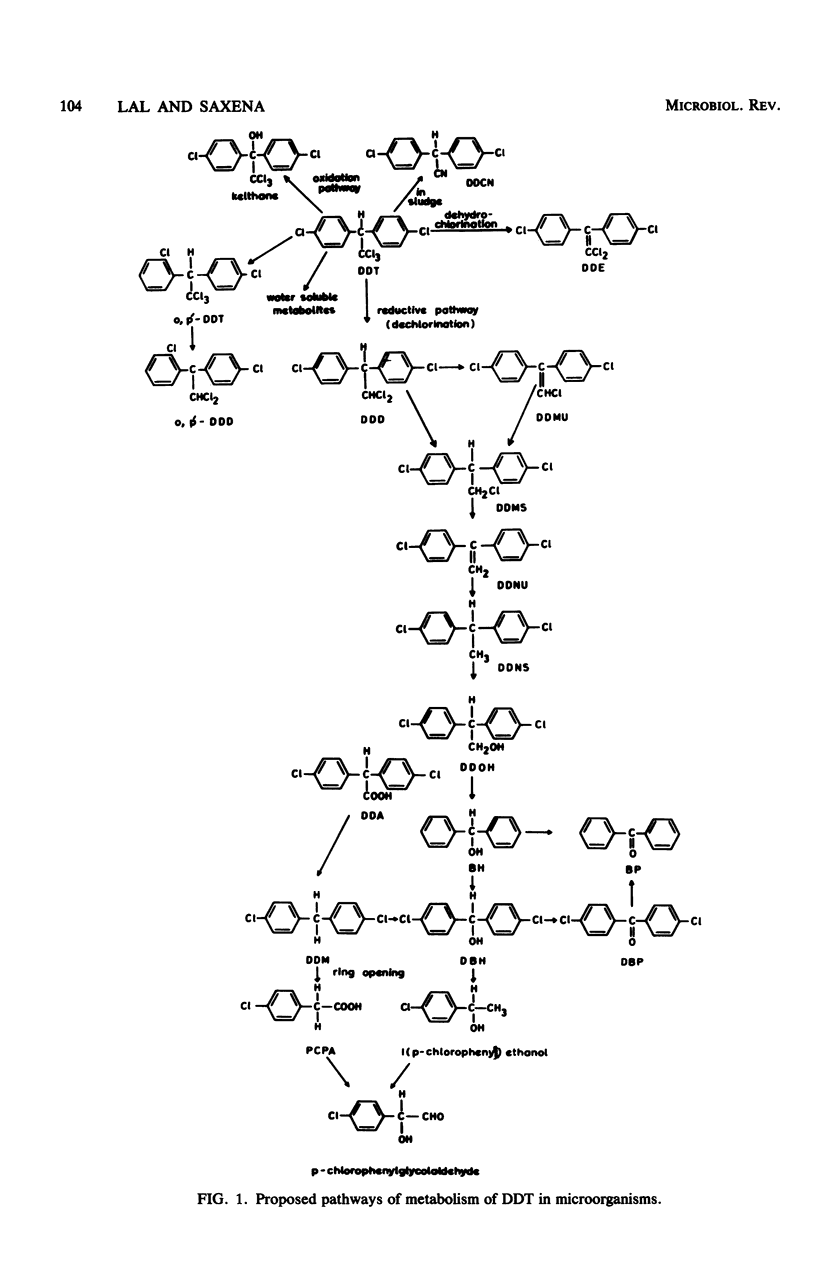
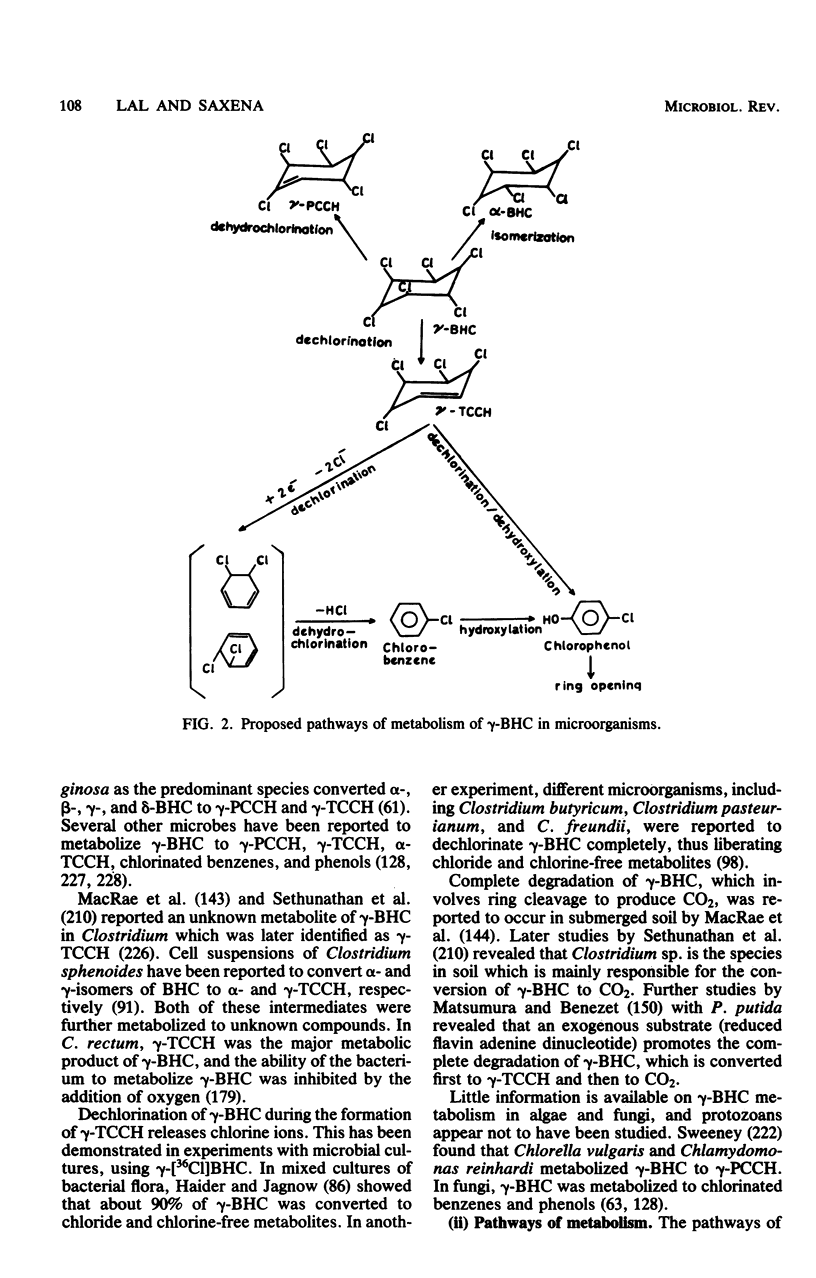
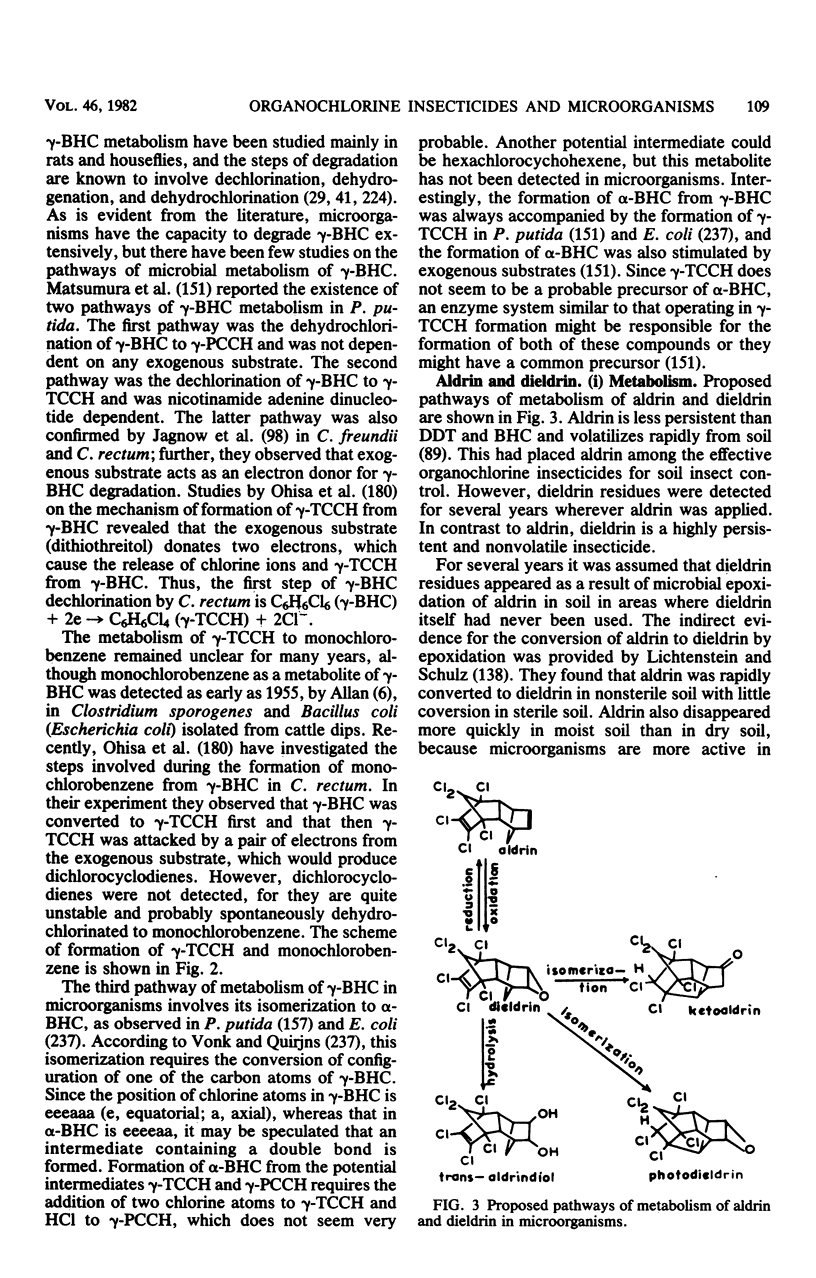
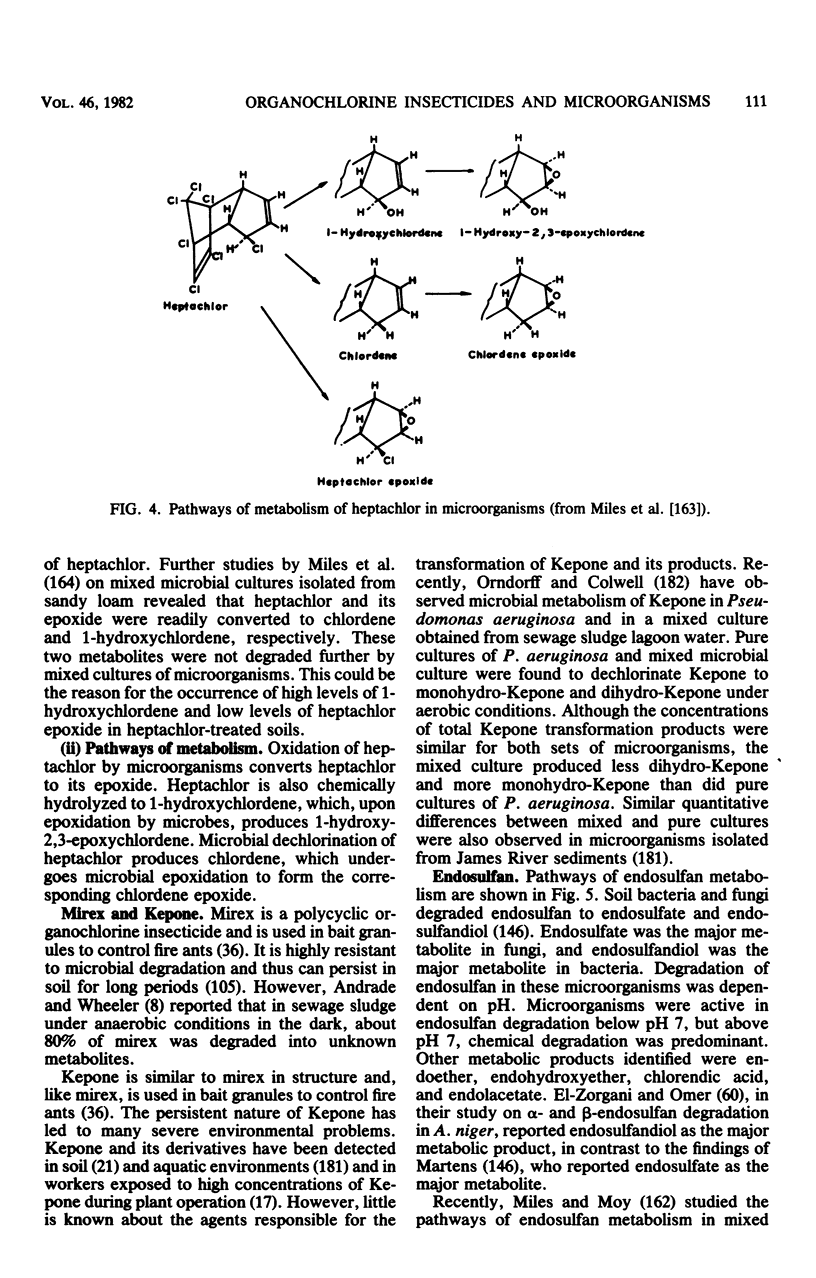
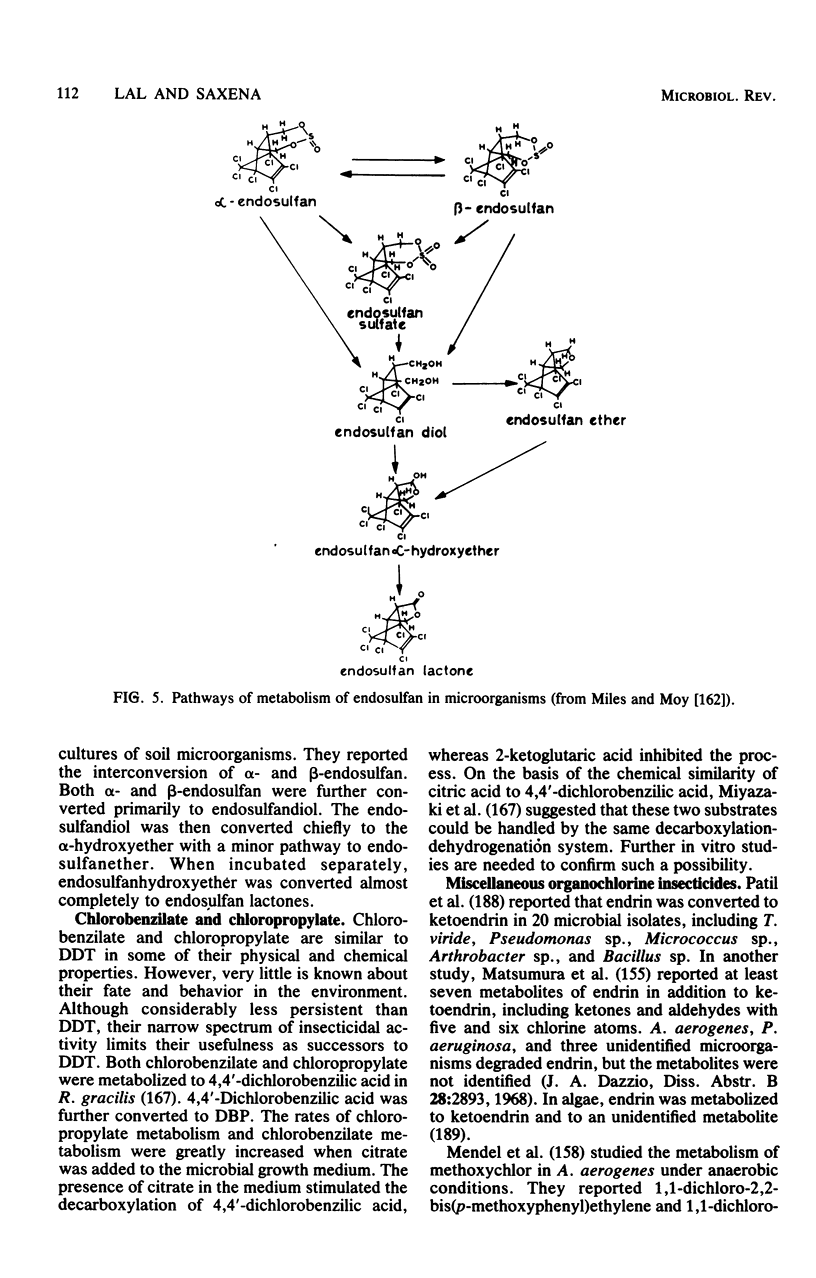
Full text
PDF























Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLAN J. Loss of biological efficiency of cattle-dipping wash containing benzene hexachloride. Nature. 1955 Jun 25;175(4469):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/1751131b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander M. Biodegradation: problems of molecular recalcitrance and microbial fallibility. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1965;7:35–80. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. P., Lichtenstein E. P., Whittingham W. F. Effect of Mucor alternans on the persistence of DDT and Dieldrin in culture and in soil. J Econ Entomol. 1970 Oct;63(5):1595–1599. doi: 10.1093/jee/63.5.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade P. S., Jr, Wheeler W. B. Biodegradation of mirex by sewage sludge organisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 May;11(5):415–416. doi: 10.1007/BF01685296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADBURY F. R., NIELD P., NEWMAN J. F. Amount of gamma-benzene hexachloride picked up by resistant houseflies bred on a medium containing benzene hexachloride. Nature. 1953 Dec 5;172(4388):1052–1052. doi: 10.1038/1721052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterton J. C., Boush G. M., Matsumura F. Growth response of blue-green algae to aldrin, dieldrin, endrin and their metabolites. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1971 Nov-Dec;6(6):589–594. doi: 10.1007/BF01796871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevenue A. The "bioconcentration" aspects of DDT in the environment. Residue Rev. 1976;61:37–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9401-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby M. W., Boush G. M., Matsumura F. Degradation of dieldrin to carbon dioxide by a soil fungus Trichoderma koningi. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1971 Nov-Dec;6(6):491–494. doi: 10.1007/BF01796853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanke R. V., Fariss M. W., Guzelian P. S., Paterson A. R., Smith D. E. Identification of a reduced form of chlordecone (Kepone) in human stool. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1978 Dec;20(6):782–785. doi: 10.1007/BF01683600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borghi H., Puiseux-Dao S., Bonotto S., Hoursiangou-Neubrun D. The effects of lindane on Acetabularia mediterranea. Protoplasma. 1973;78(1):99–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01281525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsetti A. P., Roach J. A. Identification of kepone alteration products in soil and mullet. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1978 Aug;20(2):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF01683515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G. W., Gee R. W. Inhibition of photosynthetic electron transport by DDT and DDE. J Bioenerg. 1971 Feb;2(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01521323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G. W. Uptake and Metabolism of 2,2-bis-(p-Chlorophenyl-1,1,1-trichloroethane (DDT) by Marine Phytoplankton and Its Effects on Growth and Chloroplast Electron Transport. Plant Physiol. 1972 Feb;49(2):172–176. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson D. A., Konyha K. D., Wheeler W. B., Marshall G. P., Zaylskie R. G. Mirex in the environment: its degradation to kepone and related compounds. Science. 1976 Nov 26;194(4268):939–941. doi: 10.1126/science.62396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter F. L., Stringer C. A. Residues and degradation products of technical heptachlor in various soil types. J Econ Entomol. 1970 Apr;63(2):625–628. doi: 10.1093/jee/63.2.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacke C. I., Lockwood J. L., Zabik M. Chlorinated hydrocarbon pesticides: degradation by microbes. Science. 1966 Nov 18;154(3751):893–895. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3751.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko C. I., Lockwood J. L. Accumulation of DDT and dieldrin by microorganisms. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):1123–1126. doi: 10.1139/m67-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark J. M., Matsumura F. Metabolism of toxaphene by aquatic sediment and a camphor-degrading pseudomonad. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979;8(3):285–298. doi: 10.1007/BF01056245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope O. B. Interactions between pesticides and wildlife. Annu Rev Entomol. 1971;16:325–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.16.010171.001545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. L. DDT residues in marine phytoplankton. Residue Rev. 1972;44:23–38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8491-9_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Koning H. W., Mortimer D. C. DDT uptake and growth of Euglena gracilis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1971 May-Jun;6(3):244–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01539934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deo P. G., Alexander M. Ring hydroxylation of p-chlorophenylacetate by an arthrobacter strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):195–196. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.195-196.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Zorgani G. A., Omer M. E. Metabolism of Endolsulfan isomers by Aspergillus niger. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Aug;12(2):182–185. doi: 10.1007/BF01684958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engst R., Fritsche W., Knoll R., Kujawa M., Macholz R. M., Straube G. Interim results of studies of microbial isomerization of gamma-hexachlorocyclohexane. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Jul;22(4-5):699–707. doi: 10.1007/BF02027010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engst R., Macholz R. M., Kujawa M. Identifizierung von Metaboliten und der Abbauweg des Hexachlorbenzols in einer Schimmelpilzkultur. Nahrung. 1975;19(7):603–606. doi: 10.1002/food.19750190711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):20–22. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. DDT metabolites and analogs: ring fission by Hydrogenomonas. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):91–92. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Alexander M. DDT metabolites and analogs: ring fission by Hydrogenomonas. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):91–92. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A. J., Spanggord R. J., Ouchi G. I. Degradation of lindane by Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):567–568. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.567-568.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French A. L., Hoopingarner R. A. Dechlorination of DDT by membranes isolated from Escherichia coli. J Econ Entomol. 1970 Jun;63(3):756–759. doi: 10.1093/jee/63.3.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geike F., Parasher C. D. Effect of hexachlorobenzene (HCB) on growth of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1976 Sep;16(3):347–354. doi: 10.1007/BF01685899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geike F., Parasher C. D. Effect of hexachlorobenzene on some growth parameters of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1976 Jun;15(6):670–677. doi: 10.1007/BF01685616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glooschenko V., Holdrinet M., Lott J. N., Frank R. Bioconcentration of chlordane by the green alga Scenedesmus quadricauda. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Mar;21(4-5):515–520. doi: 10.1007/BF01685463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory W. W., Jr, Reed J. K., Priester L. E., Jr Accumulation of parathion and DDT by some algae and protozoa. J Protozool. 1969 Feb;16(1):69–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1969.tb02234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenzi W. D., Beard W. E. Anaerobic biodegradation of DDT to DDD in soil. Science. 1967 May 26;156(3778):1116–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3778.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYNES H. B., WILLIAMS T. R. The effect of DDT on the fauna of a Central African stream. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1962 Apr;56:78–91. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1962.11686094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider K., Jagnow G. Abbau von 14C-, 3H- und 36Cl-markiertem gamma-Hexachlorcyclohexan durch anaerobe Bodenmikroorganismen. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):113–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00447310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen P. D. Experiments on the accumulation of lindane (gamma-BHC) by the primary producers Chlorella spec. and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979;8(6):721–731. doi: 10.1007/BF01054873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. R. Laboratory studies on the persistence of biological activity of some insecticides in soils. J Econ Entomol. 1969 Dec;62(6):1437–1441. doi: 10.1093/jee/62.6.1437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. B., Holmes D. C., Roburn J., Tatton J. O. The fate of some organochlorine pesticides on leaves. J Sci Food Agric. 1967 Jan;18(1):10–15. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2740180104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heritage A. D., MacRae I. C. Degradation of lindane by cell-free preparations of Clostridium sphenoides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):222–224. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.222-224.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heritage A. D., Rae I. C. Identification of intermediates formed during the degradation of hexachlorocyclohexanes by Clostridium sphenoides. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jun;33(6):1295–1297. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.6.1295-1297.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks G. F., Jr, Corner T. R. Location and consequences of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl) ethane uptake by Bacillus megaterium. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):381–387. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.381-387.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlbert S. H. Secondary effects of pesticides on aquatic ecosystems. Residue Rev. 1975;57:81–148. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9391-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagnow G., Haider K., Ellwardt P. C. Anaerobic dechlorination and degradation of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers by anaerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Dec 15;115(3):285–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00446454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsen R. E. DDT metabolism in microbial systems. Residue Rev. 1976;61:1–28. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9401-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. T., Goodman R. N., Goldberg H. S. Conversion of DDT to DDD by pathogenic and saprophytic bacteria associated with plants. Science. 1967 Aug 4;157(3788):560–561. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3788.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. T., Kennedy J. O. Biomagnification of p, p'-DDT and methoxychlor by bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.66-71.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. S., Hodges C. S. Persistence of mirex and its effects on soil microorganisms. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 May-Jun;22(3):435–439. doi: 10.1021/jf60193a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juengst F. W., Jr, Alexander M. Conversion of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) to water-soluble products by microorganisms. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Jan-Feb;24(1):111–115. doi: 10.1021/jf60203a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLMAN B. J., ANDREWS A. K. REDUCTIVE DECHLORINATION OF DDT TO DDD BY YEAST. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN D. D., KEARNEY P. C. MICROBIAL DEGRADATION OF ISOPROPYL-N-3 -CHLOROPHENYLCARBAMATE AND 2-CHLOROETHYL-N-3-CHLOROPHENYLCARBAMATE. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:443–446. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.443-446.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN A. K., LAUG E. P., DATTA P. R., MENDEL J. L. EVIDENCE FOR THE CONVERSION OF O,P-DDT (1,1,1-TRICHLORO-2-O-CHLOROPHENYL-2-P-CHLOROPHENYLETHANE) TO P,P'-DDT (1,1,1-TRICHLORO-2,2-BIS(P-CHLOROPHENYL)ETHANE IN RATS. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jun 5;87:2520–2522. doi: 10.1021/ja01089a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kar S., Singh P. K. Effect of nutrients on the toxicity of pesticides carbofuran and hexachlorocyclohexane to blue-green alga Nostoc muscorum. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1979;19(7):467–472. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3630190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan M. A., Kamal A., Wolin R. J., Runnels J. In vivo and in vitro epoxidation of aldrin by aquatic food chain organisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1972 Oct;8(4):219–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01839516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. C., Harmon L. G. Relationship between some chlorinated hydrocarbon insecticides and lactic culture organisms in milk. J Dairy Sci. 1970 Feb;53(2):155–160. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(70)86173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko W. H., Lockwood J. L. Conversion of DDT to DDD in soil and the effect of these compounds on soil microorganisms. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Oct;14(10):1069–1073. doi: 10.1139/m68-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohnen R., Haider K., Jagnow G. Investigations on the microbial degradation of Lindane in submerged and aerated moist soil. Environ Qual Saf Suppl. 1975;3:222–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokke R. Pesticide and herbicide interaction with microbial ecosystems. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1970;36(4):580–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricher J. C., Urey J. C., Hawes M. L. The effects of mirex and methoxychlor on the growth and productivity of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1975 Nov;14(5):617–620. doi: 10.1007/BF01683381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujawa M., Härtig M., Macholz R. M., Engst R. Der Abbau von 14-C-Lindan durch eine Schimmelpilzkultur. Nahrung. 1976;20(2):181–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutches A. J., Church D. C. DDT- 14 C-metabolism by rumen bacteria and protozoa in vitro. J Dairy Sci. 1971 Apr;54(4):540–543. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(71)85883-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal R., Saxena D. M. Effect of DDT on cell population growth, cell division, and DNA synthesis in Stylonychia notophora (Stokes). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1980;9(2):163–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01055371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois B. E., Collins J. A., Sides K. G. Some factors affecting degradation of organochlorine pesticides by bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 1970 Dec;53(12):1671–1675. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(70)86461-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRae I. C., Raghu K., Bautista E. M. Anaerobic degradation of the insecticide lindane by Clostridium sp. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):859–860. doi: 10.1038/221859a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Boush G. M. Degradation of insecticides by a soil fungus, trichoderma viride. J Econ Entomol. 1968 Jun;61(3):610–612. doi: 10.1093/jee/61.3.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Boush G. M. Dieldrin: degradation by soil microorganism. Science. 1967 May 19;156(3777):959–961. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3777.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Boush G. M., Tai A. Breakdown of dieldrin in the soil by a micro-organism. Nature. 1968 Aug 31;219(5157):965–967. doi: 10.1038/219965a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Khanvilkar V. G., Patil K. C., Boush G. M. Metabolism of endrin by certain soil microorganisms. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):27–31. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Patil K. C., Boush G. M. DDT metabolized by microorganisms from Lake Michigan. Nature. 1971 Apr 2;230(5292):325–326. doi: 10.1038/230325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura F., Patil K. C., Boush G. M. Formation of "photodieldrin" by microorganisms. Science. 1970 Dec 11;170(3963):1206–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3963.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel J. L., Walton M. S. Conversion of p,p' -DDT to p,p' -DDD by intestinal flora of the rat. Science. 1966 Mar 25;151(3717):1527–1528. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3717.1527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel D. W., Anderson J., Randtke A. Marine phytoplankton vary in their response to chlorinated hydrocarbons. Science. 1970 Mar 27;167(3926):1724–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3926.1724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf R. L., Sanborn J. R., Lu P. Y., Nye D. Laboratory model ecosystem studies of the degradation and fate of radiolabeled tri-, tetra-, and pentachlorobiphenyl compared with DDE. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1975;3(2):151–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02220785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. R., Moy P. Degradation of endosulfan and its metabolites by a mixed culture of soil microorganisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1979 Sep;23(1-2):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01769908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. R., Tu C. M., Harris C. R. Degradation of heptachlor epoxide and heptachlor by a mixed culture of soil microorganisms. J Econ Entomol. 1971 Aug;64(4):839–841. doi: 10.1093/jee/64.4.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. R., Tu C. M., Harris C. R. Metabolism of heptachlor and its degradation products by soil microorganism. J Econ Entomol. 1969 Dec;62(6):1334–1338. doi: 10.1093/jee/62.6.1334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Boush G. M., Matsumura F. Metabolism of 14C-chlorobenzilate and 14C-chloropropylate by Rhodotorula gracilis. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Dec;18(6):972–976. doi: 10.1128/am.18.6.972-976.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Thorsteinson A. J. Metabolism of DDT by fresh water diatoms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1972 Aug;8(2):81–83. doi: 10.1007/BF01684510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Fisher N. S., Teng T. C., Wurster C. F. Polychlorinated biphenyls: toxicity to certain phytoplankters. Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):191–192. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Fisher N. S., Wurster C. F. Polychlorinated biphenyls and DDT alter species composition in mixed cultures of algae. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):533–535. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Teng T. C., Walther W. G., Wurster C. F. Interactions of PCBs, DDT and DDE in a marine diatom. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Dec;12(6):665–668. doi: 10.1007/BF01685910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakas J. P., Litchfield C. D. Evidence for the subcellular localization and specificity of chlordane inhibition in the marine bacterium Aeromonas proteolytica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):471–479. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.471-479.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B. D., Williams C. Action of cyclodiene pesticides on oxidative metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Mar-Apr;19(2):339–341. doi: 10.1021/jf60174a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neudorf S., Khan M. A. Pick-up and metabolism of DDT, dieldrin and photodieldrin by a fresh water alga (Ankistrodesmus amalloides) and a microcrustacean (Daphnia pulex). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1975 Apr;13(4):443–450. doi: 10.1007/BF01721850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff S. A., Colwell R. R. Microbial transformation of kepone. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):398–406. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.398-406.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris D. F., Lewis D. L. Accumulation of methoxychlor by microorganisms isolated from aqueous systems. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1976 Jan;15(1):24–32. doi: 10.1007/BF01686192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris D. F., Lewis D. L., Barnett J. T. Bioconcentration of toxaphene by microorganisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977 May;17(5):564–572. doi: 10.1007/BF01685979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil K. C., Matsumura F., Boush G. M. Degradation of endrin, aldrin, and DDT by soil microorganisms. Appl Microbiol. 1970 May;19(5):879–881. doi: 10.1128/am.19.5.879-881.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaender F. K., Alexander M. Extensive microbial degradation of DDT in vitro and DDT metabolism by natural communities. J Agric Food Chem. 1972 Jul-Aug;20(4):842–846. doi: 10.1021/jf60182a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollero R., de Pollero S. C. Degradation of DDT by a soil amoeba. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1978 Mar;19(3):345–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01685809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puiseux-Dao S., Jeanne-Levain N., Roux F., Ribier J., Borghi H., Brun C. Analyse des effets du lindane, insecticide organochloré au niveau cellulaire. Protoplasma. 1977;91(3):325–341. doi: 10.1007/BF01281955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu K., MacRae I. C. Biodegradation of the gamma isomer of benzene hexachloride in submerged soils. Science. 1966 Oct 14;154(3746):263–264. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3746.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghu K., MacRae I. C. The effect of the gamma-isomer of benzene hexachloride upon the microflora of submerged rice soils. I. Effect upon algae. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Feb;13(2):173–180. doi: 10.1139/m67-024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. P., Sikka H. C. Fate of dieldrin in selected species of marine algae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1973 Feb;9(2):116–123. doi: 10.1007/BF01684766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. P., Sikka H. C. Uptake and metabolism of DDT by six species of marine algae. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Mar-Apr;21(2):148–152. doi: 10.1021/jf60186a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosas S. B., Secco M., Ghittoni N. E. Effects of pesticides on the fatty acid and phospholipid composition of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):231–234. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.231-234.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena D. M., Shivaji S., Lal R. Effect of DDT on DNA, RNA & protein synthesis in Tetrahymena pyriformis. Indian J Exp Biol. 1981 Jun;19(6):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N., Bautista E. M., Yoshida T. Degradation of benzene hexachloride by a soil bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1969 Dec;15(12):1349–1354. doi: 10.1139/m69-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subba-Rao R. V., Alexander M. Cometabolism of products of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis (p-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) by Pseudomonas putida. J Agric Food Chem. 1977 Jul-Aug;25(4):855–856. doi: 10.1021/jf60212a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabet J. C., Lichtenstein E. P. Degradation of [14C]photodieldrin by Trichoderma viride as affected by other insecticides. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1345–1356. doi: 10.1139/m76-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. M. Effects of pesticide seed treatments on Rhizobium japonicum and its symbiotic relationship with soybean. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977 Aug;18(2):190–199. doi: 10.1007/BF01686066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu C. M., Miles J. R., Harris C. R. Soil microbial degradation of aldrin. Life Sci. 1968 Mar 15;7(6):311–322. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(68)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware G. W., Roan C. C. Interaction of pesticides with aquatic microorganisms and plankton. Residue Rev. 1970;33:15–45. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8467-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedemeyer G. Partial hydrolysis of dieldrin by Aerobacter aerogenes. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Apr;16(4):661–662. doi: 10.1128/am.16.4.661-662.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. P. Metabolism of synthetic organic pesticides by anaerobic microorganisms. Residue Rev. 1977;66:63–135. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-6352-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoro J. A., Hunter J. M., Eglinton G., Ware G. C. Degradation of p,p'-DDT in reducing environments. Nature. 1974 Jan 25;247(5438):235–237. doi: 10.1038/247235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



