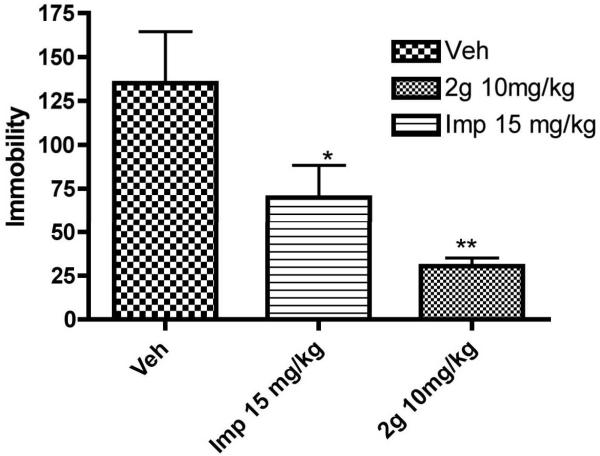
Figure 3.
Effect of sub-chronic administration of vehicle (Veh), 2g, and imipramine (Imp) on the duration of immobility in the forced swimming test in rats. One way ANOVA analysis demonstrates significant effect among treatments: F (3,95) = 8.93 (P< 0.0042). Dunnett’s analysis showed that the effect of 2g at a dose (10 mg/kg) on immobility was statistically significant different compared to vehicle (P< 0.01). The effect of reference imipramine (15 mg/kg) on immobility was also statistically significantly different (P< 0.05) from vehicle. Asterisks indicate a statistically significant difference toward control group that received saline i.p. **P < 0.01. Each treatment group contained six to eight rats.