Abstract
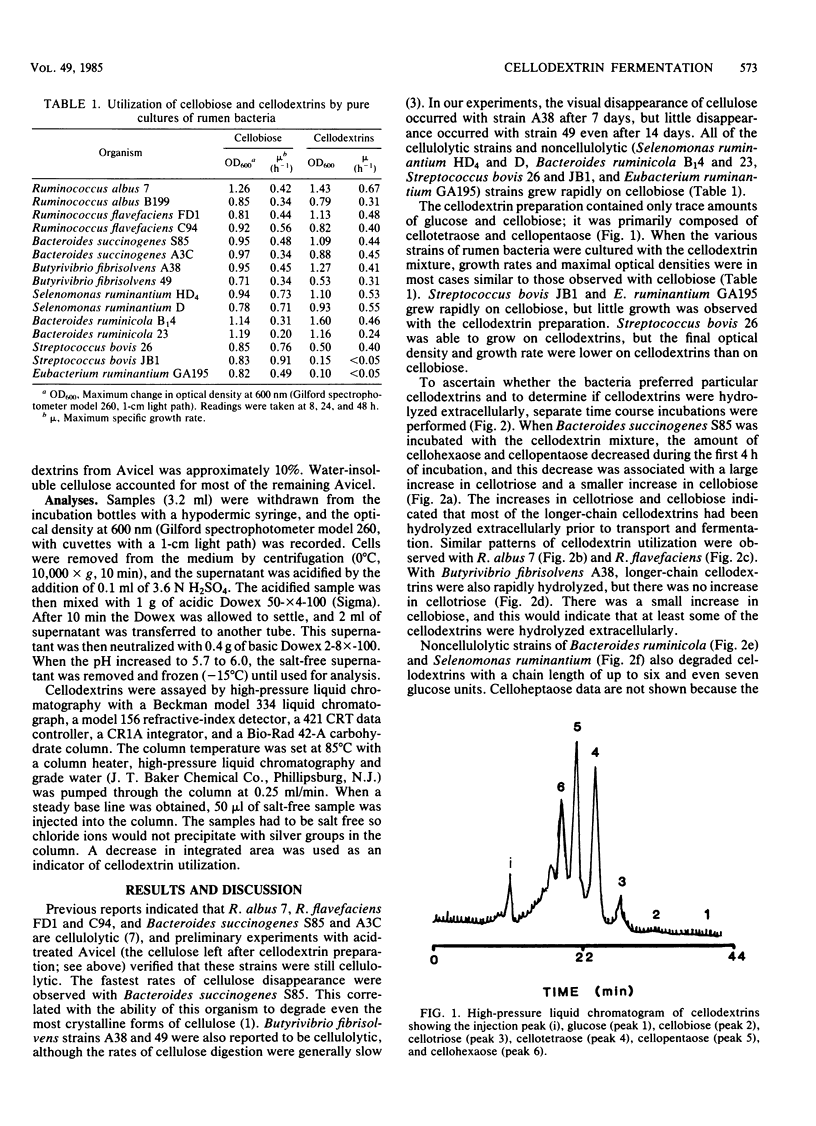
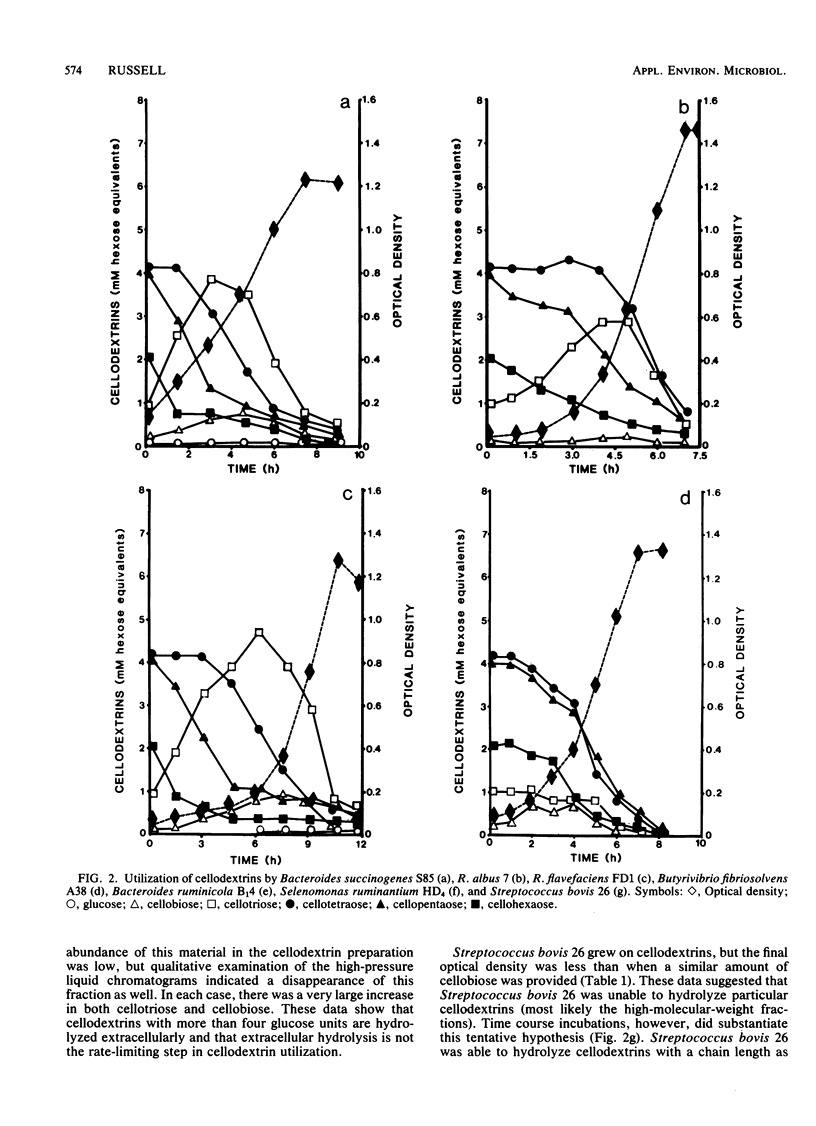
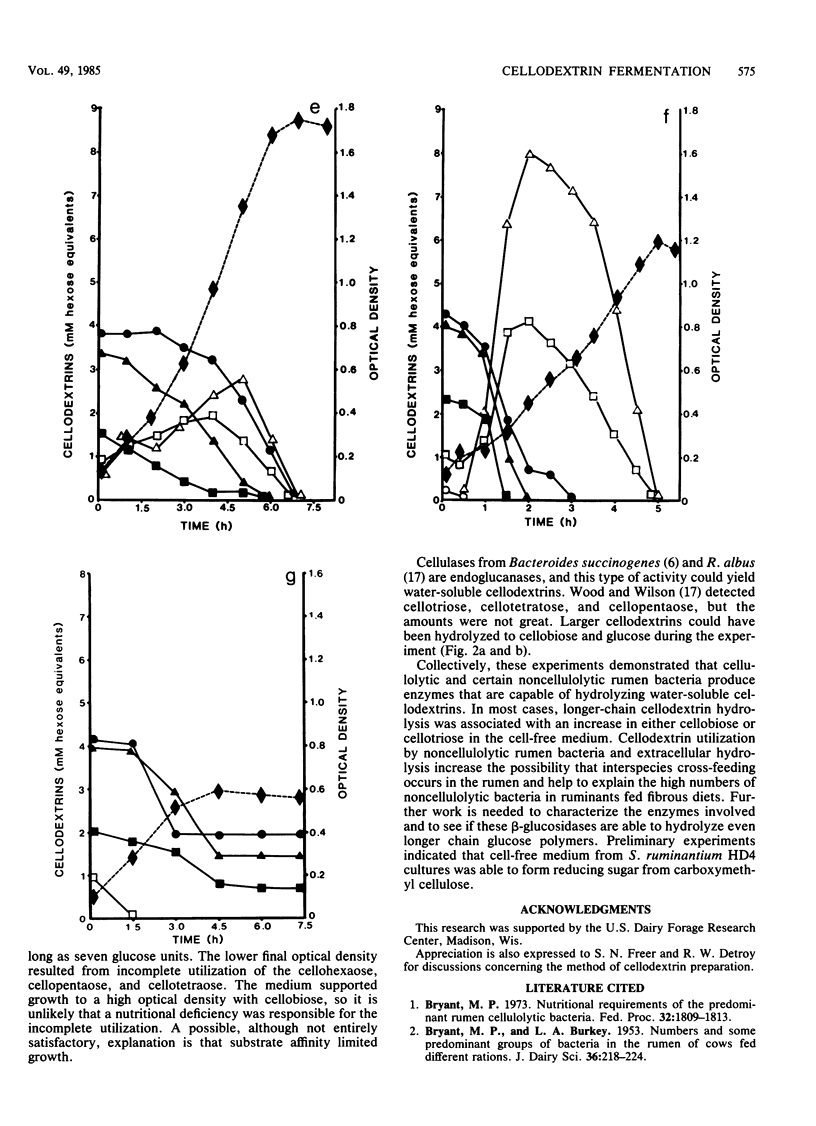
Water-soluble cellodextrins were prepared from microcrystalline cellulose by using fuming hydrochloric acid and acetone precipitation. This cellodextrin preparation contained only trace amounts of glucose and cellobiose and was primarily composed of cellotetraose and cellopentaose. When various species of cellulolytic and noncellulolytic bacteria were cultured with cellodextrins, their growth rates and maximal optical densities were in most cases similar to those observed with cellobiose. Time course samplings and analyses of cellodextrins by high-pressure liquid chromatography indicated that longer-chain cellodextrins were hydrolyzed extracellularly to cellobiose and cellotriose. Cellodextrin utilization by noncellulolytic rumen bacteria and extracellular hydrolysis of cellodextrins increase the possibility that cross-feeding occurs in the rumen and help to explain the high numbers of noncellulolytic bacteria in ruminants fed fibrous diets.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. The anaerobic monotrichous butyric acid-producing curved rod-shaped bacteria of the rumen. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.16-21.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Beveridge T. J., Hellstrom A. Cellulase and Xylanase Release from Bacteroides succinogenes and Its Importance in the Rumen Environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):886–896. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.886-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groleau D., Forsberg C. W. Cellulolytic activity of the rumen bacterium Bacteroides succinogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):517–530. doi: 10.1139/m81-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Stack R. J. Phenylpropanoic Acid: Growth Factor for Ruminococcus albus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):79–83. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.79-83.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheifinger C. C., Wolin M. J. Propionate formation from cellulose and soluble sugars by combined cultures of Bacteroides succinogenes and Selenomonas ruminantium. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):789–795. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.789-795.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


